入門kaggle,開始機器學習應用之旅。
參看一些入門的博客,感覺pandas,sklearn需要熟練掌握,同時也學到了一些很有用的tricks,包括數據分析和機器學習的知識點。下面記錄一些有趣的數據分析方法和一個自己擼的小程序。
?
1.Tricks
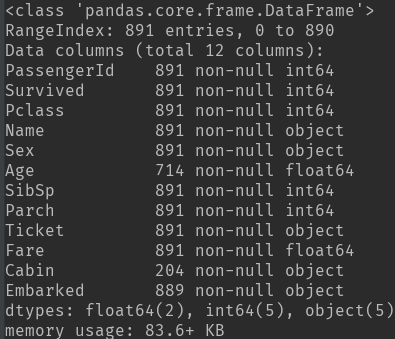
1) df.info():數據的特征屬性,包括數據缺失情況和數據類型。
? ? df.describe(): 數據中各個特征的數目,缺失值為NaN,以及數值型數據的一些分布情況,而類目型數據看不到。
? ? 缺失數據處理:缺失的樣本占總數比例極高,則直接舍棄;缺失樣本適中,若為非連續性特征則將NaN作為一個新類別加到類別特征中(0/1化),若為連續性特征可以將其離散化后把NaN作為新類別加入,或用平均值填充。
2)數據分析方法:將特征分為連續性數據:年齡、票價、親人數目;類目數據:生存與否、性別、等級、港口;文本類數據:姓名、票名、客艙名
3)數據分析技巧(畫圖、求相關性)
- 畫圖
類目特征分布圖&&特征與生存情況關聯柱狀圖:


fig1 = plt.figure(figsize=(12,10)) # 設定大尺寸后使得圖像標注不重疊
fig1.set(alpha=0.2) # 設定圖表顏色alpha參數
plt.subplot2grid((2,3),(0,0)) # 在一張大圖里分列幾個小圖
data_train.Survived.value_counts().plot(kind='bar')# 柱狀圖
plt.title(u"獲救情況 (1為獲救)") # 標題
plt.ylabel(u"人數")plt.subplot2grid((2,3),(0,1))
data_train.Pclass.value_counts().plot(kind="bar")
plt.ylabel(u"人數")
plt.title(u"乘客等級分布")plt.subplot2grid((2,3),(0,2))
plt.scatter(data_train.Survived, data_train.Age)
plt.ylabel(u"年齡") # 設定縱坐標名稱
plt.grid(b=True, which='major', axis='y')
plt.title(u"按年齡看獲救分布 (1為獲救)")plt.subplot2grid((2,3),(1,0), colspan=2)
data_train.Age[data_train.Pclass == 1].plot(kind='kde')
data_train.Age[data_train.Pclass == 2].plot(kind='kde')
data_train.Age[data_train.Pclass == 3].plot(kind='kde')
plt.xlabel(u"年齡")# plots an axis lable
plt.ylabel(u"密度")
plt.title(u"各等級的乘客年齡分布")
plt.legend((u'頭等艙', u'2等艙',u'3等艙'),loc='best') # sets our legend for our graph. 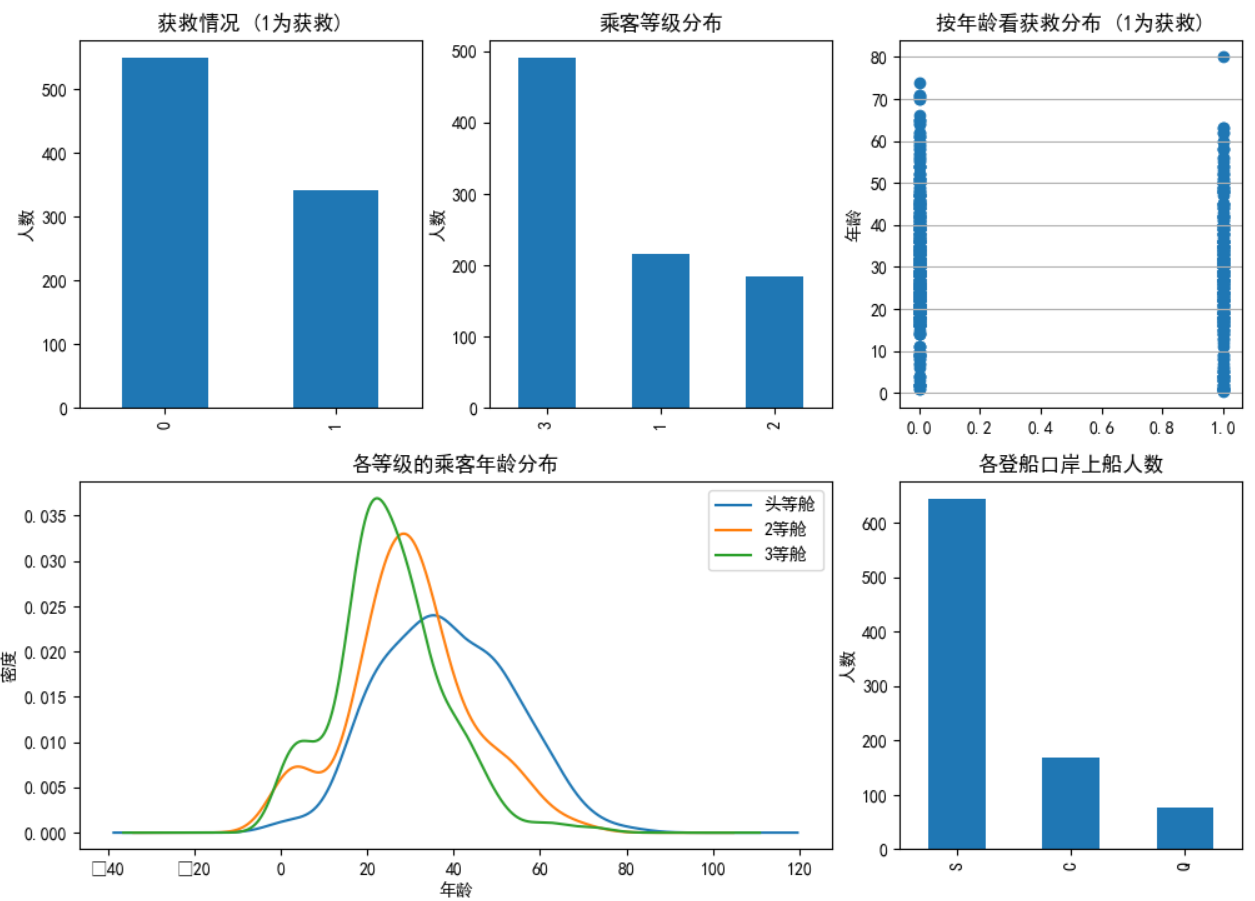 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
以上為3種在一張畫布實現多張圖的畫法:


