題目鏈接:http://acm.split.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5794
題意:讓一個棋子從(1,1)走到(n,m),要求像馬一樣走日字型并只能往右下角走。里面還有r個障礙點不能經過或者到達,問有多少種走法可以走到(n,m)。
思路:畫個圖可以發現走的點像一個斜著的楊輝三角。所以可以得到一個從點 i 走到點 j 的路徑數是一個組合數。?
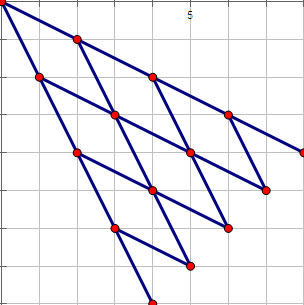 大概就是長這樣,楊輝三角的每個點的數如下。
大概就是長這樣,楊輝三角的每個點的數如下。
1
1???????1
1??????2??????1
1???????3??????3??????1
1??????4???????6??????4??????1
1???????5??????10??????10??????5??????1
1??????6??????15??????20??????15??????6??????1
1??????7??????21??????35??????35??????21??????7??????1
?
找到規律:路徑數為C(在這一步的位置,走過的步數)。走過的步數是當前的點 i 坐標(x,y),(x+y)/3就是步數了。當前的位置是min(x,y)-步數。這里的步數就相當于三角的層數。
首先對全部障礙從小到大進行排序,對于每個障礙 i,求出從(1,1)走到其的路徑總數,減去之前的障礙(0 <= j < i)可以走到現在的障礙的路徑總數(dp[i] -= dp[j] * 從點 j 走到點 i 的路徑數)。組合數的計算要用到Lucas定理進行計算。
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include <string> 5 #include <cmath> 6 #include <iostream> 7 #include <stack> 8 using namespace std; 9 #define MOD 110119 10 typedef long long LL; 11 struct node 12 { 13 LL x, y; 14 }p[115]; 15 LL dp[115]; 16 LL f[MOD+10]; 17 /* 18 dp[i]一開始表示從(0, 0)走到第i個點的路徑數 19 后面要減去如果前面有障礙,那么會有一部分路徑是不能走的 20 減去的路徑數為分別為第j個點(0<=j<i)走到第i個點的路徑數*dp[j] 21 */ 22 23 bool cmp(const node &a, const node &b) 24 { 25 if(a.x == b.x) return a.y < b.y; 26 return a.x < b.x; 27 } 28 29 void biao() //打出階乘表 30 { 31 f[0] = f[1] = 1; 32 for(int i = 2; i <= MOD; i++) { 33 f[i] = f[i-1] * i % MOD; 34 } 35 } 36 37 LL quick_pow(LL a, LL b) 38 { 39 a %= MOD, b %= MOD; 40 LL ans = 1; 41 while(b) { 42 if(b & 1) ans = ans * a % MOD; 43 a = a * a % MOD; 44 b >>= 1; 45 } 46 return ans; 47 } 48 49 LL C(LL n, LL m) 50 { 51 if(m > n) return 0; 52 if(m < 0) return 0; 53 LL ans = 1; 54 ans = ans * f[n] % MOD * quick_pow(f[m] * f[n-m] % MOD, MOD - 2) % MOD; 55 return ans; 56 } 57 58 LL Lucas(LL n, LL m) 59 { 60 if(m == 0) return 1; 61 return C(n % MOD, m % MOD) % MOD * Lucas(n / MOD, m / MOD) % MOD; 62 } 63 64 int main() 65 { 66 LL n, m, r; 67 int cas = 0; 68 biao(); 69 while(~scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d", &n, &m, &r)) { 70 memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp)); 71 bool flag = 0; 72 for(int i = 0; i < r; i++) { 73 scanf("%I64d%I64d", &p[i].x, &p[i].y); 74 if(p[i].x == n && p[i].y == m) flag = 1; 75 p[i].x--, p[i].y--; 76 } 77 sort(p, p + r, cmp); 78 p[r].x = n - 1, p[r].y = m - 1; //把目標點加入 79 printf("Case #%d: ", ++cas); 80 if(flag || (p[r].x + p[r].y) % 3 != 0) { //如果障礙在目標點上或者不能走到目標點 81 puts("0"); continue; 82 } 83 for(int i = 0; i <= r; i++) { 84 if((p[i].x + p[i].y) % 3 == 0) { //如果這個障礙是可以走到的 85 LL a = (p[i].x + p[i].y) / 3; //第幾層 86 LL b = min(p[i].x, p[i].y) - a; //位置 87 dp[i] = Lucas(a, b); //類似于楊輝三角的組合數 88 for(int j = 0; j < i; j++) { 89 if(p[j].y >= p[i].y || p[j].x >= p[i].x) continue; //題目要求只能往右下角走 90 LL xx = (p[i].x - p[j].x); 91 LL yy = (p[i].y - p[j].y); 92 if((xx + yy) % 3 == 0) { //要能夠從j點走到i點 93 LL aa = (xx + yy) / 3; 94 LL bb = min(xx, yy) - aa; //減去可以從j點走到i點的路徑數 95 dp[i] -= (Lucas(aa, bb) * dp[j]) % MOD; 96 dp[i] = (dp[i] + MOD) % MOD; 97 } 98 } 99 } 100 } 101 printf("%I64d\n", dp[r]); 102 } 103 return 0; 104 }
?














 中斷處理程序中斷服務例程)




