大家好,我是若川。持續組織了8個月源碼共讀活動,感興趣的可以點此加我微信 ruochuan12?參與,每周大家一起學習200行左右的源碼,共同進步。同時極力推薦訂閱我寫的《學習源碼整體架構系列》?包含20余篇源碼文章。歷史面試系列
前言
談及 Babel,必然離不開 AST。有關 AST 這個知識點其實是很重要的,但由于涉及到代碼編譯階段,大多情況都是由各個框架內置相關處理,所以作為開發(使用)者本身,往往會忽視這個過程。希望通過這篇文章,帶各位同學走進 AST,借助 AST 發揮更多的想象力。
AST 概述
想必大家總是聽到 AST 這個概念,那么到底什么是 AST?
AST 全稱是是 Abstract Syntax Tree,中文為抽象語法樹,將我們所寫的代碼轉換為機器能識別的一種樹形結構。其本身是由一堆節點(Node)組成,每個節點都表示源代碼中的一種結構。不同結構用類型(Type)來區分,常見的類型有:Identifier(標識符),Expression(表達式),VariableDeclaration(變量定義),FunctionDeclaration(函數定義)等。
AST 結構
隨著 JavaScript 的發展,為了統一ECMAScript標準的語法表達。社區中衍生出了ESTree Spec[1],是目前社區所遵循的一種語法表達標準。
ESTree 提供了例如Identifier、Literal等常見的節點類型。
節點類型
| 類型 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| File | 文件 (頂層節點包含 Program) |
| Program | 整個程序節點 (包含 body 屬性代表程序體) |
| Directive | 指令 (例如 "use strict") |
| Comment | 代碼注釋 |
| Statement | 語句 (可獨立執行的語句) |
| Literal | 字面量 (基本數據類型、復雜數據類型等值類型) |
| Identifier | 標識符 (變量名、屬性名、函數名、參數名等) |
| Declaration | 聲明 (變量聲明、函數聲明、Import、Export 聲明等) |
| Specifier | 關鍵字 (ImportSpecifier、ImportDefaultSpecifier、ImportNamespaceSpecifier、ExportSpecifier) |
| Expression | 表達式 |
公共屬性
| 類型 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| type | AST 節點的類型 |
| start | 記錄該節點代碼字符串起始下標 |
| end | 記錄該節點代碼字符串結束下標 |
| loc | 內含 line、column 屬性,分別記錄開始結束的行列號 |
| leadingComments | 開始的注釋 |
