文章目錄
- 前言
- 字符串復制-strcpy
- 字符串復制(按照位數)-strncpy
- 字符串比較-strcmp
- 字符串比較(按照位數)-strncmp
- 不區分大小寫的字符串比較-strcasecmp
- 不區分大小寫的比較(前n位)-strncasecmp
- 字符串按照格式寫入-sprintf
- 字符串按照格式和個數寫入-snprintf
- 字符串拼接-strcat
- 字符串拼接(前n位)-strncat
- 字符串切割-strtok
- 字符串切割-strsep
- 查找字符串是否在另一個字符串中-strstr
- 查找字符串是否在另一個字符串中-不區分大小寫-strcasestr
- 查找某個字符是否在字符串中-strchr
- 字符串轉數字-atoi
- 在字符串提取前面的數字字符并轉換成數字(根據參數選擇轉換后的數字類型)-strtoul
- 判斷字符是否為空-isspace
- 檢查字符是否是十進制數字字符-isdigit
前言
當前文檔為C語言字符串的基本操作(用過的以及man時發現的),用于本人記錄使用,會持續更新
字符串復制-strcpy
#include <string.h>
char *strcpy(char *dest, const char *src);// 將后面的變量賦值給前面
// 函數返回一個指向目標字符串dest的指針。
// 需要注意前面變量的長度,要大于等于 后面的長度,要不然編譯報警告,還容易越界后報錯
字符串復制(按照位數)-strncpy
#include <string.h>
char *strncpy(char *dest, const char *src, size_t n);// 將后面的字符串賦值給前面的字符串 復制 n 個
// 函數返回一個指向目標字符串dest的指針。
字符串比較-strcmp
#include <string.h>
int strcmp(const char *s1, const char *s2);// 字符串比較,完整比較
// 比較方式為 按照字符串每個字符的ASCII碼按位比較,不相同時,前面的大 返回 大的數,后面的大,返回負的少的個數
字符串比較(按照位數)-strncmp
#include <string.h>
int strncmp(const char *s1, const char *s2, size_t n);// 前后字符串比較,比較前n位,比較方式同上
不區分大小寫的字符串比較-strcasecmp
#include <strings.h>
int strcasecmp(const char *s1, const char *s2);// 不區分大小寫的比較,比較方式同上
不區分大小寫的比較(前n位)-strncasecmp
#include <strings.h>
int strncasecmp(const char *s1, const char *s2, size_t n);// 不區分大小寫的比較,比較前n位,比較方式同上
字符串按照格式寫入-sprintf
#include <stdio.h>
int sprintf(char *str, const char *format, ...);// 按照 中間的格式,將后面的變量 寫入到 前面的字符串中
char buf[128] = {0};
if(sprintf(buf,"%s: %d\n","name",18) > 0){//成功 返回 寫入的字符數
}else{//失敗返回 負數
}
字符串按照格式和個數寫入-snprintf
#include <stdio.h>
int snprintf(char *str, size_t size, const char *format, ...);// 按照中間格式,將后面的變量們,寫入到第一個變量中,寫入 size個
// 注意: size為最大限制個數,實際寫入最大個數為 size - 1 個,最后一位會被 寫入 '\0'
