上一節我們實現了單機版的緩存服務,但是我們的目標是分布式緩存。那么,我們就需要把緩存服務部署到多態機器節點上,對外提供訪問接口。客戶端就可以通過這些接口去實現緩存的增刪改查。
分布式緩存需要實現節點間通信,而通信方法常見的有HTTP和RPC。建立基于 HTTP 的通信機制是比較常見和簡單的做法。
所以,我們基于 Go 語言標準庫 http 搭建 HTTP Server。
net/http標準庫
簡單實現一個http服務端例子。
type server intfunc (s *server) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {w.Write([]byte("Hello World!"))
}func main() {var s serverhttp.ListenAndServe("localhost:9999", &s)
}//下面的是http源碼
type Handler interface {ServeHTTP(w ResponseWriter, r *Request)
}在該代碼中,創建任意類型 server,并實現?ServeHTTP?方法。
http.ListenAndServe?接收 2 個參數,第一個參數是服務啟動的地址,第二個參數是 Handler,實現了?ServeHTTP?方法的對象都可以作為 HTTP 的 Handler。
Cache HTTP 服務端
我們需要創建一個結構體去實現Handler接口,而該結構體應該是有些屬性變量來支撐我們做一些事情的。
HTTPPool?有 2 個參數,一個是 addr,用來記錄自己的地址,包括主機名/IP 和端口。- 另一個是 basePath,作為節點間通訊地址的前綴,默認是?
/geecache/。比如http://example.com/geecache/開頭的請求,就用于節點間的訪問。因為一個主機上還可能承載其他的服務,加一段 Path 是一個好習慣。比如,大部分網站的 API 接口,一般以?/api?作為前綴。
HTTPPool實現了ServeHTTP方法,即是Handler接口。?
const defaultBasePath = "/geecache/"type HTTPPool struct {addr string //本地IP端口, 比如:"localhost:10000"basePath string
}func (pool *HTTPPool) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {//處理請求和響應,后面會實現的
}//創建HTTPPool方法
func NewHTTPPool(addr string, basePath string) *HTTPPool {return &HTTPPool{addr: addr,basePath: basePath,}
}接下來實現最為核心的ServeHTTP方法。
func (pool *HTTPPool) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {if !strings.HasPrefix(r.URL.Path, pool.basePath) {panic("HTTPPool serving unexpected path: " + r.URL.Path)}parts := strings.SplitN(r.URL.Path[len(pool.basePath):], "/", 2)if len(parts) != 2 {http.Error(w, "bad request", http.StatusBadRequest)return}groupName := parts[0]group := GetGroup(groupName)if group == nil {http.Error(w, "no such group: "+groupName, http.StatusNotFound)return}view, err := group.Get(parts[1])if err != nil {http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError)return}w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/octet-stream")w.Write(view.ByteSlice())
}該方法是先判斷前綴是否相等,若不相等,返回錯誤,之后再判斷分組名字,再判斷key。
url.Path的格式是/<basepath>/<groupname>/<key>。舉個例子,r.URL.Path是/geecache/scores/tom,那r.URL.Path[len(pool.basePath):]即是scores/tom,接著就是使用strings.SplitN函數進行分割來獲取分組名字和key。
測試
// 緩存中沒有的話,就從該db中查找
var db = map[string]string{"tom": "100","jack": "200","sam": "444",
}func main() {//傳函數入參cache.NewGroup("scores", 2<<10, cache.GetterFunc(funcCbGet))//傳結構體入參,也可以// cbGet := &search{}// cache.NewGroup("scores", 2<<10, cbGet)addr := "localhost:10000"peers := cache.NewHTTPPool(addr, cache.DefaultBasePath)log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(addr, peers))
}// 函數的
func funcCbGet(key string) ([]byte, error) {fmt.Println("callback search key: ", key)if v, ok := db[key]; ok {return []byte(v), nil}return nil, fmt.Errorf("%s not exit", key)
}// 結構體,實現了Getter接口的Get方法,
type search struct {
}func (s *search) Get(key string) ([]byte, error) {fmt.Println("struct callback search key: ", key)if v, ok := db[key]; ok {return []byte(v), nil}return nil, fmt.Errorf("%s not exit", key)
}執行 go run main.go,查看效果
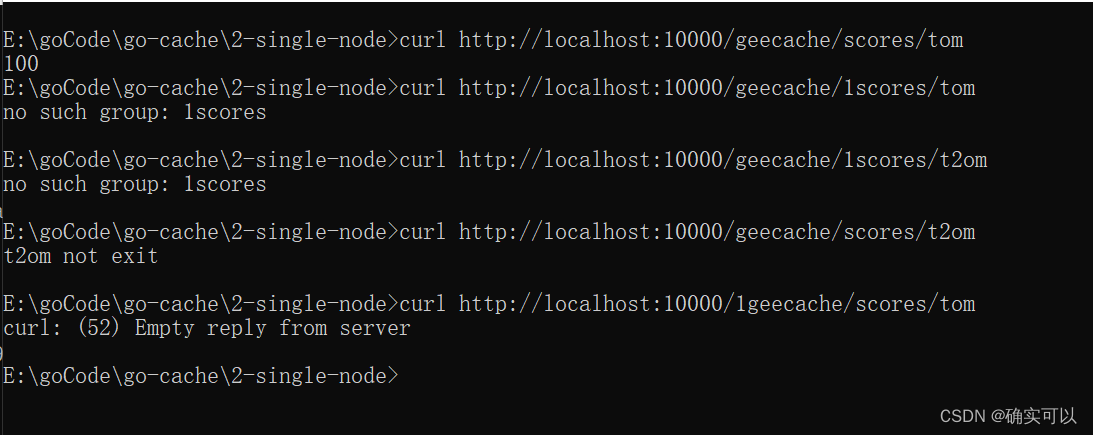
完整代碼:https://github.com/liwook/Go-projects/tree/main/go-cache/3-httpServer






)


)
)






及其貝葉斯定理數學解釋)

)