| innerComments | 中間的注釋 |
| trailingComments | 結尾的注釋 |
| extra | 額外信息 |
AST 示例
有的同學可能會問了,這么多類型都需要記住么? 其實并不是,我們可以借助以下兩個工具來查詢 AST 結構。
AST Explorer (常用)[2]
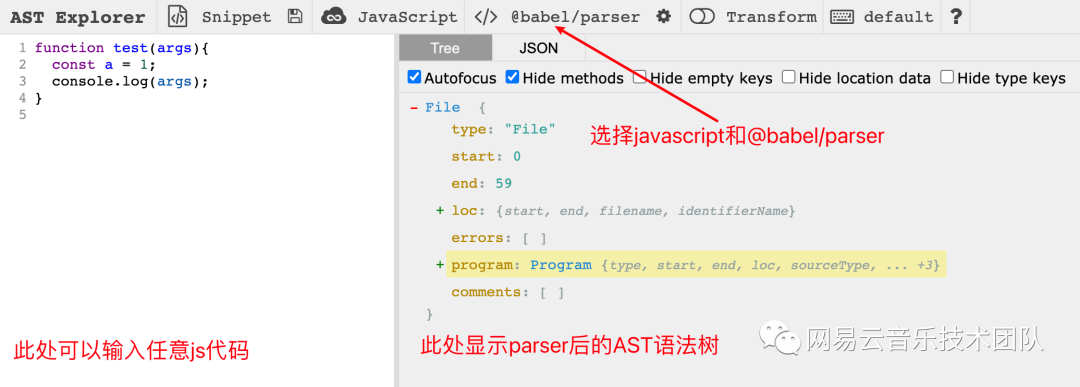
AST 可視化[3]
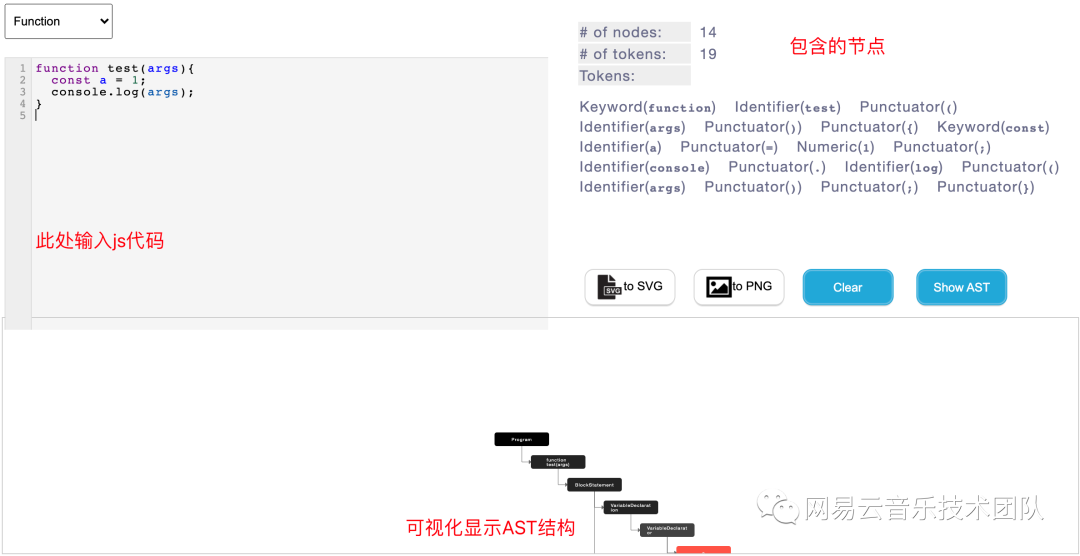
結合一個示例,帶大家快速了解一下 AST 結構。
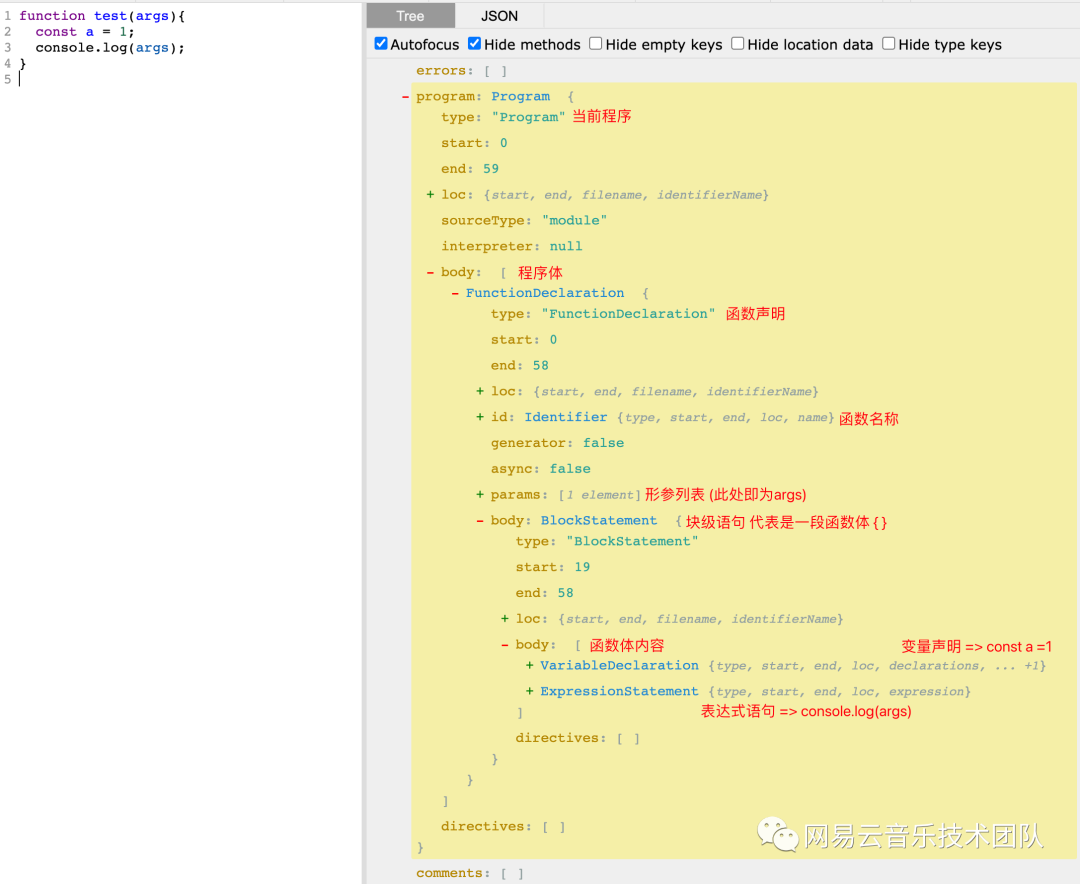
function?test(args)?{const?a?=?1;console.log(args);
}上述代碼,聲明了一個函數,名為test,有一個形參args。
函數體中:
聲明了一個
const類型變量a,值為1執行了一個 console.log 語句
將上述代碼粘貼至AST Explorer[4],結果如圖所示:
接下來我們繼續分析內部結構,以const a = 1為例:
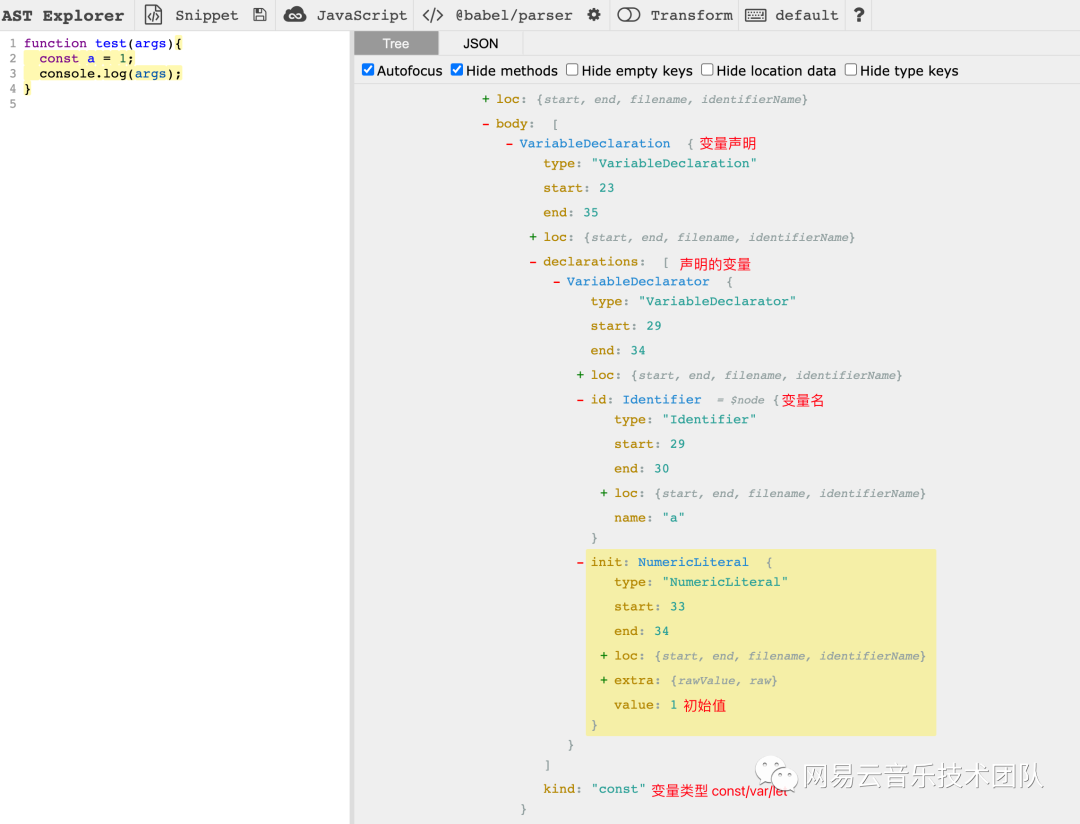
變量聲明在 AST 中對應的就是 type 為VariableDeclaration的節點。該節點包含kind和declarations兩個必須屬性,分別代表聲明的變量類型和變量內容。
細心的同學可能發現了declarations是一個數組。這是為什么呢?因為變量聲明本身支持const a=1,b=2的寫法,需要支持多個VariableDeclarator,故此處為數組。
而 type 為VariableDeclarator的節點代表的就是a=1這種聲明語句,其中包含id和init屬性。
id即為Identifier,其中的name值對應的就是變量名稱。
init即為初始值,包含type,value屬性。分別表示初始值類型和初始值。此處 type 為NumberLiteral,表明初始值類型為number類型。
Babel 概述
Babel 是一個 JavaScript 編譯器,在實際開發過程中通常借助Babel來完成相關 AST 的操作。
Babel 工作流程
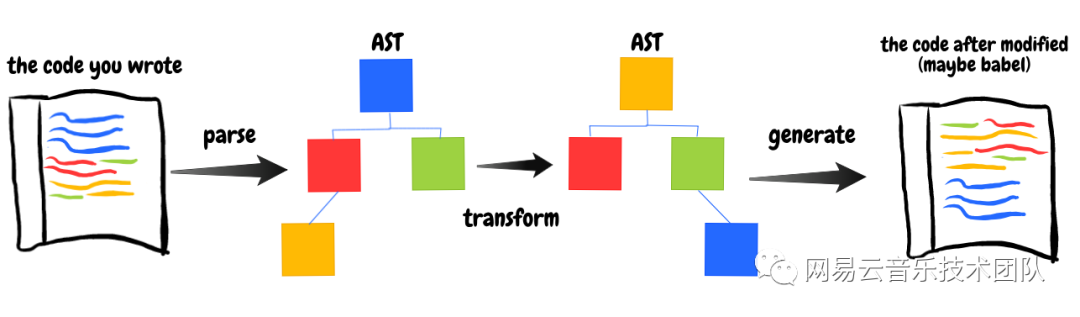
Babel AST
Babel 解析代碼后生成的 AST 是以ESTree[5]作為基礎,并略作修改。
官方原文如下:
The Babel parser generates AST according to Babel AST format. It is based on ESTree spec with the following deviations:
Literal token is replaced with StringLiteral, NumericLiteral, BigIntLiteral, BooleanLiteral, NullLiteral, RegExpLiteral
