參考鏈接
- Linux加密框架應用示例(二)_家有一希的博客-CSDN博客
- linux加密框架 crypto 算法管理 - 應用角度講解加密框架的運行流程_CHYabc123456hh的博客-CSDN博客
在應用模塊中創建并初始化哈希算法實例
- 假設某個SA配置使用的認證算法為"hmac(md5)"(即x->aalg->alg_name為"hmac(md5)"),在調用ah_init_state函數初始化SA狀態時,將創建認證算法對應的異步哈希算法實例ahash,并設置HMAC密鑰(密鑰數據保存在SA中,即x->aalg->alg_key)
?ah_init_state函數
- 調用ah_init_state函數初始化SA狀態
static int ah_init_state(struct xfrm_state *x)
{struct ah_data *ahp = NULL;struct xfrm_algo_desc *aalg_desc;struct crypto_ahash *ahash;if (!x->aalg)goto error;if (x->encap)goto error;ahp = kzalloc(sizeof(*ahp), GFP_KERNEL);if (!ahp)return -ENOMEM;ahash = crypto_alloc_ahash(x->aalg->alg_name, 0, 0);if (IS_ERR(ahash))goto error;ahp->ahash = ahash;if (crypto_ahash_setkey(ahash, x->aalg->alg_key,(x->aalg->alg_key_len + 7) / 8))goto error;/** Lookup the algorithm description maintained by xfrm_algo,* verify crypto transform properties, and store information* we need for AH processing. This lookup cannot fail here* after a successful crypto_alloc_ahash().*/aalg_desc = xfrm_aalg_get_byname(x->aalg->alg_name, 0);BUG_ON(!aalg_desc);if (aalg_desc->uinfo.auth.icv_fullbits/8 !