持續更新...
github鏈接:https://github.com/x2mercy/Leetcode_Solution
?
為什么括號200道呢!因為準備按照200道這樣的周期刷,每200道刷兩遍,第一遍按難度刷,第二遍按類別刷!
先整理binarytree這一類別也是因為在刷題的過程中,由于沒有系統的算法基礎,這類題目算是遇到的比較大的障礙。
下面按照題目難度來說:
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
EASY:
1. Same Tree:
Given two binary trees, write a function to check if they are the same or not.
Two binary trees are considered the same if they are structurally identical and the nodes have the same value.
這是我做的第一道二叉樹的題目。
一開始的思路是二叉樹的遍歷,找到的資料:http://blog.csdn.net/bone_ace/article/details/46718683 主要說了樹的構造和幾種遍歷方式
所以第一種方法是用層次遍歷做的,代碼如下:
# this solution is Time Limit Exceeded # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = Noneclass Solution(object):def isSameTree(self, p, q):""":type p: TreeNode:type q: TreeNode:rtype: bool"""result1=[]result1.append(p.val)while p:if p.left!=None:result1.append(p.left)if p.right!=None:result1.append(p.right)result2=[]result2.append(q.val)while q:if q.left!=None:result1.append(q.left)if q.right!=None:result1.append(q.right)result=cmp(result1,result2)if result==0:return Trueelse:return False
滿心歡喜的以為可以過,但是卻報了time limit exceed的錯誤,于是開始找第二種方法!
上代碼:
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = Noneclass Solution(object):def isSameTree(self, p, q):""":type p: TreeNode:type q: TreeNode:rtype: bool"""if p==None and q==None:return Trueif p==None or q==None:return Falseif p.val==q.val:return self.isSameTree(p.left,q.left) and self.isSameTree(p.right,q.right)return False
這種做法寫完之后呢。。emmmm覺得自己上一種方法簡直是智障兒童
這種方法很簡單吶,重點是用了遞歸。遞歸真是一種邏輯簡潔的好東西,利用遞歸比較子樹的各個節點是否相同。
2. Symmetric Tree:
Given a binary tree, check whether it is a mirror of itself (ie, symmetric around its center).
先上代碼:
# recursive answer # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = Noneclass Solution(object):def isSymmetric(self, root):""":type root: TreeNode:rtype: bool"""if root==None:return Truereturn self.isMirror(root.left,root.right)def isMirror(self,p,q):if p==None and q==None:return Trueif p==None or q==None:return Falsereturn p.val==q.val and self.isMirror(p.left,q.right) and self.isMirror(p.right,q.left)
這道題的重點在于調用了另一個函數,因為需要比較是否對稱的本質是比較左子樹的左節點和右子樹的右節點、左子樹的右節點和右子樹的左節點是否相等,所以需要調用IsMirror函數,可以接收兩個arg,isMirror返回的boolean值主要由節點值是否相等以及下個節點是否對稱來決定,所以這里用了遞歸。
注意:用了遞歸,就一定要有遞歸停止的條件,不能無限循環下去
3.??Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, find its maximum depth.
The maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
這道題算法很經典,mark一下,可以用在很多二叉樹的題目中。
上代碼:
#iterator # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = Noneclass Solution(object):def maxDepth(self, root):""":type root: TreeNode:rtype: int"""if root==None:return 0DL=self.maxDepth(root.left)DR=self.maxDepth(root.right)return max(DL,DR)+1
后面還有一道求最短路徑的題目,和這個做法類似
主要也是用了遞歸,最后返回的時候注意要+1,因為返回的是節點數
4.?Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
Given a binary tree, return the?bottom-up level order?traversal of its nodes' values. (ie, from left to right, level by level from leaf to root).
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = Noneclass Solution(object):def levelOrderBottom(self, root):""":type root: TreeNode:rtype: List[List[int]]"""if root==None:return []p=collections.deque()p.append((root,0))result=[]while p:node,index=p.popleft()if index>len(result)-1:result.append([node.val])else:result[index].append(node.val)if node.left:p.append((node.left,index+1))if node.right:p.append((node.right,index+1))result.reverse()return result