Property token is replaced with ObjectProperty and ObjectMethod
MethodDefinition is replaced with ClassMethod
Program and BlockStatement contain additional directives field with Directive and DirectiveLiteral
ClassMethod, ObjectProperty, and ObjectMethod value property's properties in FunctionExpression is coerced/brought into the main method node.
ChainExpression is replaced with OptionalMemberExpression and OptionalCallExpression
ImportExpression is replaced with a CallExpression whose callee is an Import node.
Babel 核心包
| 工具包 | 說明 |
|---|---|
@babel/core | Babel 轉碼的核心包,包括了整個 babel 工作流(已集成@babel/types) |
@babel/parser | 解析器,將代碼解析為 AST |
@babel/traverse | 遍歷/修改 AST 的工具 |
@babel/generator | 生成器,將 AST 還原成代碼 |
@babel/types | 包含手動構建 AST 和檢查 AST 節點類型的方法 |
@babel/template | 可將字符串代碼片段轉換為 AST 節點 |
npm?i?@babel/parser?@babel/traverse?@babel/types?@babel/generator?@babel/template?-DBabel 插件
Babel 插件大致分為兩種:語法插件和轉換插件。語法插件作用于 @babel/parser,負責將代碼解析為抽象語法樹(AST)(官方的語法插件以 babel-plugin-syntax 開頭);轉換插件作用于 @babel/core,負責轉換 AST 的形態。絕大多數情況下我們都是在編寫轉換插件。
Babel 工作依賴插件。插件相當于是指令,來告知 Babel 需要做什么事情。如果沒有插件,Babel 將原封不動的輸出代碼。
Babel 插件本質上就是編寫各種 visitor 去訪問 AST 上的節點,并進行 traverse。當遇到對應類型的節點,visitor 就會做出相應的處理,從而將原本的代碼 transform 成最終的代碼。
