網絡結構在線可視化工具
http://ethereon.github.io/netscope/#/editor
參考主頁:
caffe 可視化的資料可在百度云盤下載
鏈接: http://pan.baidu.com/s/1jIRJ6mU
提取密碼:xehi
http://cs.stanford.edu/people/karpathy/cnnembed/
http://lijiancheng0614.github.io/2015/08/21/2015_08_21_CAFFE_Features/
http://nbviewer.ipython.org/github/BVLC/caffe/blob/master/examples/00-classification.ipynb
http://www.cnblogs.com/platero/p/3967208.html
http://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/gathered/examples/feature_extraction.html
http://caffecn.cn/?/question/21
caffe程序是由c++語言寫的,本身是不帶數據可視化功能的。只能借助其它的庫或接口,如opencv, python或matlab。使用python接口來進行可視化,因為python出了個比較強大的東西:ipython notebook, 最新版本改名叫jupyter notebook,它能將python代碼搬到瀏覽器上去執行,以富文本方式顯示,使得整個工作可以以筆記的形式展現、存儲,對于交互編程、學習非常方便。
使用CAFFE( http://caffe.berkeleyvision.org )運行CNN網絡,并提取出特征,將其存儲成lmdb以供后續使用,亦可以對其可視化
使用已訓練好的模型進行圖像分類在 http://nbviewer.ipython.org/github/BVLC/caffe/blob/master/example/00-classification.ipynb 中已經很詳細地介紹了怎么使用已訓練好的模型對測試圖像進行分類了。由于CAFFE不斷更新,這個頁面的內容和代碼也會更新。以下只記錄當前能運行的主要步驟。下載CAFFE,并安裝相應的dependencies,說白了就是配置好caffe。
1. 下載CAFFE,并安裝相應的dependencies,說白了就是配置好caffe運行環境。2. 配置好 python ipython notebook,具體可參考網頁:
http://blog.csdn.net/jiandanjinxin/article/details/50409448
3. 在caffe_root下運行./scripts/download_model_binary.py models/bvlc_reference_caffenet獲得預訓練的CaffeNet。獲取CaffeNet網絡并儲存到models/bvlc_reference_caffenet目錄下。
cd caffe-root
python ./scripts/download_model_binary.py models/bvlc_reference_caffenet 4. 在python文件夾下進入ipython模式(或python,但需要把部分代碼注釋掉)運行以下代碼
cd ./python #(×) 后面會提到
ipython notebook 在命令行輸入 ipython notebook,會出現一下畫面
接著 點擊 New Notebook,就可以輸入代碼,按 shift+enter 執行
python環境不能單獨配置,必須要先編譯好caffe,才能編譯python環境。
安裝jupyter
sudo pip install jupyter安裝成功后,運行notebook
jupyter notebook 輸入下面代碼:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline# Make sure that caffe is on the python path:
caffe_root = '../'
# this file is expected to be in {caffe_root}/examples
#這里注意路徑一定要設置正確,記得前后可能都有“/”,路徑的使用是
#{caffe_root}/examples,記得 caffe-root 中的 python 文件夾需要包括 caffe 文件夾。#caffe_root = '/home/bids/caffer-root/' #為何設置為具體路徑反而不能運行呢import sys
sys.path.insert(0, caffe_root + 'python')
import caffe #把 ipython 的路徑改到指定的地方(這里是說剛開始在終端輸入ipython notebook命令時,一定要確保是在包含caffe的python文件夾,這就是上面代碼(×)),以便可以調入 caffe 模塊,如果不改路徑,import 這個指令只會在當前目錄查找,是找不到 caffe 的。plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (10, 10)
plt.rcParams['image.interpolation'] = 'nearest'
plt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray'
#顯示的圖表大小為 10,圖形的插值是以最近為原則,圖像顏色是灰色import os
