一、Loss Functions損失函數
損失函數的作用:
1,損失函數就是實際輸出值和目標值之間的差
2,由這個差便可以通過反向傳播對之后的數據進行更新
Loss Functions官網給的API
里面由很多種損失函數,不同的損失函數有其不同的用途及表達式

二、L1Loss損失函數
torch.nn.L1Loss(size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction=‘mean’)
由官網給的各參數使用可知,size_average和reduce參數都已經被棄用了
而reduction有三個模式,none、mean、sum

import torch
from torch.nn import L1Lossinput = torch.tensor([1,2,3],dtype=torch.float32)
target = torch.tensor([4,5,6],dtype=torch.float32)input = torch.reshape(input,(1,1,1,3))
target = torch.reshape(target,(1,1,1,3))loss_1 = L1Loss(reduction='sum')
result_1 = loss_1(input,target)
print(result_1)#tensor(9.) 4-1 + 5-2 + 6-3 = 9loss_2 = L1Loss(reduction='mean')
result_2 = loss_2(input,target)
print(result_2)#tensor(3.) (4-1 + 5-2 + 6-3) / 3 = 3loss_3 = L1Loss(reduction='none')
result_3 = loss_3(input,target)
print(result_3)#tensor([[[[3., 3., 3.]]]])
三、MSELoss均方誤差損失函數
torch.nn.MSELoss(size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction=‘mean’)

import torchinput = torch.tensor([1,2,3],dtype=torch.float32)
target = torch.tensor([4,5,6],dtype=torch.float32)input = torch.reshape(input,(1,1,1,3))
target = torch.reshape(target,(1,1,1,3))loss_mse = torch.nn.MSELoss()
result = loss_mse(input,target)
print(result)#tensor(9.) [(4-1)^2 + (5-2)^2 + (6-3)^2] / 3 = 9
四、CrossEntropyLoss交叉熵損失函數
torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=None, size_average=None, ignore_index=- 100, reduce=None, reduction=‘mean’, label_smoothing=0.0)

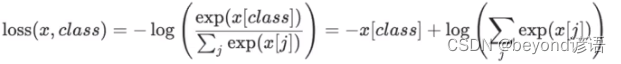
假設x為三類:狗0、貓1、豬2,對應的輸出概率為(1.0,2.0,3.0)
最后的真實目標結果為豬,對應的是(2)
import torchx = torch.tensor([1.0,2.0,3.0])
target = torch.tensor([2])x = torch.reshape(x,(1,3))#將x變成(N,C)形式 ,1維,3類
print(x.shape)#torch.Size([1, 3])loss_cross = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
result = loss_cross(x,target)print(result)#tensor(0.4076)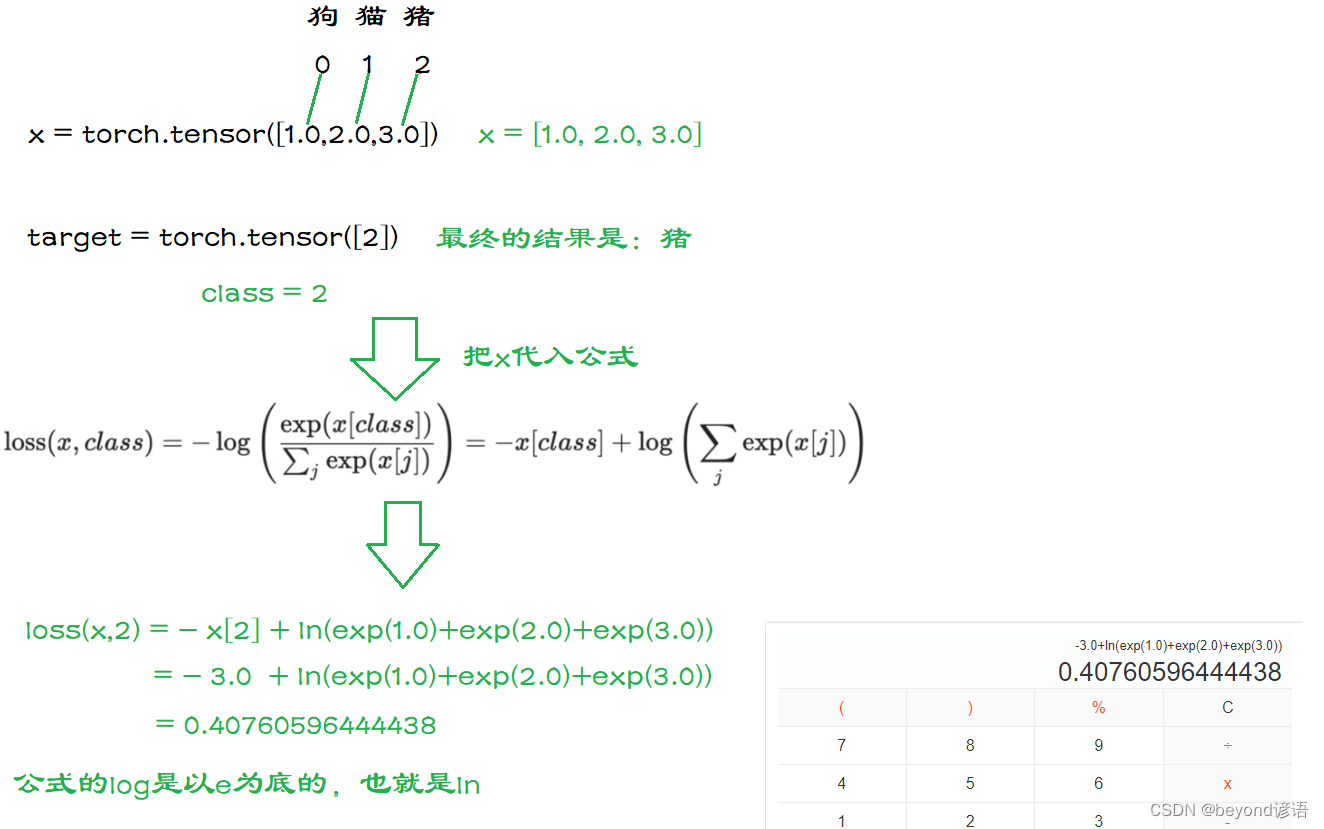
)




)


)