=crypto_ahash_digestsize(ahash)) {pr_info("%s: %s digestsize %u != %hu\n",__func__, x->aalg->alg_name,crypto_ahash_digestsize(ahash),aalg_desc->uinfo.auth.icv_fullbits / 8);goto error;}ahp->icv_full_len = aalg_desc->uinfo.auth.icv_fullbits/8;ahp->icv_trunc_len = x->aalg->alg_trunc_len/8;if (x->props.flags & XFRM_STATE_ALIGN4)x->props.header_len = XFRM_ALIGN4(sizeof(struct ip_auth_hdr) +ahp->icv_trunc_len);elsex->props.header_len = XFRM_ALIGN8(sizeof(struct ip_auth_hdr) +ahp->icv_trunc_len);if (x->props.mode == XFRM_MODE_TUNNEL)x->props.header_len += sizeof(struct iphdr);x->data = ahp;return 0;error:if (ahp) {crypto_free_ahash(ahp->ahash);kfree(ahp);}return -EINVAL;
}
- 創建認證算法對應的異步哈希算法實例ahash
ahash = crypto_alloc_ahash(x->aalg->alg_name, 0, 0);if (IS_ERR(ahash))goto error;- 并設置HMAC密鑰(密鑰數據保存在SA中,即x->aalg->alg_key)
ahp->ahash = ahash;if (crypto_ahash_setkey(ahash, x->aalg->alg_key,(x->aalg->alg_key_len + 7) / 8))goto error;
/* Data for transformer */struct xfrm_algo_auth *aalg; //認證算法struct xfrm_algo *ealg; //加密算法struct xfrm_algo *calg; //壓縮算法struct xfrm_algo_aead *aead; //AEAD算法
- 這一塊有點繞
- 由于默認算法以異步方式實現,因此在ah_init_state函數中將調用crypto_alloc_ahash函數創建與認證算法"hmac(md5)"對應的異步哈希算法實例,記為hmac_md5_ahash。
- 由于MD5算法是以同步方式實現的,由其衍生的"hmac(md5)"算法也是以同步方式實現的,因此也會同步創建"hmac(md5)"算法的同步哈希算法實例,記為hmac_md5_shash。
- 由于"hmac(md5)"算法是在MD5算法基礎上構造的,具體的算法運算由MD5算法實現,因此還會同步創建MD5算法的同步哈希算法實例,記為md5_shash。