if not os.path.isfile(caffe_root + 'models/bvlc_reference_caffenet/bvlc_reference_caffenet.caffemodel'):print("Downloading pre-trained CaffeNet model...")!../scripts/download_model_binary.py ../models/bvlc_reference_caffenet#設置網絡為測試階段,并加載網絡模型prototxt和數據平均值mean_npycaffe.set_mode_cpu()# 采用CPU運算
net = caffe.Net(caffe_root + 'models/bvlc_reference_caffenet/deploy.prototxt',caffe_root + 'models/bvlc_reference_caffenet/bvlc_reference_caffenet.caffemodel',caffe.TEST)# input preprocessing: 'data' is the name of the input blob == net.inputs[0]
transformer = caffe.io.Transformer({'data': net.blobs['data'].data.shape})
transformer.set_transpose('data', (2,0,1))
transformer.set_mean('data', np.load(caffe_root + 'python/caffe/imagenet/ilsvrc_2012_mean.npy').mean(1).mean(1))
# mean pixel,ImageNet的均值
transformer.set_raw_scale('data', 255)
# the reference model operates on images in [0,255] range instead of [0,1]。參考模型運行在【0,255】的灰度,而不是【0,1】transformer.set_channel_swap('data', (2,1,0)) # the reference model has channels in BGR order instead of RGB,因為參考模型本來頻道是 BGR,所以要將RGB轉換# set net to batch size of 50
net.blobs['data'].reshape(50,3,227,227)#加載測試圖片,并預測分類結果。net.blobs['data'].data[...] = transformer.preprocess('data', caffe.io.load_image(caffe_root + 'examples/images/cat.jpg'))
out = net.forward()
print("Predicted class is #{}.".format(out['prob'][0].argmax()))plt.imshow(transformer.deprocess('data', net.blobs['data'].data[0]))# load labels,加載標簽,并輸出top_k
imagenet_labels_filename = caffe_root + 'data/ilsvrc12/synset_words.txt'
try:labels = np.loadtxt(imagenet_labels_filename, str, delimiter='\t')
except:!../data/ilsvrc12/get_ilsvrc_aux.shlabels = np.loadtxt(imagenet_labels_filename, str, delimiter='\t')
# sort top k predictions from softmax outputtop_k = net.blobs['prob'].data[0].flatten().argsort()[-1:-6:-1]
print labels[top_k]# CPU 與 GPU 比較運算時間
# CPU modenet.forward() # call once for allocation
%timeit net.forward()# GPU mode
caffe.set_device(0)
caffe.set_mode_gpu()
net.forward() # call once for allocation
%timeit net.forward()#****提取特征并可視化****#網絡的特征存儲在net.blobs,參數和bias存儲在net.params,以下代碼輸出每一層的名稱和大小。這里亦可手動把它們存儲下來。[(k, v.data.shape) for k, v in net.blobs.items()]#顯示出各層的參數和形狀,第一個是批次,第二個 feature map 數目,第三和第四是每個神經元中圖片的長和寬,可以看出,輸入是 227*227 的圖片,三個頻道,卷積是 32 個卷積核卷三個頻道,因此有 96 個 feature map[(k, v[0].data.shape) for k, v in net.params.items()]
#輸出:一些網絡的參數#**可視化的輔助函數**
