AQS 概念
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer(AQS) 是 Java 并發包 (java.util.concurrent.locks) 的核心基礎框架,它的實現關鍵是先進先出 (FIFO) 等待隊列和一個用volatile修飾的鎖狀態status。具體實現有 : ReentrantLock、Semaphore、CountDownLatch、ReentrantReadWriteLock 等常用的同步工具類。
AQS 的核心思想
AQS 的核心思想是 : 如果被請求的共享資源空閑,則將當前請求資源的線程設置為有效的工作線程,并且將共享資源設置為鎖定狀態。如果被請求的共享資源被占用,那么就需要一套線程阻塞等待以及被喚醒時鎖分配的機制,這個機制 AQS 是用 CLH 隊列鎖 實現的,即將暫時獲取不到鎖的線程加入到隊列中。
CLH 隊列:Craig, Landin, and Hagersten (CLH) locks,是一種基于鏈表的可擴展、高性能、公平的自旋鎖。AQS 中的隊列是 CLH 變體的虛擬雙向隊列(FIFO)。
AQS 的核心架構
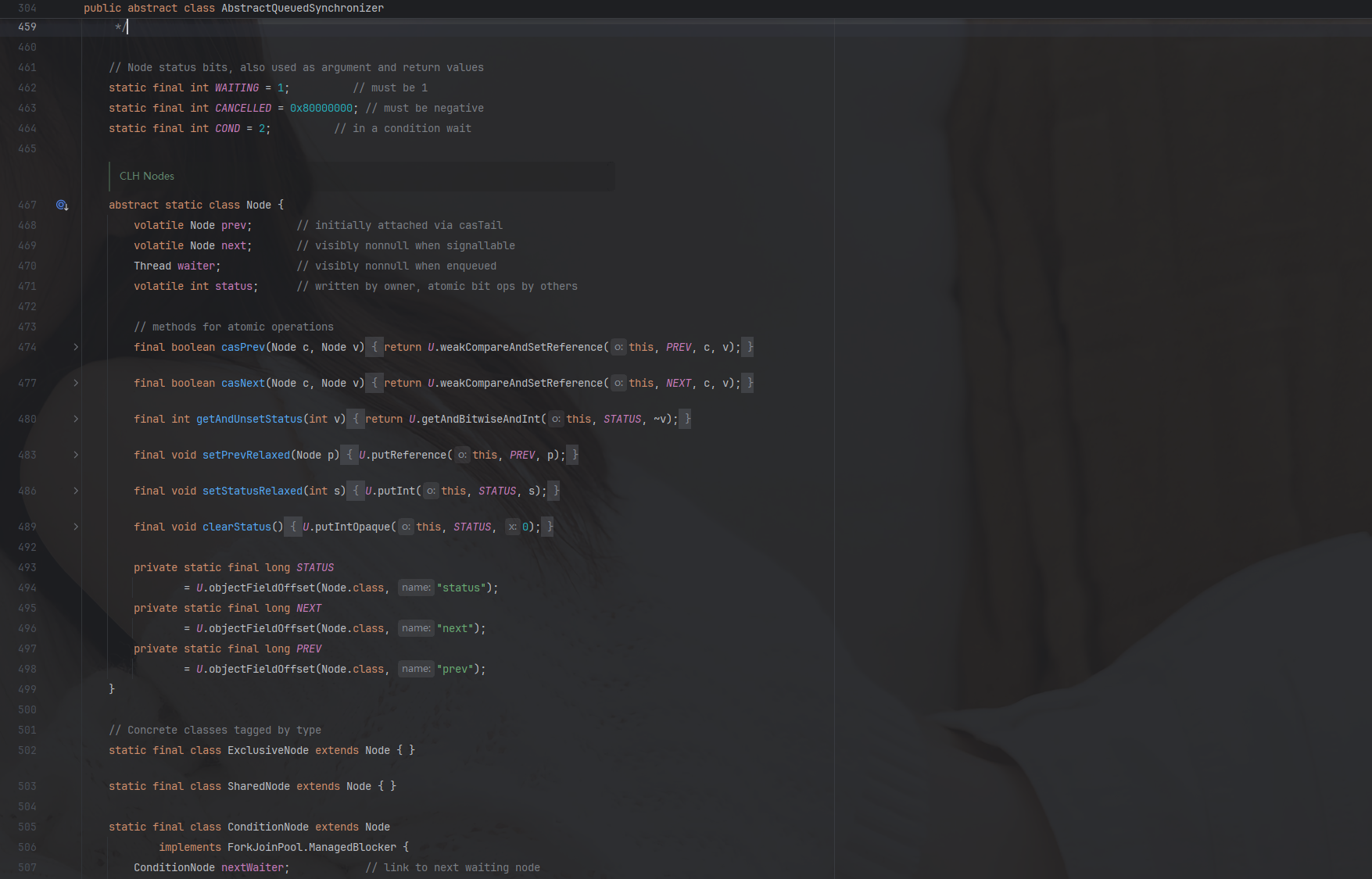
- AQS 使用一個 volatile int state 成員變量來表示同步狀態
- 通過內置的 FIFO 隊列 來完成資源獲取線程的排隊工作。
- Node中的thread變量用來存放進入AQS隊列里面的線程,Node節點內部:
- prev記錄當前節點的前驅節點
- next 記錄當前節點的后繼節點
- SHARED用來標記該線程是獲取共享資源時被阻塞掛起后放入AQS隊列的
- EXCLUSIVE用來標記線程是獲取獨占資源時被掛起后放入AQS隊列的
- waitStatus 記錄當前線程等待狀態,可以為
- CANCELLED (線程被取消了)
- SIGNAL(線程需要被喚醒)
- CONDITION(線程在CONDITION條件隊列里面等待)
- PROPAGATE(釋放共享資源時需要要通知其他節點);
圖中源碼解釋 :
static final int WAITING = 1; // 等待狀態,必須為1
static final int CANCELLED = 0x80000000; // 取消狀態,必須為負數(最高位為1)
static final int COND = 2; // 在條件等待中/** CLH 節點 */
abstract static class Node {volatile Node prev; // 前驅節點,最初通過 casTail 附加volatile Node next; // 當可發出信號時 visibly nonnullThread waiter; // 當入隊時 visibly nonnullvolatile int status; // 由所有者寫入,其他線程通過原子位操作讀取// 用于 cleanQueue 的比較并交換前驅節點final boolean casPrev(Node c, Node v) {return U.weakCompareAndSetReference(this, PREV, c, v);}// 用于 cleanQueue 的比較并交換后繼節點final boolean casNext(Node c, Node v) {return U.weakCompareAndSetReference(this, NEXT, c, v);}// 用于信號傳遞的獲取并清除狀態位final int getAndUnsetStatus(int v) {return U.getAndBitwiseAndInt(this, STATUS, ~v);}// 用于離隊賦值的寬松設置前驅節點final void setPrevRelaxed(Node p) {U.putReference(this, PREV, p);}// 用于離隊賦值的寬松設置狀態final void setStatusRelaxed(int s) {U.putInt(this, STATUS, s);}// 用于減少不必要信號的狀態清除final void clearStatus() {U.putIntOpaque(this, STATUS, 0);}// 內存偏移量常量private static final long STATUS = U.objectFieldOffset(Node.class, "status");private static final long NEXT = U.objectFieldOffset(Node.class, "next");private static final long PREV = U.objectFieldOffset(Node.class, "prev");
