文章目錄
- 一、String類的重要性
- 二、String類中的常用方法
- 1.字符串構造
- 2.String對象的比較
- 3.字符串查找
- 4.轉換
- 5.字符串替換
- 6.字符串拆分
- 7.字符串截取
- 8.其他操作方法
- 9.字符串的不可變性
- 10.字符串修改
- 三、StringBuilder和StringBuffer
一、String類的重要性
在C語言中已經涉及到字符串了,但是在C語言中要表示字符串只能使用字符數組或者字符指針,可以使用標準庫提供的字符串系列函數完成大部分操作,但是這種將數據和操作數據方法分離開的方式不符合面相對象的思想,而字符串應用又非常廣泛,因此Java語言專門提供了String類
二、String類中的常用方法
1.字符串構造
String類提供的構造方式非常多,常用的有以下三種:
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {String s = "hello";System.out.println(s);String s1 = new String("hello");System.out.println(s1);char[] s3 = {'h','e','l','l','o'};System.out.println(s3);}
}

注意:
1.String類是引用類型,內部并不存儲字符串本身
2.在Java中""引起來的也是String類型對象
2.String對象的比較
Java中提供了四種比較方式:
1.==比較是否引用同一對象
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {int a = 10;int b = 20;int c = 10;System.out.println(a==b);System.out.println(a==c);System.out.println("********");String s = new String("hello");String s1 = new String("hello");String s2 = new String("word");String s3 = s;System.out.println(s==s1);System.out.println(s1==s2);System.out.println(s==s3);}
}

注意: 對于內置類型,== 比較的是變量中的值;對于引用類型==比較的是引用中的地址
2.boolean equals(Object anObject) 方法:按照字典序比較
字典序:字符大小的順序
String類重寫了父類Object中equals方法,Object中equals默認按照==比較,String重寫equals方法后,按照如下規則進行比較
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {String s = new String("hello");String s1 = new String("hello");String s2 = new String("Hello");// equals比較:String對象中的逐個字符// s與s2引用的不是同一個對象,而且兩個對象中內容也不同,因此輸出false// s與s1引用的不是同一個對象,但是兩個對象中放置的內容相同,因此輸出trueSystem.out.println(s.equals(s2));System.out.println(s.equals(s1));}
}

3.int compareTo(String s) 方法: 按照字典序進行比較
與equals不同的是,equals返回的是boolean類型,而compareTo返回的是int類型。具體比較方式:
1.先按照字典次序大小比較,如果出現不等的字符,直接返回這兩個字符的大小差值
2.如果前k個字符相等(k為兩個字符長度最小值),返回值兩個字符串長度差值
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {String s = new String("abc");String s1 = new String("ac");String s2 = new String("abc");String s3 = new String("abcde");System.out.println(s.compareTo(s1));//不同輸出字符的差值為-1System.out.println(s.compareTo(s2));//輸出字符相同為0System.out.println(s.compareTo(s3));//前幾個字符相同,輸出長度差值為-2}
}
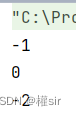
4. int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) 方法:與compareTo方式相同,但是忽略大小寫比較
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {String s = new String("abc");String s1 = new String("ac");String s2 = new String("ABc");String s3 = new String("abcde");System.out.println(s.compareToIgnoreCase(s1));//不同輸出字符的差值為-1System.out.println(s.compareToIgnoreCase(s2));//輸出字符相同為0System.out.println(s.compareToIgnoreCase(s3));//前幾個字符相同,輸出長度差值為-2}
}
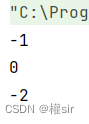
3.字符串查找
字符串查找也是字符串中非常常見的操作,String類提供的常用查找的方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| char charAt(int index) | 返回index位置上字符,如果index為負數或者越界,拋出IndexOutOfBoundsException異常 |
| int indexOf(int ch) | 返回ch第一次出現的位置,沒有返回-1 |
| int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) | 從fromIndex位置開始找ch第一次出現的位置,沒有返回-1 |
| int indexOf(String str) | 返回str第一次出現的位置,沒有返回-1 |
| int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | 從fromIndex位置開始找str第一次出現的位置,沒有返回-1 |
| int lastIndexOf(int ch) | 從后往前找,返回ch第一次出現的位置,沒有返回-1 |
| int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) | 從fromIndex位置開始找,從后往前找ch第一次出現的位置,沒有返回-1 |
| :int lastIndexOf(String str) | 從后往前找,返回str第一次出現的位置,沒有返回-1: |
| int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | 從fromIndex位置開始找,從后往前找str第一次出現的位置,沒有返回-1 |
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {String s = "aaabbbcccaaabbbccc";System.out.println(s.charAt(3)); System.out.println(s.indexOf('c'));System.out.println(s.indexOf('c', 10));System.out.println(s.indexOf("bbb"));System.out.println(s.indexOf("bbb", 10));System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf('c'));System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf('c', 10));System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("bbb"));System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("bbb", 10));}
}
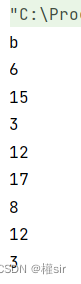
4.轉換
1.數值和字符串轉換化
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {String s1 = String.valueOf(1234);String s2 = String.valueOf(12.34);String s3 = String.valueOf(true);System.out.println(s1);System.out.println(s2);System.out.println(s3);System.out.println("=================================");// 字符串轉數字// 注意:Integer、Double等是Java中的包裝類型int data1 = Integer.parseInt("1234");double data2 = Double.parseDouble("12.34");System.out.println(data1);System.out.println(data2);}
}