char buf[128] = {0};
if(snprintf(buf,32,"%s: %d\n","name",18) > 0){ //按照 %s: %d 格式將 name 跟 18 寫入到 buf中,最多寫入 32個//成功 返回 寫入的字符數
}else{//失敗返回 負數
}
字符串拼接-strcat
#include <string.h>
char *strcat(char *dest, const char *src);// 將src字符串 拼接到 dest 字符串中,替換dest的'\0'。需要注意dest字符串足夠大。
字符串拼接(前n位)-strncat
#include <string.h>
char *strncat(char *dest, const char *src, size_t n);// 將src字符串中的前n位 拼接到 dest 字符串中,替換dest的'\0'。需要注意dest字符串足夠大。
字符串切割-strtok
#include <string.h>
char *strtok(char *str, const char *delim);// 字符串切割,將str 按照 delim 樣式切割。將切割完的字符串的指針返回
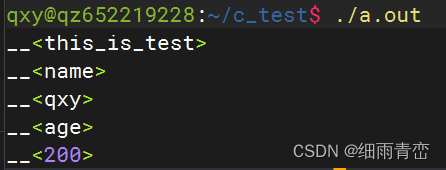
// 第二次切割時,str 寫為 NULLint main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{char buf[128] = "this_is_test:name:qxy:age:200";char *temp = NULL;temp = strtok(buf,":");while(temp != NULL){printf("__<%s>\n",temp);temp = strtok(NULL,":");}return 0;
}
字符串切割-strsep
#include <string.h>
char *strsep(char **stringp, const char *delim);// 字符串切割:將stringp 字符串 按照 字符 delim 進行切割
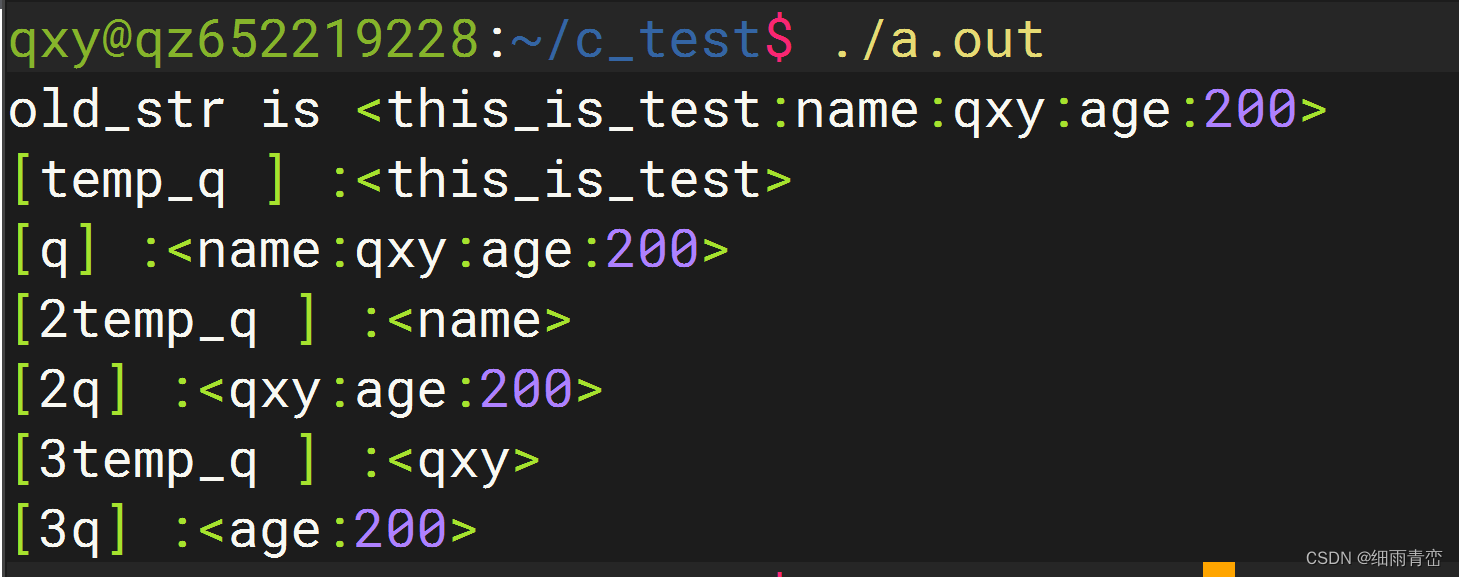
// 切割完 前面的部分 通過返回值返回,剩余部分 保存在 stringp 字符串中int main()
{char query[] ="this_is_test:name:qxy:age:200";char *q, *temp_q;q = query;printf("old_str is <%s>\n",query);temp_q = strsep(&q,":"); printf("[temp_q ] :<%s>\n", temp_q); //但是printf("[q] :<%s>\n", q);temp_q = strsep(&q,":"); printf("[2temp_q ] :<%s>\n", temp_q);printf("[2q] :<%s>\n", q);temp_q = strsep(&q,":");printf("[3temp_q ] :<%s>\n", temp_q);printf("[3q] :<%s>\n", q);return 0;
}
查找字符串是否在另一個字符串中-strstr
#include <string.h>
char *strstr(const char *haystack, const char *needle);// 字符串查找,查找后面的字符串 是否在 前面的字符串中
// 沒找到返回 NULL
// 找到,返回查找字符串的在haystack字符串的第一位指針
查找字符串是否在另一個字符串中-不區分大小寫-strcasestr
#include <string.h>
char *strcasestr(const char *haystack, const char *needle);// 查找后面字符串 是否在 前面字符串中,不區分大小的的查找