- 綜上所述,調用crypto_alloc_ahash函數實際上創建了三個算法實例,其中hmac_md5_ahash是面向具體算法應用(如IPSEC模塊)的,md5_shash是面向具體算法實現(如MD5算法)的,hmac_md5_shash負責將hmac_md5_ahash和md5_shash兩個算法實例串聯在一起,三個算法實例的關系如下所示。

創建哈希算法實例hmac_md5_ahash
- 下面將按照函數調用關系逐步說明如何創建哈希算法實例hmac_md5_ahash。
1)ah_init_state函數
- ah_init_state函數調用crypto_alloc_ahash函數異步哈希算法實例hmac_md5_ahash時,輸入參數包括算法alg_name(=“hmac(md5)”)、算法類型type(=0)和算法類型屏蔽字mask(=0)
ahash = crypto_alloc_ahash(x->aalg->alg_name, 0, 0);if (IS_ERR(ahash))goto error;- 從函數的輸入參數可知,ah_init_state函數不關心認證算法的實現方式,只關心是否有可提供服務的認證算法。
2)crypto_alloc_ahash函數
- 實際上crypto_alloc_ahash函數是一個包裹函數(wrapper),具體工作由crypto_alloc_tfm函數實現。crypto_alloc_tfm函數繼承了調用者所有的輸入參數。
- ahash.c - crypto/ahash.c - Linux source code (v5.15.12) - Bootlin
- 由于crypto_alloc_tfm函數并不是創建特定的算法實例(即特定數據結構指針),而是返回一個通用指針(即void *),由調用者具體解釋通用指針的含義(即將通用指針轉換為特定算法實例數據結構指針)。不同類型算法實例占用的內存空間不同、初始化流程存在差異,這些不同和差異由crypto_alloc_tfm函數的輸入參數frontend說明,在這里參數frontend按照字面理解為算法前端,按照數據結構實際上就是算法類型常量指針。
- frontend的類型是?crypto_type
- internal.h - crypto/internal.h - Linux source code (v5.15.12) - Bootlin??
- 由于crypto_alloc_ahash函數用于創建異步哈希算法實例,因此在調用crypto_alloc_tfm函數時傳遞的frontend參數為異步哈希算法類型常量crypto_shash_type,調用結束后將crypto_alloc_tfm函數返回地通用指針隱式地強制轉換為異步哈希算法實例指針。
3)crypto_alloc_tfm函數
- api.c - crypto/api.c - Linux source code (v5.15.12) - Bootlin
