路徑參數、查詢參數,和請求體混合
首先,我們需要導入所需的庫。我們將使用FastAPI、Path和Annotated來處理路由和參數,并使用BaseModel和Union來自定義數據模型。
完整示例代碼
from typing import Annotated, Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPI, Path
from pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Book(BaseModel):title: strauthor: Union[str, None] = Nonepages: int@app.put("/books/{book_id}")
async def update_book(book_id: Annotated[int, Path(title="The ID of the book to get", ge=0, le=1000)],q: Union[str, None] = None,book: Union[Book, None] = None,
):results = {"book_id": book_id}if q:results.update({"q": q})if book:results.update({"book": book})return results代碼分析
class Book(BaseModel):title: strauthor: Union[str, None] = Nonepages: int
定義一個自定義的數據模型類。在這個例子中,我們將創建一個名為Book的類,它包含以下字段:title(字符串)、author(字符串,可選)和pages(整數):
接下來,我們定義一個帶有查詢參數和路徑參數的路由。這個路由將用于更新一本書的信息:
@app.put("/books/{book_id}")
async def update_book(book_id: Annotated[int, Path(title="The ID of the book to get", ge=0, le=1000)],q: Union[str, None] = None,book: Union[Book, None] = None,
):results = {"book_id": book_id}if q:results.update({"q": q})if book:results.update({"book": book})return results
在這個例子中,我們定義了一個PUT請求的路由,其路徑為"/books/{book_id}"。我們使用了Path對象來指定路徑參數book_id的約束條件:大于等于0且小于等于1000。
我們還添加了一個名為q的查詢參數,它可以是字符串或None。
最后,我們添加了一個名為book的參數,它可以是一個Book對象或None。這個參數允許用戶在請求體中傳遞書籍的詳細信息。
打開自動化測試文檔,我們可以看到如下內容
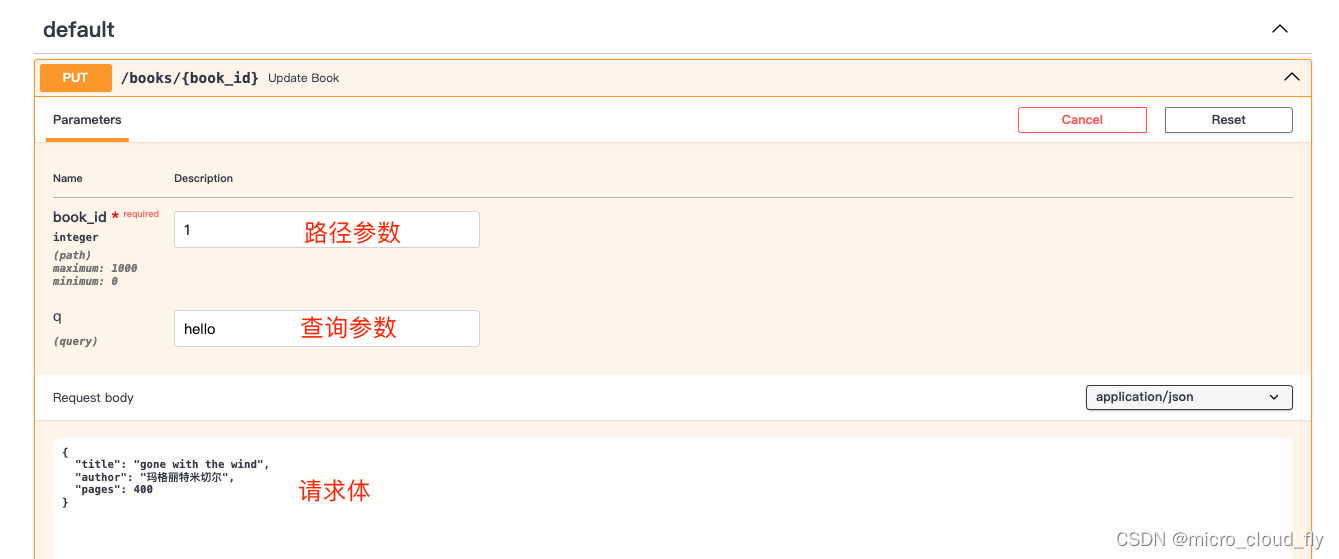
發起請求進行測試