}// 按類型標記的具體節點類
static final class ExclusiveNode extends Node { } // 獨占模式節點
static final class SharedNode extends Node { } // 共享模式節點// 條件節點,實現 ManagedBlocker 接口用于 ForkJoinPool
static final class ConditionNode extends Node implements ForkJoinPool.ManagedBlocker {ConditionNode nextWaiter; // 鏈接到下一個等待節點/*** 允許條件在 ForkJoinPools 中使用,而不會冒險耗盡固定池。* 這僅適用于非定時條件等待,不適用于定時版本。*/public final boolean isReleasable() {return status <= 1 || Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted();}public final boolean block() {while (!isReleasable()) LockSupport.park();return true;}
}// 等待隊列頭節點,延遲初始化
private transient volatile Node head;// 等待隊列尾節點。初始化后,僅通過 casTail 修改
private transient volatile Node tail;// 同步狀態
private volatile int state;/*** 返回同步狀態的當前值。* @return 當前狀態值*/
protected final int getState() {return state;
}
AQS 底層數據結構
state
state 是 AQS 的核心字段,表示共享資源的狀態。不同的同步器對 state 的解釋不同:
- ReentrantLock:
state表示當前線程獲取鎖的可重入次數(如果發現可以可重入,則state+1; 執行完成則-1; 為0時可以釋放) - Semaphore:
state表示當前可用信號的個數 - CountDownLatch:
state表示計數器當前的值
AQS 提供了一系列訪問 state 的方法:
// 獲取當前同步狀態
protected final int getState() {return state;
}// 設置同步狀態
protected final void setState(int newState) {state = newState;
}// 使用CAS原子性地設置同步狀態
protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) {return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, expect, update);
}
同步隊列:Node 節點
AQS 內部維護了一個 FIFO 雙向隊列,隊列中的每個元素都是一個 Node 對象:
static final class Node {// 節點模式:共享模式static final Node SHARED = new Node();// 節點模式:獨占模式static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;// 等待狀態:線程已取消static final int CANCELLED = 1;// 等待狀態:后繼節點的線程需要被喚醒static final int SIGNAL = -1;// 等待狀態:節點在條件隊列中等待static final int CONDITION = -2;// 