????假設某主題只有1個分區,該分區有兩個副本:Leader 副本在 Broker1 上,Follower 副本在 Broker2 上,其 Leader 副本寫入數據和 Follower 副本同步數據的流程如下圖:
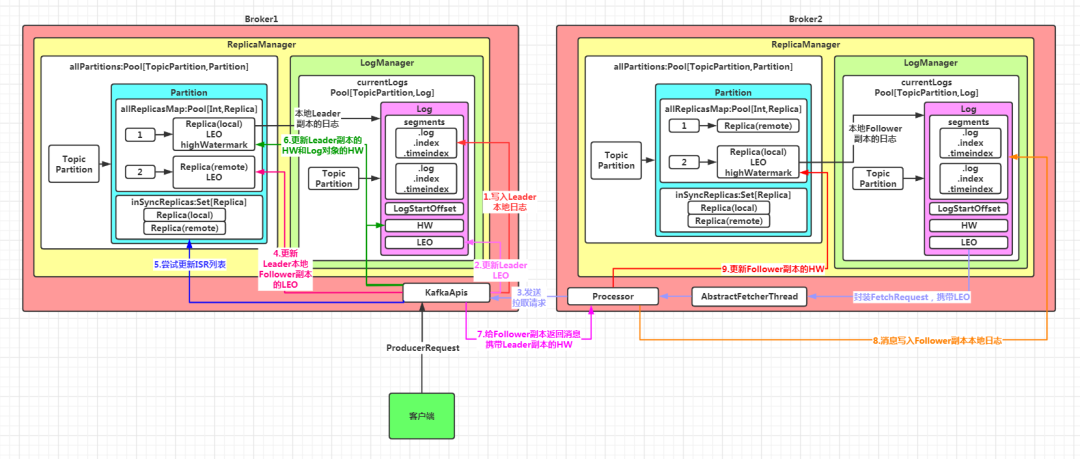
1.leader?副本將數據寫入本地磁盤 KafkaApis.handleProduceRequest(){ replicaManager.appendRecords(){ appendToLocalLog(){ Partition.appendRecordsToLeader(){ Log.appendAsLeader(){ Log.append(){ //通過LogSegment.append()方法寫入磁盤 LogSegment.append() } } } } } }2.leader 副本更新LEO KafkaApis.handleProduceRequest(){ replicaManager.appendRecords(){ appendToLocalLog(){ Partition.appendRecordsToLeader(){ Log.appendAsLeader(){ Log.append(){ //更新Leader副本的LEO值 updateLogEndOffset(appendInfo.lastOffset + 1) } } } } } }3.follower?副本同步數據,攜帶自身的LEO AbstractFetchThread.doWork(){ maybeFetch(){ buildFetch(fetchStates){ //這里的fetchState.fetchOffset 就是Follower副本的LEO值 builder.add(topicPartition, new FetchRequest.PartitionData( fetchState.fetchOffset, logStartOffset, fetchSize, Optional.of(fetchState.currentLeaderEpoch))) } } }4.leader 副本更新本地保存的Follower副本的LEO ReplicaManager.fetchMessages(){ //獲取讀取結果 val logReadResults = readFromLog(){ if (isFromFollower) updateFollowerLogReadResults(replicaId, result){ //TODO 更新leader保存的各個follower副本的LEO partition.updateReplicaLogReadResult(replica, readResult){ //TODO 最終更新所有的replica的LEO的值 replica.updateLogReadResult(logReadResult){ //更新LEO對象 logEndOffsetMetadata = logReadResult.info.fetchOffsetMetadata } } } } }5.leader 副本嘗試更新ISR列表 ReplicaManager.fetchMessages(){ //獲取讀取結果 val logReadResults = readFromLog(){ if (isFromFollower) updateFollowerLogReadResults(replicaId, result){ //TODO 嘗試更新ISR列表 val leaderHWIncremented = maybeExpandIsr(replicaId, logReadResult){ //更新ISR列表 updateIsr(newInSyncReplicas) } } } }6.leader 副本更新HW ReplicaManager.fetchMessages(){ //獲取讀取結果 val logReadResults = readFromLog(){ if (isFromFollower) updateFollowerLogReadResults(replicaId, result){ //TODO 嘗試更新ISR列表及Leader副本的HW val leaderHWIncremented = maybeExpandIsr(replicaId, logReadResult){ //TODO 嘗試更新leader的HW maybeIncrementLeaderHW(leaderReplica, logReadResult.fetchTimeMs){ //取ISR列表中副本的最小的LEO作為新的HW val newHighWatermark = allLogEndOffsets.min(new LogOffsetMetadata.OffsetOrdering) //獲取舊的HW val oldHighWatermark = leaderReplica.highWatermark //如果新的HW值大于舊的HW值,就更新 if (oldHighWatermark.messageOffset < newHighWatermark.messageOffset || (oldHighWatermark.messageOffset == newHighWatermark.messageOffset && oldHighWatermark.onOlderSegment(newHighWatermark))) { //更新 Leader 副本的 HW????????????????????????????leaderReplica.highWatermark?=?newHighWatermark } } } } } }7.leader 副本給 follower副本 返回數據,攜帶leader 副本的 HW 值 ReplicaManager.fetchMessages(){ //獲取讀取結果 val logReadResults = readFromLog(){ readFromLocalLog(){ read(){ val readInfo = partition.readRecords(){ //獲取Leader Replica的高水位 val initialHighWatermark = localReplica.highWatermark.messageOffset } } } } }8.follower 副本寫入數據,更新自身LEO、 ReplicaFetcherThread.processPartitionData(){ partition.appendRecordsToFollowerOrFutureReplica(records, isFuture = false){ doAppendRecordsToFollowerOrFutureReplica(){ Log.appendAsFollower(){ Log.append(){ //更新Follower副本的LEO值 updateLogEndOffset(appendInfo.lastOffset + 1) } } } } }9.follower 副本更新本地的 HW 值 ReplicaFetcherThread.processPartitionData(){ //根據leader返回的HW,更新Follower本地的HW:取Follower本地LEO 和 Leader HW 的較小值 val followerHighWatermark = replica.logEndOffset.min(partitionData.highWatermark) //TODO 更新Follower副本的 HW 對象 replica.highWatermark = new LogOffsetMetadata(followerHighWatermark)??}對于HW,Leader 副本和 Follower 副本只保存自身的
對于LEO,Follower 副本只保存自身的,但是 Leader 副本除了保存自身的外,還會保存所有 Follower 副本的 LEO 值
無論是Leader副本所在節點,還是Follower副本所在節點,分區對應的Partition 對象都會保存所有的副本對象,但是只有本地副本對象有對應的日志文件
整個數據寫入及同步的過程分為九個步驟:
- leader 副本將數據寫入本地磁盤
- leader?副本更新 LEO
- follower 副本發送同步數據請求,攜帶自身的 LEO
- leader 副本更新本地保存的其它副本的 LEO
- leader 副本嘗試更新 ISR 列表
- leader?副本更新 HW
- leader 副本給 follower 副本返回數據,攜帶 leader 副本的 HW 值
- follower 副本接收響應并寫入數據,更新自身 LEO
- follower 副本更新本地的 HW 值
? ?下面具體分析這幾個步驟。第一、二步在分析日志對象的寫數據流程時已經詳細介紹過,這里不再贅述(《深入理解Kafka服務端之日志對象的讀寫數據流程》)。?對于后面的幾個步驟,由于發生在不同的節點上,并沒有按照這個順序進行分析,而是分成了
- Follower副本的相關操作:即 第三步、第八步、第九步
- Leader副本的相關操作:即 第四步、第五步、第六步、第七步
- 抽象類:AbstractFetcherThread
- 實現類:ReplicaFetcherThread