# take an array of shape (n, height, width) or (n, height, width, channels)用一個格式是(數量,高,寬)或(數量,高,寬,頻道)的陣列
# and visualize each (height, width) thing in a grid of size approx. sqrt(n) by sqrt(n)每個可視化的都是在一個由一個個網格組成def vis_square(data, padsize=1, padval=0):data -= data.min()data /= data.max()# force the number of filters to be squaren = int(np.ceil(np.sqrt(data.shape[0])))padding = ((0, n ** 2 - data.shape[0]), (0, padsize), (0, padsize)) + ((0, 0),) * (data.ndim - 3)data = np.pad(data, padding, mode='constant', constant_values=(padval, padval))# tile the filters into an imagedata = data.reshape((n, n) + data.shape[1:]).transpose((0, 2, 1, 3) + tuple(range(4, data.ndim + 1)))data = data.reshape((n * data.shape[1], n * data.shape[3]) + data.shape[4:])plt.imshow(data)#根據每一層的名稱,選擇需要可視化的層,可以可視化filter(參數)和output(特征)
# the parameters are a list of [weights, biases],各層的特征,第一個卷積層,共96個過濾器
filters = net.params['conv1'][0].data
vis_square(filters.transpose(0, 2, 3, 1))
#使用 ipt.show()觀看圖像#過濾后的輸出,96 張 featuremap
feat = net.blobs['conv1'].data[4, :96]
vis_square(feat, padval=1)
#使用 ipt.show()觀看圖像:feat = net.blobs['conv1'].data[0, :36]
vis_square(feat, padval=1)#第二個卷積層:有 128 個濾波器,每個尺寸為 5X5X48。我們只顯示前面 48 個濾波器,每一個濾波器為一行。輸入:
filters = net.params['conv2'][0].data
vis_square(filters[:48].reshape(48**2, 5, 5))
#使用 ipt.show()觀看圖像:#第二層輸出 256 張 feature,這里顯示 36 張。輸入:
feat = net.blobs['conv2'].data[4, :36]
vis_square(feat, padval=1)
#使用 ipt.show()觀看圖像feat = net.blobs['conv2'].data[0, :36]
vis_square(feat, padval=1)#第三個卷積層:全部 384 個 feature map,輸入:
feat = net.blobs['conv3'].data[4]
vis_square(feat, padval=0.5)
#使用 ipt.show()觀看圖像:#第四個卷積層:全部 384 個 feature map,輸入:
feat = net.blobs['conv4'].data[4]
vis_square(feat, padval=0.5)
#使用 ipt.show()觀看圖像:#第五個卷積層:全部 256 個 feature map,輸入:
feat = net.blobs['conv5'].data[4]
vis_square(feat, padval=0.5)
#使用 ipt.show()觀看圖像:#第五個 pooling 層:我們也可以觀察 pooling 層,輸入:
feat = net.blobs['pool5'].data[4]
vis_square(feat, padval=1)
#使用 ipt.show()觀看圖像:#用caffe 的python接口提取和保存特征比較方便。
features = net.blobs['conv5'].data # 提取卷積層 5 的特征
np.savetxt('conv5_feature.txt', features) # 將特征存儲到本文文件中#然后我們看看第六層(第一個全連接層)輸出后的直方分布:
feat = net.blobs['fc6'].data[4]
plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
plt.plot(feat.flat)
plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
_ = plt.hist(feat.flat[feat.flat > 0], bins=100)
#使用 ipt.show()觀看圖像:#第七層(第二個全連接層)輸出后的直方分布:可以看出值的分布沒有這么平均了。
feat = net.blobs['fc7'].data[4]
plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
plt.plot(feat.flat)
plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
_ = plt.hist(feat.flat[feat.flat > 0], bins=100)
#使用 ipt.show()觀看圖像:#The final probability output, prob
feat = net.blobs['prob'].data[0]
plt.plot(feat.flat)#最后看看標簽:Let's see the top 5 predicted labels.
# load labels
imagenet_labels_filename = caffe_root + 'data/ilsvrc12/synset_words.txt'
try:labels = np.loadtxt(imagenet_labels_filename, str, delimiter='\t')