ax1 = plt.subplot2grid((3,3), (0,0), colspan=3) ax2 = plt.subplot2grid((3,3), (1,0), colspan=2) ax3 = plt.subplot2grid((3,3), (1, 2), rowspan=2) ax4 = plt.subplot2grid((3,3), (2, 0)) ax5 = plt.subplot2grid((3,3), (2, 1)) plt.suptitle("subplot2grid")
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
此外,還有兩種方法等效:


f=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.plot(x,y)plt.figure()
plt.subplot(111)
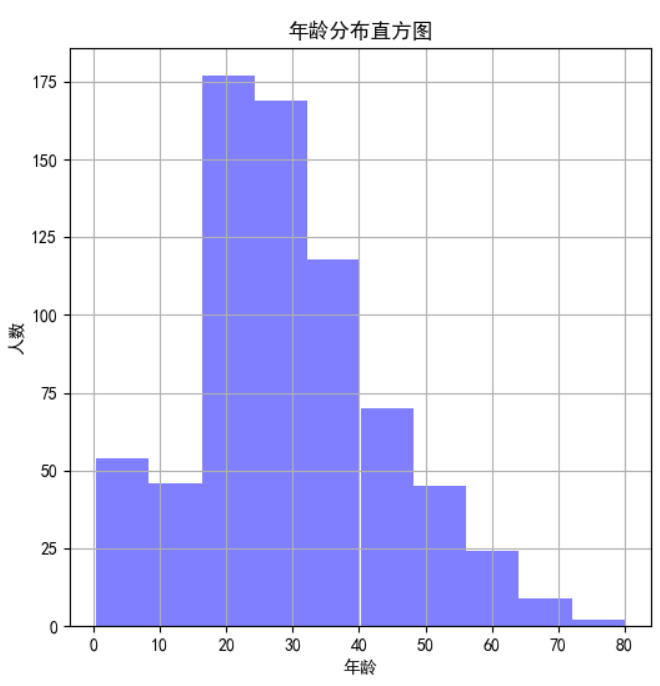
plt.plot(x,y) 連續性特征分布可以用直方圖hist來實現(見上圖-年齡分布直方圖):


