2、認識C++
2.1、例子
一個簡單的C++例子
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std; //使用名稱空間cout << "Com up and C++ me some time.";cout << endl; //換行符,還可以cout<<"\n";cout << "You won't regret it!" << endl;std::cout << "You won't regret it!" << endl;return 0;
}
對于頭文件的命名約束
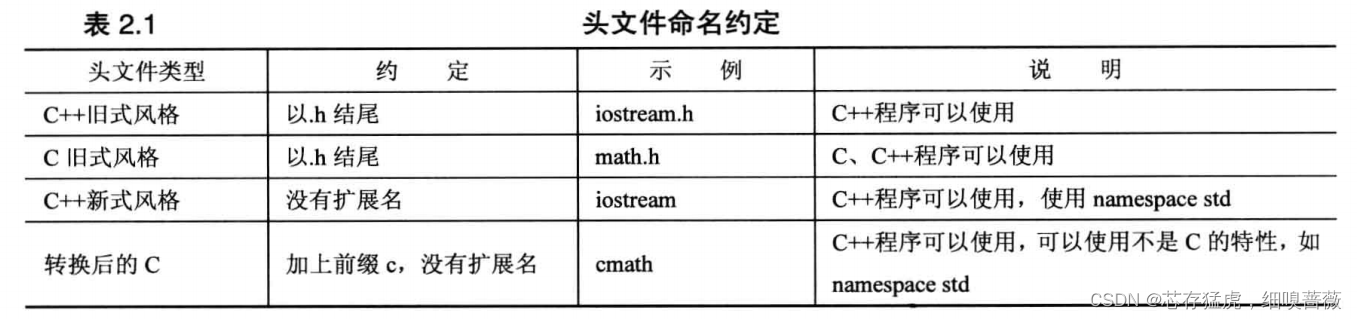
2.2、變量
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;int carrots; //定義或聲明變量carrots = 25;cout << "I have ";cout << carrots;cout << " carrots. " << endl;carrots = carrots - 1;cout << "Now I have " << carrots << " carrots." << endl;return 0;
}
cout和printf()
cout能夠識別類型的功能說明,其設計更靈活、好用。另外,它時可擴展的,也就是說,可以重新定義<<運算符,使cout能夠識別和顯示所開發的新數據類型。
而對于printf(),需要使用%d、%s等格式化控制符
2.3、其他C++語句
使用cin
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;int carrots;cout << "How many carrots do you have?" << endl;cin >> carrots; //inputcout << "Here are two more.";carrots = carrots + 2;cout << "Now you have " << carrots << " carrots." << endl; //使用<<將多個輸出語句拼接return 0;
}
2.4、函數
對于函數
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>int main() {using namespace std;double area;cout << "Enter the floor area." << endl;cin >> area;double size;size = sqrt(area);cout << "That's the equivalent of a square " << size << " feet to the side." << endl;return 0;
}
對于函數的調用,有下面的圖展示
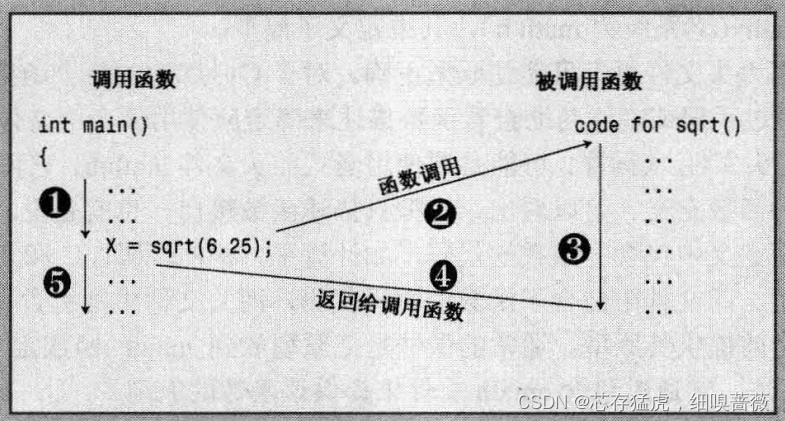
也可以自己定義函數
#include <iostream>
void simon(int); //函數的聲明int main() {using namespace std;simon(3);cout << "Pick an integer:";int count;cin >> count;simon(count);return 0;
}//函數的定義
void simon(int n) {using namespace std;cout << "Simon says touch your toes " << n << " times." << endl;
}函數的定義在文件中依次出現,如下圖所示
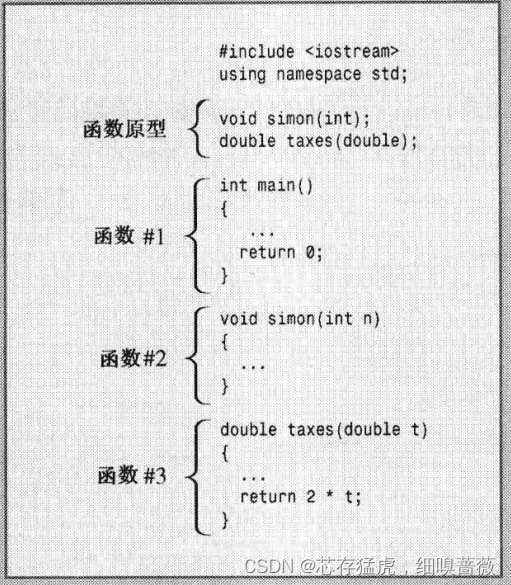

)









)
低功耗模式)





基本運算符)
