文章目錄
- 1.線性表
- 2.順序表分類
- 2.1 靜態順序表
- 2.2 動態順序表
- 3. 順序表各接口實現
- 1. 定義結構體`(Seqlist)`
- 2. 結構體初始化`(SLInit)`
- 3.檢查容量 `(SLCheckCapacity)`
- 4.打印數據 `(SLPrintf)`
- 5.插入操作
- 5.1 從數據頭部插入`(SLPushFront)`
- 5.2 從數據尾部插入`(SLPushBack)`
- 5.3 從任意下標位置的插入`(SLInsert)`
- 6.刪除操作
- 6.1 從數據頭部刪除`(SLPopFront)`
- 6.2 從數據尾部刪除`(SLPopBack)`
- 6.3 從任意下標位置的刪除`(SLErase)`
- 7 銷毀操作 `(SLDestroy)`
- 4.完整代碼
- 4.1 SeqList.h文件
- 4.2 SeqList.c文件
- 4.3 Test.c文件
1.線性表
1.線性表(linear list)是n個具有相同特性的數據元素的有限序列。 線性表是?種在實際中廣泛使用的數據結構,常見的線性表:順序表、鏈表、棧、隊列、字符串
2.線性表在邏輯上是線性結構,也就說是連續的?條直線。但是在物理結構上并不一定是連續的,線性表在物理上存儲時,通常以數組和鏈式結構的形式存儲。
案例:蔬菜分為綠葉類、瓜類、菌菇類。線性表指的是具有部分相同特性的一類數據結構的集合
2.順序表分類
順序表和數組的區別:
順序表的底層結構是數組,對數組的封裝,實現了常用的增刪改查等接口
2.1 靜態順序表
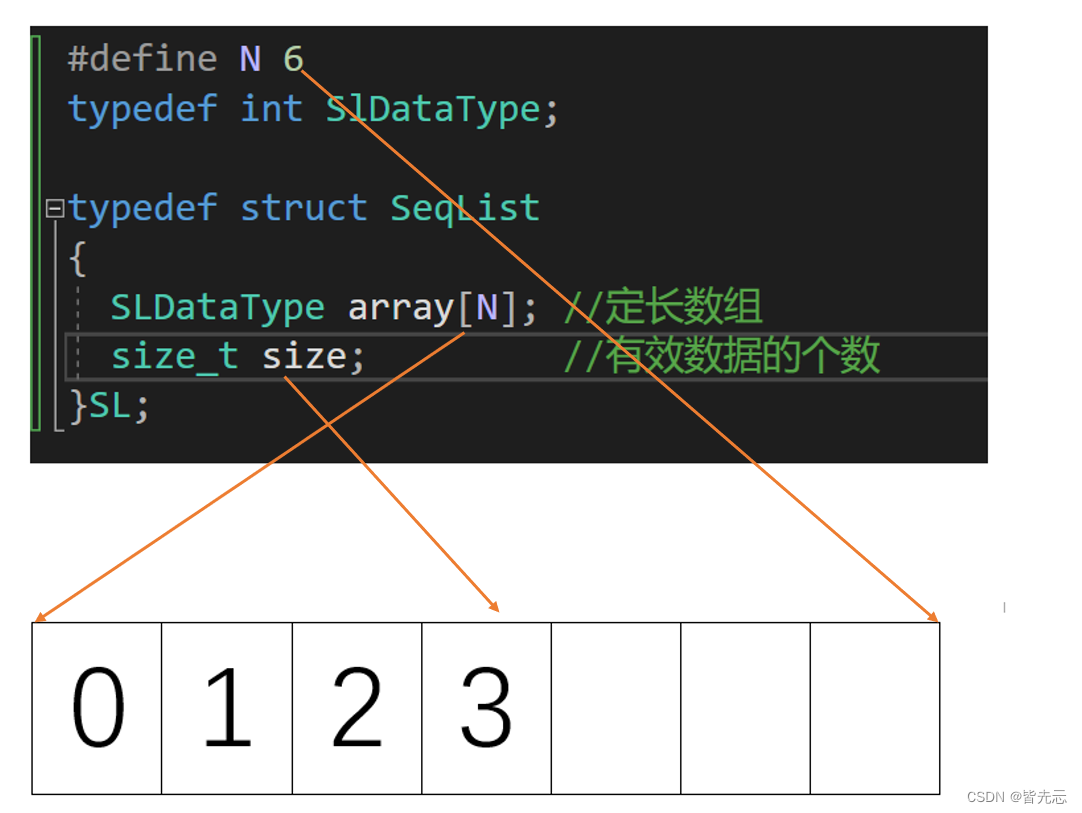
靜態順序表概念:使用定長數組存儲元素
缺點是定義空間小了不夠用,定義大了浪費,不好把控。
2.2 動態順序表
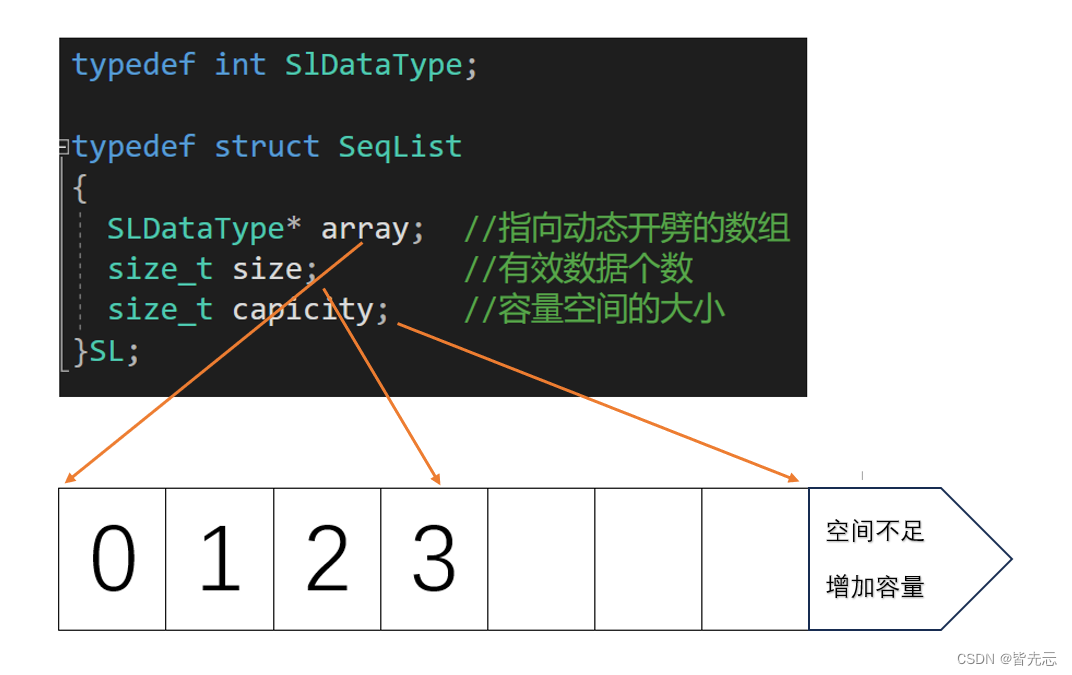
動態順序表概念:使用動態開辟的數組存儲。
動態順序表 根據自己的需求調整大小,
3. 順序表各接口實現
首先建立3個文件
1.SeqList.h頭文件,用來聲明函數
2.SeqList.c文件,用來定義函數
3.Test.c文件,用來測試函數
靜態順序表只適用于確定知道需要存多少數據的場景。靜態順序表的定長數組導致N定大了,空間開多了浪費,開少了不夠用。所以現實中基本都是使用動態順序表,根據需要動態的分配空間大小,所以下面我們實現動態順序表。
1. 定義結構體(Seqlist)
在SeqList.h頭文件中
typedef int SLDataType;typedef struct Seqlist
{SLDataType* a;int size; // 有效數據int capacity; // 空間容量
}SL;
2. 結構體初始化(SLInit)
注意下述代碼皆是:
在SeqList.h頭文件中定義函數
在SeqList.c文件中實現函數
在Test.c文件中測試函數
SeqList.h文件中
定義函數:

SeqList.c文件中
實現函數:
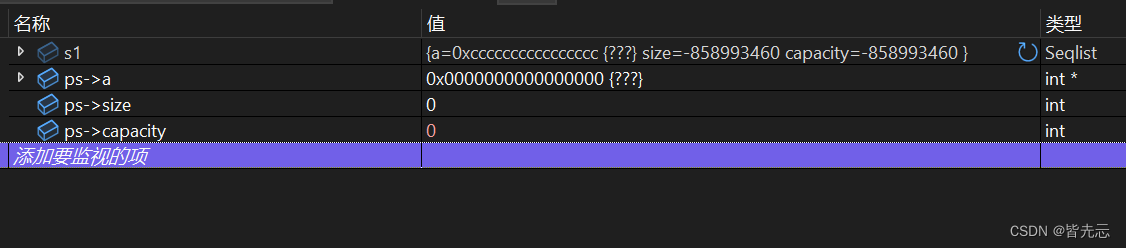
void SLInit(SL *ps) // 數據表初始化
{assert(ps);ps->a = NULL;ps->size = 0;ps->capacity = 0;
}
Test.c文件中
測試函數:
int main()
{SL s1;SLInit(&s1);return 0;
}
調試結果:
3.檢查容量 (SLCheckCapacity)
定義函數:

實現函數:
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps) // 檢查內存是否足夠,不夠就擴容。
{//一般情況為了避免頻繁插入數據而增容,或者一下開辟很大的空間,我們一般是每次增容2倍assert(ps);if (ps->size == ps->capacity){int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(SLDataType) * newCapacity);if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity = newCapacity;}
}
測試函數:
int main()
{SL s1;SLInit(&s1);SLCheckCapacity(&s1);return 0;
}
調試結果:

4.打印數據 (SLPrintf)
定義函數:

實現函數:
void SLPrintf(SL* ps) // 數據表打印
{assert(ps);for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++){printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);}printf("\n");
}
5.插入操作
5.1 從數據頭部插入(SLPushFront)
定義函數:

實現函數:
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x) // 頭插
{assert(ps);SLCheckCapacity(ps);int end = ps->size - 1;while (end >= 0){ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];end--;}ps->a[0] = x;ps->size++;
}
動圖解析:
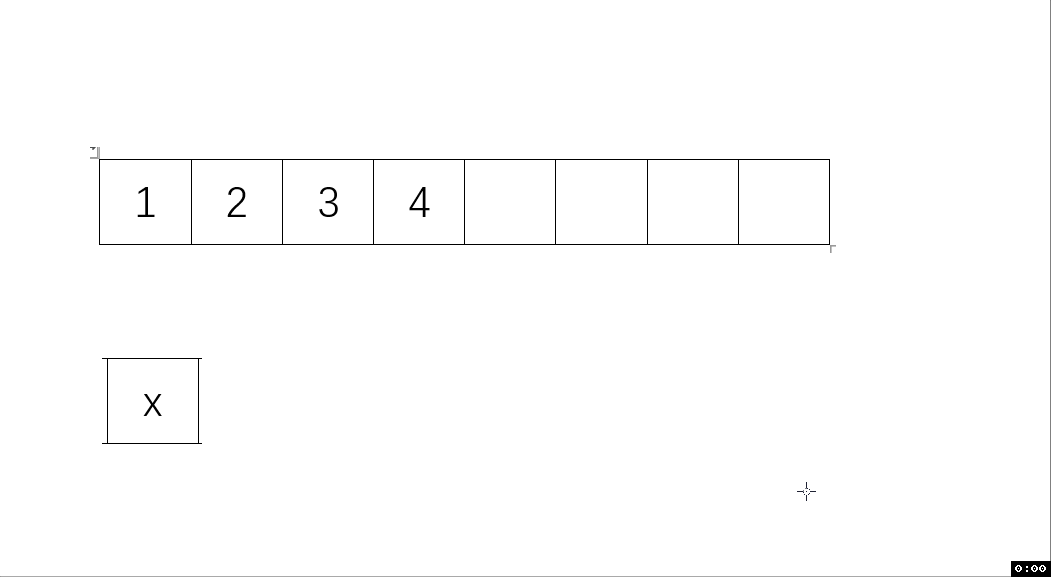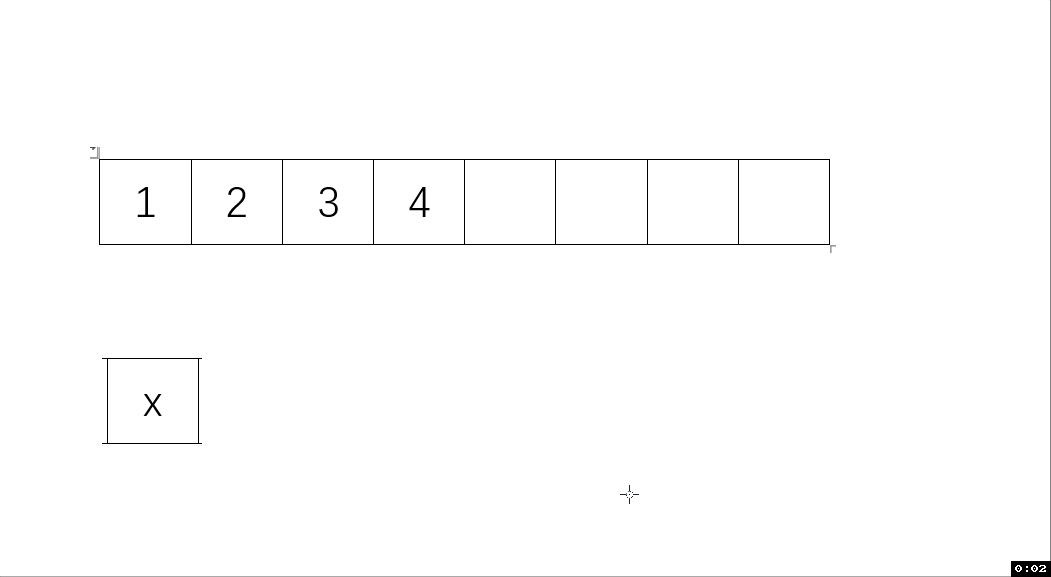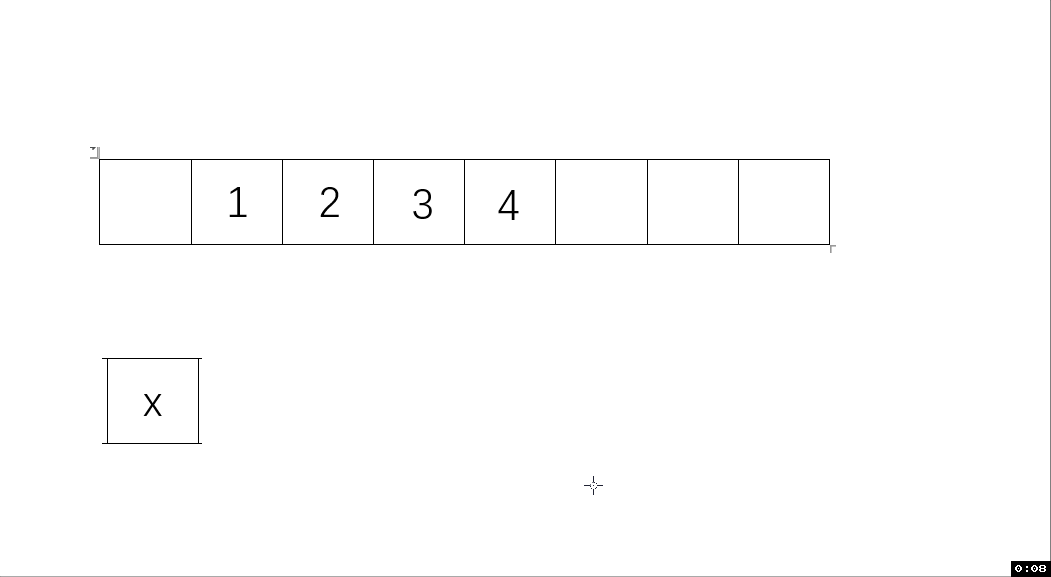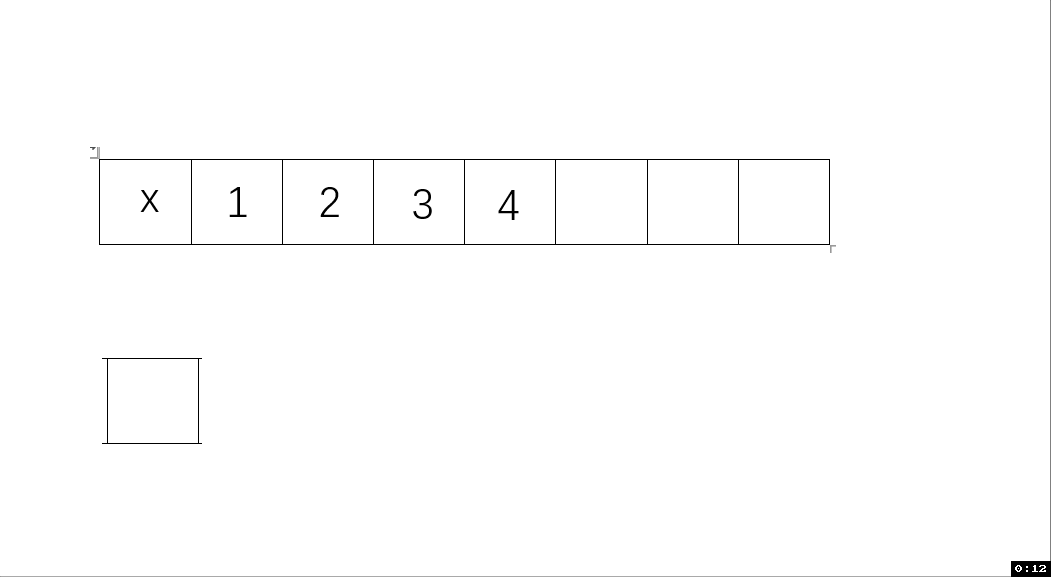
測試函數結果:
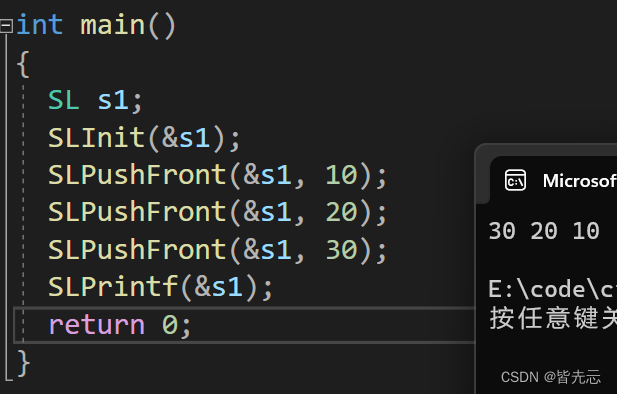
5.2 從數據尾部插入(SLPushBack)
定義函數:

