在多線程開發中停止線程是非常重要的技術點。
停止線程在Java語言中并不像break語句那樣干脆。須要一些技巧性的處理。
一、 ?異常法
採用異常法來停止一個線程。首先我們須要了解一下兩個方法的使用方法:
1、interrupt()方法
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
System.out.println("i="+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
MyThread thread=new MyThread();
thread.start();
thread.sleep(10);
thread.interrupt();
}
}
上面的樣例調用interrupt()方法來停止線程,但interrupt()方法的使用效果并不像for+break語句那樣。立即就能停止循環。
調用interrupt()方法不過在當前線程打了一個停止的標記,并非真的停止。那么假設停止線程了?我們接著往以下看。
2、推斷線程是否是停止狀態
1)、 ?interrupted()
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
System.out.println("i="+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
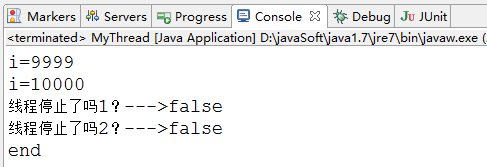
try{
MyThread thread=new MyThread();
thread.start();
thread.sleep(100);
thread.interrupt();
System.out.println("線程停止了嗎1?--->"+thread.interrupted());
System.out.println("線程停止了嗎2?--->"+thread.interrupted());
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
從控制臺打印的結果來看,線程沒有停止。這就是說,interrupted()測試當前線程是否中斷,由于這個當前線程就是main。它沒有中斷過,所以打印的結果是兩個false。
怎樣使main線程產生中斷效果了。我們在看下,以下的樣例:
public class MyThread{
public static void main(String[] args){
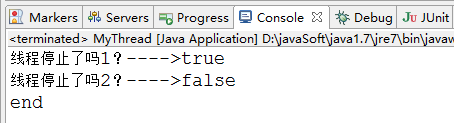
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
System.out.println("線程停止了嗎1?---->"+Thread.interrupted());
System.out.println("線程停止了嗎2?---->"+Thread.interrupted());
System.out.println("end");
}
}
從上面的結果來看。interrupted()方法的確推斷當前線程是否是停止狀態。
可是為什么第2個值是false。原來。連續兩次調用該方法第一次會清除中斷狀態后。第二次調用所以返回flase。
2)、 ?isInterrupted()
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
System.out.println("i="+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
MyThread thread=new MyThread();
thread.start();
thread.sleep(10);
thread.interrupt();
System.out.println("線程停止了嗎1?--->"+thread.isInterrupted());
System.out.println("線程停止了嗎2?--->"+thread.isInterrupted());
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
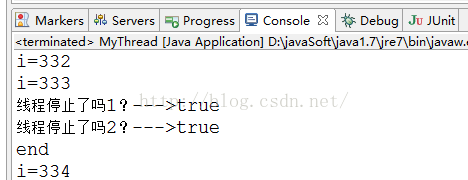
從結果看出方法isInterrupted()并未清除,所以打印出了兩個true.
3、停止線程
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
if(this.interrupted()){
System.out.println("線程是停止狀態了,我要退出了.");
break;
}
System.out.println("i="+i);
}
System.out.println("假設此處還是循環,那么我就會繼續運行.線程并沒有停止");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
MyThread thread=new MyThread();
thread.start();
thread.sleep(10);
thread.interrupt();
System.out.println("end");
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
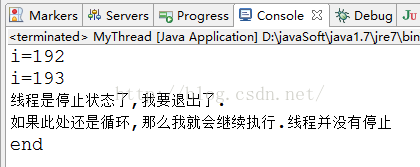
假設這么寫的話,線程并沒有停止。如今我們在改動下代碼。也就是所謂的異常法停止線程。
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
try{
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
if(this.interrupted()){
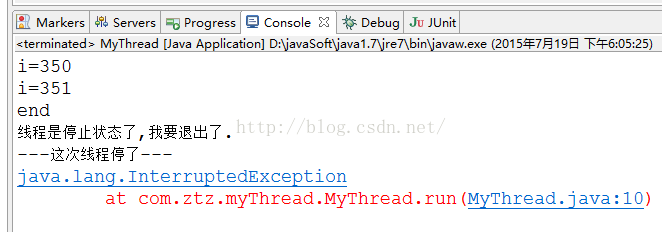
System.out.println("線程是停止狀態了,我要退出了.");
throw new InterruptedException();
}
System.out.println("i="+i);
}
System.out.println("我被運行了嗎?");
}catch(InterruptedException e){
System.out.println("---這次線程停了---");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
MyThread thread=new MyThread();
thread.start();
thread.sleep(10);
thread.interrupt();
System.out.println("end");
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
二、 ?在沉睡中停止
假設線程在sleep()狀態下停止線程會有什么效果了?