figure1 = plt.figure(figsize=(6,6))
value_age = train_data['Age']
value_age.hist(color='b', alpha=0.5) # 年齡分布直方圖
plt.xlabel(u'年齡')
plt.ylabel(u'人數')
plt.title(u'年齡分布直方圖') 類目特征與生存關系柱狀圖(見上圖-各乘客等級的獲救情況):


fig2 = plt.figure(figsize=(6,5))
fig2.set(alpha=0.2)
Survived_0 = data_train.Pclass[data_train.Survived==0].value_counts()
Survived_1 = data_train.Pclass[data_train.Survived==1].value_counts()
df = pd.DataFrame({u'獲救':Survived_1, u'未獲救':Survived_0})
df.plot(kind='bar', stacked=True) # stacked=False時不重疊
plt.title(u"各乘客等級的獲救情況")
plt.xlabel(u"乘客等級")
plt.ylabel(u"人數")
plt.show() 各屬性與生存率進行關聯:
eg:艙位和性別?與存活率的關系:利用pandas中的groupby函數


Pclass_Gender_grouped=dt_train_p.groupby(['Sex','Pclass']) #按照性別和艙位分組聚合 PG_Survival_Rate=(Pclass_Gender_grouped.sum()/Pclass_Gender_grouped.count())['Survived'] #計算存活率 x=np.array([1,2,3]) width=0.3 plt.bar(x-width,PG_Survival_Rate.female,width,color='r') plt.bar(x,PG_Survival_Rate.male,width,color='b') plt.title('Survival Rate by Gender and Pclass') plt.xlabel('Pclass') plt.ylabel('Survival Rate') plt.xticks([1,2,3]) plt.yticks(np.arange(0.0, 1.1, 0.1)) plt.grid(True,linestyle='-',color='0.7') plt.legend(['Female','Male']) plt.show() #畫圖

可以看到,不管是幾等艙位,都是女士的存活率遠高于男士。
?將連續性數據年齡分段后,畫不同年齡段的分布以及存活率:


age_train_p=dt_train_p[~np.isnan(dt_train_p['Age'])] #去除年齡數據中的NaN ages=np.arange(0,85,5) #0~85歲,每5歲一段(年齡最大80歲) age_cut=pd.cut(age_train_p.Age,ages) age_cut_grouped=age_train_p.groupby(age_cut) age_Survival_Rate=(age_cut_grouped.sum()/age_cut_grouped.count())['Survived'] #計算每年齡段的存活率 age_count=age_cut_grouped.count()['Survived'] #計算每年齡段的總人數 ax1=age_count.plot(kind='bar') ax2=ax1.twinx() #使兩者共用X軸 ax2.plot(age_Survival_Rate.values,color='r') ax1.set_xlabel('Age') ax1.set_ylabel('Number') ax2.set_ylabel('Survival Rate') plt.title('Survival Rate by Age') plt.grid(True,linestyle='-',color='0.7') plt.show()

