本次作業來源于:https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gzcc/GZCC-16SE1/homework/2822
中文詞頻統計
1. 下載一長篇中文小說。
下載長篇小說《西游記》
本次作業小說保存在txt文檔:xyj.txt
2. 從文件讀取待分析文本。
xyj = open(r'F:/xyj.txt','r',encoding='utf-8').read() wordsls = jieba.lcut(xyj)
3. 安裝并使用jieba進行中文分詞。
pip install jieba
import jieba
jieba.lcut(text)

?
4. 更新詞庫,加入所分析對象的專業詞匯。
jieba.add_word('天罡北斗陣')? #逐個添加
jieba.load_userdict(word_dict)? #詞庫文本文件
jieba.add_word('美猴王')
參考詞庫下載地址:https://pinyin.sogou.com/dict/
轉換代碼:scel_to_text
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import struct import os# 拼音表偏移, startPy = 0x1540;# 漢語詞組表偏移 startChinese = 0x2628;# 全局拼音表 GPy_Table = {}# 解析結果 # 元組(詞頻,拼音,中文詞組)的列表# 原始字節碼轉為字符串 def byte2str(data):pos = 0str = ''while pos < len(data):c = chr(struct.unpack('H', bytes([data[pos], data[pos + 1]]))[0])if c != chr(0):str += cpos += 2return str# 獲取拼音表 def getPyTable(data):data = data[4:]pos = 0while pos < len(data):index = struct.unpack('H', bytes([data[pos],data[pos + 1]]))[0]pos += 2lenPy = struct.unpack('H', bytes([data[pos], data[pos + 1]]))[0]pos += 2py = byte2str(data[pos:pos + lenPy])GPy_Table[index] = pypos += lenPy# 獲取一個詞組的拼音 def getWordPy(data):pos = 0ret = ''while pos < len(data):index = struct.unpack('H', bytes([data[pos], data[pos + 1]]))[0]ret += GPy_Table[index]pos += 2return ret# 讀取中文表 def getChinese(data):GTable = []pos = 0while pos < len(data):# 同音詞數量same = struct.unpack('H', bytes([data[pos], data[pos + 1]]))[0]# 拼音索引表長度pos += 2py_table_len = struct.unpack('H', bytes([data[pos], data[pos + 1]]))[0]# 拼音索引表pos += 2py = getWordPy(data[pos: pos + py_table_len])# 中文詞組pos += py_table_lenfor i in range(same):# 中文詞組長度c_len = struct.unpack('H', bytes([data[pos], data[pos + 1]]))[0]# 中文詞組pos += 2word = byte2str(data[pos: pos + c_len])# 擴展數據長度pos += c_lenext_len = struct.unpack('H', bytes([data[pos], data[pos + 1]]))[0]# 詞頻pos += 2count = struct.unpack('H', bytes([data[pos], data[pos + 1]]))[0]# 保存 GTable.append((count, py, word))# 到下個詞的偏移位置pos += ext_lenreturn GTabledef scel2txt(file_name):print('-' * 60)with open(file_name, 'rb') as f:data = f.read()print("詞庫名:", byte2str(data[0x130:0x338])) # .encode('GB18030')print("詞庫類型:", byte2str(data[0x338:0x540]))print("描述信息:", byte2str(data[0x540:0xd40]))print("詞庫示例:", byte2str(data[0xd40:startPy]))getPyTable(data[startPy:startChinese])getChinese(data[startChinese:])return getChinese(data[startChinese:])if __name__ == '__main__':# scel所在文件夾路徑in_path = r"F:\text" #修改為你的詞庫文件存放文件夾# 輸出詞典所在文件夾路徑out_path = r"F:\text" # 轉換之后文件存放文件夾fin = [fname for fname in os.listdir(in_path) if fname[-5:] == ".scel"]for f in fin:try:for word in scel2txt(os.path.join(in_path, f)):file_path=(os.path.join(out_path, str(f).split('.')[0] + '.txt'))# 保存結果with open(file_path,'a+',encoding='utf-8')as file:file.write(word[2] + '\n')os.remove(os.path.join(in_path, f))except Exception as e:print(e)pass
?
5. 生成詞頻統計
wcdict = {} for word in tokens:if len(word)==1:continueelse:wcdict[word] = wcdict.get(word,0)+1
6. 排序
wcls = list(wcdict.items()) wcls.sort(key=lambda x:x[1],reverse=True)
for i in range(20):print(wcls[i])
?
7. 排除語法型詞匯,代詞、冠詞、連詞等停用詞。
stops
tt = open(r'F:/stops_chinese.txt','r',encoding='utf-8').read() stops = tt.split()
? ? ? ·排除
wordsls = jieba.lcut(xyj) tokens = [token for token in wordsls if token not in stops]
8. 輸出詞頻最大TOP20,把結果存放到文件里
import jieba xyj = open(r'F:/xyj.txt','r',encoding='utf-8').read() tt = open(r'F:/stops_chinese.txt','r',encoding='utf-8').read() stops = tt.split() #jieba.load_userdict(r'F:\text/xyj.txt') wordsls = jieba.lcut(xyj) tokens = [token for token in wordsls if token not in stops] print(len(wordsls),len(tokens)) wcdict = {} for word in tokens:if len(word)==1:continueelse:wcdict[word] = wcdict.get(word,0)+1 wcls = list(wcdict.items()) wcls.sort(key=lambda x:x[1],reverse=True) for i in range(20):print(wcls[i])

