文章目錄
- 目錄
- 1.繼承
- 2.重載
- 3.多態 && 虛函數
目錄
1.繼承
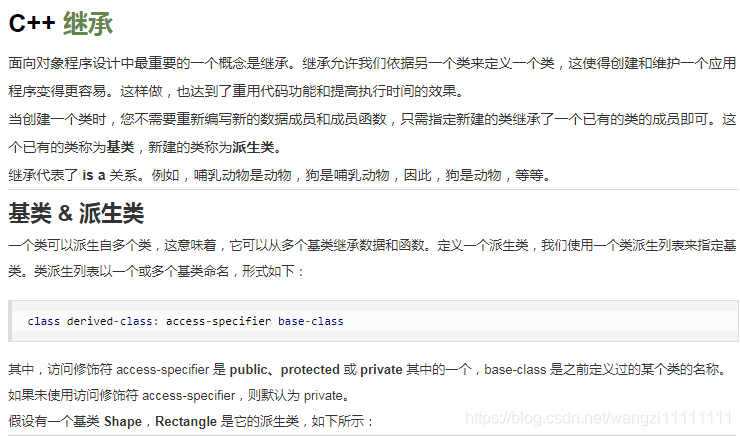
#include <iostream>using namespace std;// 基類
class Shape
{public:void setWidth(int w){width = w;}void setHeight(int h){height = h;}protected:int width;int height;
};// 派生類
class Rectangle: public Shape
{public:int getArea(){ return (width * height); }
};int main(void)
{Rectangle Rect;Rect.setWidth(5);Rect.setHeight(7);// 輸出對象的面積cout << "Total area: " << Rect.getArea() << endl;return 0;
}
當上面的代碼被編譯和執行時,它會產生下列結果:
Total area: 35
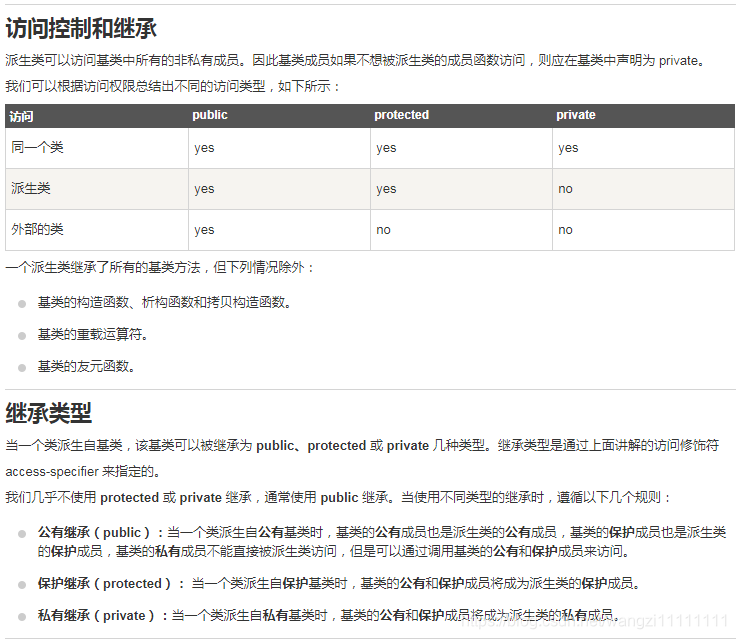
#include <iostream>using namespace std;// 基類 Shape
class Shape
{public:void setWidth(int w){width = w;}void setHeight(int h){height = h;}protected:int width;int height;
};// 基類 PaintCost
class PaintCost
{public:int getCost(int area){return area * 70;}
};// 派生類
class Rectangle: public Shape, public PaintCost
{public:int getArea(){ return (width * height); }
};int main(void)
{Rectangle Rect;int area;Rect.setWidth(5);Rect.setHeight(7);area = Rect.getArea();// 輸出對象的面積cout << "Total area: " << Rect.getArea() << endl;// 輸出總花費cout << "Total paint cost: $" << Rect.getCost(area) << endl;return 0;
}
當上面的代碼被編譯和執行時,它會產生下列結果:
Total area: 35
Total paint cost: $2450
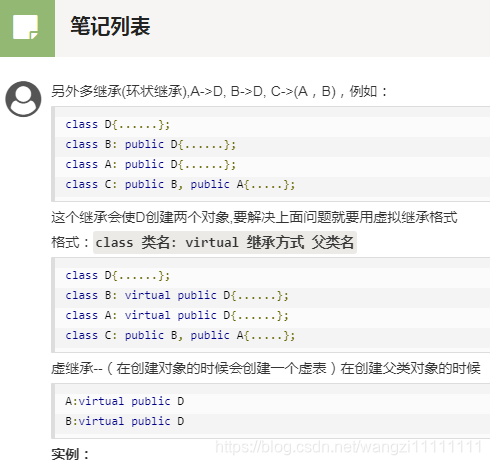
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
//基類class D
{
public:D(){cout<<"D()"<<endl;}~D(){cout<<"~D()"<<endl;}
protected:int d;
};class B:virtual public D
{
public:B(){cout<<"B()"<<endl;}~B(){cout<<"~B()"<<endl;}
protected:int b;
};class A:virtual public D
{
public:A(){cout<<"A()"<<endl;}~A(){cout<<"~A()"<<endl;}
protected:int a;
};class C:public B, public A
{
public:C(){cout<<"C()"<<endl;}~C(){cout<<"~C()"<<endl;}
protected:int c;
};int main()
{cout << "Hello World!" << endl;C c; //D, B, A ,Ccout<<sizeof(c)<<endl;return 0;
}
Hello World!
D()
B()
A()
C()
40
~C()
~A()
~B()
~D()
2.重載

