文章目錄
- 一、類的6個默認成員函數
- 二、日期類的實現
- 2.1 運算符重載部分
- 2.2 日期之間的運算
- 2.3 整體代碼
- 1.Date.h部分
- 2. Date.cpp部分
- 三. const成員函數
- 四. 取地址及const取地址操作符重載
- 擴展內容
- 總結
ヾ(????)ノ" 人總要為過去的懶惰而付出代價ヾ(????)ノ"
一、類的6個默認成員函數
如果一個類中什么成員都沒有,簡稱為空類。
空類中并不是什么都沒有,任何類在什么都不寫時,編譯器會自動生成以下6個默認成員函數。
????????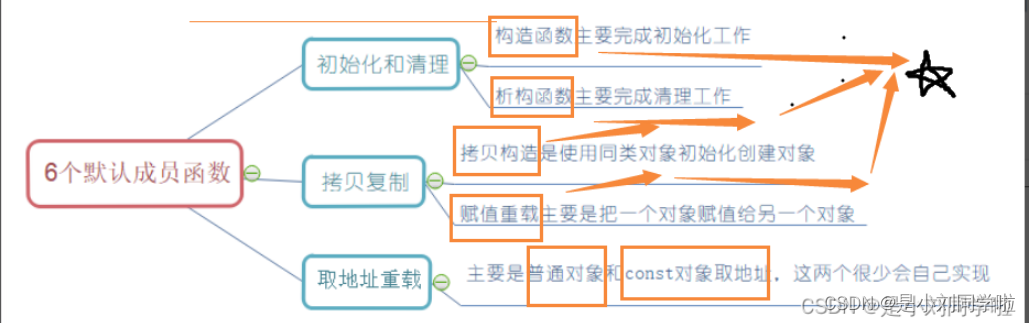
默認成員函數:用戶沒有顯式實現,編譯器會生成的成員函數稱為默認成員函數
二、日期類的實現
2.1 運算符重載部分
- inline不支持聲明與定義分離,所以成員函數要成為inline,最好直接在類里面定義
- 類里面定義成員函數的默認就是inline。代碼較長的部分采用聲明與定義分離的方法
1. 運算符重載部分1
此部分在Date.h類里面部分
//運算符重載部分1bool operator==(const Date& d);bool operator<(const Date& d);bool operator>(const Date& d){return !(*this <= d);}bool operator>=(const Date& d){return !(*this < d);}bool operator!=(const Date& d){return !(*this == d);}//思路:把小于的情況寫出來,剩下的就是大于的情況bool operator<=(const Date& d){return *this < d || *this == d;//this是一個指針,指向類的指針//小于和等于都已經實現過了,所以就可以復用}//運算符重載部分,【+-】Date operator+(int day) const;Date& operator+=(int day);Date operator-(int day) const;Date& operator-=(int day);
- 運算符重載部分【比較大小】,能復用其他函數的時候,盡可能的去復用
- 此部分寫一個小于等于,那么別的函數就都可以復用
- 內聯函數聲明定義不能分離(符號表里沒有函數的地址,所以使用的時候找不到函數定義),所以這部分代碼,如果想設置成inline函數,就直接放到類里面。內聯函數是在調用的地方,被展開,以空間換取時間的方法
- 類里面的函數默認是內聯函數
2. 運算符重載部分2
此部分在Date.cpp部分
//運算符重載部分2,==和<部分,
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)//訪問的本質上是:this->_year == d._year(一個是指針訪問,一個是類直接訪問)……//_year并不是類里面的_year(僅僅是一個聲明),而是比較的另一個類
{if (_year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day == d._day){return true;}else{return false;}
}
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)//要加上Date::(在類外面寫)
{if (_year < d._year|| (_year == d._year && _month < d._month)|| (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day)){return true;}else{return false;}
}
//運算符重載
//d1+2=d2;因為此處運算符是+,d1是不變的,所以,不能直接對d1進行改動
Date Date::operator+(int day) const//這里的返回值不能用Date&,因為出了函數,空間就被回收了
{//+復用+=Date ret(*this);//拷貝構造ret += day;return ret;//Date ret(*this);//拷貝構造//ret._day += day;//while (ret._day > GetMonthDay(ret._year, ret._month))//{// ret._day = ret._day - GetMonthDay(ret._year, ret._month);// ret._month++;// while (ret._month > 13)// {// ret._month = 1;// ret._year++;// }//}//return ret;
}Date& Date::operator+=(int day)//因為出了作用域this還在,所以用引用比較好【在能用引用的情況下,盡可能去用引用】
{//+=復用+//*this = *this + day;//return *this;if (day < 0){return *this -= -day;}_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _day)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _day);_month++;if (_month = 13){_month = 1;_year++;}}return *this;
}Date Date::operator-(int day) const
{Date ret(*this);ret -= day;return ret;
}
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{if (day < 0){return *this += -day;}_day -= day;while (_day <= 0)//日期是不能有0日的{_month--;while (_month == 0){_month = 12;_year--;}_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);}return *this;
}
- 運算法重載部分【比較大小】
因為代碼較長,不適合用inline函數,所以使用聲明與定義的方法【==和<的代碼更加容易實現】
- 運算符重載部分【+、+=、-、-=】
- d1=10,注意:這里是+和-,并不是+=和-=,所以d1是不變的,不要對d1直接進行改動。【利用拷貝構造】
- +和+=之間和-和-=之間可以相互復用【寫整塊代碼的時候,代碼之間能相互復用,就相互復用【即簡單又很大程度上保證了代碼的正確性】】【+復用+=更優】
- 加減法注意:這里的day要求必須是正數,否則減去一個負數,相當于加上一個正數;加上一個負數,相當于減去一個正數(相互復用即可)【因為-復用-=,所以-的函數就不用考慮負數問題】
補充知識點(1):
Date d1(2000, 9, 17); Date d2 = d1;//這里是拷貝構造,不是賦值【因為一個已經創建的對象去初始化另一個對象就是拷貝構造】
【賦值是兩個已經創建好的對象進行初始化】
補充知識點(2):
寫賦值重載函數和拷貝構造函數時,函數的形參要加const,因為既可以防止修改值,又可以防止當形參是函數的返回值【具有const屬性】,會權限擴大,導致錯誤【無法修改的右值】。
2.2 日期之間的運算
前置++后置++,前置–,后置–【區分++是前置還是后置的,函數重載】