實現函數:
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x) // 尾插
{assert(ps);SLCheckCapacity(ps);ps->a[ps->size++] = x;
}
動圖解析:

測試函數結果:
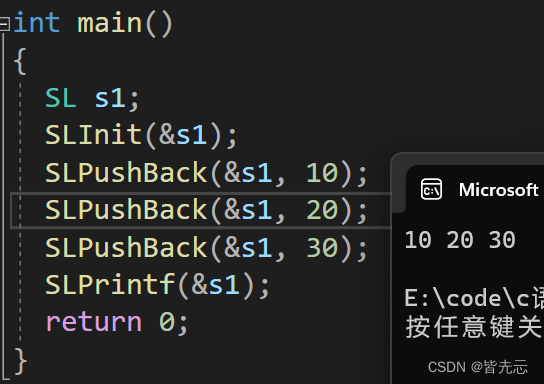
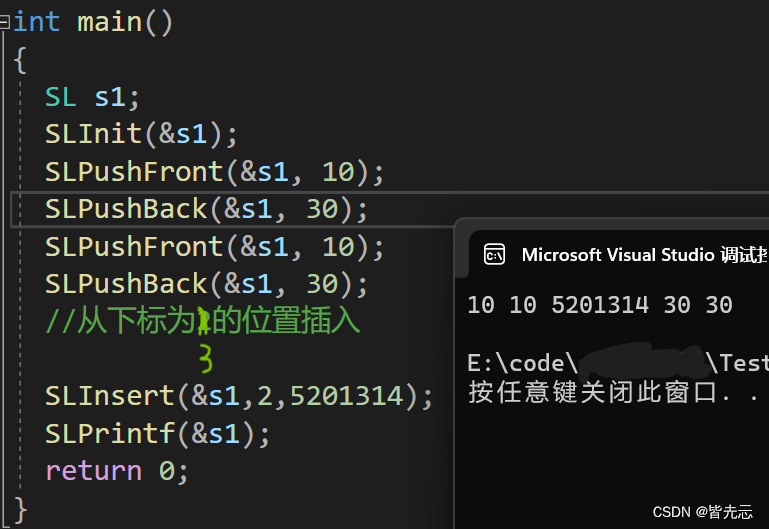
5.3 從任意下標位置的插入(SLInsert)
定義函數:

