2019獨角獸企業重金招聘Python工程師標準>>> 
使用AtomicInteger原子類進行 i ++ 操作 可以有類似 synchronized 實現同步的效果。
原子操作是不能分割的整體,沒有其他線程能夠中斷或檢查正在原子操作中的變量。一個原子類型就是一個原子操作可用的類型,它可以在沒有鎖的情況下做到線程安全。
示例1:
AddCountThread.java
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;public class AddCountThread extends Thread {private AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);@Overridepublic void run() {for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){System.out.println(count.incrementAndGet());}}
}Run_Atomic.java
public class Run_Atomic {public static void main(String[] args) {AddCountThread countService = new AddCountThread();Thread t1 = new Thread(countService);t1.start();Thread t2 = new Thread(countService);t2.start();Thread t3 = new Thread(countService);t3.start();Thread t4 = new Thread(countService);t4.start();Thread t5 = new Thread(countService);t5.start();}
}輸出結果成功地累加到 50000?
但是原子類也并不是完全安全的,比如以下例子
示例2:
MyService.java
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;public class MyService {public static AtomicLong aiRef = new AtomicLong();public void addNum() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "加了100之后的結果是:" + aiRef.addAndGet(100));aiRef.addAndGet(1);}
} MyThread.java
public class MyThread extends Thread {private MyService myService;public MyThread (MyService myService) {super();this.myService = myService;}@Overridepublic void run() {myService.addNum();}
} Run3_1.java
public class Run3_1 {public static void main(String[] args) {try {MyService myService = new MyService();MyThread[] array = new MyThread[8];for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++) {array[i] = new MyThread(myService);}for (int i = 0;i<array.length;i++ ){array[i].start();}Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println(myService.aiRef.get());}catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
} 輸出結果:
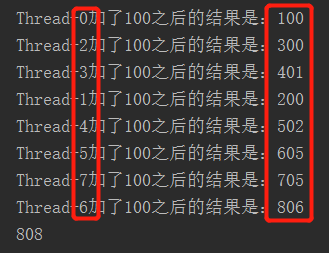
出現這種情況是因為,addAndGet()方法是原子性的,但方法和方法之間的調用卻不是原子的。解決這樣的問題必須用到同步。
給addNum() 方法加上 同步鎖既解決以上問題。
?
?
?

之二:以接口的方式編程)






)