2.大小寫轉換
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {String s = "hello";String s1 = "HELLO";System.out.println(s.toUpperCase());//小寫轉大寫System.out.println(s1.toLowerCase());//大寫轉小寫}
}

這兩個函數只轉換字母
3.字符串轉數組
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {String s = "hello";// 字符串轉數組char[] ch = s.toCharArray();for (int i = 0; i < ch.length; i++) {System.out.print(ch[i]);}System.out.println();// 數組轉字符串String s2 = new String(ch);System.out.println(s2);}
}

4.格式化
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {String s = String.format("%d-%d-%d", 2019, 9,14);System.out.println(s);}
}

5.字符串替換
使用一個指定的新的字符串替換掉已有的字符串數據,可用的方法如下:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) | 替換所有的指定內容 |
| String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement) | 替換收個內容 |
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {String s = "hellohello";System.out.println(s.replaceAll("l", "z"));System.out.println(s.replaceFirst("l", "z"));}
}

注意事項: 由于字符串是不可變對象, 替換不修改當前字符串, 而是產生一個新的字符串
6.字符串拆分
可以將一個完整的字符串按照指定的分隔符劃分為若干個子字符串
方法如下:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| String[] split(String regex) | 將字符串全部拆分 |
| String[] split(String regex, int limit) | 將字符串以指定的格式,拆分為limit組 |
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "hello word is you";String[] s = str.split(" ");//按照空格拆分for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {System.out.println(s[i]);}}
}

public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "hello word is you";String[] s = str.split(" ",2);//按照空格拆分成兩份for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {System.out.println(s[i]);}}
}

拆分是特別常用的操作. 一定要重點掌握. 另外有些特殊字符作為分割符可能無法正確切分, 需要加上轉義
注意事項:
1.字符"|“,”*“,”+“都得加上轉義字符,前面加上 “\”
2.而如果是 “” ,那么就得寫成 “\\”
3.如果一個字符串中有多個分隔符,可以用”|"作為連字符
多次拆分:
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "name=zhagnsan&age=10";String[] s = str.split("&");for (String ss:s) {String[] ret = ss.split("=");for (String sss:ret) {System.out.println(sss);}}}
}

7.字符串截取
從一個完整的字符串之中截取出部分內容
方法如下:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| String substring(int beginIndex) | 從指定索引截取到結尾 |
| String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) | 截取部分內容 |
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "helloword";System.out.println(str.substring(5));System.out.println(str.substring(0, 5));}
}