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
try{
System.out.println("run start");
Thread.sleep(1000000);
System.out.println("run end");
}catch(InterruptedException e){
System.out.println("sleep被停止,狀態:--->"+this.isInterrupted());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
MyThread thread=new MyThread();
thread.start();
thread.interrupt();
thread.sleep(1000);
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("main catch");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
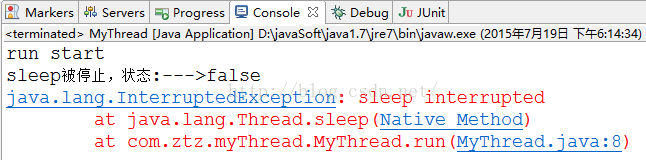
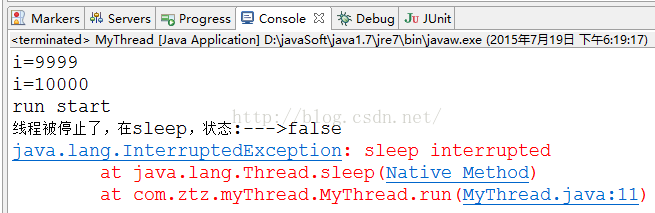
從結果我們能夠看出,在線程睡眠時候停止某一線程,會異常。而且清除停止狀態。我們前面異常停止線程,都是先睡眠,在停止線程,與之相反的操作,我寫代碼的時候須要注意下。
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
try{
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
System.out.println("i="+i);
}
System.out.println("run start");
Thread.sleep(1000000);
System.out.println("run end");
}catch(InterruptedException e){
System.out.println("線程被停止了。在sleep,狀態:--->"+this.isInterrupted());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
MyThread thread=new MyThread();
thread.start();
thread.interrupt();
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("main catch");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
三、 ?暴力停止
public class MyThread extends Thread{
private int i=0;
@Override
public void run() {
try{
while (true) {
i++;
System.out.println("i="+i);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
MyThread thread=new MyThread();
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(6000);
thread.stop();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
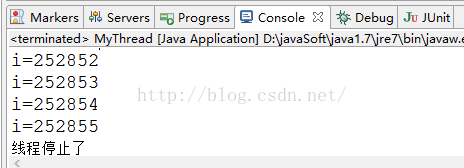
stop()方法已經被棄用,假設強制讓線程停止。能夠會有一些清理工作沒得到完畢。還有就是對鎖定的對象進行了解鎖,導致數據不同步的現象,所以開發時候禁止使用該方法去暴力停止線程。
四、 ?使用return停止線程
public class MyThread extends Thread{
private int i=0;
@Override
public void run() {
try{
while (true) {
i++;
if(this.interrupted()){
System.out.println("線程停止了");
return;
}
System.out.println("i="+i);
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
MyThread thread=new MyThread();
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
thread.interrupt();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
PS:只是還是建議使用異常法來停止線程,由于在catch塊中還能夠將異常向上拋,使線程停止事件得到傳播。
)










)



)