// 沒找到返回 NULL
// 找到,返回查找字符串的在haystack字符串的第一位指針
查找某個字符是否在字符串中-strchr
#include <string.h>
char *strchr(const char *s, int c);// 函數返回一個指針,指向前面字符串中 最后一次出現的字符c 的位置
// 沒找到返回 NULL
字符串轉數字-atoi
#include <stdlib.h>
int ret = atoi(const char* buf);// 出錯返回 0
在字符串提取前面的數字字符并轉換成數字(根據參數選擇轉換后的數字類型)-strtoul
#include <stdlib.h>
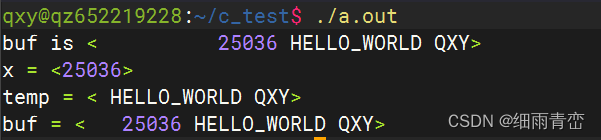
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{char buf[128] = " 25036 HELLO_WORLD QXY";//char buf[128] = " HELLO_WORLD QXY 2525252"; //這個不行.....printf("buf is <%s>\n",buf);char *temp = NULL;unsigned long int x = strtoul(buf,&temp,10);printf("x = <%lu>\n",x);printf("temp = <%s>\n",temp);printf("buf = <%s>\n",buf);return 0;
}
unsigned long strtoul(const char nptr, char **endptr, int base);
strtoul()函數根據給定的基數將nptr中字符串的初始部分轉換為無符號長值,該值必須為介于2和36之間(包括2和36)或者是特殊值0。
基本上就是 0 2 8 10 16 (如果是 0 字符串以0x開頭就是16進制讀取,以0開頭 就是8進制,否則一律按十進制處理)
給定基數中的數字。(在10以上的base中,大寫或小寫字母“A”表示10,“B”表示11,依此類推 “Z”表示35。)
字符串可以以任意數量的空格 tab 開頭,后跟一個可選的“+”或“-”號。
字符串的剩余部分以顯而易見的方式轉換為無符號長值,在第一個無效字符處停止
如果endptr不為NULL,strtoul()將第一個無效字符的地址存儲在endptr中。如果根本沒有數字,strtoul()將存儲endptr中nptr的原始值(并返回0)。特別是,如果返回時nptr不是“\0”,但**endptr是“\0”時,則整個字符串為有效的
strtoull()函數的工作原理與strtoul()函數類似,但返回一個無符號長-長值。
判斷字符是否為空-isspace
’ ’ (0x20) space (SPC) 空格符
‘\t’ (0x09) horizontal tab (TAB) 水平制表符
‘\n’ (0x0a) newline (LF) 換行符
‘\v’ (0x0b) vertical tab (VT) 垂直制表符
‘\f’ (0x0c) feed (FF) 換頁符
‘\r’ (0x0d) carriage return (CR) 回車符
#inlcude <ctype.h>
int ret = isspace(char c);//為空返回非0,不為空返回 0
檢查字符是否是十進制數字字符-isdigit
#inlcude <ctype.h>
int ret = isdigit(char c);//是一個數字,則該函數返回非零值,否則返回 0。
)
)
)




】線索化二叉樹(3))


![[動態規劃]最長公共子序列](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[動態規劃]最長公共子序列)




)
)


