This section provides an overview of PeopleCode and Application Engine programs and discusses how to:
本節概述了PeopleCode和應用程序引擎程序,并討論了如何:
- Decide when to use PeopleCode.
- 決定何時使用PeopleCode。
- Consider the program environment.
- 考慮程序環境。
- Access state records with PeopleCode.
- 使用PeopleCode訪問狀態記錄。
- Use If/Then logic.
- 使用如果/那么邏輯。
- Use PeopleCode in loops.
- 在循環中使用PeopleCode。
- Use the AESection class.
- 使用AESection類。
- Make synchronous online calls to Application Engine programs.
- 對應用程序引擎程序進行同步聯機調用。
- Use the file class.
- 使用文件類。
- Call COBOL modules.
- 調用COBOL模塊
- Call PeopleTools application programming interfaces (APIs).
- 調用PeopleTools應用程序編程接口(API)。
- Use the CommitWork function.
- 使用CommitWork功能。
- Call WINWORD Mail Merge
- 調用WINWORD郵件合并
- Use PeopleCode examples.
- 使用PeopleCode示例。
Understanding PeopleCode and Application Engine Programs 理解PeopleCode和應用引擎程序
Inserting PeopleCode into Application Engine programs enables you to reuse common function libraries and improve performance. In many cases, a small PeopleCode program used instead of Application Engine PeopleCode is an excellent way to build dynamic SQL, perform simple If/Else edits, set defaults, and perform other tasks that do not require a trip to the database.
將PeopleCode插入到Application Engine程序中使您能夠重用公共函數庫并提高性能。在許多情況下,一個小的PeopleCode程序用來代替應用程序引擎PeopleCod是一個很好的方式來構建動態SQL,執行簡單的If/else編輯、設置默認值和執行其他不需要訪問數據庫的任務。
Scope of Variables
變量的作用域
This table presents the different types of variables typically used in Application Engine programs and their scope:
下表顯示了應用程序引擎程序中通常使用的不同類型的變量及其作用域:
| Type of Variable | Scope | Comments |
| State record (work record) | Transaction (unit of work) | Using a work record as your Application Engine state record means that the values in the work record cannot be committed to the database. Commits happen as directed, but any values in work records are not retained after a commit. |
| State record (database record) | Application Engine program | Using a database record as your Application Engine state record preserves the values in the state record on commit, and the committed values are available in the event of a restart. |
| Local PeopleCode variables | PeopleCode program | Local PeopleCode variables are available only for the duration of the PeopleCode program that is using them. |
| Global PeopleCode variables | Application Engine program | Global PeopleCode variables are available during the life of the program that is currently running. Any global PeopleCode variables are saved when an Application Engine program commits and checks points; therefore, they are available in the event of a restart. |
| Component PeopleCode variables | Application Engine program | Component PeopleCode variables act like global variables in Application Engine. |
Action Execution Order
操作執行順序
A step can contain only one PeopleCode action because no other types of actions are required within a step in conjunction with a PeopleCode action (or program). If you include other actions with your PeopleCode action within the same step, keep in mind the hierarchy when you run it.
一個步驟只能包含一個PeopleCode操作,因為在一個步驟中不需要與PeopleCode操作(或程序)結合的其他類型的操作。如果您在同一步驟中包含其他操作與您的People Code操作,請在運行它時記住層次結構。
With PeopleCode actions, Application Engine runs the PeopleCode program before the SQL, Call Section, or Log Message actions, but a PeopleCode program runs after any program flow checks.
使用PeopleCode操作時,應用程序引擎將在SQL、CallSection或日志消息操作之前運行PeopleCode程序,但在任何程序流檢查之后運行PeopleCode程序。
Because multiple action types exist, they must execute in agreement within a system; therefore, the order in which actions execute is significant. At runtime, actions defined for a given step are evaluated based on their action type. All of the action types exist within a strict hierarchy of execution. For example, if both a Do When action and a PeopleCode action exist within a given step, then the Do When action always runs first.