except:!../data/ilsvrc12/get_ilsvrc_aux.shlabels = np.loadtxt(imagenet_labels_filename, str, delimiter='\t')# sort top k predictions from softmax output
top_k = net.blobs['prob'].data[0].flatten().argsort()[-1:-6:-1]
print labels[top_k]
備注:用 caffe 的 python 接口提取和保存特征到text文本下
features = net.blobs['conv5'].data # 提取卷積層 5 的特征
np.savetxt('conv5_feature.txt', features) # 將特征存儲到本文文件中現在Caffe的Matlab接口 (matcaffe3) 和python接口都非常強大, 可以直接提取任意層的feature map以及parameters, 所以本文僅僅作為參考, 更多最新的信息請參考:
http://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/tutorial/interfaces.html
提取特征并儲存
CAFFE提供了一個提取特征的tool,見 http://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/gathered/examples/feature_extraction.html 。
數據模型與準備
安裝好Caffe后,在examples/images文件夾下有兩張示例圖像,本文即在這兩張圖像上,用Caffe提供的預訓練模型,進行特征提取,并進行可視化。
1. 選擇需要特征提取的圖像
./examples/_temp
(1) 進入caffe根目錄(本文中caffe的根目錄都為caffe-root),創建臨時文件夾,用于存放所需要的臨時文件
mkdir examples/_temp(2) 根據examples/images文件夾中的圖片,創建包含圖像列表的txt文件,并添加標簽(0)
find `pwd`/examples/images -type f -exec echo {} \; > examples/_temp/temp.txt
sed "s/$/ 0/" examples/_temp/temp.txt > examples/_temp/file_list.txt(3) 執行下列腳本,下載imagenet12圖像均值文件,在后面的網絡結構定義prototxt文件中,需要用到該文件 (data/ilsvrc212/imagenet_mean.binaryproto).下載模型以及定義prototxt。
sh ./data/ilsvrc12/get_ilsvrc_aux.sh(4) 將網絡定義prototxt文件復制到_temp文件夾下
cp examples/feature_extraction/imagenet_val.prototxt examples/_temp使用特征文件進行可視化
參考 http://www.cnblogs.com/platero/p/3967208.html 和 lmdb的文檔 https://lmdb.readthedocs.org/en/release ,讀取lmdb文件,然后轉換成mat文件,再用matlab調用mat進行可視化。
使用caffe的 extract_features.bin 工具提取出的圖像特征存為lmdb格式, 為了方便觀察特征,我們將利用下列兩個python腳本將圖像轉化為matlab的.mat格式 (請先安裝caffe的python依賴庫)。extract_features.bin的運行參數為
extract_features.bin $MODEL $PROTOTXT $LAYER $LMDB_OUTPUT_PATH $BATCHSIZE上面不是執行代碼,只是運行參數,不需要執行上式。
下面給出第一個例子是提取特征并儲存。
(1) 安裝CAFFE的python依賴庫,并使用以下兩個輔助文件把lmdb轉換為mat。在caffe 根目錄下創建feat_helper_pb2.py 和lmdb2mat.py,直接copy 下面的python程序即可。
cd caffe-root
sudo gedit feat_helper_pb2.py
sudo gedit lmdb2mat.py需要添加的內容如下
feat_helper_pb2.py:
# Generated by the protocol buffer compiler. DO NOT EDIT!from google.protobuf import descriptor
from google.protobuf import message
from google.protobuf import reflection
from google.protobuf import descriptor_pb2
# @@protoc_insertion_point(imports)DESCRIPTOR = descriptor.FileDescriptor(name='datum.proto',package='feat_extract',serialized_pb='\n\x0b\x64\x61tum.proto\x12\x0c\x66\x65\x61t_extract\"i\n\x05\x44\x61tum\x12\x10\n\x08\x63hannels\x18\x01 \x01(\x05\x12\x0e\n\x06height\x18\x02 \x01(\x05\x12\r\n\x05width\x18\x03 \x01(\x05\x12\x0c\n\x04\x64\x61ta\x18\x04 \x01(\x0c\x12\r\n\x05label\x18\x05 \x01(\x05\x12\x12\n\nfloat_data\x18\x06 \x03(\x02')_DATUM = descriptor.Descriptor(name='Datum',full_name='feat_extract.Datum',filename=None,file=DESCRIPTOR,containing_type=None,fields=[descriptor.FieldDescriptor(name='channels', full_name='feat_extract.Datum.channels', index=0,number=1, type=5, cpp_type=1, label=1,has_default_value=False, default_value=0,message_type=None, enum_type=None, containing_type=None,is_extension=False, extension_scope=None,options=None),descriptor.FieldDescriptor(name='height', full_name='feat_extract.Datum.height', index=1,number=2, type=5, cpp_type=1, label=1,has_default_value=False, default_value=0,message_type=None, enum_type=None, containing_type=None,is_extension=False, extension_scope=None,options=None),descriptor.FieldDescriptor(name='width', full_name='feat_extract.Datum.width', index=2,number=3, type=5, cpp_type=1, label=1,has_default_value=False, default_value=0,message_type=None, enum_type=None, containing_type=None,is_extension=False, extension_scope=None,options=None),descriptor.FieldDescriptor(name='data', full_name='feat_extract.Datum.data', index=3,number=4, type=12, cpp_type=9, label=1,has_default_value=False, default_value="",message_type=None, enum_type=None, containing_type=None,is_extension=False, extension_scope=None,options=None),descriptor.FieldDescriptor(name='label', full_name='feat_extract.Datum.label', index=4,number=5, type=5, cpp_type=1, label=1,has_default_value=False, default_value=0,message_type=None, enum_type=None, containing_type=None,is_extension=False, extension_scope=None,options=None),descriptor.FieldDescriptor(name='float_data', full_name='feat_extract.Datum.float_data', index=5,number=6, type=2, cpp_type=6, label=3,has_default_value=False, default_value=[],message_type=None, enum_type=None, containing_type=None,is_extension=False, extension_scope=None,options=None),],extensions=[],nested_types=[],enum_types=[],options=None,is_extendable=False,extension_ranges=[],serialized_start=29,serialized_end=134,
)DESCRIPTOR.message_types_by_name['Datum'] = _DATUMclass Datum(message.Message):__metaclass__ = reflection.GeneratedProtocolMessageTypeDESCRIPTOR = _DATUM# @@protoc_insertion_point(class_scope:feat_extract.Datum)# @@protoc_insertion_point(module_scope)./lmdb2mat.py
import lmdb
import feat_helper_pb2
import numpy as np
import scipy.io as sio
