Java多線程實戰
java多線程(超詳細)
java自定義線程池總結
Java創建線程方式
-
方法1,繼承Thread類
-
方法2,實現Runable接口
-
方法2-2,匿名內部類形式+lambda表達式
-
方法3,實現Callable接口,允許有返回值
-
方法4,線程池方式
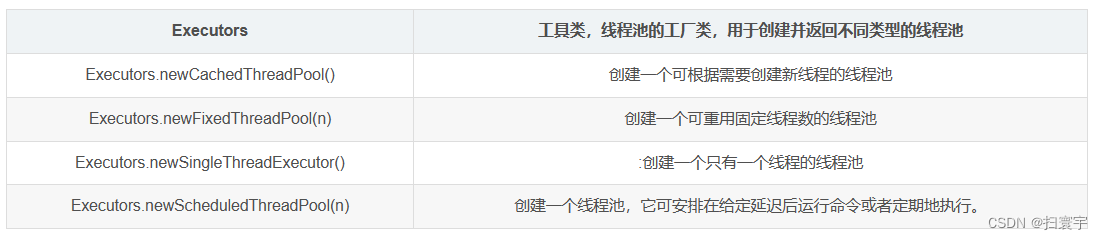
常見線程池:
public class ThreadTest {public static void main(String[] args) {// 方法一MyThread myThread = new MyThread();myThread.start();// 方法2MyRunable myRunable = new MyRunable();Thread thread = new Thread(myRunable);thread.start();// 方法2-2Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(5);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "匿名線程形式運行中");Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}});thread1.start();// 方法3MyCallable myCallable = new MyCallable();FutureTask futureTask = new FutureTask<>(myCallable);Thread thread2 = new Thread(futureTask);thread2.start();try {Object o = futureTask.get();System.out.println(o);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (ExecutionException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}// 方法4-線程池,常有線程池ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);threadPool.execute(myThread);threadPool.execute(myRunable);Future<?> ret = threadPool.submit(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(5);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "Callable形式運行中");Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}return "yangshun";});try {System.out.println(ret.get());} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (ExecutionException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}threadPool.shutdown();// 方法4-2:自定義線程池ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, //coreSize2, //MaxSize60, //60TimeUnit.SECONDS,new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(3), //指定一種隊列 (有界隊列),new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy() //自定義拒絕策略//, new DiscardOldestPolicy() //可以使用默認拒絕策略);ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(// 核心線程數3,// 最大線程數5,// 空閑線程最大存活時間60L,// 空閑線程最大存活時間單位TimeUnit.SECONDS,// 等待隊列及大小new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(100),// 創建新線程時使用的工廠Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),// 當線程池達到最大時的處理策略
// new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy() // 拋出RejectedExecutionHandler異常new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy() // 交由調用者的線程執行
// new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy() // 丟掉最早未處理的任務
// new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy() // 丟掉新提交的任務);// 總共5個任務for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {int taskIndex = i;executor.execute(() -> {System.out.println("線程 " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 正在執行任務 " + taskIndex);// 每個任務耗時1秒try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});}executor.shutdown();System.out.println("主線程運行結束");}@Testpublic void test() {ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在執行中。。。");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});}threadPool.shutdown();}}
class MyCallable implements Callable{@Overridepublic Object call() throws Exception {try {Thread.sleep(5);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "Callable形式運行中");Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}return "運行成功!yes";}
}
class MyThread extends Thread {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Thread.sleep(5);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "運行中");Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}class MyRunable implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Thread.sleep(5);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "Runable形式運行中");Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}SpringBoot創建線程方式
【并發編程】SpringBoot創建線程池的六種方式
java并發學習–第二章 spring boot實現線程的創建
CompletableFuture使用
Java多線程(十): FutureTask CompletableFuture詳解





、總消耗能量和節點消耗能量以及延遲研究(Matlab代碼實現))





)