abstract class AbstractFetcherThread(name: String,//線程名稱 clientId: String,//Cliend ID,用于日志輸出 val sourceBroker: BrokerEndPoint,//數據源Broker地址 failedPartitions: FailedPartitions,//線程處理過程報錯的分區集合 fetchBackOffMs: Int = 0,//拉取的重試間隔,默認是 Broker 端參數 replica.fetch.backoff.ms 值。 isInterruptible: Boolean = true)//是否允許線程中斷 extends ShutdownableThread(name, isInterruptible) { type FetchData = FetchResponse.PartitionData[Records] type EpochData = OffsetsForLeaderEpochRequest.PartitionData //泛型 PartitionFetchState:表征分區讀取狀態,包含已讀取偏移量和對應的副本讀取狀態 //副本狀態由 ReplicaState 接口定義,包含 讀取中 和 截斷中 兩個 private val partitionStates = new PartitionStates[PartitionFetchState] ...}其中,type 的用法是:給指定的類起一個別名,如:
type FetchData = FetchResponse.PartitionData[Records]后面就可以用 FetchData 來表示 FetchResponse.PartitionData[Records] 類;EpochData 同理。
????FetchResponse.PartitionData:FetchResponse是封裝的FETCH請求的響應類,PartitionData是一個嵌套類,表示響應中單個分區的拉取信息,包括對應Leader副本的高水位,分區日志的起始偏移量,拉取到的消息集合等。
public static final class PartitionData<T extends BaseRecords> { public final Errors error;//錯誤碼 public final long highWatermark;//從Leader返回的分區的高水位值 public final long lastStableOffset;// 最新LSO值 public final long logStartOffset;//日志起始偏移量 public final Optional preferredReadReplica;// 期望的Read Replica;KAFKA 2.4之后支持部分Follower副本可以對外提供讀服務 public final List abortedTransactions;// 該分區對應的已終止事務列表 public final T records;//消息集合}public static class PartitionData { public final Optional currentLeaderEpoch; public final int leaderEpoch;}????PartitionFetchState:樣例類,用來表征分區的讀取狀態。包含已拉取的偏移量,當前leader的epoch,副本讀取狀態等
case class PartitionFetchState(fetchOffset: Long,//已拉取的偏移量 currentLeaderEpoch: Int,//當前epoch delay: DelayedItem, state: ReplicaState//副本讀取狀態 ) { //表征分區的讀取狀態 //1.可拉取,表明副本獲取線程當前能夠讀取數據。判斷條件是:副本處于Fetching且未被推遲執行 def isReadyForFetch: Boolean = state == Fetching && !isDelayed //2.截斷中,表明分區副本正在執行截斷操作(比如該副本剛剛成為 Follower 副本)。判斷條件是:副本處于Truncating且未被推遲執行 def isTruncating: Boolean = state == Truncating && !isDelayed //3.被推遲,表明副本獲取線程獲取數據時出現錯誤,需要等待一段時間后重試。判斷條件是:存在未過期的延遲任務 def isDelayed: Boolean = delay.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) > 0}- isReadyForFetch:可拉取,表明副本獲取線程當前能夠讀取數據。判斷條件是:副本處于Fetching且未被推遲執行
- isTruncating:截斷中,表明分區副本正在執行截斷操作(比如該副本剛剛成為 Follower 副本)。判斷條件是:副本處于Truncating且未被推遲執行
- isDelayed:被推遲,表明副本獲取線程獲取數據時出現錯誤,需要等待一段時間后重試。判斷條件是:存在未過期的延遲任務
副本讀取的狀態
????ReplicaState:特質,用來表征副本讀取狀態。
sealed trait ReplicaState//截斷中case object Truncating extends ReplicaState//拉取中case object Fetching extends ReplicaState- Truncating:截斷中
- Fetching:拉取中
- buildFetch:封裝拉取數據的請求
- truncate:進行日志截斷
- processPartitionData:處理返回的響應
- doWork:將上面定義的三個方法串聯起來,形成一個閉環,并不斷地重復執行。從而實現從Leader副本所在的節點同步消息
class ReplicaFetcherThread(name: String, fetcherId: Int,//Follower 拉取的線程 Id,也就是線程的編號。 // 單臺 Broker 上,允許存在多個 ReplicaFetcherThread 線程。 // Broker 端參數 num.replica.fetchers,決定了 Kafka 到底創建多少個 Follower 拉取線程。 sourceBroker: BrokerEndPoint, brokerConfig: KafkaConfig,//服務端配置類,用來獲取配置信息 failedPartitions: FailedPartitions, replicaMgr: ReplicaManager,//副本管理器。該線程類通過副本管理器來獲取分區對象、副本對象以及它們下面的日志對象。 metrics: Metrics, time: Time, quota: ReplicaQuota,//用做限流。作用是控制 Follower 副本拉取速度 leaderEndpointBlockingSend: Option[BlockingSend] = None//用于實現同步發送請求的類。 // 所謂的同步發送,是指該線程使用它給指定 Broker 發送請求,然后線程處于阻塞狀態,直到接收到 Broker 返回的 Response。 )extends AbstractFetcherThread( name = name, clientId = name, sourceBroker = sourceBroker, failedPartitions, fetchBackOffMs = brokerConfig.replicaFetchBackoffMs, isInterruptible = false) { //Follower副本所在Broker的Id private val replicaId = brokerConfig.brokerId //用于執行請求發送的類 private val leaderEndpoint = leaderEndpointBlockingSend.getOrElse( new ReplicaFetcherBlockingSend(sourceBroker, brokerConfig, metrics, time, fetcherId, s"broker-$replicaId-fetcher-$fetcherId", logContext)) //Follower發送的FETCH請求被處理返回前的最長等待時間,由參數:replica.fetch.wait.max.ms 配置,默認 500 毫秒 private val maxWait = brokerConfig.replicaFetchWaitMaxMs //每個FETCH Response返回前必須要累積的最少字節數,由參數:replica.fetch.min.bytes 配置,默認 1 字節 private val minBytes = brokerConfig.replicaFetchMinBytes //每個合法FETCH Response的最大字節數,由參數:replica.fetch.response.max.bytes 配置,默認 10 M private val maxBytes = brokerConfig.replicaFetchResponseMaxBytes //單個分區能夠獲取到的最大字節數,由參數:replica.fetch.max.bytes 配置,默認 1 M private val fetchSize = brokerConfig.replicaFetchMaxBytes ...}buildFetch() 方法:為指定分區集合構建對應的FetchRequest.Builder 對象,而該對象是構建 FetchRequest 的核心組件。
這個方法中有一個重要的操作:
封裝拉取請求時,攜帶了Follower副本的 LogStartOffset 和 LEO 值(對應同步數據的第三步)