import timedef main(argv):lmdb_name = sys.argv[1]print "%s" % sys.argv[1]batch_num = int(sys.argv[2]);batch_size = int(sys.argv[3]);window_num = batch_num*batch_size;start = time.time()if 'db' not in locals().keys():db = lmdb.open(lmdb_name)txn= db.begin()cursor = txn.cursor()cursor.iternext()datum = feat_helper_pb2.Datum()keys = []values = []for key, value in enumerate( cursor.iternext_nodup()):keys.append(key)values.append(cursor.value())ft = np.zeros((window_num, int(sys.argv[4])))for im_idx in range(window_num):datum.ParseFromString(values[im_idx])ft[im_idx, :] = datum.float_dataprint 'time 1: %f' %(time.time() - start)sio.savemat(sys.argv[5], {'feats':ft})print 'time 2: %f' %(time.time() - start)print 'done!'if __name__ == '__main__':import sysmain(sys.argv)備注:用 caffe 的 python 接口提取和保存特征到text文本下
features = net.blobs['conv5'].data # 提取卷積層 5 的特征
np.savetxt('conv5_feature.txt', features) # 將特征存儲到本文文件中(2) 在caffe 根目錄下創建腳本文件extract_feature_example1.sh, 并執行,將在examples/_temp文件夾下得到lmdb文件(features_conv1)和.mat文件(features_conv1.mat)
下載已經生成的模型
sudo gedit ./examples/imagenet/get_caffe_reference_imagenet_model.sh
添加編輯內容如下:
#!/usr/bin/env sh
# This scripts downloads the caffe reference imagenet model
# for ilsvrc image classification and deep feature extractionMODEL=caffe_reference_imagenet_model
CHECKSUM=bf44bac4a59aa7792b296962fe483f2bif [ -f $MODEL ]; thenecho "Model already exists. Checking md5..."os=`uname -s`if [ "$os" = "Linux" ]; thenchecksum=`md5sum $MODEL | awk '{ print $1 }'`elif [ "$os" = "Darwin" ]; thenchecksum=`cat $MODEL | md5`fiif [ "$checksum" = "$CHECKSUM" ]; thenecho "Model checksum is correct. No need to download."exit 0elseecho "Model checksum is incorrect. Need to download again."fi
fiecho "Downloading..."wget --no-check-certificate https://www.dropbox.com/s/n3jups0gr7uj0dv/$MODELecho "Done. Please run this command again to verify that checksum = $CHECKSUM."cd caffe-root
sudo gedit extract_feature_example1.sh需要添加的內容如下:
#!/usr/bin/env sh
# args for EXTRACT_FEATURE
TOOL=./build/tools
MODEL=./examples/imagenet/caffe_reference_imagenet_model #下載得到的caffe model
PROTOTXT=./examples/_temp/imagenet_val.prototxt # 網絡定義
LAYER=conv1 # 提取層的名字,如提取fc7等
LEVELDB=./examples/_temp/features_conv1 # 保存的leveldb路徑
BATCHSIZE=10# args for LEVELDB to MAT
DIM=290400 # 需要手工計算feature長度
OUT=./examples/_temp/features_conv1.mat #.mat文件保存路徑
BATCHNUM=1 # 有多少個batch, 本例只有兩張圖, 所以只有一個batch$TOOL/extract_features.bin $MODEL $PROTOTXT $LAYER $LEVELDB $BATCHSIZE lmdb
python lmdb2mat.py $LEVELDB $BATCHNUM $BATCHSIZE $DIM $OUT執行之后,
cd caffe-root
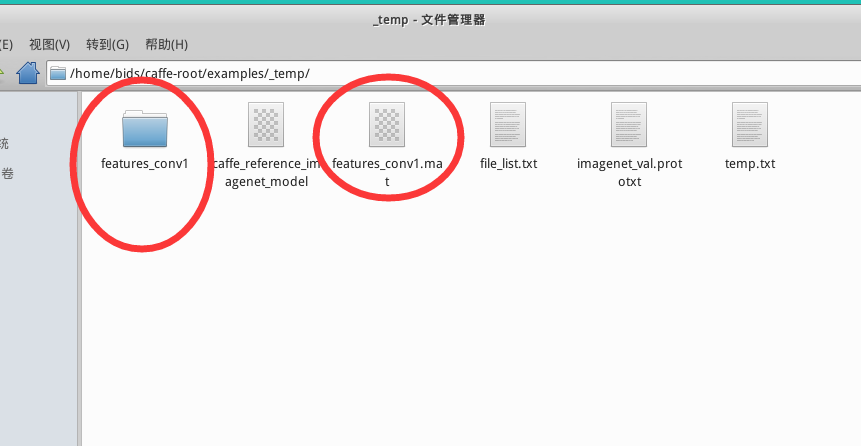
sh extract_feature_example1.sh你會在/examples/_temp/ 下發現多了兩個文件:文件夾 features_conv1,文件features_conv1.mat
如果執行出現lmdb2mat.py的相關問題,有可能是沒有安裝lmdb,可在caffe 根目錄下執行下面的程式安裝。具體問題具體分析。
Lmdb的安裝
pip install lmdb特別備注:在執行一次 sh extract_feature_example1.sh 之后,在文件夾 _temp里面就會出現文件夾features_conv1和文件features_conv1.mat。若再次執行一次,會出現報錯,可將文件夾 _temp中的文件夾features_conv1和文件features_conv1.mat 都刪除,即可通過編譯。
