1.第一題
int main()
{int a = 128;printf("%u\n", a);system("pause");
}輸出結果
128
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int main()
{char a = 128;printf("%u\n", a);system("pause");
}輸出結果
4294967168
因為有符號字符型其范圍為-128~127
127用二進制表示為:0111 1111,
128表示為1000 0000,這里發生溢出,因為第一位為1,為符號位,表示負數,即-128
看到這里是不是一頭霧水,網上有很多方法解釋一同看完還是不懂。所以我畫了一張圖來解釋

有符號字符型其范圍為-128~127
所以127的下一個數字是-128不是128
2.第二題
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int main()
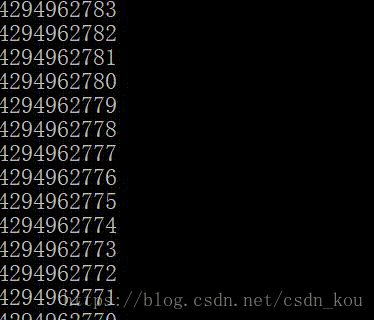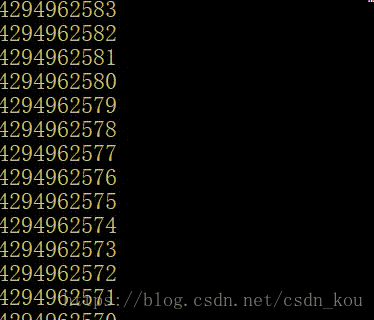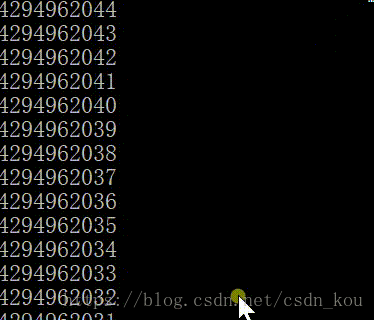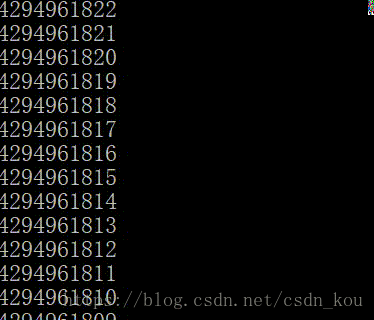
{unsigned i;for (i = 0; i >= 0; i--){printf("%u\n", i);}system("pause");
}為什么輸出結果是這樣呢?
無符號數永遠大于0
2.1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
unsigned char i = 0;
int main()
{for (i = 0; i <= 255; i++){puts("Hello World");}
}3.第三題
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int main()
{char a[1000];int i;for (i = 0; i < 1000; i++){a[i] = -1 - i;}printf("%d\n", strlen(a));system("pause");
}strlen()遇到0就停止,那么他什么時候遇到’\0’呢?
當i = 127的時候 a[i] = -128;那么他的下一個數字是多少呢?是-129嗎?
4.第四題
int main()
{short num = 32767;short int a = num + 1;printf("%d\n", a);system("pause");
}32767(有符號的短整型能表示的最大值)
結果:-32768
記:有符號的短整型能表示的最大值







 2)









)