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class printData
{public:void print(int i) {cout << "整數為: " << i << endl;}void print(double f) {cout << "浮點數為: " << f << endl;}void print(string c) {cout << "字符串為: " << c << endl;}
};int main(void)
{printData pd;// 輸出整數pd.print(5);// 輸出浮點數pd.print(500.263);// 輸出字符串pd.print("Hello C++");return 0;
}
當上面的代碼被編譯和執行時,它會產生下列結果:
整數為: 5
浮點數為: 500.263
字符串為: Hello C++
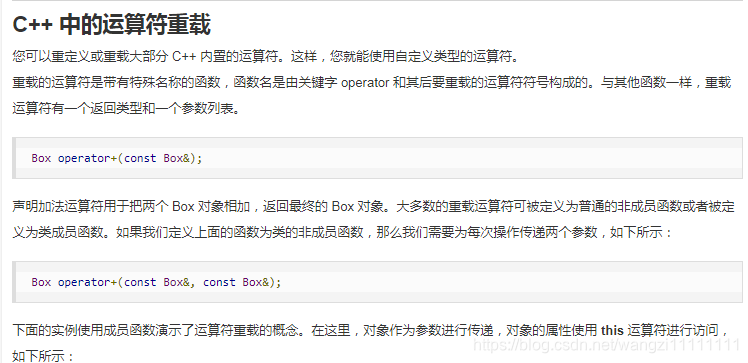
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Box
{public:double getVolume(void){return length * breadth * height;}void setLength( double len ){length = len;}void setBreadth( double bre ){breadth = bre;}void setHeight( double hei ){height = hei;}// 重載 + 運算符,用于把兩個 Box 對象相加Box operator+(const Box& b){Box box;box.length = this->length + b.length;box.breadth = this->breadth + b.breadth;box.height = this->height + b.height;return box;}private:double length; // 長度double breadth; // 寬度double height; // 高度
};
// 程序的主函數
int main( )
{Box Box1; // 聲明 Box1,類型為 BoxBox Box2; // 聲明 Box2,類型為 BoxBox Box3; // 聲明 Box3,類型為 Boxdouble volume = 0.0; // 把體積存儲在該變量中// Box1 詳述Box1.setLength(6.0); Box1.setBreadth(7.0); Box1.setHeight(5.0);// Box2 詳述Box2.setLength(12.0); Box2.setBreadth(13.0); Box2.setHeight(10.0);// Box1 的體積volume = Box1.getVolume();cout << "Volume of Box1 : " << volume <<endl;// Box2 的體積volume = Box2.getVolume();cout << "Volume of Box2 : " << volume <<endl;// 把兩個對象相加,得到 Box3Box3 = Box1 + Box2;// Box3 的體積volume = Box3.getVolume();cout << "Volume of Box3 : " << volume <<endl;return 0;
}
當上面的代碼被編譯和執行時,它會產生下列結果:
Volume of Box1 : 210
Volume of Box2 : 1560
Volume of Box3 : 5400

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Distance
{private:int feet; // 0 到無窮int inches; // 0 到 12public:// 所需的構造函數Distance(){feet = 0;inches = 0;}Distance(int f, int i){feet = f;inches = i;}// 顯示距離的方法void displayDistance(){cout << "F: " << feet << " I:" << inches <<endl;}// 重載負運算符( - )Distance operator- () {feet = -feet;inches = -inches;return Distance(feet, inches);}
};
int main()
{Distance D1(11, 10), D2(-5, 11);-D1; // 取相反數D1.displayDistance(); // 距離 D1-D2; // 取相反數D2.displayDistance(); // 距離 D2return 0;
}
當上面的代碼被編譯和執行時,它會產生下列結果:
F: -11 I:-10
F: 5 I:-11