(3). 參考UFLDL里的display_network函數,對mat文件里的特征進行可視化。
在/examples/_temp/ 中創建 display_network.m
cd ./examples/_temp/
sudo gedit display_network.m需要添加的內容如下:
display_network.m
function [h, array] = display_network(A, opt_normalize, opt_graycolor, cols, opt_colmajor)
% This function visualizes filters in matrix A. Each column of A is a
% filter. We will reshape each column into a square image and visualizes
% on each cell of the visualization panel.
% All other parameters are optional, usually you do not need to worry
% about it.
% opt_normalize: whether we need to normalize the filter so that all of
% them can have similar contrast. Default value is true.
% opt_graycolor: whether we use gray as the heat map. Default is true.
% cols: how many columns are there in the display. Default value is the
% squareroot of the number of columns in A.
% opt_colmajor: you can switch convention to row major for A. In that
% case, each row of A is a filter. Default value is false.
warning off allif ~exist('opt_normalize', 'var') || isempty(opt_normalize)opt_normalize= true;
endif ~exist('opt_graycolor', 'var') || isempty(opt_graycolor)opt_graycolor= true;
endif ~exist('opt_colmajor', 'var') || isempty(opt_colmajor)opt_colmajor = false;
end% rescale
A = A - mean(A(:));if opt_graycolor, colormap(gray); end% compute rows, cols
[L M]=size(A);
sz=sqrt(L);
buf=1;
if ~exist('cols', 'var')if floor(sqrt(M))^2 ~= Mn=ceil(sqrt(M));while mod(M, n)~=0 && n<1.2*sqrt(M), n=n+1; endm=ceil(M/n);elsen=sqrt(M);m=n;end
elsen = cols;m = ceil(M/n);
endarray=-ones(buf+m*(sz+buf),buf+n*(sz+buf));if ~opt_graycolorarray = 0.1.* array;
endif ~opt_colmajork=1;for i=1:mfor j=1:nif k>M, continue; endclim=max(abs(A(:,k)));if opt_normalizearray(buf+(i-1)*(sz+buf)+(1:sz),buf+(j-1)*(sz+buf)+(1:sz))=reshape(A(:,k),sz,sz)'/clim;elsearray(buf+(i-1)*(sz+buf)+(1:sz),buf+(j-1)*(sz+buf)+(1:sz))=reshape(A(:,k),sz,sz)'/max(abs(A(:)));endk=k+1;endend
elsek=1;for j=1:nfor i=1:mif k>M, continue; endclim=max(abs(A(:,k)));if opt_normalizearray(buf+(i-1)*(sz+buf)+(1:sz),buf+(j-1)*(sz+buf)+(1:sz))=reshape(A(:,k),sz,sz)'/clim;elsearray(buf+(i-1)*(sz+buf)+(1:sz),buf+(j-1)*(sz+buf)+(1:sz))=reshape(A(:,k),sz,sz)';endk=k+1;endend
endif opt_graycolorh=imagesc(array);
elseh=imagesc(array,'EraseMode','none',[-1 1]);
end
axis image offdrawnow;warning on all(4)在matlab里運行以下代碼:
首先要進入 /examples/_temp/ 在執行下面的matlab程序。
在caffe 根目錄下輸入
cd ./examples/_temp/
matlab在matlab 中輸入下面的命令
nsample = 3;num_output = 96; % conv1
% num_output = 256; % conv5
%num_output = 4096; % fc7load features_conv1.mat
width = size(feats, 2);