- crypto_alloc_tfm函數內部調用? crypto_alloc_tfm_node 函數
- crypto_alloc_tfm_node 函數的基本邏輯是先調用crypto_find_alg函數查找符合條件(包括算法名alg_name、算法類型type和算法類型屏蔽字)的算法alg,然后再調用crypto_create_tfm_node函數創建與算法alg關聯的算法實例tfm。
void *crypto_alloc_tfm_node(const char *alg_name,const struct crypto_type *frontend, u32 type, u32 mask,int node)
{void *tfm;int err;for (;;) {struct crypto_alg *alg;alg = crypto_find_alg(alg_name, frontend, type, mask);if (IS_ERR(alg)) {err = PTR_ERR(alg);goto err;}tfm = crypto_create_tfm_node(alg, frontend, node);if (!IS_ERR(tfm))return tfm;crypto_mod_put(alg);err = PTR_ERR(tfm);err:if (err != -EAGAIN)break;if (fatal_signal_pending(current)) {err = -EINTR;break;}}return ERR_PTR(err);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(crypto_alloc_tfm_node);- 假設第一次使用"hmac(md5)“算法,算法查找不命中,因此加密框架將根據算法模板(HMAC模板)和基礎算法(MD5算法)動態創建新的算法(通用算法說明記為hmac_md5_alg)并注冊。
- 截至到目前為止,函數接口調用關系如下圖所示
?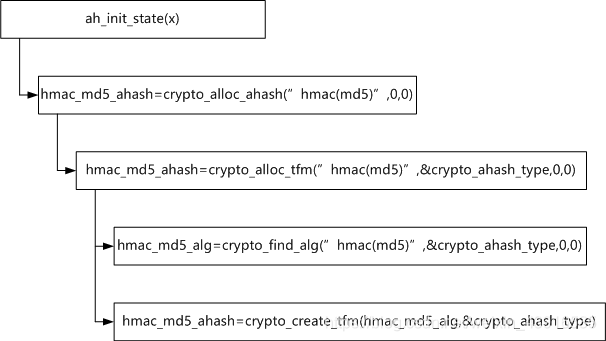
- ?crypto_find_alg 函數調用之前,alg_name指代hmac(md5),crypto_find_alg函數轉化之后輸出alg,alg已經指定的是hmac_md5_alg
3. 創建動態算法"hmac(md5)”
- 1)crypto_find_alg函數
- crypto_find_alg函數的主要功能是確認算法查找的預期算法類型(包括算法類型type以及算法類型屏蔽字mask)和算法查找接口lookup
- api.c - crypto/api.c - Linux source code (v5.15.12) - Bootlin
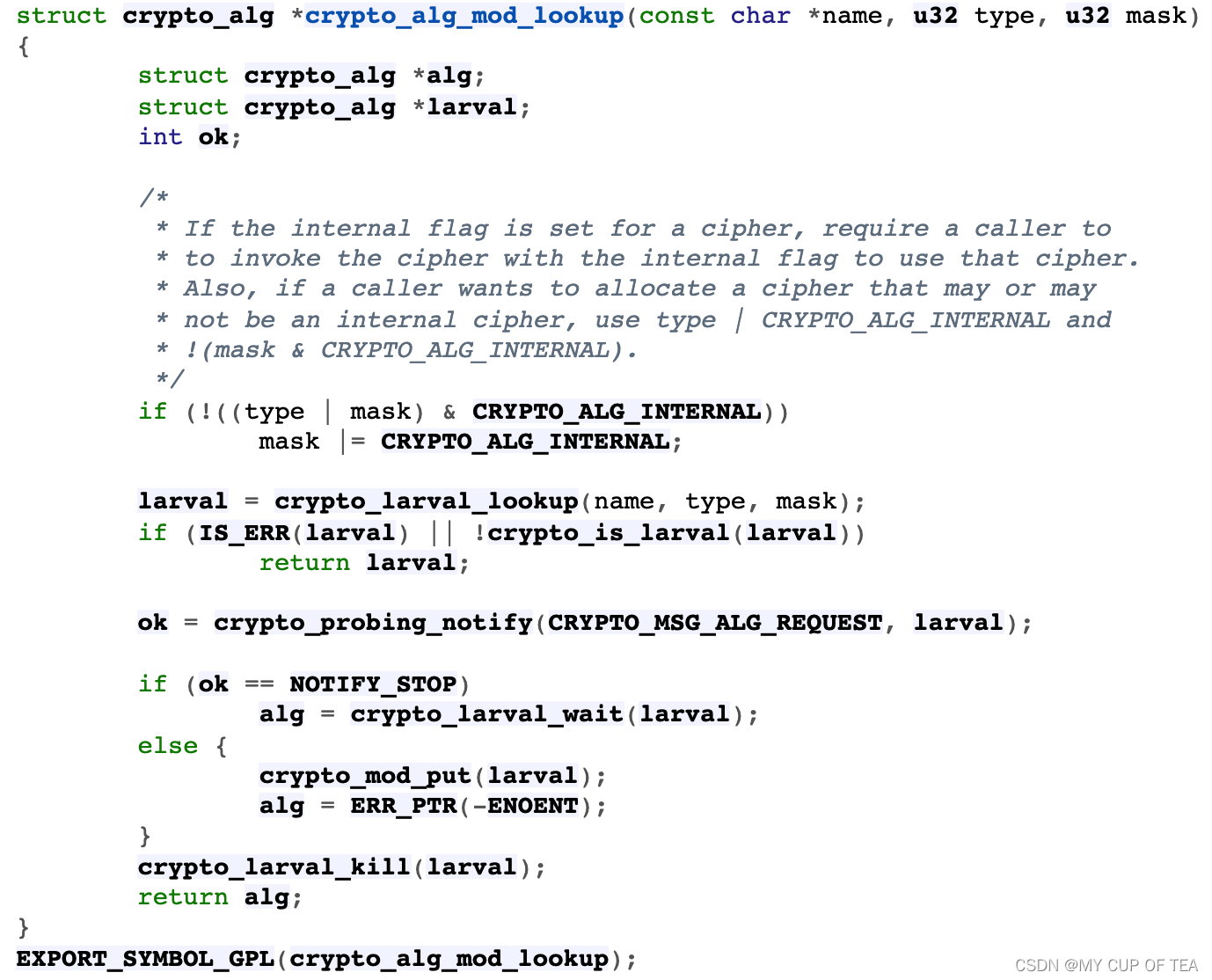