可以看到年齡主要在15~50歲左右,65~80歲死亡率較高,后面80歲存活率高是因為只有1人。
?
- 相關性分析:
Parch、SibSp取值少,分布不均勻,不適合作為連續值來處理。可以將其分段化。這里分析一下Parch和SibSp與生存的關聯性
from sklearn.feature_selection import chi2
print("Parch:", chi2(train_data.filter(["Parch"]), train_data['Survived']))
print("SibSp:", chi2(train_data.filter(["SibSp"]), train_data['Survived']))
# chi2(X,y) X.shape(n_samples, n_features_in) y.shape(n_samples,)
# 返回 chi2 和 pval, chi2值描述了自變量與因變量之間的相關程度:chi2值越大,相關程度也越大,
# http://guoze.me/2015/09/07/chi-square/
# 可以看到Parch比SibSp的卡方校驗取值大,p-value小,相關性更強。 ?
4)數據預處理:
PassengerId 舍掉
Pclass為類目屬性,3類。本身有序的,暫時不進行dummy coding
Name 為文本屬性,舍掉,暫時不考慮
Sex為類目屬性,2類。本身無序,進行dummy coding
Age為連續屬性,確實較多可以用均值填充。幅度變化大。可以將其以5歲為step進行離散化或利用scaling將其歸一化到[-1,1]之間
SibSp為連續屬性,但比較離散,不適合按照連續值處理,暫時不用處理。或者可以按照其數量>3和<=3進行dummy coding
Parch為連續屬性。但比較離散,不適合按照連續值處理,暫時不用處理。
Ticket為文本屬性,舍掉,暫時不考慮
Fare為連續屬性,幅度變化大,可以利用scaling將其歸一化到[-1,1]之間
Cabin為類目屬性,但缺失嚴重,可以按照是否缺失來0/1二值化,進行dummy coding
Embarked為類目屬性,缺失值極少,先填充后進行dummy coding
?綜上,可用的數據特征有:Pclass,Sex,Age,SibSp,Parch,Fare,Cabin,Embarked
?此外需注意的是,需對訓練集和測試集的數據做同樣的處理。
?
?
2.實例。
根據以上思路,一個小baseline誕生了:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pandas import Series, DataFrame
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from learning_curve import *
from pylab import mpl
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] #使得plt操作可以顯示中文
from sklearn.feature_extraction import DictVectorizerdata_train = pd.read_csv('train.csv')
data_test = pd.read_csv('test.csv')feature = ['Pclass','Age','Sex','Fare','Cabin','Embarked','SibSp','Parch'] # 考慮的特征X_train = data_train[feature]
y_train = data_train['Survived']X_test = data_test[feature]X_train.loc[data_train['SibSp']<3, 'SibSp'] = 1 #按照人數3來劃分
X_train.loc[data_train['SibSp']>=3, 'SibSp'] = 0
X_train['Age'].fillna(X_train['Age'].mean(), inplace=True)
X_test.loc[data_test['SibSp']<3, 'SibSp']=1
X_test.loc[data_test['SibSp']>=3, 'SibSp'] = 0
X_test['Age'].fillna(X_test['Age'].mean(), inplace=True) # 缺失的年齡補以均值
X_test['Fare'].fillna(X_test['Fare'].mean(), inplace=True)
# X_train.loc[X_train['Age'].isnull(), 'Age'] = X_train['Age'].mean()
dummies_SibSp = pd.get_dummies(X_train['SibSp'], prefix='SibSp') #進行dummy coding
dummies_Sex = pd.get_dummies(X_train['Sex'], prefix= 'Sex')
dummies_Pclass = pd.get_dummies(X_train['Pclass'], prefix='Pclass')
dummies_Emabrked = pd.get_dummies(X_train['Embarked'], prefix='Embarked')ss=StandardScaler()X_train.loc[X_train['Cabin'].isnull(), 'Cabin'] = 1
X_train.loc[X_train['Cabin'].notnull(), 'Cabin'] = 0
X_train['Age_new'] = (X_train['Age']/5).astype(int)
X_train['Fare_new'] = ss.fit_transform(X_train.filter(['Fare']))
X_train = pd.concat([X_train, dummies_Sex, dummies_Pclass, dummies_Emabrked, dummies_SibSp], axis=1)
X_train.drop(['Age', 'Sex', 'Pclass', 'Fare','Embarked', 'SibSp'], axis=1, inplace=True)dummies_SibSp = pd.get_dummies(X_test['SibSp'], prefix='SibSp')
dummies_Sex = pd.get_dummies(X_test['Sex'], prefix= 'Sex')
dummies_Pclass = pd.get_dummies(X_test['Pclass'], prefix='Pclass')
dummies_Emabrked = pd.get_dummies(X_test['Embarked'], prefix='Embarked')X_test['Age_new'] = (X_test['Age']/5).astype('int')
X_test['Fare_new'] = ss.fit_transform(X_test.filter(['Fare']))
X_test = pd.concat([X_test, dummies_Sex, dummies_Pclass, dummies_Emabrked, dummies_SibSp], axis=1)
X_test.drop(['Age', 'Sex', 'Pclass', 'Fare','Embarked','SibSp'], axis=1, inplace=True)
X_test.loc[X_test['Cabin'].isnull(), 'Cabin'] = 1
X_test.loc[X_test['Cabin'].notnull(), 'Cabin'] = 0dec = LogisticRegression() # logistic回歸
dec.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pre = dec.predict(X_test)# 交叉驗證
all_data = X_train.filter(regex='Cabin|Age_.*|Fare_.*|Sex.*|Pclass_.*|Embarked_.*|SibSp_.*_Parch')
X_cro = all_data.as_matrix()
y_cro = y_train.as_matrix()
est = LogisticRegression(C=1.0, penalty='l1', tol=1e-6)
print(cross_val_score(dec, X_cro, y_cro, cv=5))# 保存結果
# result = pd.DataFrame({'PassengerId':data_test['PassengerId'].as_matrix(), 'Survived':y_pre.astype(np.int32)})
# result.to_csv("my_logisticregression_1.csv", index=False)# 學習曲線
plot_learning_curve(dec, u"學習曲線", X_train, y_train)# 查看各個特征的相關性
columns = list(X_train.columns)
plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
plot_df = pd.DataFrame(dec.coef_.ravel(), index=columns)
plot_df.plot(kind='bar')
plt.show()# 分析SibSp
# survived_0 = data_train.SibSp[data_train['Survived']==0].value_counts()
# survived_1 = data_train.SibSp[data_train['Survived']==1].value_counts()
# df = pd.DataFrame({'獲救':survived_1, '未獲救':survived_0})
# df.plot(kind='bar', stacked=True)
# plt.xlabel('兄妹個數')
# plt.ylabel('獲救情況')
# plt.title('兄妹個數與獲救情況')
# 不加SibSp [ 0.70 0.80446927 0.78651685 0.76966292 0.79661017]
# 加上SibSp [ 0.70 0.78212291 0.80337079 0.79775281 0.81355932]# logistic:[ 0.78212291 0.80446927 0.78651685 0.76966292 0.80225989] why? ?
3.結果分析與總結
1)學習曲線函數:


import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.model_selection import learning_curve# 用sklearn的learning_curve得到training_score和cv_score,使用matplotlib畫出learning curve def plot_learning_curve(estimator, title, X, y, ylim=None, cv=None, n_jobs=1,train_sizes=np.linspace(.05, 1., 20), verbose=0, plot=True):"""畫出data在某模型上的learning curve.參數解釋----------estimator : 你用的分類器。title : 表格的標題。X : 輸入的feature,numpy類型y : 輸入的target vectorylim : tuple格式的(ymin, ymax), 設定圖像中縱坐標的最低點和最高點cv : 做cross-validation的時候,數據分成的份數,其中一份作為cv集,其余n-1份作為training(默認為3份)n_jobs : 并行的的任務數(默認1)"""train_sizes, train_scores, test_scores = learning_curve(estimator, X, y, cv=cv, n_jobs=n_jobs, train_sizes=train_sizes, verbose=verbose)train_scores_mean = np.mean(train_scores, axis=1)train_scores_std = np.std(train_scores, axis=1)test_scores_mean = np.mean(test_scores, axis=1)test_scores_std = np.std(test_scores, axis=1)if plot:plt.figure(1)plt.title(title)if ylim is not None:plt.ylim(*ylim)plt.xlabel(u"訓練樣本數")plt.ylabel(u"得分")plt.gca().invert_yaxis()plt.grid()plt.fill_between(train_sizes, train_scores_mean - train_scores_std, train_scores_mean + train_scores_std,alpha=0.1, color="b")plt.fill_between(train_sizes, test_scores_mean - test_scores_std, test_scores_mean + test_scores_std,alpha=0.1, color="r")plt.plot(train_sizes, train_scores_mean, 'o-', color="b", label=u"訓練集上得分")plt.plot(train_sizes, test_scores_mean, 'o-', color="r", label=u"交叉驗證集上得分")plt.legend(loc="best")plt.draw()plt.show()plt.gca().invert_yaxis()midpoint = ((train_scores_mean[-1] + train_scores_std[-1]) + (test_scores_mean[-1] - test_scores_std[-1])) / 2diff = (train_scores_mean[-1] + train_scores_std[-1]) - (test_scores_mean[-1] - test_scores_std[-1])return midpoint, diff
見下圖:將learning_curve畫出可以看到兩者在0.8左右趨于平行,但是正確率不夠高,應該是屬于欠擬合。所以可以考慮加入新的特征,再對特征進行更深的挖掘 。
 ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ?
?
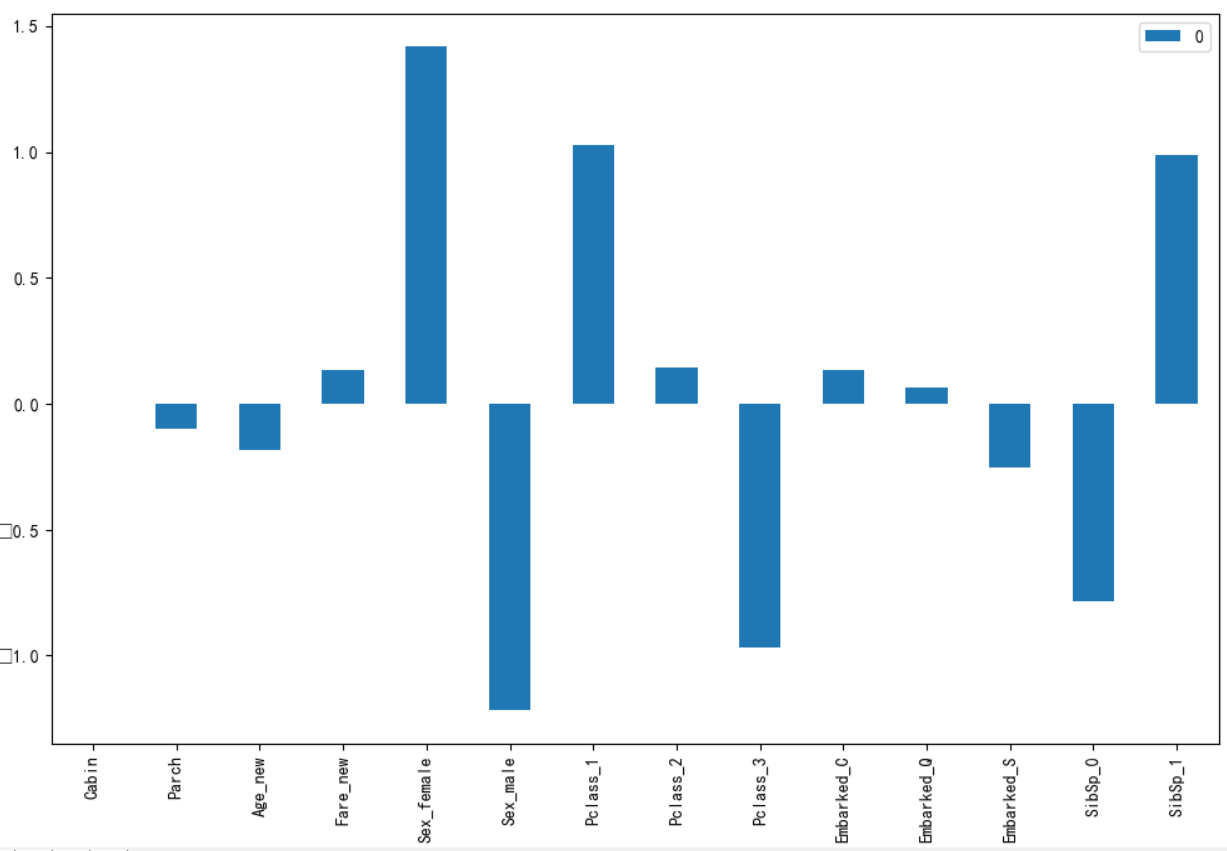
2)特征相關性分析圖