注意事項:
1.索引從0開始
2.注意前閉后開區間的寫法,substring(0,5)表示包含0下標的字符,不包含5下標的字符
8.其他操作方法
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| String trim() | 去掉字符串中的左右空格,保留中間空格 |
| String toUpperCase() | 字符串轉大寫 |
| String toLowerCase() | 字符串轉小寫 |
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = " hello word ";System.out.println(str.trim());}
}

trim 會去掉字符串開頭和結尾的空白字符(空格, 換行, 制表符等)
9.字符串的不可變性
String是一種不可變對象. 字符串中的內容是不可改變。字符串不可被修改,是因為:
1.String類在設計時就是不可改變的,String類實現描述中已經說明了
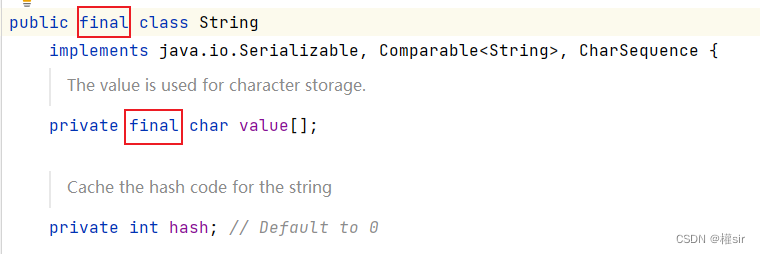
String類中的字符實際保存在內部維護的value字符數組中,從上圖中可以看出:
1.String類被final修飾,表示該類不能被繼承
2.value被final修飾,表明value自身的值不能改變,即不能引用其它字符數組,但是其引用空間中的內容可以修改
2. 所有涉及到可能修改字符串內容的操作都是創建一個新對象,改變的是新對象
字符串不可變是因為其內部保存字符的數組被final修飾了,因此不能改變。
這種說法是錯誤的,不是因為String類自身,或者其內部value被final修飾而不能被修改。
final修飾類表明該類不想被繼承,final修飾引用類型表明該引用變量不能引用其他對象,但是其引用對象中的內容是可以修改的
10.字符串修改
注意: 盡量避免直接對String類型對象進行修改,因為String類是不能修改的,所有的修改都會創建新對象,效率非常低下
三、StringBuilder和StringBuffer
由于String的不可更改特性,為了方便字符串的修改,Java中又提供StringBuilder和StringBuffer類。這兩個類大部分功能是相同的
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| StringBuff append(String str) | 在尾部追加,相當于String的+=,可以追加:boolean、char、char[]、double、float、int、long、Object、String、StringBuff的變量 |
| char charAt(int index) | 獲取index位置的字符 |
| int length() | 獲取字符串的長度 |
| int capacity() | 獲取底層保存字符串空間總的大小 |
| void ensureCapacity(int mininmumCapacity) | 擴容 |
| void setCharAt(int index,char ch) | 將index位置的字符設置為ch |
| int indexOf(String str) | 返回str第一次出現的位置 |
| int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | 從fromIndex位置開始查找str第一次出現的位置 |
| int lastIndexOf(String str) | 返回最后一次出現str的位置 |
| int lastIndexOf(String str,int fromIndex) | 從fromIndex位置開始找str最后一次出現的位置 |
| StringBuff insert(int offset, String str) | 在offset位置插入:八種基類類型 & String類型 & Object類型數據 |
| StringBuffer deleteCharAt(int index) | 刪除index位置字符 |
| StringBuffer delete(int start, int end) | 刪除[start, end)區間內的字符 |
| StringBuffer replace(int start, int end, String str) | 將[start, end)位置的字符替換為str |
| String substring(int start) | 從start開始一直到末尾的字符以String的方式返回 |
| String substring(int start,int end) | 將[start, end)范圍內的字符以String的方式返回 |
| StringBuffer reverse() | 反轉字符串 |
| String toString() | 將所有字符按照String的方式返回 |
String和StringBuilder最大的區別在于String的內容無法修改,而StringBuilder的內容可以修改。頻繁修改字符串的情況考慮使用StringBuilder
注意: String和StringBuilder類不能直接轉換。如果要想互相轉換,可以采用如下原則:
1.String變為StringBuilder: 利用StringBuilder的構造方法或append()方法
2.StringBuilder變為String: 調用toString()方法
String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder的區別
1.String的內容不可修改,StringBuffer與StringBuilder的內容可以修改.
2.StringBuffer與StringBuilder大部分功能是相似的
3.StringBuffer采用同步處理,屬于線程安全操作;而StringBuilder未采用同步處理,屬于線程不安全操作


)




(C:前綴和+滑動窗口,E:位運算加分塊))




C語言之符號常量概述)