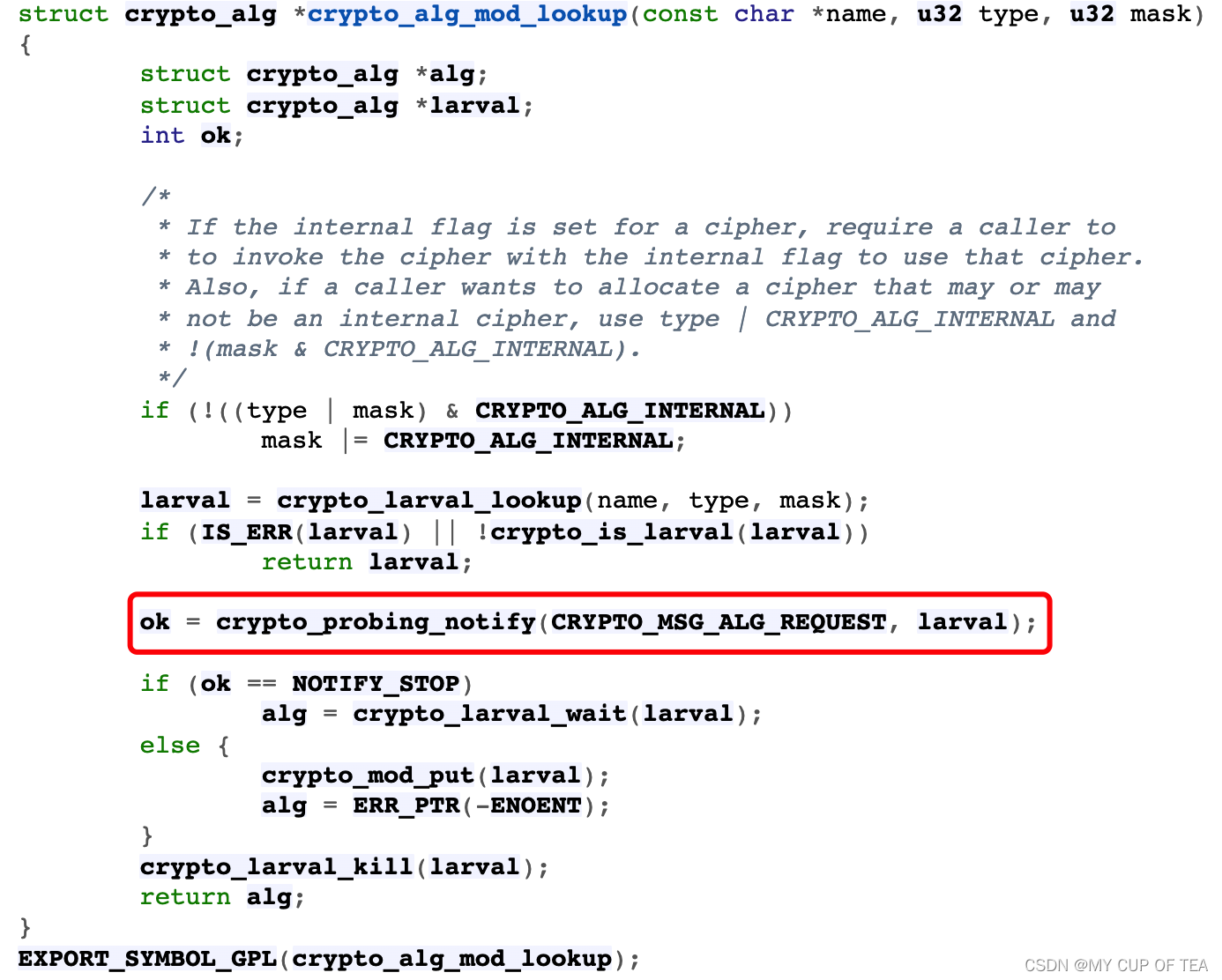
struct crypto_alg *crypto_find_alg(const char *alg_name,const struct crypto_type *frontend,u32 type, u32 mask)
{if (frontend) {type &= frontend->maskclear;mask &= frontend->maskclear;type |= frontend->type;mask |= frontend->maskset;}return crypto_alg_mod_lookup(alg_name, type, mask);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(crypto_find_alg);
-
按照調用關系,此時傳遞給crypto_find_alg函數的算法前端frontend為異步哈希算法類型常量crypto_ahash_type,算法類型type和算法類型屏蔽字均為0,其中算法前端frontend與算法查找相關的成員變量如下所示。
static const struct crypto_type crypto_ahash_type = {.extsize = crypto_ahash_extsize,.init_tfm = crypto_ahash_init_tfm,.free = crypto_ahash_free_instance,
#ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS.show = crypto_ahash_show,
#endif.report = crypto_ahash_report,.maskclear = ~CRYPTO_ALG_TYPE_MASK,.maskset = CRYPTO_ALG_TYPE_AHASH_MASK,.type = CRYPTO_ALG_TYPE_AHASH,.tfmsize = offsetof(struct crypto_ahash, base),
};- 在調用算法查找接口lookup(默認接口crypto_alg_mod_lookup)時,算法類型type為CRYPTO_ALG_TYPE_AHASH,算法類型屏蔽字mask為CRYPTO_ALG_TYPE_AHASH_MASK。
- 注意事項:未找到證據? 在遍歷算法管理鏈表查找算法前(crypto_larval_lookup函數),還會再次更新算法類型為type=type&mask=0x08(在算法類型定義中為CRYPTO_ALG_TYPE_HASH)。
- api.c - crypto/api.c - Linux source code (v5.15.12) - Bootlin