override def buildFetch(partitionMap: Map[TopicPartition, PartitionFetchState]): ResultWithPartitions[Option[FetchRequest.Builder]] = { //定義一個保存出錯分區的集合 val partitionsWithError = mutable.Set[TopicPartition]() val builder = fetchSessionHandler.newBuilder() // 遍歷每個分區,將處于可獲取狀態的分區添加到builder后續統一處理 // 對于有錯誤的分區加入到出錯分區集合 partitionMap.foreach { case (topicPartition, fetchState) => //如果分區的狀態是可拉取的,且該分區未對follower限流 if (fetchState.isReadyForFetch && !shouldFollowerThrottle(quota, topicPartition)) { try {??????????//獲取本地Follower副本保存的分區日志的logStartOffset val logStartOffset = replicaMgr.localReplicaOrException(topicPartition).logStartOffset /**將分區和對應的PartitionData添加到builder,注意這里的PartitionData對應的是拉取請求FetchRequest,里面封裝了拉取請求的元數據信息,如: * fetchOffset:拉取消息的起始偏移量,也就是Follower副本的LEO * currentLeaderEpoch:Follower副本保存的leader epoch值 */ builder.add(topicPartition, new FetchRequest.PartitionData( fetchState.fetchOffset, logStartOffset, fetchSize, Optional.of(fetchState.currentLeaderEpoch))) } catch { case _: KafkaStorageException => //如果有異常,將該分區添加到出錯分區的集合 partitionsWithError += topicPartition } } } val fetchData = builder.build() val fetchRequestOpt = if (fetchData.sessionPartitions.isEmpty && fetchData.toForget.isEmpty) { None } else { //構造FETCH請求的Builder對象 val requestBuilder = FetchRequest.Builder .forReplica(fetchRequestVersion, replicaId, maxWait, minBytes, fetchData.toSend) .setMaxBytes(maxBytes) .toForget(fetchData.toForget) .metadata(fetchData.metadata) Some(requestBuilder) } //構建返回結果,返回Builder對象以及出錯分區列表 ResultWithPartitions(fetchRequestOpt, partitionsWithError) }truncate() 方法:用于將指定分區的日志截斷到指定的偏移量
override def truncate(tp: TopicPartition, offsetTruncationState: OffsetTruncationState): Unit = { //根據分區獲取本地副本 val replica = replicaMgr.localReplicaOrException(tp) val partition = replicaMgr.getPartition(tp).get //調用Partition.truecateTo方法進行日志截斷 // offsetTruncationState.offset:要截斷到的偏移量 partition.truncateTo(offsetTruncationState.offset, isFuture = false) if (offsetTruncationState.offset < replica.highWatermark.messageOffset) warn(s"Truncating $tp to offset ${offsetTruncationState.offset} below high watermark " + s"${replica.highWatermark.messageOffset}") if (offsetTruncationState.truncationCompleted) replicaMgr.replicaAlterLogDirsManager.markPartitionsForTruncation(brokerConfig.brokerId, tp, offsetTruncationState.offset)}????這個方法內部依次調用了:Partition.truncateTo -> LogManager.truncateTo -> Log.truncateTo -> LogSegment.truncateTo 進行日志截斷操作
processPartitionData方法:用于處理指定分區從Leader副本所在節點返回的響應,將獲取的消息寫入本地存儲,并返回寫入消息的元數據
這里有兩個個重要的操作:
寫入消息,更新 Follower 副本的 LEO(對應同步數據的第八步)
更新 Follower 副本本地的 HW 值(對應同步數據的第九步)
override def processPartitionData(topicPartition: TopicPartition, // 拉取數據的分區 fetchOffset: Long, // 拉取的消息集合的起始位移 partitionData: FetchData // 讀取到的分區消息數據 ): Option[LogAppendInfo] = { // 返回值:寫入已讀取消息數據前的元數據 //從副本管理器獲取副本對象Replica val replica = replicaMgr.localReplicaOrException(topicPartition) //從副本管理器獲取指定主題分區對象 val partition = replicaMgr.getPartition(topicPartition).get //將獲取的消息封裝成MemoryRecords val records = toMemoryRecords(partitionData.records) //判斷獲取的消息集合是否超限 maybeWarnIfOversizedRecords(records, topicPartition) //如果獲取消息的起始位移值不是本地日志LEO值則視為異常情況 if (fetchOffset != replica.logEndOffset) throw new IllegalStateException("Offset mismatch for partition %s: fetched offset = %d, log end offset = %d.".format( topicPartition, fetchOffset, replica.logEndOffset)) if (isTraceEnabled) trace("Follower has replica log end offset %d for partition %s. Received %d messages and leader hw %d" .format(replica.logEndOffset, topicPartition, records.sizeInBytes, partitionData.highWatermark)) //TODO 寫入Follower副本本地日志,更新自身的LEO val logAppendInfo = partition.appendRecordsToFollowerOrFutureReplica(records, isFuture = false) if (isTraceEnabled) trace("Follower has replica log end offset %d after appending %d bytes of messages for partition %s" .format(replica.logEndOffset, records.sizeInBytes, topicPartition)) //根據leader返回的HW,更新Follower本地的HW:取Follower本地LEO 和 Leader HW 的較小值 val followerHighWatermark = replica.logEndOffset.min(partitionData.highWatermark) //獲取從leader返回的LogStartOffset val leaderLogStartOffset = partitionData.logStartOffset //TODO 更新Follower副本的HW對象 replica.highWatermark = new LogOffsetMetadata(followerHighWatermark) //嘗試更新Follower副本的LogStartOffset replica.maybeIncrementLogStartOffset(leaderLogStartOffset) if (isTraceEnabled) trace(s"Follower set replica high watermark for partition $topicPartition to $followerHighWatermark") // 副本消息拉取限流 if (quota.isThrottled(topicPartition)) quota.record(records.sizeInBytes) replicaMgr.brokerTopicStats.updateReplicationBytesIn(records.sizeInBytes) //返回寫入消息的元數據 logAppendInfo }override def doWork() { //嘗試日志截斷 maybeTruncate() //嘗試拉取數據 maybeFetch()}這個方法很簡單,只在內部調用了兩個方法:
maybeTruncate():嘗試進行日志截斷
private def maybeTruncate(): Unit = { // 將所有處于截斷中狀態的分區依據有無Leader Epoch值進行分組 val (partitionsWithEpochs, partitionsWithoutEpochs) = fetchTruncatingPartitions() // 對于有Leader Epoch值的分區,將日志截斷到Leader Epoch值對應的位移值處 if (partitionsWithEpochs.nonEmpty) { truncateToEpochEndOffsets(partitionsWithEpochs) } // 對于沒有Leader Epoch值的分區,將日志截斷到高水位值處 if (partitionsWithoutEpochs.nonEmpty) { truncateToHighWatermark(partitionsWithoutEpochs) }}這里先看對于沒有Leader Epoch的分區,將日志截斷到高水位處:
private[server] def truncateToHighWatermark(partitions: Set[TopicPartition]): Unit = inLock(partitionMapLock) { val fetchOffsets = mutable.HashMap.empty[TopicPartition, OffsetTruncationState] // 遍歷每個要執行截斷操作的分區對象 for (tp // 獲取分區的分區讀取狀態 val partitionState = partitionStates.stateValue(tp) if (partitionState != null) { // 取出高水位值。 val highWatermark = partitionState.fetchOffset //封裝截斷狀態 val truncationState = OffsetTruncationState(highWatermark, truncationCompleted = true) info(s"Truncating partition $tp to local high watermark $highWatermark") // 執行截斷到高水位值 if (doTruncate(tp, truncationState)) //保存分區和對應的截取狀態 fetchOffsets.put(tp, truncationState) } } // 更新這組分區的分區讀取狀態 updateFetchOffsetAndMaybeMarkTruncationComplete(fetchOffsets)}private def maybeFetch(): Unit = { //獲取分區狀態集合和對應的拉取請求的集合 val (fetchStates, fetchRequestOpt) = inLock(partitionMapLock) { //獲取要拉取消息的分區和分區對應狀態的集合 val fetchStates = partitionStates.partitionStateMap.asScala // TODO 第一步:為集合中的分區構造FetchRequest.builder對象,這里的返回結果有兩個對象: //fetchRequestOpt:要讀取的分區核心信息 + FetchRequest.Builder 對象。 // 而這里的核心信息,就是指要讀取哪個分區,從哪個位置開始讀,最多讀多少字節,等等。 //partitionsWithError:一組出錯的分區 val ResultWithPartitions(fetchRequestOpt, partitionsWithError) = buildFetch(fetchStates) //TODO 第二步:處理出錯的分區,處理方式主要是將這個分區加入到有序Map末尾,等待后續重試 handlePartitionsWithErrors(partitionsWithError, "maybeFetch") // 如果當前沒有可讀取的分區,則等待fetchBackOffMs時間等候后續重試 if (fetchRequestOpt.isEmpty) { trace(s"There are no active partitions. Back off for $fetchBackOffMs ms before sending a fetch request") partitionMapCond.await(fetchBackOffMs, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) } (fetchStates, fetchRequestOpt) } //TODO 第三步:遍歷FETCH請求,發送FETCH請求給Leader副本,并處理Response fetchRequestOpt.foreach { fetchRequest => processFetchRequest(fetchStates, fetchRequest) }}val ResultWithPartitions(fetchRequestOpt, partitionsWithError) = buildFetch(fetchStates)b:處理出錯的分區。處理方式主要是將這個分區加入到有序Map末尾,等待后續重試
handlePartitionsWithErrors(partitionsWithError, "maybeFetch")//將給定的分區從map頭部移除,然后再加到尾部,以達到輪詢的目的//這里的LinkedHashMap對于插入元素是有順序的,加入插入順序是abcde,先讀取了a,// 為了保證公平性,會將a從集合中先移除,然后放到尾部,那么下次就從b開始讀public void updateAndMoveToEnd(TopicPartition topicPartition, S state) { map.remove(topicPartition); map.put(topicPartition, state); updateSize();}c:遍歷并發送FETCH請求給Leader副本,然后處理Response
fetchRequestOpt.foreach { fetchRequest => processFetchRequest(fetchStates, fetchRequest)}private def processFetchRequest(fetchStates: Map[TopicPartition, PartitionFetchState], fetchRequest: FetchRequest.Builder): Unit = { //定義出錯分區的集合 val partitionsWithError = mutable.Set[TopicPartition]() //定義接收響應數據的集合 var responseData: Seq[(TopicPartition, FetchData)] = Seq.empty try { trace(s"Sending fetch request $fetchRequest") //給Leader發送FETCH請求,獲取響應數據 responseData = fetchFromLeader(fetchRequest) } catch { case t: Throwable => if (isRunning) { warn(s"Error in response for fetch request $fetchRequest", t) inLock(partitionMapLock) { partitionsWithError ++= partitionStates.partitionSet.asScala partitionMapCond.await(fetchBackOffMs, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) } } } //更新請求發送速率指標 fetcherStats.requestRate.mark() //如果接收到了響應 if (responseData.nonEmpty) { inLock(partitionMapLock) { //遍歷響應結果中的分區和分區對應的數據 responseData.foreach { case (topicPartition, partitionData) => Option(partitionStates.stateValue(topicPartition)).foreach { currentFetchState => //獲取分區對應的拉取狀態 val fetchState = fetchStates(topicPartition) // 處理Response的條件: // 1. 獲取的消息集合的起始偏移量和之前已保存的下一條待寫入偏移量相等 // 2. 