export?default?function?(babel)?{//?即@babel/types,用于生成AST節點const?{?types:?t?}?=?babel;return?{name:?"ast-transform",?//?not?requiredvisitor:?{Identifier(path)?{path.node.name?=?path.node.name.split("").reverse().join("");},},};
}這是一段AST Explorer[6]上的 transform 模板代碼。上述代碼的作用即為將輸入代碼的所有標識符(Identifier)類型的節點名稱顛倒。
其實編寫一個 Babel 插件很簡單。我們要做的事情就是回傳一個 visitor 對象,定義以Node Type為名稱的函數。該函數接收path,state兩個參數。
其中path(路徑)提供了訪問/操作AST 節點的方法。path 本身表示兩個節點之間連接的對象。例如path.node可以訪問當前節點,path.parent可以訪問父節點等。path.remove()可以移除當前節點。具體 API 見下圖。其他可見handlebook[7]。
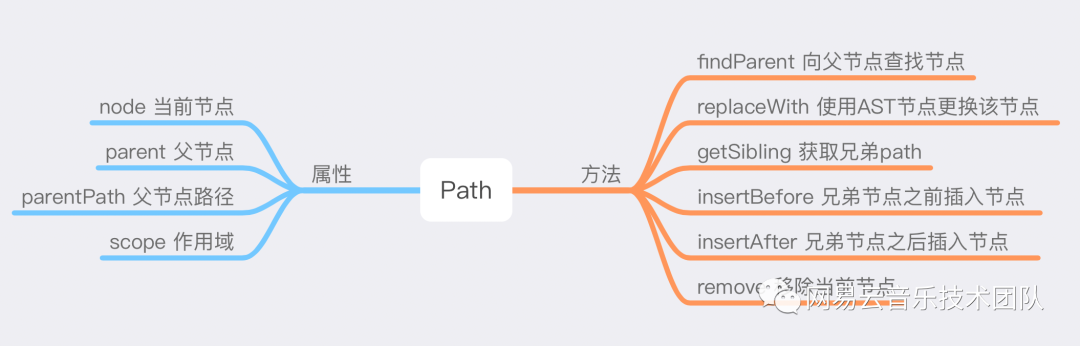
Babel Types
Babel Types 模塊是一個用于 AST 節點的 Lodash 式工具庫,它包含了構造、驗證以及變換 AST 節點的方法。
類型判斷
Babel Types 提供了節點類型判斷的方法,每一種類型的節點都有相應的判斷方法。更多見babel-types API[8]。
import?*?as?types?from?"@babel/types";//?是否為標識符類型節點
if?(types.isIdentifier(node))?{//?...
}//?是否為數字字面量節點
if?(types.isNumberLiteral(node))?{//?...
}//?是否為表達式語句節點
if?(types.isExpressionStatement(node))?{//?...
}創建節點
Babel Types 同樣提供了各種類型節點的創建方法,詳見下屬示例。
注: Babel Types 生成的 AST 節點需使用@babel/generator轉換后得到相應代碼。
import?*?as?types?from?"@babel/types";
import?generator?from?"@babel/generator";const?log?=?(node:?types.Node)?=>?{console.log(generator(node).code);
};log(types.stringLiteral("Hello?World"));?//?output:?Hello?World基本數據類型
types.stringLiteral("Hello?World");?//?string