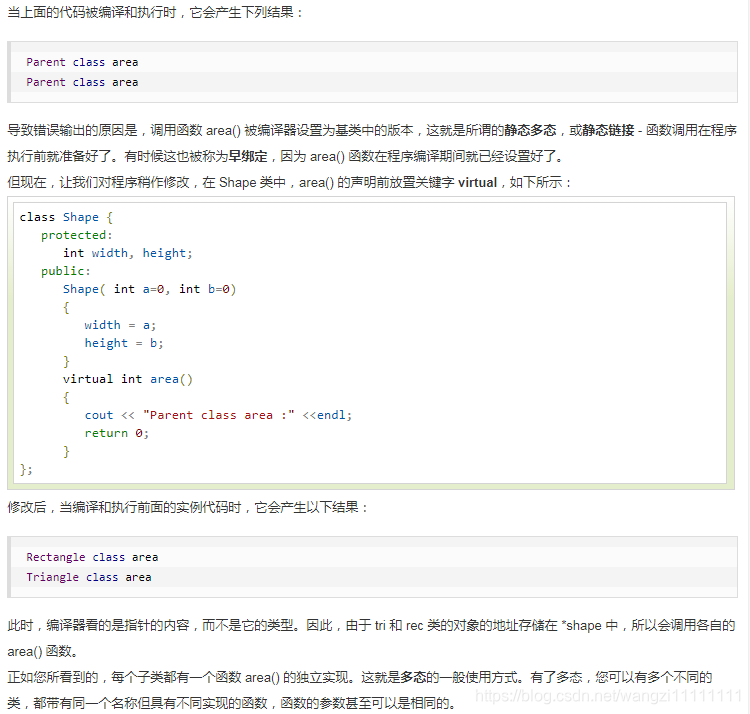
3.多態 && 虛函數

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Shape {protected:int width, height;public:Shape( int a=0, int b=0){width = a;height = b;}int area(){cout << "Parent class area :" <<endl;return 0;}
};
class Rectangle: public Shape{public:Rectangle( int a=0, int b=0):Shape(a, b) { }int area (){ cout << "Rectangle class area :" <<endl;return (width * height); }
};
class Triangle: public Shape{public:Triangle( int a=0, int b=0):Shape(a, b) { }int area (){ cout << "Triangle class area :" <<endl;return (width * height / 2); }
};
// 程序的主函數
int main( )
{Shape *shape;Rectangle rec(10,7);Triangle tri(10,5);// 存儲矩形的地址shape = &rec;// 調用矩形的求面積函數 areashape->area();// 存儲三角形的地址shape = &tri;// 調用三角形的求面積函數 areashape->area();return 0;
}
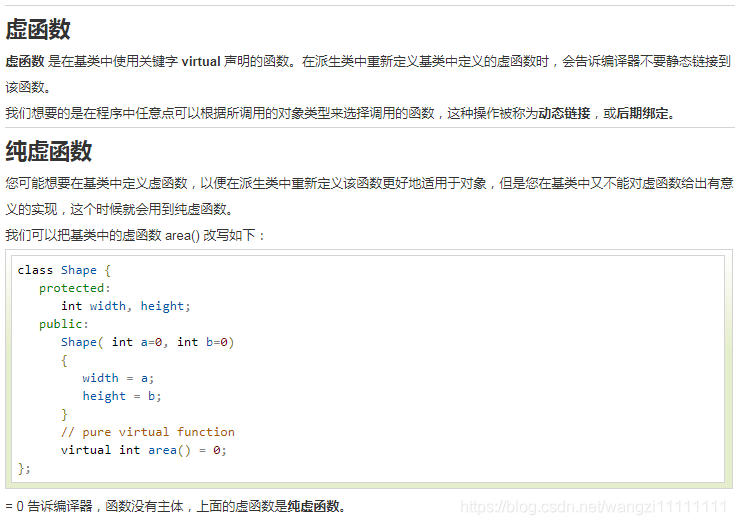


--(數據抽象、數據封裝、接口))

--(文件、流、異常處理、動態內存、命名空間))
---字符串(c++))

--(STL、標準庫))
)
--(模板、預處理器、信號處理))

--(多線程、Web編程))
迭代器模式)

---棧和隊列(c++))

---數組,動態內存,vector(c++))
---鏈表(c++))

---二叉樹(c++))