實現函數:
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x) // 任意下標位置的插入
{assert(ps);assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);SLCheckCapacity(ps);int end = ps->size - 1;while (end >= pos){ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];end--;}ps->a[pos] = x;ps->size++;
}
動圖解析:
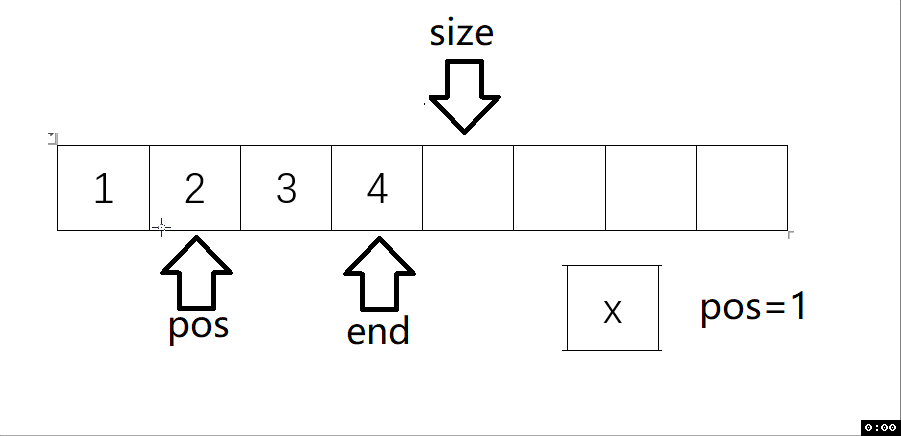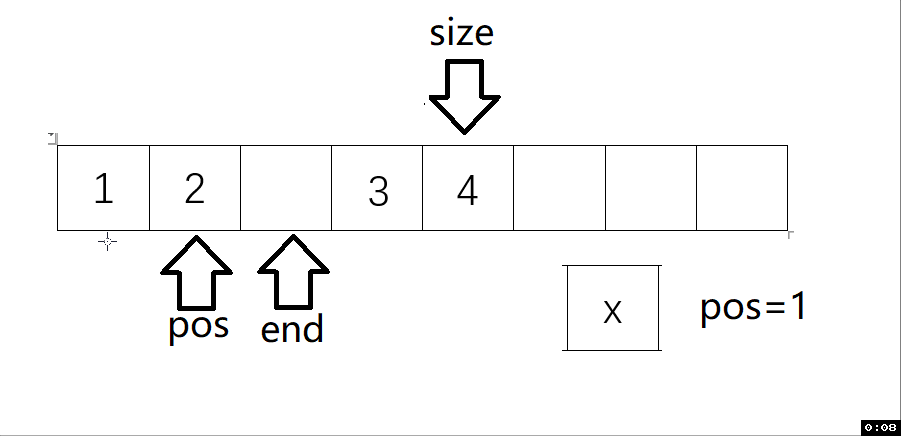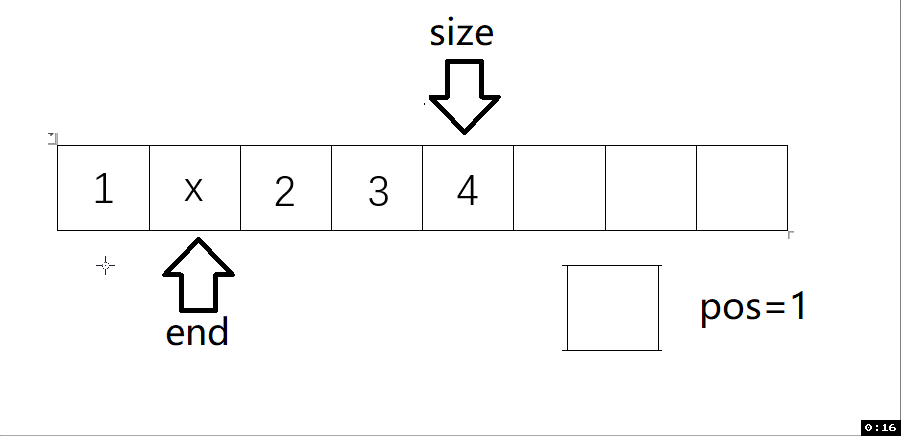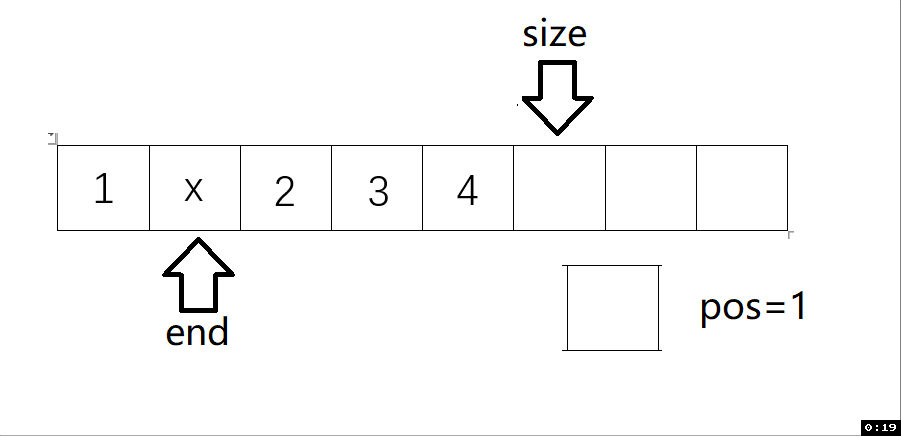
測試函數結果:
6.刪除操作
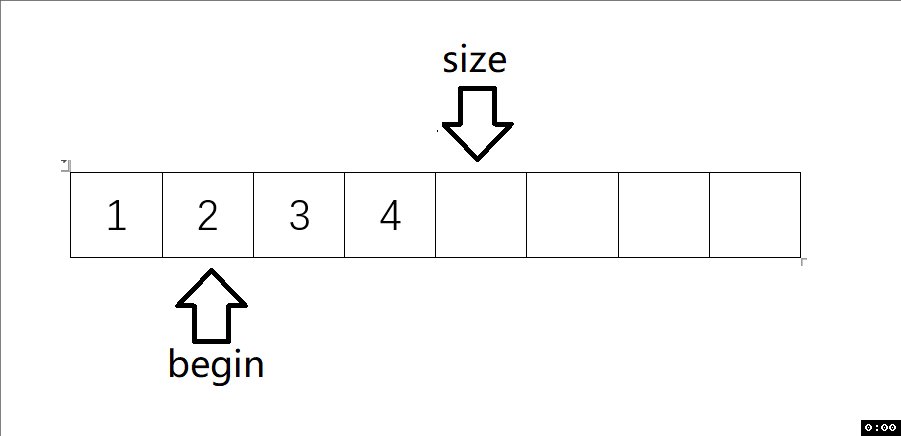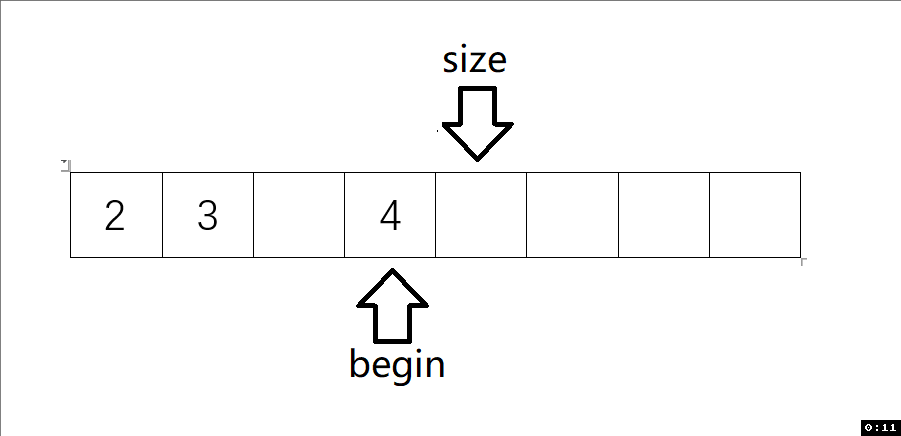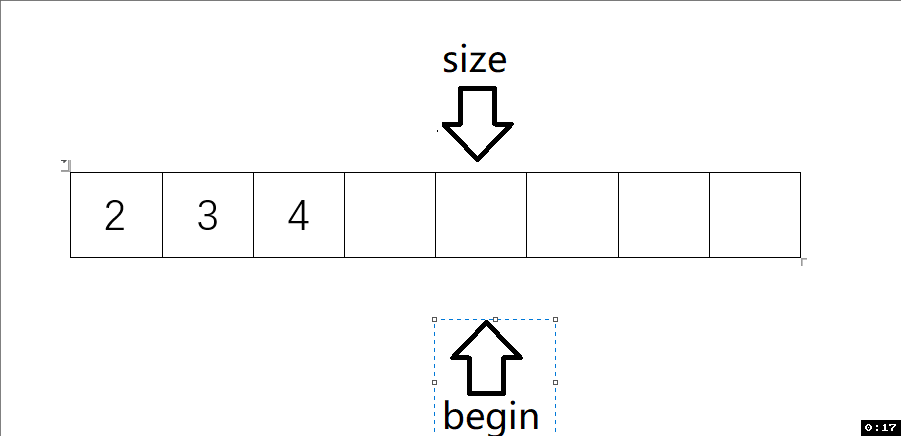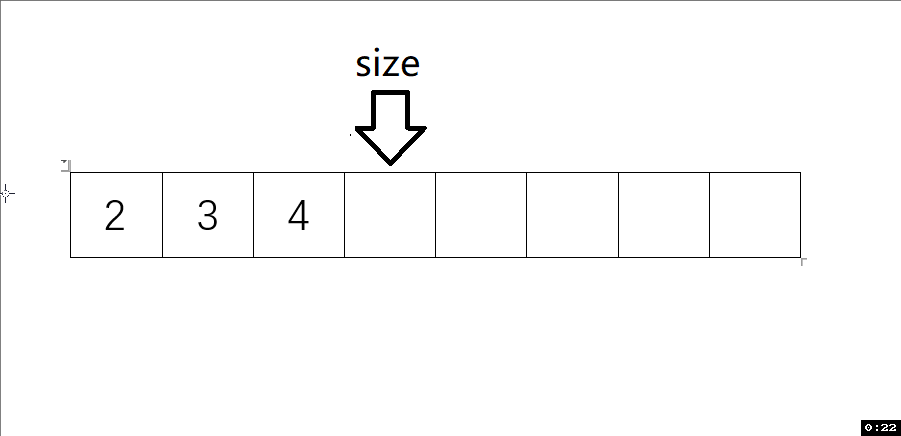
6.1 從數據頭部刪除(SLPopFront)
定義函數:

實現函數:
void SLPopFront(SL* ps) // 頭刪
{assert(ps);assert(ps->size>0);int begin = 1;while (begin < ps->size){ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin];begin++;}ps->size--;
}
動圖解析:
測試函數結果:

6.2 從數據尾部刪除(SLPopBack)
定義函數:

實現函數:
void SLPopBack(SL* ps) // 尾刪
{assert(ps);assert(ps->size>0);ps->size--;
}
動圖解析:
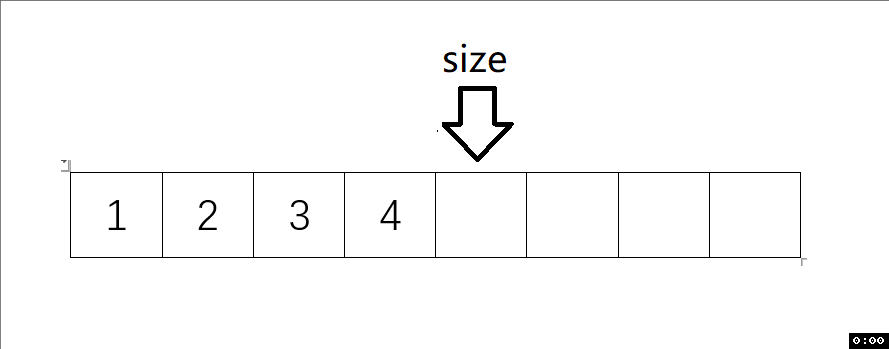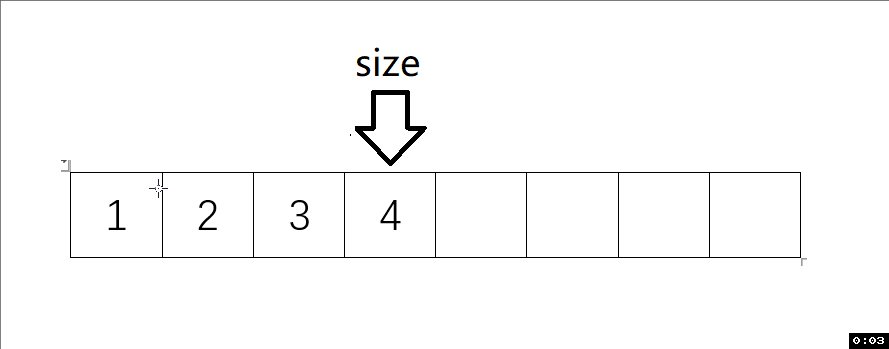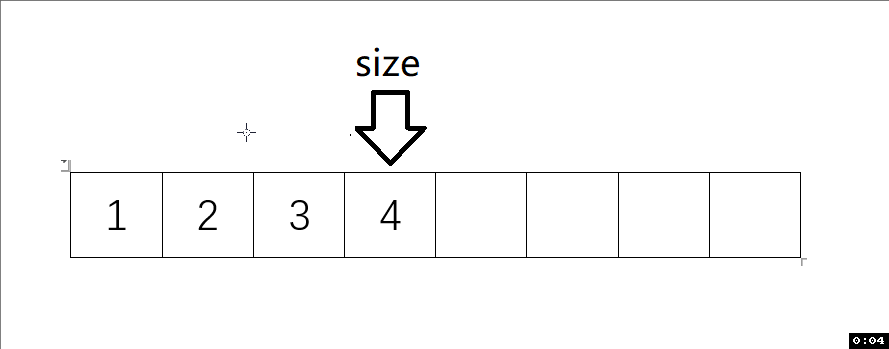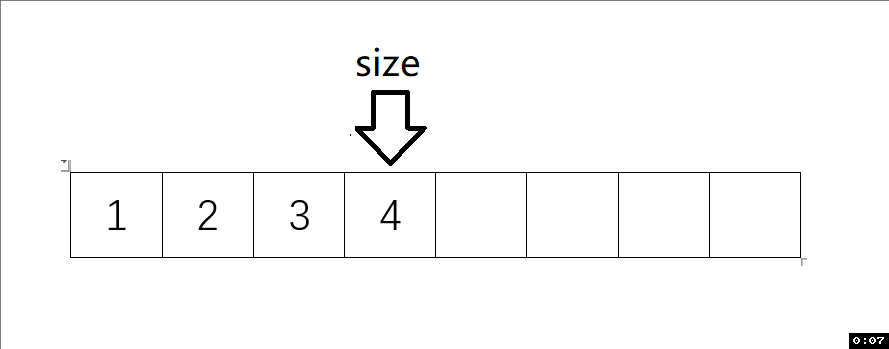
測試函數結果:
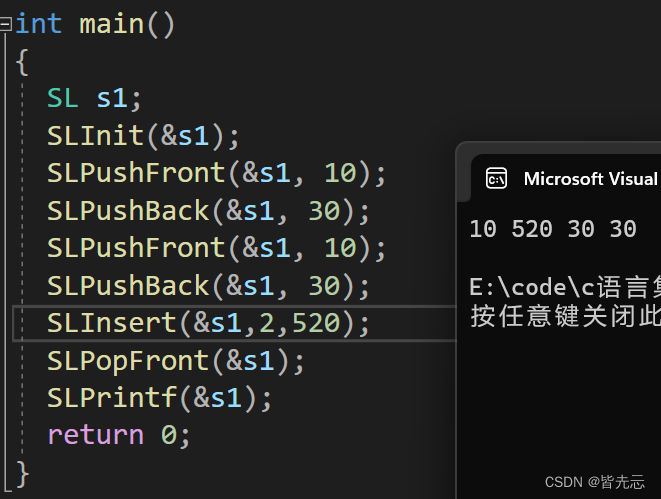
6.3 從任意下標位置的刪除(SLErase)
定義函數:

實現函數:
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos) // 任意下標位置的刪除
{assert(ps);assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size); // 這里刪除不能用等于ps->size,ps->size看作下標的話相當于下標的最后一個位置+1int begin = pos + 1;while (begin < ps->size){ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin];begin++;}ps->size--;
}
動圖解析:

測試函數結果:

7 銷毀操作 (SLDestroy)
定義函數:

實現函數:
void SLDestroy(SL* ps) // 數據表銷毀
{assert(ps);if (ps->a != NULL){free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->size = 0;ps->capacity = 0;}
}
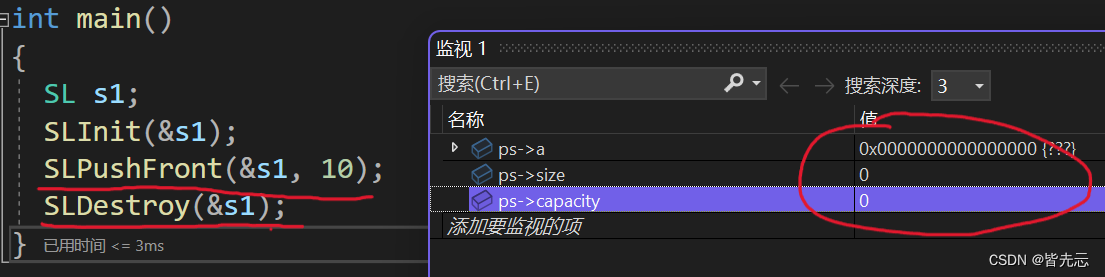
4.完整代碼
4.1 SeqList.h文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int SLDataType;typedef struct Seqlist
{SLDataType* a;int size; // 有效數據int capacity; // 空間容量
}SL;void SLInit(SL *ps); // 數據表初始化
void SLDestroy(SL *ps); // 數據表銷毀void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x); // 頭插
void SLPushBack(SL *ps ,SLDataType x); // 尾插void SLPopFront(SL* ps); // 頭刪
void SLPopBack(SL* ps); // 尾刪void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps); // 檢查內存是否足夠,不夠就擴容。
void SLPrintf(SL* ps); // 數據表打印void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x); //任意下標位置的插入
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos); //任意下標位置的刪除
4.2 SeqList.c文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"SeqList.h"void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps) // 檢查內存是否足夠,不夠就擴容。
{assert(ps);if (ps->size == ps->capacity){int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(SLDataType) * newCapacity);if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity = newCapacity;}
}void SLPrintf(SL* ps) // 數據表打印
{assert(ps);for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++){printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);}printf("\n");
}void SLInit(SL *ps) // 數據表初始化
{assert(ps);ps->a = NULL;ps->size = 0;ps->capacity = 0;
}void SLDestroy(SL* ps) // 數據表銷毀
{assert(ps);if (ps->a != NULL){free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->size = 0;ps->capacity = 0;}
}void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x) // 頭插
{assert(ps);SLCheckCapacity(ps);int end = ps->size - 1;while (end >= 0){ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];end--;}ps->a[0] = x;ps->size++;
}void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x) // 尾插
{assert(ps);SLCheckCapacity(ps);ps->a[ps->size++] = x;
}void SLPopFront(SL* ps) // 頭刪
{assert(ps);assert(ps->size > 0);int begin = 1;while (begin < ps->size){ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin];begin++;}ps->size--;
}void SLPopBack(SL* ps) // 尾刪
{assert(ps);assert(ps->size>0);ps->size--;
}// pos是下標
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x) // 任意下標位置的插入
{assert(ps);assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);SLCheckCapacity(ps);int end = ps->size - 1;while (end >= pos){ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];end--;}ps->a[pos] = x;ps->size++;
}void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos) // 任意下標位置的刪除
{assert(ps);assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size); // 這里刪除不能用等于ps->size,ps->size看作下標的話相當于下標的最后一個位置+1int begin = pos + 1;while (begin < ps->size){ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin];begin++;}ps->size--;
}4.3 Test.c文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"SeqList.h"void TestSL1() // 頭插,尾插
{printf("TestSL1:\n");SL s1;SLInit(&s1);SLPushFront(&s1, 10);SLPushBack(&s1, 30);SLPrintf(&s1);
}void TestSL2() // 頭刪,尾刪
{printf("TestSL2:\n");SL s1;SLInit(&s1);SLPushFront(&s1, 10);SLPushBack(&s1, 30);SLPushFront(&s1, 10);SLPushBack(&s1, 30);SLPrintf(&s1);SLPopBack(&s1);SLPopFront(&s1);SLPrintf(&s1);
}void TestSL3()//任意下標位置的插入,刪除測試
{printf("TestSL3:\n");SL s1;SLInit(&s1);SLPushFront(&s1, 10);SLPushBack(&s1, 30);SLPrintf(&s1);SLInsert(&s1, 1, 520);SLPrintf(&s1);SLErase(&s1, 2);SLPrintf(&s1);
}int main()
{TestSL1();TestSL2();TestSL3();
}
運行結果如下:

——第106天:Pyecharts繪制多種炫酷桑基圖參數說明+代碼實戰)


