當前分區處于可獲取狀態 if (fetchState.fetchOffset == currentFetchState.fetchOffset && currentFetchState.isReadyForFetch) { //獲取請求中攜帶的Follower副本保存的 leader epoch 值 val requestEpoch = if (fetchState.currentLeaderEpoch >= 0) Some(fetchState.currentLeaderEpoch) else None partitionData.error match { // 如果沒有錯誤 case Errors.NONE => try { // 交由子類完成Response的處理 val logAppendInfoOpt = processPartitionData(topicPartition, currentFetchState.fetchOffset, partitionData) logAppendInfoOpt.foreach { logAppendInfo => val validBytes = logAppendInfo.validBytes val nextOffset = if (validBytes > 0) logAppendInfo.lastOffset + 1 else currentFetchState.fetchOffset fetcherLagStats.getAndMaybePut(topicPartition).lag = Math.max(0L, partitionData.highWatermark - nextOffset) if (validBytes > 0 && partitionStates.contains(topicPartition)) { val newFetchState = PartitionFetchState(nextOffset, fetchState.currentLeaderEpoch, state = Fetching) // 將該分區放置在有序Map讀取順序的末尾,保證公平性 partitionStates.updateAndMoveToEnd(topicPartition, newFetchState) fetcherStats.byteRate.mark(validBytes) } } } catch { case ime: CorruptRecordException => error(s"Found invalid messages during fetch for partition $topicPartition " + s"offset ${currentFetchState.fetchOffset}", ime) partitionsWithError += topicPartition case e: KafkaStorageException => error(s"Error while processing data for partition $topicPartition " + s"at offset ${currentFetchState.fetchOffset}", e) markPartitionFailed(topicPartition) case t: Throwable => error(s"Unexpected error occurred while processing data for partition $topicPartition " + s"at offset ${currentFetchState.fetchOffset}", t) markPartitionFailed(topicPartition) } // 如果讀取位移值越界,通常是因為Leader發生變更 case Errors.OFFSET_OUT_OF_RANGE => //調整越界,主要辦法是做截斷 if (handleOutOfRangeError(topicPartition, currentFetchState, requestEpoch)) //如果依然不能成功,將該分區添加到出錯分區集合 partitionsWithError += topicPartition //如果Follower本地保存的Leader Epoch值比Leader所在Broker上的Epoch值要新 case Errors.UNKNOWN_LEADER_EPOCH => debug(s"Remote broker has a smaller leader epoch for partition $topicPartition than " + s"this replica's current leader epoch of ${fetchState.currentLeaderEpoch}.") // 加入到出錯分區集合 partitionsWithError += topicPartition // 如果Follower本地保存的Leader Epoch值比Leader所在Broker上的Epoch值要舊 case Errors.FENCED_LEADER_EPOCH => //將該分區標記為失效,從分區拉取狀態集合中移除,并加入到失效分區集合 if (onPartitionFenced(topicPartition, requestEpoch)) partitionsWithError += topicPartition // 如果Leader發生變更 case Errors.NOT_LEADER_FOR_PARTITION => debug(s"Remote broker is not the leader for partition $topicPartition, which could indicate " + "that the partition is being moved") // 加入到出錯分區列表 partitionsWithError += topicPartition case _ => error(s"Error for partition $topicPartition at offset ${currentFetchState.fetchOffset}", partitionData.error.exception) // 加入到出錯分區集合 partitionsWithError += topicPartition } } } } } } // 處理出錯分區集合,主要就是將該分區放到map數據結構的末尾 if (partitionsWithError.nonEmpty) { handlePartitionsWithErrors(partitionsWithError, "processFetchRequest") } }內部調用了ReplicaManager.fetchMessages() 方法:
def handleFetchRequest(request: RequestChannel.Request) { ... //TODO 這里是處理Follower Replica 拉取消息請求的具體方法 replicaManager.fetchMessages( fetchRequest.maxWait.toLong, fetchRequest.replicaId, fetchRequest.minBytes, fetchRequest.maxBytes, versionId <= 2, interesting, replicationQuota(fetchRequest), processResponseCallback, fetchRequest.isolationLevel) ...}fetchMessages() 方法:
def fetchMessages(timeout: Long, replicaId: Int, fetchMinBytes: Int, fetchMaxBytes: Int, hardMaxBytesLimit: Boolean, fetchInfos: Seq[(TopicPartition, PartitionData)], quota: ReplicaQuota = UnboundedQuota, responseCallback: Seq[(TopicPartition, FetchPartitionData)] => Unit, isolationLevel: IsolationLevel) { val isFromFollower = Request.isValidBrokerId(replicaId) val fetchOnlyFromLeader = replicaId != Request.DebuggingConsumerId && replicaId != Request.FutureLocalReplicaId val fetchIsolation = if (isFromFollower || replicaId == Request.FutureLocalReplicaId) FetchLogEnd else if (isolationLevel == IsolationLevel.READ_COMMITTED) FetchTxnCommitted else FetchHighWatermark //從本地磁盤讀取數據 def readFromLog(): Seq[(TopicPartition, LogReadResult)] = { val result = readFromLocalLog( replicaId = replicaId, fetchOnlyFromLeader = fetchOnlyFromLeader, fetchIsolation = fetchIsolation, fetchMaxBytes = fetchMaxBytes, hardMaxBytesLimit = hardMaxBytesLimit, readPartitionInfo = fetchInfos, quota = quota) if (isFromFollower) updateFollowerLogReadResults(replicaId, result) else result } //獲取讀取結果 val logReadResults = readFromLog() var bytesReadable: Long = 0 var errorReadingData = false val