題目來源
- P3376 【模板】網絡最大流
- P2756 飛行員配對方案問題
- P3381 【模板】最小費用最大流
最大流
最大流問題是網絡流的經典類型之一,用處廣泛,個人認為網絡流問題最具特點的操作就是建反向邊,這樣相當于給了反悔的機會,不斷地求增廣路的,最終得到最大流


#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<queue> #include<string> #include<fstream> #include<vector> #include<stack> #include <map> #include <iomanip> #define bug cout << "**********" << endl #define show(x,y) cout<<"["<<x<<","<<y<<"] " //#define LOCAL = 1; using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; const ll mod = 1e6 + 3; const int Max = 1e5 + 10;struct Edge {int to, next, flow; //flow記錄這條邊當前的邊殘量 }edge[Max << 1];int n, m, s, t; int head[Max], tot; bool vis[Max];void init() {memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));tot = 0; }void add(int u, int v, int flow) {edge[tot].to = v;edge[tot].flow = flow;edge[tot].next = head[u];head[u] = tot++; }//向圖中增加一條容量為exp的邊(增廣路) int dfs(int u,int exp) {if (u == t) return exp; //到達匯點,當前水量全部注入vis[u] = true; //表示已經到了過了for(int i = head[u] ; i != -1 ;i = edge[i].next){int v = edge[i].to;if(!vis[v] && edge[i].flow > 0){int flow = dfs(v, min(exp, edge[i].flow));if(flow > 0) //形成了增廣路 {edge[i].flow -= flow;edge[i ^ 1].flow += flow;return flow;}}}return 0; //無法形成增廣路的情況 }//求最大流 int max_flow() {int flow = 0;while(true){memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));int part_flow = dfs(s, inf);if (part_flow == 0) return flow;flow += part_flow;} }int main() { #ifdef LOCALfreopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout); #endifwhile (scanf("%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &s, &t) != EOF){init();for (int i = 1, u, v, flow;i <= m; i++){scanf("%d%d%d", &u, &v, &flow);add(u, v, flow);add(v, u, 0);}printf("%d\n", max_flow());}return 0; }


#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<queue> #include<string> #include<fstream> #include<vector> #include<stack> #include <map> #include <iomanip> #define bug cout << "**********" << endl #define show(x,y) "["<<x<<","<<y<<"]" //#define LOCAL = 1; using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; const ll mod = 1e6 + 3; const int Max = 1e5 + 10;struct Edge {int to, next, flow; //flow記錄這條邊當前的邊殘量 }edge[Max << 1];int n, m, s, t; int head[Max], tot; int dis[Max];void init() {memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));tot = 0; }void add(int u, int v, int flow) {edge[tot].to = v;edge[tot].flow = flow;edge[tot].next = head[u];head[u] = tot++; }bool bfs() //判斷圖是否連通 {queue<int>q;memset(dis, -1, sizeof(dis));dis[s] = 0;q.push(s);while (!q.empty()){int u = q.front();q.pop();for (int i = head[u]; i != -1; i = edge[i].next){int v = edge[i].to;if (dis[v] == -1 && edge[i].flow > 0) //可以借助邊i到達新的結點 {dis[v] = dis[u] + 1; //求頂點到源點的距離編號 q.push(v);}}}return dis[t] != -1; //確認是否連通 }int dfs(int u, int flow_in) {if (u == t) return flow_in;int flow_out = 0; //記錄這一點實際流出的流量for (int i = head[u]; i != -1;i = edge[i].next){int v = edge[i].to;if (dis[v] == dis[u] + 1 && edge[i].flow > 0){int flow_part = dfs(v, min(flow_in, edge[i].flow));if (flow_part == 0)continue; //無法形成增廣路flow_in -= flow_part; //流出了一部分,剩余可分配流入就減少了flow_out += flow_part; //記錄這一點最大的流出 edge[i].flow -= flow_part;edge[i ^ 1].flow += flow_part; //減少增廣路上邊的容量,增加其反向邊的容量if (flow_in == 0)break;}}return flow_out; }int max_flow() {int sum = 0;while (bfs()){sum += dfs(s, inf);}return sum; }int main() { #ifdef LOCALfreopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout); #endifwhile (scanf("%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &s, &t) != EOF){init();for (int i = 1, u, v, flow;i <= m; i++){scanf("%d%d%d", &u, &v, &flow);add(u, v, flow);add(v, u, 0);}printf("%d\n", max_flow());}return 0; }
?二分圖匹配
要解決這類問題,我們需要先了解什么是二分圖?
二分圖:一個圖中的所有頂點可以分為兩個集合 V,K ,其實兩個集合內部的點彼此之間無邊,如下圖所示:(藍色的點和紅色的點分屬于兩個集合V,K)
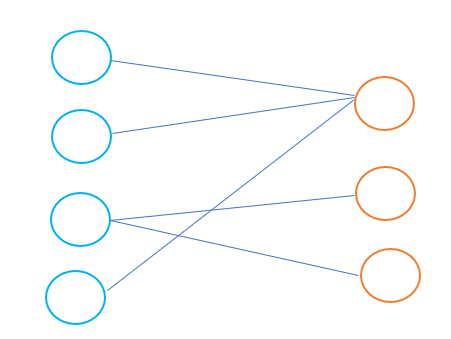
然后我們回到這個題目上來,這個題目求的是最大可出戰人數,實際上就是在二分圖中找到兩個集合中的最大匹配數,這類問題我們稱之為二分圖最大匹配數問題
屬于網絡流經典題目之一,下面說明一下建圖的過程
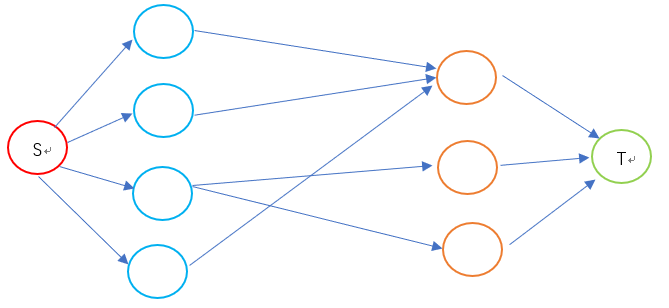
1)由源點向集合V中每個點建一條容量為1的邊
2)對于V,K集合之間存在的邊e,v 為V中的點,k為K中的點,我們建一條容量為1的邊,方向為 v --> k?
3)由K中每個點向匯點建一條容量為1的邊
當我們將圖建好了后,我們求這個圖的最大流,這個最大流即為二分圖最大匹配數,下面展示一下建成的圖:(S代表源點,T代表匯點,藍色的邊代表容量為1的邊)


