1. CMU 15213_15513 CSAPP 深入理解計算機系統 Lecture 01 Course Overview 中英字幕_嗶哩嗶哩_bilibili
從這個課程中可以學到什么?(為什么要學這門課)
Great Reality #1(數字類型): Ints are not Integers, Floats are not Reals
對于整數的理解可能不像是你期望的那樣。
Example1:數的平方一定大于等于0嗎?![]()
Float: yes!
Int:

Example2: 加法結合律?![]()
Unsigned & Signed Int:Yes!
Float:?
![]()
Great Reality #2(匯編語言): You’ve Got to Know Assembly
可以學到匯編語言。它是 機器級別模型運行 的關鍵。
Great Reality #3(存儲結構): Memory Matters
memory referencing bug example
typedef struct{int a[2];double d;
} struct_t;double fun(int i){volatile struct_t s;s.d = 3.14;s.a[i] = 1073741824; /* possibly out of bounds */return s.d;
}?運行結果:

為什么會出現這樣的運行結果?
答:與數據如何在內存中布局有關。
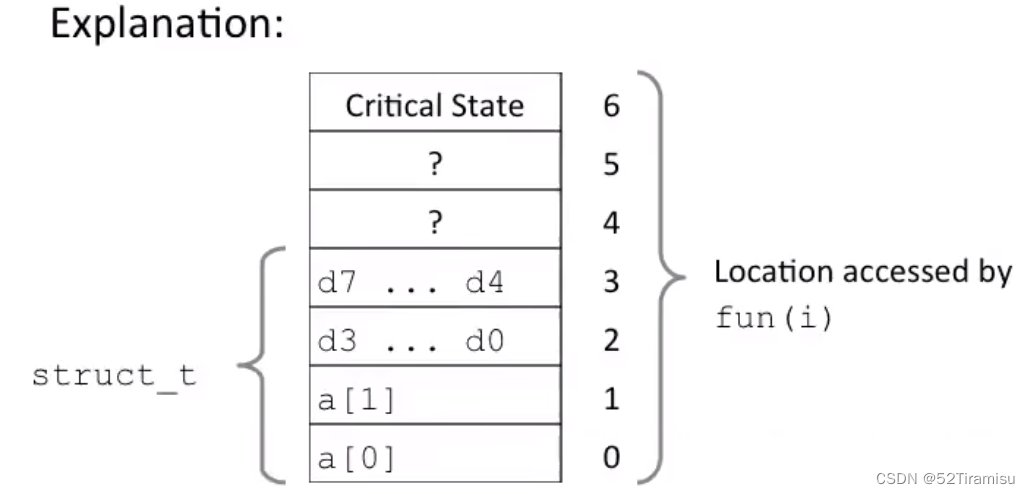
調用 fun(3)、fun(4) 時,是在改變這個浮點數d的字節。
當輸入 6 時,修改了該程序的某些狀態(它被用于維持程序運行,最有可能是記錄已經分配的內存),這就導致了程序崩潰。
理解數據結構的機器級別表示、以及他們如何運行對于你處理這些漏洞的能力十分重要。
Great Reality #4: There’s more to performance than asymptotic complexity
程序中需要用到一些低級的優化,就需要了解系統的運行規律。 是什么讓它運行得很好,是什么讓它運行不佳。
Memory system performance example
將一個矩陣從源地址src 復制到 目標地址dst
void copyij(int src[2048][2048], int dst[2048][2048]){int i, j;for(i = 0; i < 2048; i++)for(j = 0; j < 2048; j++)dst[i][j] = src[i][j];
}
// 4.3ms
void copyij(int src[2048][2048], int dst[2048][2048]){int i, j;for(j = 0; j < 2048; i++)for(i = 0; i < 2048; i++)dst[i][j] = src[i][j];
}
// 81.8ms第一個 比 第二個 快得多,與內存層次結構中的緩存有關。
Great Reality #5(網絡): Computers do more than execute programs
網絡。
學習方法
每章閱讀三遍,然后做練習題。

學習筆記,(二)機器學習和深度學習綜述)
--注冊中心)

)




)





)

方式)