columns = list(X_train.columns) plt.figure(figsize=(8,8)) plot_df = pd.DataFrame(dec.coef_.ravel(), index=columns) plot_df.plot(kind='bar') plt.show()
結果見下圖:通過logistic學到的參數權重
?性別、等級和親屬相關性較強,而親屬在前面已經了解到相關性并不強,所以可以對這一特征加以優化,例如將Parch+SibSp作為一個新特征。
?其他特征或正相關或負相關,但都不太明顯。
?cabin怎么沒有相關性呢?
?
3)交叉驗證


# 交叉驗證 all_data = X_train.filter(regex='Cabin|Age_.*|Fare_.*|Sex.*|Pclass_.*|Embarked_.*|SibSp_.*_Parch') X_cro = all_data.as_matrix() y_cro = y_train.as_matrix() est = LogisticRegression(C=1.0, penalty='l1', tol=1e-6) print(cross_val_score(dec, X_cro, y_cro, cv=5))
每次通過訓練集學習到參數后進行分類,但是怎么評價結果的好壞呢,可以利用交叉驗證來實現,根據交叉驗證的結果大致可以知道運用于測試集的結果。
?這是本次測試的交叉驗證結果: ?[ 0.78212291 0.80446927 0.78651685 0.76966292 0.80225989]
實際提交到Kaggle上時候準確率為0.7751

?
?
?
參考:


![【BZOJ1500】[NOI2005]維修數列 Splay](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/【BZOJ1500】[NOI2005]維修數列 Splay)
(主席樹))


及readLine()方法的使用心得)









)

![關于拓撲排序的問題-P3116 [USACO15JAN]會議時間Meeting Time](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/關于拓撲排序的問題-P3116 [USACO15JAN]會議時間Meeting Time)