#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<queue> #include<string> #include<fstream> #include<vector> #include<stack> #include <map> #include <iomanip> #define bug cout << "**********" << endl #define show(x,y) cout<<"["<<x<<","<<y<<"] " //#define LOCAL = 1; using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; const ll mod = 1e6 + 3; const int Max = 1e6 + 10;struct Edge {int to, next, flow; }edge[Max << 1];;int n, m, a, b, s, t; int head[Max], tot; int dis[Max]; int ans; bool vis[Max];void init() {memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));tot = 0;ans = 0; }void add(int u, int v, int flow) {edge[tot].to = v;edge[tot].flow = flow;edge[tot].next = head[u];head[u] = tot++; }bool bfs() {memset(dis, -1, sizeof(dis));dis[s] = 0;queue<int>q;q.push(s);while (!q.empty()){int u = q.front();q.pop();for (int i = head[u]; i != -1;i = edge[i].next){int v = edge[i].to;if (dis[v] == -1 && edge[i].flow > 0){dis[v] = dis[u] + 1;if (v == t) return true;q.push(v);}}}return false; }int dfs(int u, int flow_in) {if (u == t) return flow_in;int flow_out = 0;for (int i = head[u]; i != -1;i = edge[i].next){int v = edge[i].to;if (dis[v] == dis[u] + 1 && edge[i].flow > 0){int flow_part = dfs(v, min(flow_in, edge[i].flow));if (flow_part == 0) continue;flow_in -= flow_part;flow_out += flow_part;edge[i].flow -= flow_part;edge[i ^ 1].flow += flow_part;if (flow_in == 0)break;}}return flow_out; }int max_val() {int sum = 0;while (bfs()){sum += dfs(s, inf);}return sum; }int main() { #ifdef LOCALfreopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout); #endifwhile (scanf("%d%d", &m, &n) != EOF){init();s = 0, t = n + 1;for (int i = 1;i <= m;i++){add(s, i, 1);add(i, s, 0); //由源點向外籍飛行員建邊 }for (int i = m + 1; i <= n;i++){add(i, t, 1);add(t, i, 0);}while (scanf("%d%d", &a, &b) != EOF && a != -1 && b != -1){add(a, b, 1);add(b, a, 0);}printf("%d\n", max_val());for (int u = 1;u <= m;u++){for (int i = head[u]; i != -1;i = edge[i].next){if (edge[i].flow == 0 && edge[i].to != s && edge[i].to != t){printf("%d %d\n", u, edge[i].to);}}}}return 0; }
?最小費用最大流
這類題目相比于最大流問題新增了每天邊單位流量的價格,問在最大流的情況下求出最小的費用。
這類題目和最大流很想,不過也有不小區別,對于這類問題,我們為每條邊建的反邊的價格是每天邊的相反數,如圖
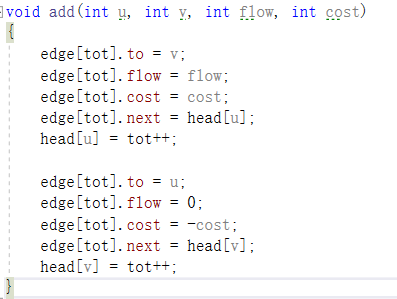
然后我們的算法也不再是Dinic算法了,而是用spfa或者dijkstra