types.numericLiteral(100);?//?number
types.booleanLiteral(true);?//?boolean
types.nullLiteral();?//?null
types.identifier();?//?undefined
types.regExpLiteral("\\.js?$",?"g");?//?正則"Hello?World"
100
true
null
undefined
/\.js?$/g復雜數據類型
數組
types.arrayExpression([types.stringLiteral("Hello?World"),types.numericLiteral(100),types.booleanLiteral(true),types.regExpLiteral("\\.js?$",?"g"),
]);["Hello?World",?100,?true,?/\.js?$/g];對象
types.objectExpression([types.objectProperty(types.identifier("key"),types.stringLiteral("HelloWorld")),types.objectProperty(//?字符串類型?keytypes.stringLiteral("str"),types.arrayExpression([])),types.objectProperty(types.memberExpression(types.identifier("obj"),types.identifier("propName")),types.booleanLiteral(false),//?計算值?keytrue),
]);{key:?"HelloWorld","str":?[],[obj.propName]:?false
}JSX 節點
創建 JSX AST 節點與創建數據類型節點略有不同,此處整理了一份關系圖。
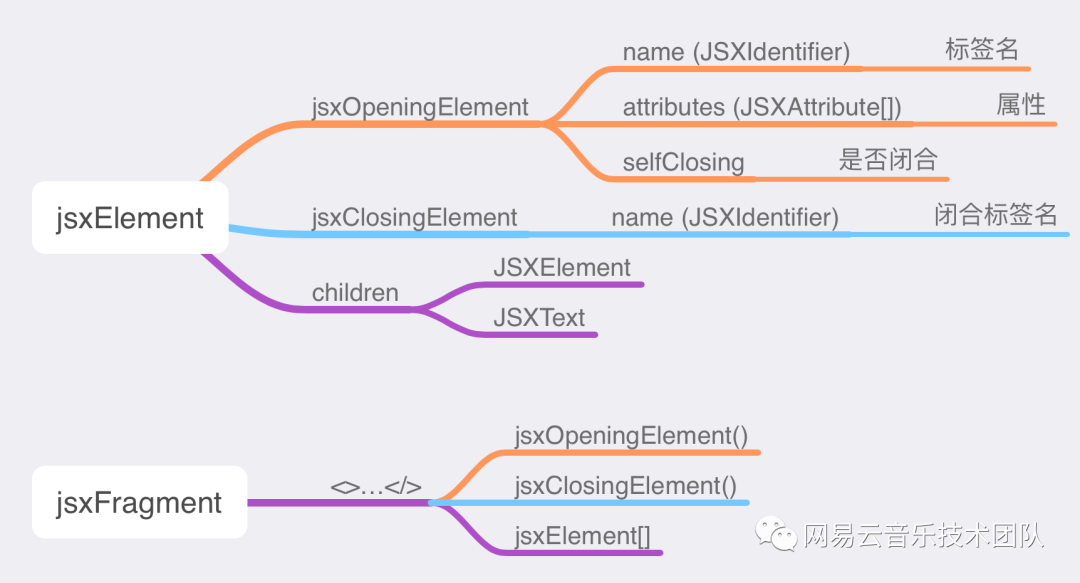
JSXElement
types.jsxElement(types.jsxOpeningElement(types.jsxIdentifier("Button"),?[]),types.jsxClosingElement(types.jsxIdentifier("Button")),[types.jsxExpressionContainer(types.identifier("props.name"))] );<Button>{props.name}</Button>JSXFragment
