Java基礎教程:多線程基礎(3)——阻塞隊列
快速開始
引入問題
生產者消費者問題是線程模型中的經典問題:生產者和消費者在同一時間段內共用同一存儲空間,生產者向空間里生產數據,而消費者取走數據。
模擬情景
這里我們實現如下的情況的生產-消費模型:
生產者不斷交替地生產兩組數據“姓名--1-->內容--1”,“姓名--2-->內容--2”,這里的“姓名--1”和“姓名--2”模擬為數據的名稱,“內容--1 ”和“內容--2 ”模擬為數據的內容。
由于本程序中牽扯到線程運行的不確定性,因此可能會出現以下問題:
1.假設生產者線程剛向數據存儲空間添加了數據的名稱,還沒有加入該信息的內容,程序就切換到了消費者線程,消費者線程把信息的名稱和上一個信息的內容聯系到了一起;
2.生產者生產了若干條數據,消費者才可以取數據,或者是,消費者取完一次數據后,還沒等生產者放入新的數據,又重復取出了已取過的數據。
通過分析我們可知:
第一個問題可以通過同步來解決,第二個問題就需要用到線程通信。生產者線程放入數據后,通知消費者線程取出數據,消費者線程取出數據后,通知生產者線程生產數據,這里用wait\notigy機制來實現。
Java代碼
定義信息類
package thread;public class Info {private String name = "name";private String content = "content";//設置標志位,用來進行線程通信private boolean flag =true;/*** 設置消息,此處用到線程同步* @param name* @param content*/public synchronized void set(String name,String content){while (!flag){try {super.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}this.name=name; //設置名稱try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}this.content=content; //設置內容flag =false; //設置標志位,表示現在生產停止,可以取走!}public synchronized void get(){while (flag){try {super.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}try {Thread.sleep(300);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(name +" --> " + content) ;flag = true ; // 改變標志位,表示可以生產super.notify();}} 定義生產者
public class Producer implements Runnable {private Info info=null;public Producer(Info info){this.info=info;}@Overridepublic void run() {boolean flag = true ; // 定義標記位for(int i=0;i<10;i++){if(flag){this.info.set("姓名--1","內容--1") ; // 設置名稱flag = false ;}else{this.info.set("姓名--2","內容--2") ; // 設置名稱flag = true ;}}}
}定義消費者
public class Consumer implements Runnable {private Info info = null ;public Consumer(Info info){this.info = info ;}public void run(){for(int i=0;i<10;i++){this.info.get() ;}}public static void main(String[] args) {Info info = new Info(); // 實例化Info對象Producer pro = new Producer(info) ; // 生產者Consumer con = new Consumer(info) ; // 消費者new Thread(pro).start() ;//啟動了生產者線程后,再啟動消費者線程try{Thread.sleep(500) ;}catch(InterruptedException e){e.printStackTrace() ;}new Thread(con).start() ;}
}?使用阻塞隊列來實現相同功能
引入BlockingQueue
任何有效的生產者-消費者問題解決方案都是通過控制生產者put()方法(生產資源)和消費者take()方法(消費資源)的調用來實現的,一旦你實現了對方法的阻塞控制,那么你將解決該問題。Java通過BlockingQueue提供了開箱即用的支持來控制這些方法的調用(一個線程創建資源,另一個消費資源)。java.util.concurrent包下的BlockingQueue接口是一個線程安全的可用于存取對象的隊列。
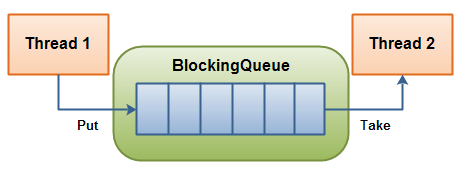
BlockingQueue是一種數據結構,支持一個線程往里存資源,另一個線程從里取資源。這正是解決生產者消費者問題所需要的,那么讓我們開始解決該問題吧。
Java代碼
消息類
public class InfoPlus {private String name = "name";private String content = "content";public InfoPlus(String name, String content) {this.name = name;this.content = content;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public String getContent() {return content;}public void setContent(String content) {this.content = content;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "InfoPlus{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", content='" + content + '\'' +'}';}
}生產者
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;public class ProducerPlus implements Runnable {private BlockingQueue<InfoPlus> queue;public ProducerPlus(BlockingQueue<InfoPlus> queue) {this.queue = queue;}@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i=0;i<10;i++){try {Thread.sleep(1000);queue.put(new InfoPlus("name"+i,"content"+i));} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
}消費者
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;public class ConsumerPlus implements Runnable{private BlockingQueue<InfoPlus> queue;public ConsumerPlus(BlockingQueue<InfoPlus> queue) {this.queue = queue;}public void run() {while (true) {try {System.out.println(this.queue.take());} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}public static void main(String[] args) {BlockingQueue<InfoPlus> blockingQueue = new LinkedBlockingDeque<>();ProducerPlus producerPlus = new ProducerPlus(blockingQueue);ConsumerPlus consumerPlus = new ConsumerPlus(blockingQueue);ConsumerPlus consumerPlus1 = new ConsumerPlus(blockingQueue);new Thread(producerPlus).start();new Thread(consumerPlus).start();new Thread(consumerPlus1).start();}
}
?




(僅存放))



)