logReadResultMap = new mutable.HashMap[TopicPartition, LogReadResult] logReadResults.foreach { case (topicPartition, logReadResult) => if (logReadResult.error != Errors.NONE) errorReadingData = true bytesReadable = bytesReadable + logReadResult.info.records.sizeInBytes logReadResultMap.put(topicPartition, logReadResult) } if (timeout <= 0 || fetchInfos.isEmpty || bytesReadable >= fetchMinBytes || errorReadingData) { val fetchPartitionData = logReadResults.map { case (tp, result) => tp -> FetchPartitionData(result.error, result.highWatermark, result.leaderLogStartOffset, result.info.records, result.lastStableOffset, result.info.abortedTransactions) } responseCallback(fetchPartitionData) } else { val fetchPartitionStatus = new mutable.ArrayBuffer[(TopicPartition, FetchPartitionStatus)] fetchInfos.foreach { case (topicPartition, partitionData) => logReadResultMap.get(topicPartition).foreach(logReadResult => { val logOffsetMetadata = logReadResult.info.fetchOffsetMetadata fetchPartitionStatus += (topicPartition -> FetchPartitionStatus(logOffsetMetadata, partitionData)) }) } val fetchMetadata = FetchMetadata(fetchMinBytes, fetchMaxBytes, hardMaxBytesLimit, fetchOnlyFromLeader, fetchIsolation, isFromFollower, replicaId, fetchPartitionStatus) val delayedFetch = new DelayedFetch(timeout, fetchMetadata, this, quota, responseCallback) val delayedFetchKeys = fetchPartitionStatus.map { case (tp, _) => new TopicPartitionOperationKey(tp) } delayedFetchPurgatory.tryCompleteElseWatch(delayedFetch, delayedFetchKeys) } }def readFromLocalLog(replicaId: Int, fetchOnlyFromLeader: Boolean, fetchIsolation: FetchIsolation, fetchMaxBytes: Int, hardMaxBytesLimit: Boolean, readPartitionInfo: Seq[(TopicPartition, PartitionData)], quota: ReplicaQuota): Seq[(TopicPartition, LogReadResult)] = { def read(tp: TopicPartition, fetchInfo: PartitionData, limitBytes: Int, minOneMessage: Boolean): LogReadResult = { //讀取的起始偏移量 val offset = fetchInfo.fetchOffset //讀取的大小 val partitionFetchSize = fetchInfo.maxBytes //follower Replica 的LogStartOffset val followerLogStartOffset = fetchInfo.logStartOffset brokerTopicStats.topicStats(tp.topic).totalFetchRequestRate.mark() brokerTopicStats.allTopicsStats.totalFetchRequestRate.mark() val adjustedMaxBytes = math.min(fetchInfo.maxBytes, limitBytes) try { trace(s"Fetching log segment for partition $tp, offset $offset, partition fetch size $partitionFetchSize, " + s"remaining response limit $limitBytes" + (if (minOneMessage) s", ignoring response/partition size limits" else "")) val partition = getPartitionOrException(tp, expectLeader = fetchOnlyFromLeader) val fetchTimeMs = time.milliseconds //讀取數據,獲取讀取結果,里面包含了讀取到的消息,LEO,HW,LogStartOffset等信息 val readInfo = partition.readRecords( //讀取的起始偏移量 fetchOffset = fetchInfo.fetchOffset, //Follower副本保存的Leader epoch currentLeaderEpoch = fetchInfo.currentLeaderEpoch, maxBytes = adjustedMaxBytes, fetchIsolation = fetchIsolation, fetchOnlyFromLeader = fetchOnlyFromLeader, minOneMessage = minOneMessage) //獲取讀到的數據 val fetchDataInfo = if (shouldLeaderThrottle(quota, tp, replicaId)) { //如果分區被限流了,那么返回一個空集合 FetchDataInfo(readInfo.fetchedData.fetchOffsetMetadata, MemoryRecords.EMPTY) } else if (!hardMaxBytesLimit && readInfo.fetchedData.firstEntryIncomplete) { //如果返回的消息集合不完整,也返回一個空集合 FetchDataInfo(readInfo.fetchedData.fetchOffsetMetadata, MemoryRecords.EMPTY) } else { //正常返回 readInfo.fetchedData } //根據獲取到的數據封裝返回結果 LogReadResult(info = fetchDataInfo, highWatermark = readInfo.highWatermark,//Leader的HW leaderLogStartOffset = readInfo.logStartOffset,//Leader的LogStartOffset leaderLogEndOffset = readInfo.logEndOffset,//Leader的LEO followerLogStartOffset = followerLogStartOffset,//Follower的LogStartOffset fetchTimeMs = fetchTimeMs, readSize = adjustedMaxBytes, lastStableOffset = Some(readInfo.lastStableOffset), exception = None//異常信息 ) } catch { case e@ (_: UnknownTopicOrPartitionException | _: NotLeaderForPartitionException | _: UnknownLeaderEpochException | _: FencedLeaderEpochException | _: ReplicaNotAvailableException | _: KafkaStorageException | _: OffsetOutOfRangeException) => LogReadResult(info = FetchDataInfo(LogOffsetMetadata.UnknownOffsetMetadata, MemoryRecords.EMPTY), highWatermark = -1L, leaderLogStartOffset = -1L, leaderLogEndOffset = -1L, followerLogStartOffset = -1L, fetchTimeMs = -1L, readSize = 0, lastStableOffset = None, exception = Some(e)) case e: Throwable => brokerTopicStats.topicStats(tp.topic).failedFetchRequestRate.mark() brokerTopicStats.allTopicsStats.failedFetchRequestRate.mark() val fetchSource = Request.describeReplicaId(replicaId) error(s"Error processing fetch with max size $adjustedMaxBytes from $fetchSource " + s"on partition $tp: $fetchInfo", e) LogReadResult(info = FetchDataInfo(LogOffsetMetadata.UnknownOffsetMetadata, MemoryRecords.EMPTY), highWatermark = -1L, leaderLogStartOffset = -1L, leaderLogEndOffset = -1L, followerLogStartOffset = -1L, fetchTimeMs = -1L, readSize = 0, lastStableOffset = None, exception = Some(e)) } } //讀取的最大字節 var limitBytes = fetchMaxBytes //封裝結果對象 val result = new mutable.ArrayBuffer[(TopicPartition, LogReadResult)] //是否至少返回一條消息 var minOneMessage = !hardMaxBytesLimit //遍歷分區進行讀取 readPartitionInfo.foreach { case (tp, fetchInfo) => //獲取讀取的結果 val readResult = read(tp, fetchInfo, limitBytes, minOneMessage) //獲取每個分區讀取的字節數 val recordBatchSize = readResult.info.records.sizeInBytes if (recordBatchSize > 0) minOneMessage = false //更新還可以讀取的字節數 limitBytes = math.max(0, limitBytes - recordBatchSize) //將分區的讀取結果保存到結果集合中 result += (tp -> readResult) } //返回結果集 result }//獲取Leader Replica的高水位val initialHighWatermark = localReplica.highWatermark.messageOffsetprivate def updateFollowerLogReadResults(replicaId: Int, readResults: Seq[(TopicPartition, LogReadResult)]): Seq[(TopicPartition, LogReadResult)] = { debug(s"Recording follower broker $replicaId log end offsets: $readResults") readResults.map { case (topicPartition, readResult) => var updatedReadResult = readResult nonOfflinePartition(topicPartition) match { //如果找到了對應的分區 case Some(partition) => //根據副本id獲取Partition對象中保存的副本對象 //Partition.allReplicasMap結構中保存了當前分區的所有副本對象。其中,key是brokerid,value是對應的Replica對象 partition.getReplica(replicaId) match { //如果獲取到了Replica對象 case Some(replica) => //TODO 更新leader保存的各個follower副本的LEO partition.updateReplicaLogReadResult(replica, readResult) case None => warn(s"Leader $localBrokerId failed to record follower $replicaId's position " + s"${readResult.info.fetchOffsetMetadata.messageOffset} since the replica is not recognized to be " + s"one of the assigned replicas ${partition.assignedReplicas.map(_.brokerId).mkString(",")} " + s"for partition $topicPartition. Empty records will be returned for this partition.") updatedReadResult = readResult.withEmptyFetchInfo } //如果對應的分區沒有被創建 case None => warn(s"While recording the replica LEO, the partition $topicPartition hasn't been created.") } topicPartition -> updatedReadResult } }Partition.updateReplicaLogReadResult() 方法:
def updateReplicaLogReadResult(replica: Replica, logReadResult: LogReadResult): Boolean = { val replicaId = replica.brokerId val oldLeaderLW = if (replicaManager.delayedDeleteRecordsPurgatory.delayed > 0) lowWatermarkIfLeader else -1L //TODO 最終更新Leader副本保存的Follower副本的LEO的值 replica.updateLogReadResult(logReadResult) val newLeaderLW = if (replicaManager.delayedDeleteRecordsPurgatory.delayed > 0) lowWatermarkIfLeader else -1L val leaderLWIncremented = newLeaderLW > oldLeaderLW //TODO 嘗試更新ISR列表,在這個方法中會更新Leader副本對象的HW對象和分區對應的Log對象的HW值 val leaderHWIncremented = maybeExpandIsr(replicaId, logReadResult) val result = leaderLWIncremented || leaderHWIncremented if (result) tryCompleteDelayedRequests() debug(s"Recorded replica $replicaId log end offset (LEO) position ${logReadResult.info.fetchOffsetMetadata.messageOffset}.") result }def updateLogReadResult(logReadResult: LogReadResult) { if (logReadResult.info.fetchOffsetMetadata.messageOffset >= logReadResult.leaderLogEndOffset) _lastCaughtUpTimeMs = math.max(_lastCaughtUpTimeMs, logReadResult.fetchTimeMs) else if (logReadResult.info.fetchOffsetMetadata.messageOffset >= lastFetchLeaderLogEndOffset) _lastCaughtUpTimeMs = math.max(_lastCaughtUpTimeMs, lastFetchTimeMs) //更新Follower副本的日志起始偏移量,即 _logStartOffset 變量 logStartOffset = logReadResult.followerLogStartOffset //更新Follower副本的LEO元數據對象,即 _logEndOffsetMetadata 變量 logEndOffsetMetadata = logReadResult.info.fetchOffsetMetadata //最后一次拉取時Leader副本的LEO lastFetchLeaderLogEndOffset = logReadResult.leaderLogEndOffset lastFetchTimeMs = logReadResult.fetchTimeMs}def maybeExpandIsr(replicaId: Int, logReadResult: LogReadResult): Boolean = { inWriteLock(leaderIsrUpdateLock) { // 檢查給定的副本對象是否需要添加到ISR列表 leaderReplicaIfLocal match { case Some(leaderReplica) => //獲取給定節點的Replica對象 val replica = getReplica(replicaId).get //獲取leader副本的HW值 val leaderHW = leaderReplica.highWatermark //獲取Follower副本的LEO val fetchOffset = logReadResult.info.fetchOffsetMetadata.messageOffset //判斷是否需要更新ISR列表的條件: //1.