types.jsxFragment(types.jsxOpeningFragment(),?types.jsxClosingFragment(),?[types.jsxElement(types.jsxOpeningElement(types.jsxIdentifier("Button"),?[]),types.jsxClosingElement(types.jsxIdentifier("Button")),[types.jsxExpressionContainer(types.identifier("props.name"))]),types.jsxElement(types.jsxOpeningElement(types.jsxIdentifier("Button"),?[]),types.jsxClosingElement(types.jsxIdentifier("Button")),[types.jsxExpressionContainer(types.identifier("props.age"))]), ]);<><Button>{props.name}</Button><Button>{props.age}</Button> </>
聲明
變量聲明 (variableDeclaration)
types.variableDeclaration("const",?[types.variableDeclarator(types.identifier("a"),?types.numericLiteral(1)), ]);const?a?=?1;函數聲明 (functionDeclaration)
types.functionDeclaration(types.identifier("test"),[types.identifier("params")],types.blockStatement([types.variableDeclaration("const",?[types.variableDeclarator(types.identifier("a"),types.numericLiteral(1)),]),types.expressionStatement(types.callExpression(types.identifier("console.log"),?[types.identifier("params"),])),]) );function?test(params)?{const?a?=?1;console.log(params); }
React 函數式組件
綜合上述內容,小小實戰一下~
我們需要通過 Babel Types 生成button.js代碼。乍一看不知從何下手?
//?button.js
import?React?from?"react";
import?{?Button?}?from?"antd";export?default?(props)?=>?{const?handleClick?=?(ev)?=>?{console.log(ev);};return?<Button?onClick={handleClick}>{props.name}</Button>;
};小技巧: 先借助AST Explorer[9]網站,觀察 AST 樹結構。然后通過 Babel Types 逐層編寫代碼。事半功倍!