C++用無參數的代表前置,有一個參數的代表后置【參數只要是int類型的就符合要求,無論是整形的哪一個數字】
1. 日期之間的運算1
此部分在Date.h類里面部分
Date.h
//日期之間的運算Date& operator++(){*this += 1;return *this;}Date operator++(int){Date tmp(*this);tmp += 1;return tmp;}Date& operator--(){*this -= 1;return *this;}Date operator--(int){Date tmp(*this);tmp -= 1;return tmp;}//日期-日期int operator-(const Date& d) const;
2. 日期之間的運算2
此部分在Date.cpp里面部分
Date.c
//*this和d不確定哪一個日期大
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const
{int day = 0;int flag = 1;Date max = *this;Date min = d;if (*this < d){max = d;min = *this;flag = -1;}while (min != max){min++;day++;}day = day * flag;return day;
}
2.3 整體代碼
1.Date.h部分
#pragma once#include <iostream>
#include <assert.h>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;//在正式的項目中不要全展開
using std::endl;class Date
{
public://拷貝構造函數部分//判斷是否是閏年bool isLeapYear(int year){if (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0&& year % 400 == 0){return true;}return false;}//每一月的天數int GetMonthDay(int year, int month);//構造函數(也可以不用寫)//可能會有用戶輸入非法日期Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1);//拷貝構造函數(也可以不用寫),值拷貝Date(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}//賦值運算符重載Date& operator=(const Date& d){if (this != &d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}return *this;}//不需要寫析構函數,沒有資源清理//打印Date,在函數后面加一個const,相當于void print(const Date* const d),const對象和普通對象都可以調用此函數//如果不加const,相當于void print(Date* const d),//只要不修改this,就可以加上void print() const{cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}//運算符重載部分,【+-】Date operator+(int day) const;Date& operator+=(int day);Date operator-(int day) const;Date& operator-=(int day);//運算符重載部分1【比較大小】bool operator==(const Date& d) const;bool operator<(const Date& d) const;bool operator>(const Date& d) const{return !(*this <= d);}bool operator>=(const Date& d) const{return !(*this < d);}bool operator!=(const Date& d) const{return !(*this == d);}//思路:把小于的情況寫出來,剩下的就是大于的情況bool operator<=(const Date& d) const{return *this < d || *this == d;//this是一個指針,指向類的指針//小于和等于都已經實現過了,所以就可以復用}//日期之間的運算Date& operator++(){*this += 1;return *this;}Date operator++(int){Date tmp(*this);tmp += 1;return tmp;}Date& operator--(){*this -= 1;return *this;}Date operator--(int){Date tmp(*this);tmp -= 1;return tmp;}//日期-日期int operator-(const Date& d) const;private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};2. Date.cpp部分
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Date.h"//構造函數部分
Date::Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{if (year >= 1&& (month >= 1 && month <= 12)&& (day >= 1 && day <= GetMonthDay(year, month))){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}else{cout << "日期非法" << endl;}
}
int Date::GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{assert(year > 0 && month >= 1 && month < 13);static int monthDayArray[13] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };//因為這部分空間需要頻繁開辟,所以就用static,就可以節約時間if (month == 2 && isLeapYear(year)){return 29;}else{return monthDayArray[month];}
}//運算符重載部分2,
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d) const//訪問的本質上是:this->_year == d._year(一個是指針訪問,一個是類直接訪問)……//_year并不是類里面的_year(僅僅是一個聲明),而是比較的另一個類
{if (_year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day == d._day){return true;}else{return false;}
}
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d) const//要加上Date::(在類外面寫)