- api.c - crypto/api.c - Linux source code (v5.15.12) - Bootlin
- 在遍歷管理算法鏈表時,如果((cra_flags ^ type) & mask)=0表示當前算法滿足查找條件中的算法類型要求,否則不滿足算法類型要求,也就是說只要是哈希算法,無論是同步方式實現還是異步方式實現,都滿足算法類型要求。
- api.c - crypto/api.c - Linux source code (v5.15.12) - Bootlin

- 2)crypto_alg_mod_lookup函數
- 在crypto_alg_mod_lookup函數中,調用crypto_larval_lookup函數查找符合條件的算法。假設第一次使用"hmac(md5)"算法,算法查找不命中,在調用crypto_larval_lookup函數時將返回一個與查找算法同名的注冊用算法幼蟲,記為hmac_md5_larval_r。
- 算法查找不命中時,加密框架嘗試動態創建符合條件的算法,調用crypto_probing_notify函數在加密通知鏈發布一個算法注冊(CRYPTO_MSG_ALG_REQUEST)通知,動態創建"hmac(md5)“算法,傳遞的參數由注冊用算法幼蟲hmac_md5_larval_r指定。
- larvel 接收?crypto_larval_lookup? 返回的??算法同名的注冊用算法幼蟲,記為hmac_md5_larval_r
- larvel 指定?hmac_md5_larval_r;
- larvel 作為函數的形參輸入,由函數?crypto_probing_notify 進行 算法注冊
- api.c - crypto/api.c - Linux source code (v5.15.12) - Bootlin
- 發布算法注冊通知時,通過解析注冊用算法幼蟲hmac_md5_larval_r的算法名(即"hmac(md5)”)可獲取算法模板名hmac和基礎算法名md5,加上預期的算法類型共同組成傳遞給算法探測線程cryptomgr_probe的參數param。?
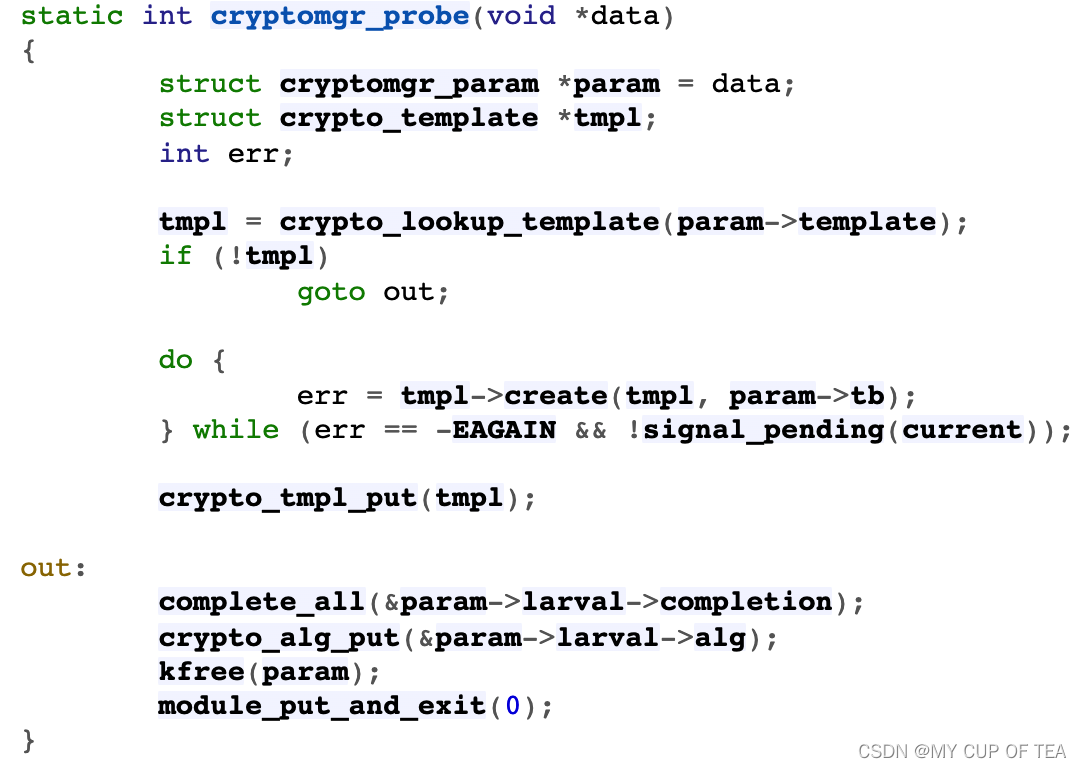
- https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/latest/source/crypto/algboss.c#L50
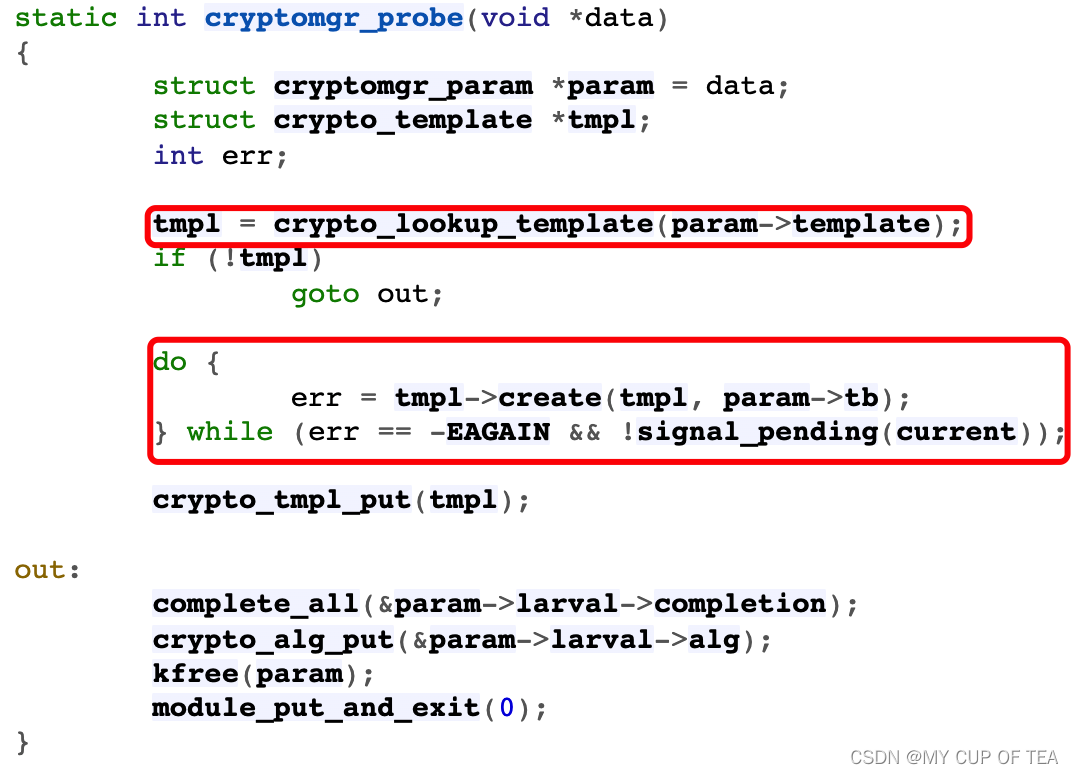
- 算法探測線程運行時,根據算法模板名hmac查找到對應的算法模板hmac_tmpl。由于算法模板hmac_tmpl定義了create接口(即hmac_create函數),將調用之根據參數列表param->tb創建并注冊動態算法。

_學小易找答案...)





)



 ——構造方程法...)