由于存在多個操作類型,它們必須在系統中以一致的方式執行;因此,操作的執行順序非常重要。在運行時,為給定步驟定義的操作將根據其操作類型進行評估。所有操作類型都存在于嚴格的執行層次結構中。例如,如果兩個Do當操作和PeopleCode操作存在于給定步驟中時,則Do When操作總是第一個運行。
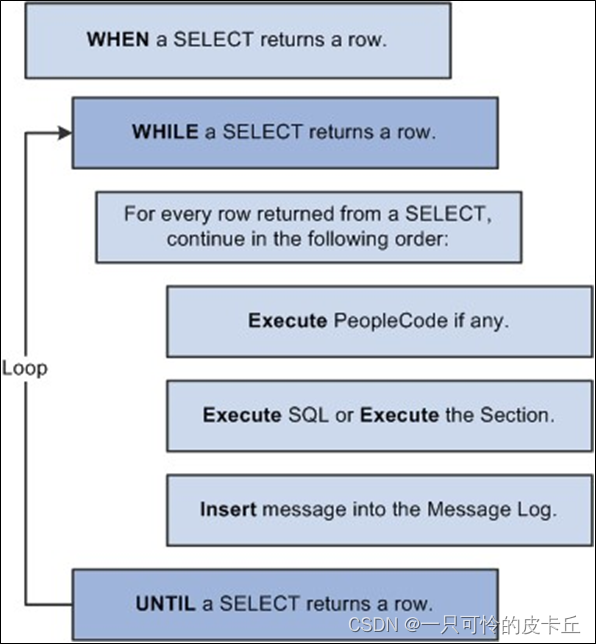
The following example shows the sequence and level of execution for each type of action:
下面的例子顯示了每種作用方式的執行順序和水平:
This is an example of action execution hierarchy.
Deciding When to Use PeopleCode 決定何時使用PeopleCode
Application Engine is not intended to run programs that include only PeopleCode actions. The primary purpose of Application Engine is to run SQL against your data.
應用程序引擎不用于運行僅包括PeopleCode操作的程序。應用程序引擎的主要目的是對數據運行SQL。
Use PeopleCode primarily for setting If, Then, Else logic constructs, performing data preparation tasks, and building dynamic portions of SQL statements; rely on SQL to complete the bulk of actual program processing. Also use PeopleCode to reuse previously developed online logic. PeopleCode is the tool to use to take advantage of new technologies such as component interfaces and application classes.
PeopleCode主要用于設置If,Then,Else邏輯結構,執行數據準備任務,構建SQL語句的動態部分;依靠SQL來完成大量的實際程序處理。還可以使用PeopleCode重用以前開發的在線邏輯。PeopleCode是一種利用新技術(如組件接口和應用程序類)的工具。
Most programs must verify that a certain condition is true before they run a particular section. For example, if the hourly wage is less than or equal to X, do Step A; if not, fetch the next row. In certain instances, you must modify variables that exist in a state record. PeopleCode enables you to set state record variables dynamically.
大多數程序在運行特定的節之前必須驗證某個條件為真。例如,如果小時工資小于或等于X,則執行步驟A;如果不是,則獲取下一行。在某些情況下,必須修改存在于狀態記錄中的變量。PeopleCode允許您動態地設置狀態記錄變量。
Avoid rowset processing in an Application Engine program. Loading data into a rowset can use a significant amount of memory, which this formula approximates:
避免在應用程序引擎程序中處理行集。將數據加載到行集中可能會使用大量的內存,以下公式近似為:
mem = nrows * (row overhead + nrecords * (rec overhead + nfields * (field overhead) + average cumulative fielddata)) where
Mem = n 行*(行開銷+ n 記錄*( rec 開銷+ nfields +*(現場開銷+平均累計現場數據))
- mem is the amount of memory required to store the rowset.
- 其中·mem是存儲行集所需的內存量。
- nrows is the number of rows.
- nrows是行數。
- row overhead is the overhead per row.
- 行開銷是指每行的開銷。
- nrecords is the number of records per row.
- n record是每行的記錄數。
- rec overhead is the record overhead (approximately 40 bytes).
- rec開銷是記錄開銷(大約40字節)。
- nfields is the number of fields in the record.
- nfields是記錄中的字段數。
- field overhead is the overhead per field (approximately 80 bytes).
- 字段開銷是每個字段的開銷(大約80字節)。
- average cumulative fielddata is the average amount of data per field.
- 平均累積字段數據是每個字段的平均數據量。
Using this formula, a rowset containing 500,000 rows with one record per row, 50 fields, and 200 bytes per field would require approximately 2.3 gigabytes of memory.
使用這個公式,包含500,000行,每行一條記錄的行集,50個字段,每個字段200字節將需要大約2.3千兆字節的內存。
)






)