{if (_year < d._year|| (_year == d._year && _month < d._month)|| (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day)){return true;}else{return false;}
}//運算符重載
//d1+2=d2;因為此處運算符是+,d1是不變的,所以,不能直接對d1進行改動
Date Date::operator+(int day) const//這里的返回值不能用Date&,因為出了函數,空間就被回收了
{//+復用+=Date ret(*this);//拷貝構造ret += day;return ret;//Date ret(*this);//拷貝構造//ret._day += day;//while (ret._day > GetMonthDay(ret._year, ret._month))//{// ret._day = ret._day - GetMonthDay(ret._year, ret._month);// ret._month++;// while (ret._month > 13)// {// ret._month = 1;// ret._year++;// }//}//return ret;
}Date& Date::operator+=(int day)//因為出了作用域this還在,所以用引用比較好【在能用引用的情況下,盡可能去用引用】
{//+=復用+//*this = *this + day;//return *this;if (day < 0){return *this -= -day;}_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _day)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _day);_month++;if (_month = 13){_month = 1;_year++;}}return *this;
}Date Date::operator-(int day) const
{Date ret(*this);ret -= day;return ret;
}
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{if (day < 0){return *this += -day;}_day -= day;while (_day <= 0)//日期是不能有0日的{_month--;while (_month == 0){_month = 12;_year--;}_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);}return *this;
}//*this和d不確定哪一個日期大
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const
{int day = 0;int flag = 1;Date max = *this;Date min = d;if (*this < d){max = d;min = *this;flag = -1;}while (min != max){min++;day++;}day = day * flag;return day;
}
三. const成員函數
將const修飾的類成員函數稱之為const成員函數,const修飾類成員函數,實際修飾該成員函數隱含的this指針,表明在該成員函數中不能對類的任何成員進行修改。
Date類中的打印函數中
void print() const{cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}
- 打印Date,在函數后面加一個const,相當于void print(const Date* const d),const對象和普通對象都可以調用此函數
- 如果不加const,相當于void print(Date* const d),
- 只要不修改this,就可以加上const
- (d+13).print();會報錯,因為d+13是傳值返回,傳值返回的是臨時拷貝,臨時拷貝具有常性。【在print沒有加const的情況下】
建議成員函數中,不修改成員變量的成員函數,都可以加上const。【普通對象和const對象都可以調用】 不加const,那么const修飾的對象就沒有辦法調用成員函數
1. const對象可以調用非const成員函數嗎?不可以,權限放大不可以
2. 非const對象可以調用const成員函數嗎?可以,權限縮小可以
3. const成員函數內可以調用其它的非const成員函數嗎?不可以,權限放大
4. 非const成員函數內可以調用其它的const成員函數嗎?可以,權限縮小
四. 取地址及const取地址操作符重載
這兩個默認成員函數一般不用重新定義 ,編譯器默認會生成。
Date* operator&(){return this;}//取地址重載const Date* operator&() const{return this;}//const取地址重載
這兩個運算符一般不需要重載,使用編譯器生成的默認取地址的重載即可,只有特殊情況,才需要重載,比如想讓別人獲取到指定的內容【不想要輸出地址,而是別的內容】!【此時才需要我們自己寫】
擴展內容
流插入運算符和流提取運算符重載
d1.operator<<(cout);//test函數中寫,可以運行
cout<<d1;//不可以運行
void operator<<(std::ostream out)
{
out << _year<< “- “<< _month<<” -” << _day<<endl;
}
Date.h 類里面
//友元函數friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const Date& d);friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& in, Date& d);
Date.cpp
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const Date& d)
{out << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day << endl;return out;
}
std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& in, Date& d)
{in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;return in;
}
- 內置類型直接支持流插入和流提取【且自動識別類型,因為函數重載】
- 全局變量函數不要放在.h里面,因為在別的文件展開的時候,會出現多個符號表里,導致重定義。【只有聲明的時候,才會鏈接的時候去找函數】
總結
以上就是今天的所有內容了,類的默認成員函數就到此結束了。本文以及【C++類和對象】類有哪些默認成員函數呢?(上)】詳細的介紹了類的默認成員函數,希望給友友們帶來幫助!






)



![自然語言處理從入門到應用——LangChain:記憶(Memory)-[自定義對話記憶與自定義記憶類]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/自然語言處理從入門到應用——LangChain:記憶(Memory)-[自定義對話記憶與自定義記憶類])

:c++實現數據的存儲和讀取(輸入流fstream))
動態規劃 JAVA)