該節點不在ISR列表,且replica.logEndOffsetMetadata.offsetDiff(leaderHW) //2.給定Follower副本的LEO大于等于leader副本的HW //3.給定的Follower副本屬于該分區 //4.leader epoch對應的起始偏移量存在且小于Follower副本的LEO //滿足這4個條件說明這個Follower副本已經和leader副本保持同步了,把這個Follower副本加入到ISR列表中 if (!inSyncReplicas.contains(replica) && assignedReplicas.map(_.brokerId).contains(replicaId) && replica.logEndOffsetMetadata.offsetDiff(leaderHW) >= 0 && leaderEpochStartOffsetOpt.exists(fetchOffset >= _)) { //將該副本加入集合 val newInSyncReplicas = inSyncReplicas + replica info(s"Expanding ISR from ${inSyncReplicas.map(_.brokerId).mkString(",")} " + s"to ${newInSyncReplicas.map(_.brokerId).mkString(",")}") // update ISR in ZK and cache //更新ISR列表 updateIsr(newInSyncReplicas) replicaManager.isrExpandRate.mark() } // check if the HW of the partition can now be incremented // since the replica may already be in the ISR and its LEO has just incremented //TODO 嘗試更新leader副本的HW對象及分區對應的Log對象的HW值 maybeIncrementLeaderHW(leaderReplica, logReadResult.fetchTimeMs) case None => false // nothing to do if no longer leader } } }maybeIncrementLeaderHW() 方法:嘗試更新 leader 副本的 HW 對象及分區對應的Log 對象的 HW 值(對應同步數據的第六步)
private def maybeIncrementLeaderHW(leaderReplica: Replica, curTime: Long = time.milliseconds): Boolean = { val allLogEndOffsets = assignedReplicas.filter { replica => curTime - replica.lastCaughtUpTimeMs <= replicaLagTimeMaxMs || inSyncReplicas.contains(replica) }.map(_.logEndOffsetMetadata) //取ISR列表中副本的最小的LEO作為新的HW val newHighWatermark = allLogEndOffsets.min(new LogOffsetMetadata.OffsetOrdering) //獲取舊的HW val oldHighWatermark = leaderReplica.highWatermark //如果新的HW值大于舊的HW值,就更新 if (oldHighWatermark.messageOffset < newHighWatermark.messageOffset || (oldHighWatermark.messageOffset == newHighWatermark.messageOffset && oldHighWatermark.onOlderSegment(newHighWatermark))) { //更新Replica的hightWatermark對象,以及對應Log對象的高水位值 leaderReplica.highWatermark = newHighWatermark debug(s"High watermark updated to $newHighWatermark") true } else { def logEndOffsetString(r: Replica) = s"replica ${r.brokerId}: ${r.logEndOffsetMetadata}" debug(s"Skipping update high watermark since new hw $newHighWatermark is not larger than old hw $oldHighWatermark. " + s"All current LEOs are ${assignedReplicas.map(logEndOffsetString)}") false } }def onHighWatermarkIncremented(highWatermark: Long): Unit = { lock synchronized { //更新高水位值??????replicaHighWatermark?=?Some(highWatermark)??????producerStateManager.onHighWatermarkUpdated(highWatermark) updateFirstUnstableOffset() } }def highWatermark_=(newHighWatermark: LogOffsetMetadata) { //如果是本地副本 if (isLocal) { if (newHighWatermark.messageOffset < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("High watermark offset should be non-negative") //高水位的元數據對象 highWatermarkMetadata = newHighWatermark //更新Log對象保存的高水位值 log.foreach(_.onHighWatermarkIncremented(newHighWatermark.messageOffset)) trace(s"Setting high watermark for replica $brokerId partition $topicPartition to [$newHighWatermark]") } else { throw new KafkaException(s"Should not set high watermark on partition $topicPartition's non-local replica $brokerId") } }//更新Replica的hightWatermark對象,以及對應Log對象的高水位值leaderReplica.highWatermark = newHighWatermarkdef?fetchMessages(){ ... logReadResults.foreach { case (topicPartition, logReadResult) => //如果讀取發生錯誤 if (logReadResult.error != Errors.NONE) errorReadingData = true bytesReadable = bytesReadable + logReadResult.info.records.sizeInBytes //將讀取結果放入集合 logReadResultMap.put(topicPartition, logReadResult) }????...}????上面所說的合適的時機,分為 立即返回 和 延時返回,當滿足下面四個條件之一時,便立即返回,否則會進行延時處理:
拉取等待的時間到了
拉取請求中沒有拉取分區的信息
已經拉取到了足夠多的數據
拉取過程中發生錯誤
Leader副本寫入數據,Follower副本進行同步的過程分為9個步驟:
- leader 副本將數據寫入本地磁盤
- leader?副本更新 LEO
- follower 副本發送同步數據請求,攜帶自身的 LEO
- leader 副本更新本地保存的其它副本的 LEO
- leader 副本嘗試更新 ISR 列表
- leader?副本更新 HW
- leader 副本給 follower 副本返回數據,攜帶 leader 副本的 HW 值
- follower 副本接收響應并寫入數據,更新自身 LEO
- follower 副本更新本地的 HW 值
關于 HW 和 LEO 的保存:
對于HW,Leader 副本和 Follower 副本只保存自身的
對于LEO,Follower 副本只保存自身的,但是 Leader 副本除了保存自身的外,還會保存所有 Follower 副本的 LEO 值
無論是Leader副本所在節點,還是Follower副本所在節點,分區對應的Partition 對象都會保存所有的副本對象,但是只有本地副本對象有對應的日志文件



