等待狀態:下一次acquireShared應無條件傳播static final int PROPAGATE = -3;// 當前節點的等待狀態volatile int waitStatus;// 前驅節點volatile Node prev;// 后繼節點volatile Node next;// 節點關聯的線程volatile Thread thread;// 指向下一個等待條件或共享模式的節點Node nextWaiter;// 判斷節點是否在共享模式下等待final boolean isShared() {return nextWaiter == SHARED;}// 獲取前驅節點final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {Node p = prev;if (p == null)throw new NullPointerException();elsereturn p;}// 構造方法Node() { // Used to establish initial head or SHARED marker}Node(Thread thread, Node mode) { // Used by addWaiterthis.nextWaiter = mode;this.thread = thread;}Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) { // Used by Conditionthis.waitStatus = waitStatus;this.thread = thread;}
}
AQS 的整體結構
AQS 的整體結構如下圖所示:
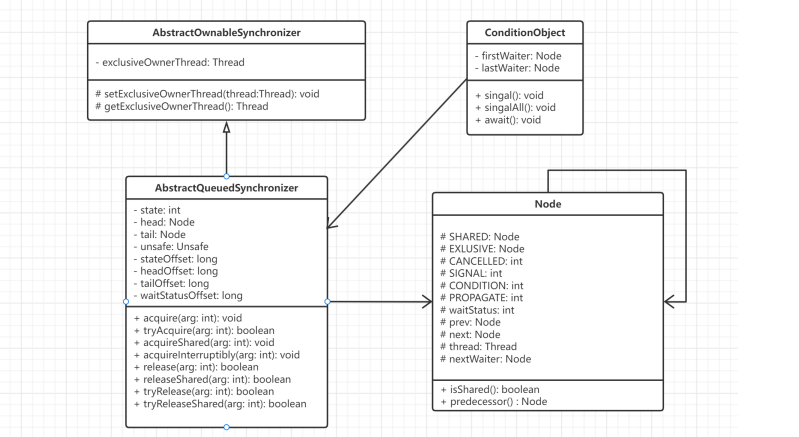
線程獲取鎖失敗時的 AQS 隊列變化
初始狀態
當沒有線程競爭鎖時,AQS 的同步隊列處于初始狀態,head 和 tail 都為 null:
// 初始狀態
head = null;
tail = null;
第一個線程獲取鎖失敗
當第一個線程嘗試獲取鎖失敗時,AQS 會初始化同步隊列:
- 創建空節點(dummy node)作為頭節點
- 將當前線程包裝成 Node 節點添加到隊列尾部
// addWaiter 方法:將當前線程包裝成Node并加入隊列
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {// 將當前線程包裝成Node節點Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);// 嘗試快速入隊Node pred = tail;if (pred != null) {node.prev = pred;if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {pred.next = node;return node;}}// 快速入隊失敗,使用enq方法自旋入隊enq(node);return node;
}// enq方法:通過自旋CAS確保節點成功入隊
private Node enq(final Node node) {for (;;) {Node t = tail;if (t == null) { // 隊列未初始化// 創建空節點(dummy node)作為頭節點if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))tail = head; // 頭尾都指向空節點} else {// 將新節點添加到隊列尾部node.prev = t;if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {t.next = node;return t;}}}
}
初始化后的隊列結構:
head → [dummy node] ← tail↑新加入的節點
后續線程獲取鎖失敗
當后續線程嘗試獲取鎖失敗時,它們會被添加到隊列的尾部:
// acquireQueued方法:線程在隊列中自旋獲取資源或阻塞