nmap = width / num_output;for i = 1 : nsamplefeat = feats(i, :);feat = reshape(feat, [nmap num_output]);figure('name', sprintf('image #%d', i));display_network(feat);
end執行之后將會出現一下結果:
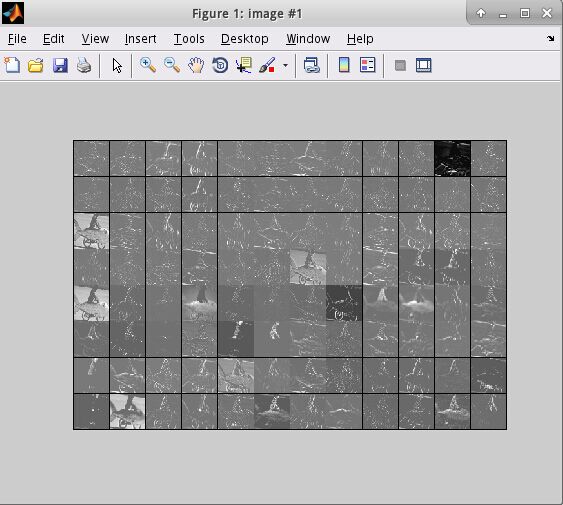
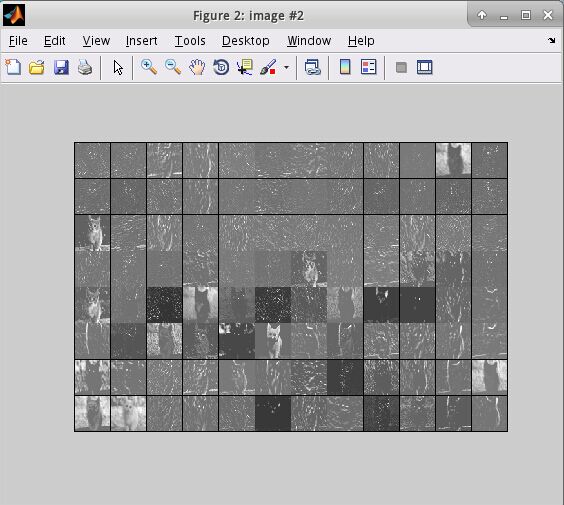

在python中讀取mat文件
在python中,使用scipy.io.loadmat()即可讀取mat文件,返回一個dict()。
import scipy.io
matfile = 'features_conv1.mat'
data = scipy.io.loadmat(matfile)下面給出第二個例子:
(1) 在caffe 根目錄下創建腳本文件extract_feature_example2.sh, 并執行,將在examples/_temp文件夾下得到lmdb文件(features_fc7)和.mat文件(features_fc7.mat)
cd caffe-root
sudo gedit extract_feature_example2.sh需要添加的內容如下:
#!/usr/bin/env sh
# args for EXTRACT_FEATURE
TOOL=./build/tools
MODEL=./models/bvlc_reference_caffenet/bvlc_reference_caffenet.caffemodel #下載得到的caffe model
PROTOTXT=./examples/_temp/imagenet_val.prototxt # 網絡定義
LAYER=fc7 # 提取層的名字,如提取fc7等
LEVELDB=./examples/_temp/features_fc7 # 保存的leveldb路徑
BATCHSIZE=10# DIM=290400 # feature長度,conv1
# DIM=43264 # conv5
# args for LEVELDB to MAT
DIM=4096 # 需要手工計算feature長度
OUT=./examples/_temp/features_fc7.mat #.mat文件保存路徑
BATCHNUM=1 # 有多少個batch, 本例只有兩張圖, 所以只有一個batch$TOOL/extract_features.bin $MODEL $PROTOTXT $LAYER $LEVELDB $BATCHSIZE lmdb
python lmdb2mat.py $LEVELDB $BATCHNUM $BATCHSIZE $DIM $OUT執行之后,
cd caffe-root
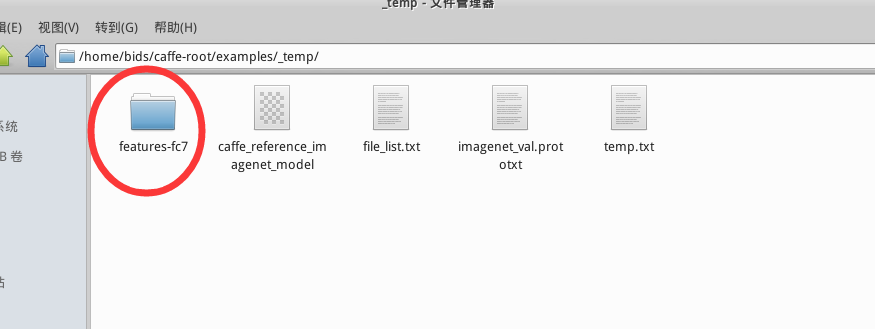
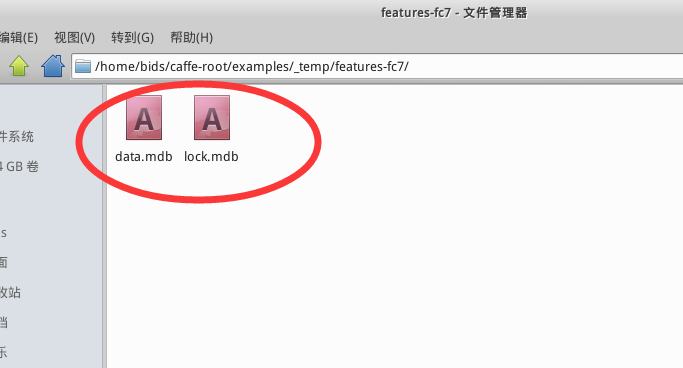
sh extract_feature_example2.sh執行之后,你會在 examples/_temp/ 下多出一個文件夾 features-fc7,里面含有data.mdb, lock.mdb 兩個文件,還會得到features-fc7.mat,如下圖所示
(2). 參考UFLDL里的display_network函數,對mat文件里的特征進行可視化。
在/examples/_temp/ 中創建 display_network.m
cd ./examples/_temp/
sudo gedit display_network.m(3)在matlab里運行以下代碼:
首先要進入 /examples/_temp/ 在執行下面的matlab程序。
在caffe 根目錄下輸入
cd ./examples/_temp/
matlab在matlab 中輸入下面的命令
nsample = 2;
% num_output = 96; % conv1
% num_output = 256; % conv5
num_output = 4096; % fc7load features_fc7.mat
width = size(feats, 2);
nmap = width / num_output;for i = 1 : nsamplefeat = feats(i, :);feat = reshape(feat, [nmap num_output]);figure('name', sprintf('image #%d', i));display_network(feat);
end執行之后將會出現一下結果:
在python中讀取mat文件
在python中,使用scipy.io.loadmat()即可讀取mat文件,返回一個dict()。
import scipy.io
matfile = ‘features_fc7.mat’
data = scipy.io.loadmat(matfile)
使用自己的網絡
只需把前面列出來的文件與參數修改成自定義的即可。
使用Model Zoo里的網絡
根據 https://github.com/BVLC/caffe/wiki/Model-Zoo 的介紹,選擇自己所需的網絡,并下載到相應位置即可。
如VGG-16:
./scripts/download_model_from_gist.sh 211839e770f7b538e2d8
mv ./models/211839e770f7b538e2d8 ./models/VGG_ILSVRC_16_layers
./scripts/download_model_binary.py ./models/VGG_ILSVRC_16_layers

)

)
![[webrtc] rtcp模塊中rtt時間計算](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[webrtc] rtcp模塊中rtt時間計算)




)



(待續))





)