types.program([types.importDeclaration([types.importDefaultSpecifier(types.identifier("React"))],types.stringLiteral("react")),types.importDeclaration([types.importSpecifier(types.identifier("Button"),types.identifier("Button")),],types.stringLiteral("antd")),types.exportDefaultDeclaration(types.arrowFunctionExpression([types.identifier("props")],types.blockStatement([types.variableDeclaration("const",?[types.variableDeclarator(types.identifier("handleClick"),types.arrowFunctionExpression([types.identifier("ev")],types.blockStatement([types.expressionStatement(types.callExpression(types.identifier("console.log"),?[types.identifier("ev"),])),]))),]),types.returnStatement(types.jsxElement(types.jsxOpeningElement(types.jsxIdentifier("Button"),?[types.jsxAttribute(types.jsxIdentifier("onClick"),types.jSXExpressionContainer(types.identifier("handleClick"))),]),types.jsxClosingElement(types.jsxIdentifier("Button")),[types.jsxExpressionContainer(types.identifier("props.name"))],false)),]))),
]);應用場景
AST 本身應用非常廣泛,例如:Babel 插件(ES6 轉化 ES5)、構建時壓縮代碼 、css 預處理器編譯、 webpack 插件等等,可以說是無處不在。
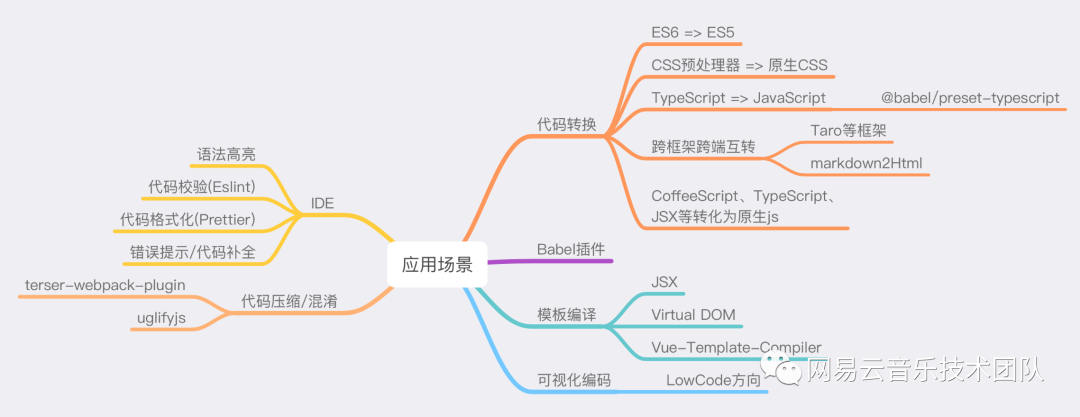
如圖所示,不難發現,一旦涉及到編譯,或者說代碼本身的處理,都和 AST 息息相關。下面列舉了一些常見應用,讓我們看看是如何處理的。
代碼轉換
//?ES6?=>?ES5?let?轉?var
export?default?function?(babel)?{const?{?types:?t?}?=?babel;return?{name:?"let-to-var",visitor:?{VariableDeclaration(path)?{if?(path.node.kind?===?"let")?{path.node.kind?=?"var";}},},};
}babel-plugin-import
在 CommonJS 規范下,當我們需要按需引入antd的時候,通常會借助該插件。
該插件的作用如下:
//?通過es規范,具名引入Button組件
import?{?Button?}?from?"antd";
ReactDOM.render(<Button>xxxx</Button>);//?babel編譯階段轉化為require實現按需引入
var?_button?=?require("antd/lib/button");
ReactDOM.render(<_button>xxxx</_button>);簡單分析一下,核心處理: 將 import 語句替換為對應的 require 語句。
export?default?function?(babel)?{const?{?types:?t?}?=?babel;return?{name:?"import-to-require",visitor:?{ImportDeclaration(path)?{if?(path.node.source.value?===?"antd")?{//?var?_button?=?require("antd/lib/button");const?_botton?=?t.variableDeclaration("var",?[t.variableDeclarator(t.identifier("_button"),t.callExpression(t.identifier("require"),?[t.stringLiteral("antd/lib/button"),])),]);//?替換當前import語句path.replaceWith(_botton);}},},};
}TIPS: 目前 antd 包中已包含esm規范文件,可以依賴 webpack 原生 TreeShaking 實現按需引入。
LowCode 可視化編碼
當下LowCode,依舊是前端一大熱門領域。目前主流的做法大致下述兩種。
Schema 驅動
目前主流做法,將表單或者表格的配置,描述為一份 Schema,可視化設計器基于 Schema 驅動,結合拖拽能力,快速搭建。
AST 驅動
通過
CloudIDE,CodeSandbox等瀏覽器端在線編譯,編碼。外加可視化設計器,最終實現可視化編碼。

大致流程如上圖所示,既然涉及到代碼修改,離不開AST的操作,那么又可以發揮 babel 的能力了。
假設設計器的初始代碼如下:
import?React?from?"react";export?default?()?=>?{return?<Container></Container>;
};此時我們拖拽了一個Button至設計器中,根據上圖的流程,核心的 AST 修改過程如下:
新增 import 聲明語句
import { Button } from "antd";將
<Button></Button>插入至<Container></Container>
話不多說,直接上代碼:
import?traverse?from?"@babel/traverse";
import?generator?from?"@babel/generator";