#pragma GCC optimize(2) #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<queue> #include<string> #include<fstream> #include<vector> #include<stack> #include <map> #include <iomanip> #define bug cout << "**********" << endl #define show(x,y) cout<<"["<<x<<","<<y<<"] " #define LOCAL = 1; using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; const ll mod = 1e9 + 7; const int Max = 5e3 + 10;struct Edge {int to, rev; //rev記錄反向邊int flow, cost;; };int n, m, k; vector<Edge>edge[Max << 1]; int h[Max]; //每個結點的勢 int dis[Max]; int pre_node[Max], pre_edge[Max]; //前驅結點和對應邊void add(int u, int v, int flow, int cost) {edge[u].push_back({ v,(int)edge[v].size(),flow,cost });edge[v].push_back({ u,(int)edge[u].size() - 1,0,-cost }); }void min_cost_flow(int s, int t, int& min_cost, int& max_flow) {fill(h + 1, h + 1 + n, 0);min_cost = max_flow = 0;int tot = inf; //源點流量無限while (tot > 0){priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int> >, greater<pair<int, int> > >q;memset(dis, inf, sizeof(dis));dis[s] = 0;q.push({ 0,s });while (!q.empty()){int u = q.top().second;int dist = q.top().first;q.pop();if (dis[u] < dist)continue; //當前的距離不是最近距離for (int i = 0;i < edge[u].size(); i++){Edge &e = edge[u][i];if (edge[u][i].flow > 0 && dis[e.to] > dis[u] + e.cost + h[u] - h[e.to]){dis[e.to] = dis[u] +e.cost + h[u] - h[e.to];pre_node[e.to] = u;pre_edge[e.to] = i;q.push({ dis[e.to],e.to });}}}if (dis[t] == inf)break; //無法增廣了,就是找到答案了for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++) h[i] += dis[i];int flow = tot; //求這一增廣路徑的流量for (int i = t; i != s; i = pre_node[i])flow = min(flow, edge[pre_node[i]][pre_edge[i]].flow);for (int i = t; i != s; i = pre_node[i]){Edge& e = edge[pre_node[i]][pre_edge[i]];e.flow -= flow;edge[i][e.rev].flow += flow;}tot -= flow;max_flow += flow;min_cost += flow * h[t];} }int main() { #ifdef LOCAL//freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);//freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout); #endifint s, t;while (scanf("%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &s, &t) != EOF){for (int i = 1, u, v, flow, cost;i <= m;i++){scanf("%d%d%d%d", &u, &v, &flow, &cost);add(u, v, flow, cost);}int min_cost, max_flow;min_cost_flow(s, t, min_cost, max_flow);printf("%d %d\n", max_flow, min_cost);}return 0; }


#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<queue> #include<string> #include<fstream> #include<vector> #include<stack> #include <map> #include <iomanip> #define bug cout << "**********" << endl #define show(x,y) cout<<"["<<x<<","<<y<<"] " //#define LOCAL = 1; using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; const ll mod = 1e9 + 7; const int Max = 1e5 + 10;struct Edge {int to, next;int flow, cost; }edge[Max << 1];int n, m, s, t; int head[Max], tot; int dis[Max]; int pre[Max]; //記錄增廣路徑此點的前一天邊 bool vis[Max];void init() {memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));tot = 0; }void add(int u, int v, int flow, int cost) {edge[tot].to = v;edge[tot].flow = flow;edge[tot].cost = cost;edge[tot].next = head[u];head[u] = tot++;edge[tot].to = u;edge[tot].flow = 0;edge[tot].cost = -cost;edge[tot].next = head[v];head[v] = tot++; }bool spfa(int s, int t) {memset(dis, inf, sizeof(dis));memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));memset(pre, -1, sizeof(pre));queue<int>q;q.push(s);dis[s] = 0;vis[s] = true;while (!q.empty()){int u = q.front();q.pop();vis[u] = false;for (int i = head[u]; i != -1; i = edge[i].next){int v = edge[i].to;if (edge[i].flow > 0 && dis[v] > dis[u] + edge[i].cost){dis[v] = dis[u] + edge[i].cost;pre[v] = i;if (!vis[v]){vis[v] = true;q.push(v);}}}}return pre[t] != -1; }void min_cost_max_flow(int s, int t, int& max_flow, int& min_cost) {max_flow = 0;min_cost = 0;while (spfa(s, t)){int flow = inf;for (int i = pre[t]; i != -1; i = pre[edge[i ^ 1].to]) //沿增廣路回溯edge[i^1]即為其反邊 {flow = min(flow, edge[i].flow);}for (int i = pre[t]; i != -1; i = pre[edge[i ^ 1].to]){edge[i].flow -= flow;edge[i ^ 1].flow += flow;min_cost += flow * edge[i].cost;}max_flow += flow;} }int main() { #ifdef LOCALfreopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout); #endifwhile (scanf("%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &s, &t) != EOF){init();for (int i = 1, u, v, flow, cost;i <= m;i++){scanf("%d%d%d%d", &u, &v, &flow, &cost);add(u, v, flow, cost);}int max_flow = 0, min_cost = 0;min_cost_max_flow(s, t, max_flow, min_cost);printf("%d %d\n", max_flow, min_cost);}return 0; }
?
: 圖與會話,變量)
)



進行反向工程,并從泰國的海灘上構建了自己的數據庫)