9. 生成詞云。
(1)詞云安裝

顯示詞云:
cut_text = " ".join(tokens) from wordcloud import WordCloud ciyun = WordCloud().generate(cut_text) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.imshow(ciyun) plt.axis("off") plt.show()
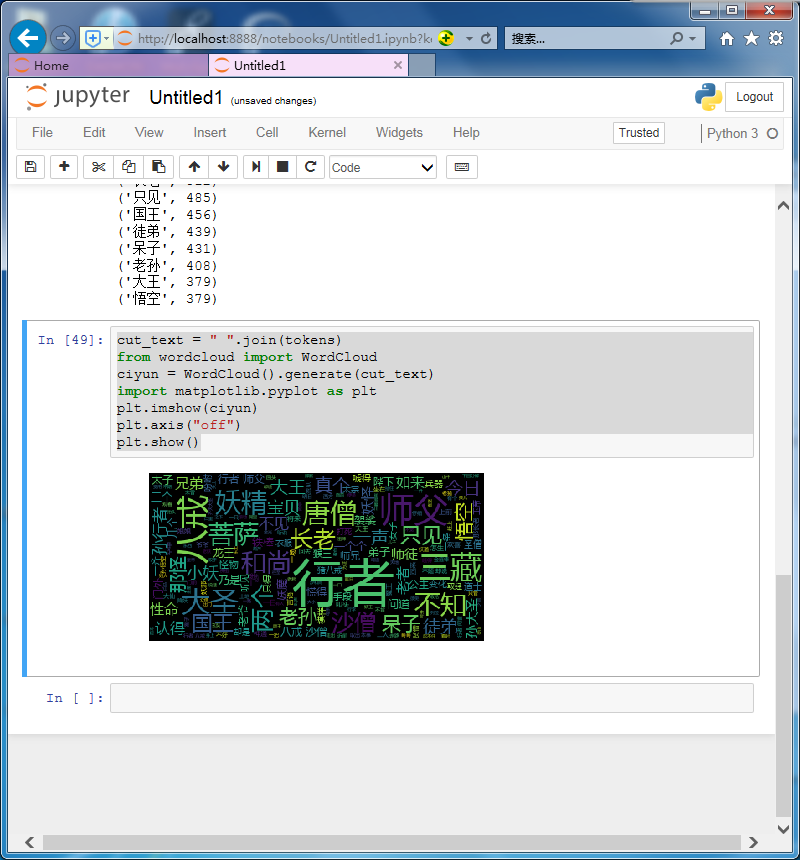
保存詞云圖片
ciyun.to_file(r'F:\xyj.jpg')
?
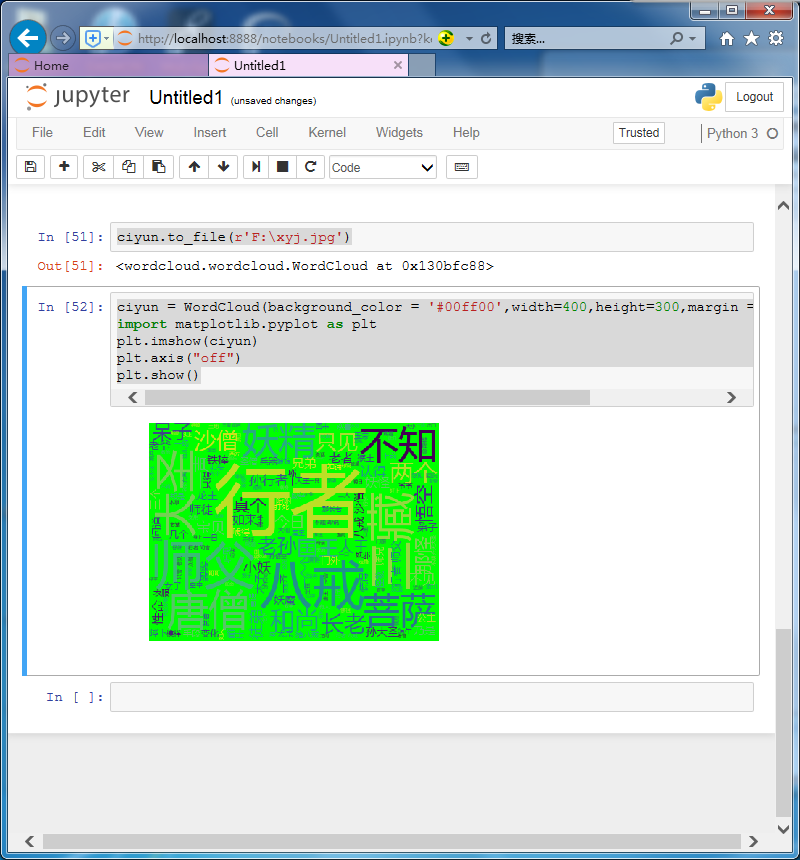
改變詞云長度和寬度,背景顏色
ciyun = WordCloud(background_color = '#00ff00',width=400,height=300,margin = 1).generate(cut_text) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.imshow(ciyun) plt.axis("off") plt.show()
改變詞云形狀
from scipy.misc import imread im = imread(r'F:/1.jpg') ciyun1 = WordCloud(background_color = '#0000FF',mask = im,margin = 2).generate(cut_text) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.imshow(ciyun1) plt.axis("off") plt.show()

?
?
?

![[JZOJ5866]【NOIP2018模擬9.13】指引](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[JZOJ5866]【NOIP2018模擬9.13】指引)


)

relative)
![洛谷P3066 [USACO12DEC]逃跑的BarnRunning Away From…](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/洛谷P3066 [USACO12DEC]逃跑的BarnRunning Away From…)






z-index)

 — Pci.Read())