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {boolean failed = true;try {boolean interrupted = false;for (;;) {// 獲取前驅節點final Node p = node.predecessor();// 如果前驅是頭節點,嘗試獲取資源if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {// 獲取成功,設置當前節點為頭節點setHead(node);p.next = null; // help GC (方便垃圾回收)failed = false;return interrupted;}// 判斷是否應該阻塞,并在需要時安全地阻塞if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&parkAndCheckInterrupt())interrupted = true;}} finally {if (failed)cancelAcquire(node);}
}
多個線程競爭后的隊列結構 :
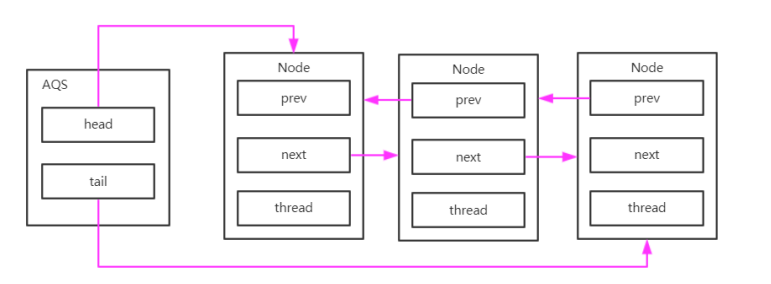
線程被喚醒時的 AQS 隊列變化
鎖釋放與線程喚醒
當持有鎖的線程釋放資源時,會喚醒隊列中的下一個線程:
// release方法:釋放獨占模式下的資源
public final boolean release(int arg) {if (tryRelease(arg)) {Node h = head;if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)unparkSuccessor(h); // 喚醒后繼節點return true;}return false;
}// unparkSuccessor方法:喚醒指定節點的后繼節點
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {int ws = node.waitStatus;if (ws < 0)compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0); // 清除狀態// 查找下一個需要喚醒的節點Node s = node.next;if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {s = null;// 從尾部向前查找,找到隊列中最前面且未取消的節點for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)if (t.waitStatus <= 0)s = t;}if (s != null)LockSupport.unpark(s.thread); // 喚醒線程
}
4.2 線程被喚醒后的隊列變化
當隊列中的線程被喚醒后,它會嘗試獲取鎖,如果獲取成功,會將自己設置為新的頭節點:
// setHead方法:將節點設置為頭節點
private void setHead(Node node) {head = node;node.thread = null; // 清空線程引用node.prev = null;
}
原來的頭節點(dummy node)會被垃圾回收,新頭節點的 thread 字段被設置為 null,表示它不再關聯任何線程。
公平鎖與非公平鎖
AQS 支持兩種鎖獲取模式:公平鎖和非公平鎖。
非公平鎖(如 ReentrantLock 的默認實現):
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();int c = getState();if (c == 0) {// 不管隊列中是否有等待線程,直接嘗試獲取鎖if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);return true;}}// 重入邏輯...
}
公平鎖:
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();int c = getState();if (c == 0) {// 只有隊列中沒有等待線程或當前線程是隊列中的第一個時才獲取鎖if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);return true;}}// 重入邏輯...