總結
通過使用FastAPI、Path和Annotated,你可以輕松地定義具有復雜參數的路由。同時,使用Pydantic的BaseModel可以讓你更方便地定義數據模型并自動進行數據驗證。
多個請求體
完整示例代碼
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPI, Body
from pydantic import BaseModelclass Product(BaseModel):name: strdescription: Union[str, None] = Noneprice: floattax: Union[float, None] = Noneclass Customer(BaseModel):username: strfull_name: Union[str, None] = Noneapp = FastAPI()@app.put("/products/{product_id}")
async def update_product(product_id: int, product: Product = Body(...), customer: Customer = Body(...)):results = {"product_id": product_id, "product": product, "customer": customer}return results
這段代碼定義了一個FastAPI應用,該應用可以處理一個PUT請求,這個請求包含了商品信息和客戶信息。下面是對這段代碼的詳細解釋。
首先,我們導入了所需的庫:
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPI, Body
from pydantic import BaseModel
然后,我們定義了兩個模型類:Product和Customer:
class Product(BaseModel):name: strdescription: Union[str, None] = Noneprice: floattax: Union[float, None] = Noneclass Customer(BaseModel):username: strfull_name: Union[str, None] = None
這兩個類分別代表商品和客戶。它們都是BaseModel的子類,這意味著它們可以被用于解析JSON數據。
接下來,我們創建了一個FastAPI應用實例:
app = FastAPI()
最后,我們編寫了一個路由處理器函數:update_product:
@app.put("/products/{product_id}")
async def update_product(product_id: int, product: Product = Body(...), customer: Customer = Body(...)):results = {"product_id": product_id, "product": product, "customer": customer}return results
這個函數接收三個參數:商品ID、商品和客戶。其中,商品和客戶是通過Body裝飾器從請求體中獲取的。當客戶端發起PUT請求到"/products/{product_id}"時,FastAPI會自動將請求體中的JSON數據轉換為Product和Customer對象。
嵌套參數
from typing import Annotated, Unionfrom fastapi import Body, FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Book(BaseModel):name: strdescription: Union[str, None] = Noneprice: floattax: Union[float, None] = None@app.put("/books/{book_id}")
async def update_book(book_id: int, book: Annotated[Book, Body(embed=True)]):results = {"book_id": book_id, "book": book}return results
效果
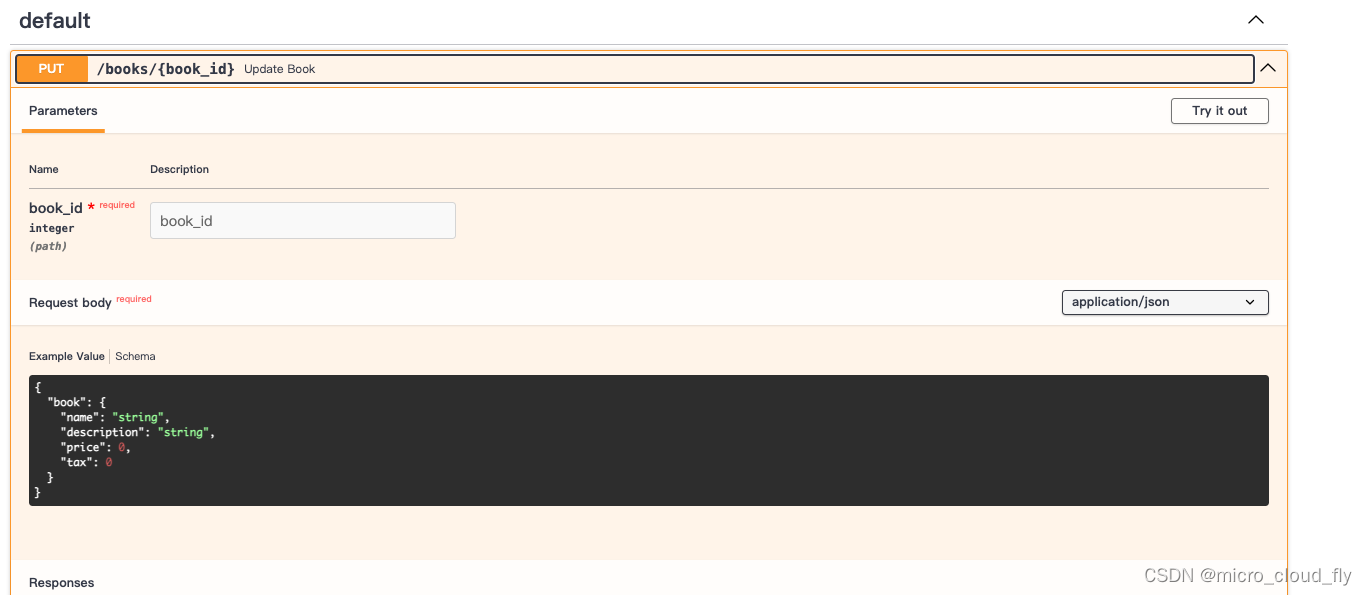






)
![laravel DB::connection 報錯 Database connection [{$name}] not configured](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/laravel DB::connection 報錯 Database connection [{$name}] not configured)






f2fs如何解決wandering tree)



高精度除法 (洛谷 P2005 A/B Problem II))