這里本來想用queue,但是發現了一個很神奇的東西:deque(學疏才淺。。),是python標準庫里的一項,直接from collections import deque,或者像我這樣collections.deque就可以用了。
它的好處在于,它可以提供類似于list的操作,比如append什么的,但是不同的是可以popleft操作,使第一位元素pop出來。(參考:http://blog.csdn.net/qins_superlover/article/details/44338415)
這一種操作對解決二叉樹問題,提供了很大的幫助!比如這道題!
這道題是讓我們把整個二叉樹倒過來,返回從最底層到最上層的節點,給的例子是這樣的:
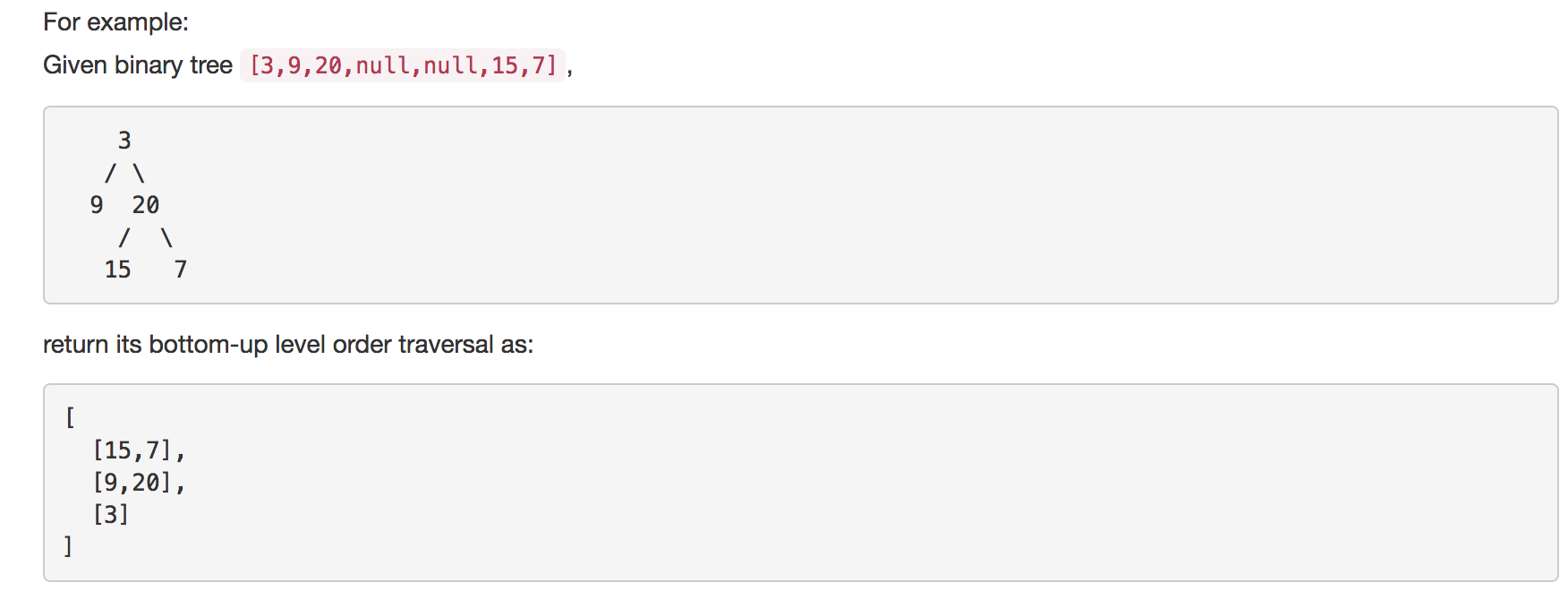
?于是我們知道了在append節點時,需要注意把它的index也append進去,這樣便于后面判斷是不是同一層的節點。
因為父節點下面的兩個子節點的index是一樣的,所以在append左邊節點之后,會出現len(result)-1是大于右邊節點index的,這時直接把右邊節點append到result[index]中,等于是個多維array
最后再reverse一下,返回,搞定
5.?Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree:
Given an array where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height balanced BST.
這里第一次遇到平衡二叉樹,所謂平衡二叉樹要滿足幾個條件:它是一棵空樹或它的左右兩個子樹的高度差的絕對值不超過1,并且左右兩個子樹都是一棵平衡二叉樹
所以又要用到遞歸
上代碼:
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = Noneclass Solution(object):def sortedArrayToBST(self, nums):""":type nums: List[int]:rtype: TreeNode"""if nums==[]:return Nonemid=len(nums)//2root=TreeNode(nums[mid])root.left=self.sortedArrayToBST(nums[:mid])root.right=self.sortedArrayToBST(nums[mid+1:])return root
?
?其實這道題很簡單,核心就是要找到根節點,而因為是sortedarray所以要找根節點,就直接找中間的那個元素,為了避免麻煩,用了"//",表示取商的整數部分
然后分別對左子樹和右子樹用遞歸,這里的nums[:mid]和nums[mid+1:],表示nums從下標為0到mid(不包括mid),nums從下標mid+1到最后
6.?Balanced Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, determine if it is height-balanced.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of?every?node never differ by more than 1.
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = Noneclass Solution(object):def isBalanced(self, root):""":type root: TreeNode:rtype: bool"""if root==None:return TrueDL=self.depth(root.left)DR=self.depth(root.right)if DL-DR<-1 or DL-DR>1:return Falsereturn self.isBalanced(root.left) and self.isBalanced(root.right)def depth(self,node):if node==None:return 0DL=self.depth(node.left)DR=self.depth(node.right)return max(DL,DR)+1
?這里要注意的是判斷是否為平衡二叉樹,需要考慮一個節點左右子樹是否都為平衡二叉樹,所以在返回時需要用and來實現
調用了depth函數(前面說了,這個函數很經典很常用)
然后就是在比較高度時,要注意-1的情況
7.?Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = Noneclass Solution(object):def minDepth(self, root):""":type root: TreeNode:rtype: int"""if root==None:return 0DL=self.minDepth(root.left)DR=self.minDepth(root.right)d=min(DL,DR)D=max(DL,DR)if DL==0 or DR==0:return D+1else:return d+1
看吧,這個算法真的很常用
但是要注意的是:如果某一子樹路徑為0, 則取左右子樹中最大的那個,如果都不為0,則取左右子樹中最小的那個
8. Path Sum:
Given a binary tree and a sum, determine if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals the given sum.
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = Noneclass Solution(object):def hasPathSum(self, root, sum):""":type root: TreeNode:type sum: int:rtype: bool"""if root==None:return Falseif root.right==None and root.left==None and root.val==sum:return Truesum=sum-root.valreturn self.hasPathSum(root.left,sum) or self.hasPathSum(root.right,sum)
這道題最開始想復雜了,一直在想用deque(),然后一個一個節點加,但其實不用,cheat了一下,看了dicuss,發現了機智的做法!
只需要依次比較每個節點,比較完之后,sum減去這個節點,然后比較下一個(左或者右),直到sum=某個節點,則返回true
否則返回false
重點在于每次都需要sum減去這個節點值!這樣如果剩下的節點值等于這個數,并且!它沒有左右子樹,則返回true?————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
?

)
)


)



 了解相等和等價的區別)







【結構型】)