import?*?as?parser?from?"@babel/parser";
import?*?as?t?from?"@babel/types";//?源代碼
const?code?=?`import?React?from?"react";export?default?()?=>?{return?<Container></Container>;};
`;const?ast?=?parser.parse(code,?{sourceType:?"module",plugins:?["jsx"],
});traverse(ast,?{//?1.?程序頂層?新增import語句Program(path)?{path.node.body.unshift(t.importDeclaration(//?importSpecifier表示具名導入,相應的匿名導入為ImportDefaultSpecifier//?具名導入對應代碼為?import?{?Button?as?Button?}?from?'antd'//?如果相同會自動合并為?import?{?Button?}?from?'antd'[t.importSpecifier(t.identifier("Button"),?t.identifier("Button"))],t.stringLiteral("antd")));},//?訪問JSX節點,插入ButtonJSXElement(path)?{if?(path.node.openingElement.name.name?===?"Container")?{path.node.children.push(t.jsxElement(t.jsxOpeningElement(t.jsxIdentifier("Button"),?[]),t.jsxClosingElement(t.jsxIdentifier("Button")),[t.jsxText("按鈕")],false));}},
});const?newCode?=?generator(ast).code;
console.log(newCode);結果如下:
import?{?Button?}?from?"antd";
import?React?from?"react";
export?default?()?=>?{return?(<Container><Button>按鈕</Button></Container>);
};ESLint
自定義 eslint-rule,本質上也是訪問 AST 節點,是不是跟 Babel 插件的寫法很相似呢?
module.exports.rules?=?{"var-length":?(context)?=>?({VariableDeclarator:?(node)?=>?{if?(node.id.name.length?<=?2)?{context.report(node,?"變量名長度需要大于2");}},}),
};Code2Code
以 Vue To React 為例,大致過程跟ES6 => ES5類似,通過vue-template-compiler編譯得到 Vue AST => 轉換為 React AST => 輸出 React 代碼。
有興趣的同學可以參考vue-to-react[10]
其他多端框架:一份代碼 => 多端,大體思路一致。
總結
在實際開發中,遇到的情況往往更加復雜,建議大家多番文檔,多觀察,用心去感受 ~
參考文章
babel-handlebook[11]
@babel/types[12]
透過製作 Babel-plugin 初訪 AST
@babel/types 深度應用
本文發布自網易云音樂技術團隊,文章未經授權禁止任何形式的轉載。我們常年招收各類技術崗位,如果你準備換工作,又恰好喜歡云音樂,那就加入我們 grp.music-fe(at)corp.netease.com!
參考資料
[1]
ESTree Spec: https://github.com/estree/estree
[2]AST Explorer (常用): https://astexplorer.net/
[3]AST 可視化: https://resources.jointjs.com/demos/rappid/apps/Ast/index.html
[4]AST Explorer: https://astexplorer.net/
[5]ESTree: https://github.com/estree/estree
[6]AST Explorer: https://astexplorer.net/
[7]handlebook: https://github.com/jamiebuilds/babel-handbook/blob/master/translations/zh-Hans/plugin-handbook.md#toc-visitors
[8]babel-types API: https://babel.docschina.org/docs/en/babel-types/
[9]AST Explorer: https://astexplorer.net/
[10]vue-to-react: https://github.com/dwqs/vue-to-react
[11]babel-handlebook: https://github.com/jamiebuilds/babel-handbook/tree/master/translations/zh-Hans
[12]@babel/types: https://babel.docschina.org/docs/en/babel-types

·················?若川簡介?·················
你好,我是若川,畢業于江西高校。現在是一名前端開發“工程師”。寫有《學習源碼整體架構系列》20余篇,在知乎、掘金收獲超百萬閱讀。
從2014年起,每年都會寫一篇年度總結,已經堅持寫了8年,點擊查看年度總結。
同時,最近組織了源碼共讀活動,幫助3000+前端人學會看源碼。公眾號愿景:幫助5年內前端人走向前列。

掃碼加我微信 ruochuan02、拉你進源碼共讀群
今日話題
假期總是短暫的,下一個小長假就是五一了。分享、收藏、點贊、在看我的文章就是對我最大的支持~
口訣與范式轉)

前端面經記錄冷冷清清的金三銀四)



)
扭曲視覺效果以支持您的偏見敘事)








)