}
hasQueuedPredecessors() 方法檢查隊列中是否有比當前線程等待時間更長的線程,這是實現公平性的關鍵。
AQS 的設計模式
模板方法模式
AQS 使用了模板方法模式,定義了同步器的主要邏輯骨架,而將一些特定操作留給子類實現。以下是需要子類實現的方法:
| 方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
boolean tryAcquire(int arg) | 嘗試以獨占方式獲取資源 |
boolean tryRelease(int arg) | 嘗試釋放獨占資源 |
int tryAcquireShared(int arg) | 嘗試以共享方式獲取資源 |
boolean tryReleaseShared(int arg) | 嘗試釋放共享資源 |
boolean isHeldExclusively() | 判斷當前線程是否獨占資源 |
以 ReentrantLock 為例的實現
ReentrantLock 中的同步器 Sync 繼承自 AQS,并實現了相關方法:
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {// 嘗試獲取鎖abstract void lock();// 非公平嘗試獲取final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();int c = getState();if (c == 0) {if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);return true;}}else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {int nextc = c + acquires;if (nextc < 0) // overflowthrow new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");setState(nextc);return true;}return false;}// 嘗試釋放鎖protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {int c = getState() - releases;if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();boolean free = false;if (c == 0) {free = true;setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);}setState(c);return free;}// 判斷當前線程是否獨占資源protected final boolean isHeldExclusively() {return getExclusiveOwnerThread() == Thread.currentThread();}
}
優勢
- 代碼復用:AQS 提供了通用的同步框架,多個同步器可以復用相同的隊列管理邏輯
- 職責分離:AQS 負責線程管理,子類專注于狀態管理
裝飾器模式
裝飾器模式動態地給一個對象添加一些額外的職責,就增加功能來說,裝飾器模式相比生成子類更為靈活。
在 AQS 中的實現
AQS 中的 Node 類可以看作是對 Thread 的裝飾,它添加了同步所需的額外信息:
static final class Node {// 節點模式:共享或獨占volatile Node nextWaiter;// 等待狀態volatile int waitStatus;// 前驅和后繼指針volatile Node prev;volatile Node next;// 被裝飾的線程對象volatile Thread thread;// 構造方法 - 裝飾線程Node(Thread thread, Node mode) { // Used by addWaiterthis.nextWaiter = mode;this.thread = thread;}
}
優勢
- 功能擴展:在不修改
Thread類的情況下為其添加同步功能 - 靈活性:可以根據需要為線程添加不同的同步屬性
狀態模式
狀態模式允許一個對象在其內部狀態改變時改變它的行為。
在 AQS 中的實現
AQS 中節點的 waitStatus 字段代表了不同的狀態,每種狀態對應不同的行為:
static final class Node {// 狀態常量static final int CANCELLED = 1; // 取消狀態static final int SIGNAL = -1; // 需要喚醒后繼節點static final int CONDITION = -2; // 在條件隊列中等待static final int PROPAGATE = -3; // 傳播喚醒操作// 狀態字段volatile int waitStatus;
}
根據狀態的不同,AQS 采取不同的處理策略:
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {int ws = pred.waitStatus;if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) // 根據狀態決定行為return true;if (ws > 0) { // 處理取消狀態do {node.prev = pred = pred.prev;} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);pred.next = node;} else {compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);}return false;
}
AQS 的使用
ReentrantLock 的實現
ReentrantLock 通過內部類 Sync 繼承 AQS,實現了可重入的獨占鎖:
public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {private final Sync sync;abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {}// 非公平鎖實現static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {final void lock() {if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());elseacquire(1);}protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);}}// 公平鎖實現static final class FairSync extends Sync {final void lock() {acquire(1);}protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {// 公平獲取邏輯}}
}
CountDownLatch 的實現
CountDownLatch 通過內部類 Sync 繼承 AQS,實現了共享模式的同步器:
public class CountDownLatch {private static final class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {Sync(int count) {setState(count);}int getCount() {return getState();}protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {return (getState() == 0) ? 1 : -1;}protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {for (;;) {int c = getState();if (c == 0)return false;int nextc = c - 1;if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))return nextc == 0;}}}
}



)

)


)
 Context)





)



的補充)