? ? ? ? ?
づ?ど
?🎉?歡迎點贊支持🎉
個人主頁:勵志不掉頭發的內向程序員;
專欄主頁:C++語言;
文章目錄
前言
一、序列式容器和關聯式容器
二、set 系列的使用
2.1、set 和 multiset 參考文檔
2.2、set 類的介紹
2.3、set 的構造和迭代器
2.4、set 的增刪查
2.5、find 和 erase 使用樣例
2.6、multiset 和 set 的差異
三、map 系列的使用
3.1、map 和 multimap 參考文檔
3.2、map 類的介紹
3.3、pair 類型介紹
3.4、map 的構造和迭代器
3.5、map 的增刪查
3.6、map 的數據修改
3.7、map 的迭代器和 [ ] 功能樣例
3.8、multimap 和 map 的差異
總結
前言
本章節我們講解 map/set 這兩個容器,它和我們之前學習的容器不太一樣,要比我們之前學習的內容復雜的多,它的底層的大致框架就是我們上一章節的二叉搜索樹,所以學習本章節前希望大家對上一章的學習能夠充分掌握,這樣我們學習本章節時就會比較輕松啦,接下來我們一起看看吧。

一、序列式容器和關聯式容器
前面我們已經接觸過了 STL 中的部分容器如:string、vector、list、deque 等,這些容器我們統稱為序列容器,因為邏輯結構為線性序列的數據結構,兩個位置存儲的值之間一般沒有緊密的關聯關系,比如交換一下,它依舊是序列式容器。順序容器中的元素是按它們在容器中的存儲位置來按順序保存和訪問的。
關聯式容器也是用來存儲數據的,與序列式容器不同的是,關聯式容器的邏輯結構通常是非線性結構,兩個位置有緊密的關聯關系,交換一下,他的存儲結構就被破壞了。順序容器中的元素是按關鍵字來保存和訪問的。關聯式容器有 map/set 系列和 unordered_map/unordered_set 系列。
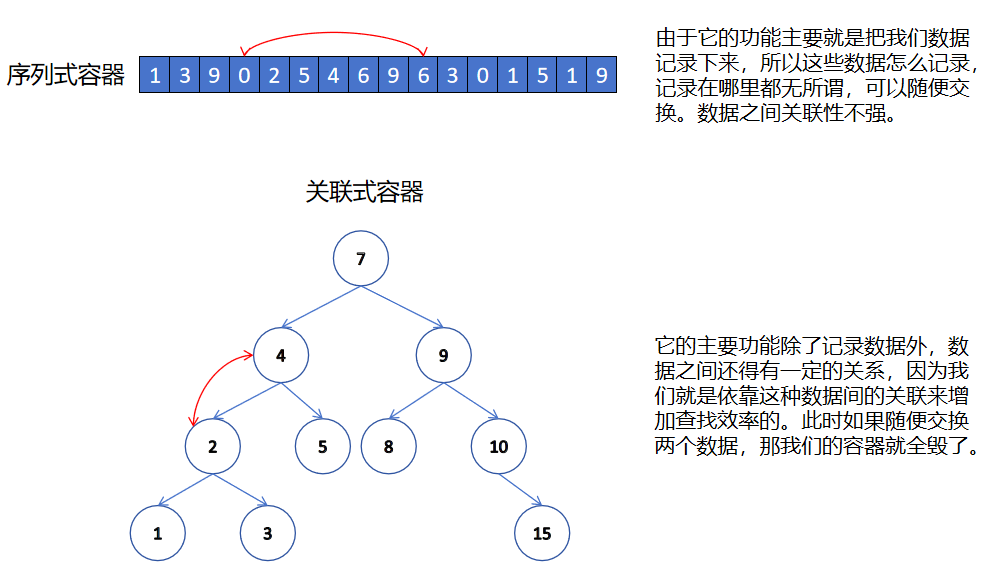
本章節所講解的 map 和 set 底層是紅黑樹,紅黑樹是一顆平衡二叉搜索樹(我們上一章節講了二叉搜索樹,明白了它的弊端,所以紅黑樹就是用來解決這種弊端的一種方法,后面會講)。set 是 key 搜索場景的結構,map 是 key/value 搜索場景的結構。
二、set 系列的使用
2.1、set 和 multiset 參考文檔
我們大家可以打開參考文檔查看:<set> - C++ Reference

2.2、set 類的介紹
set 的聲明如下,T 就是 set 底層關鍵字的類型

我們 set 就像優先級隊列一樣可以比較大小,我們上一章節也有說 set 的插入邏輯。set 默認要求 T 支持小于比較,如果不支持或者想按自己的需求走可以自行實現仿函數傳給第二個模板參數。
set 底層存儲數據的內存是從空間配置器中申請的,如果需要可以自己實現內存池,傳給第三個參數。一般情況下我們都不需要傳后兩個模板參數。
set 底層是用紅黑樹實現,增刪查的效率是 O(logN),迭代器遍歷是走的搜索樹的中序,所以是有序的。
2.3、set 的構造和迭代器
set 構造我們關注以下幾個接口即可。
1、無參的默認構造:

set<int> st1;2、迭代器區間構造

vector<int> v({ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 });
set<int> st2(v.begin() + 1, v.end() - 2);3、拷貝構造
![]()
set<int> st3(st2);4、列表構造(C++11 后才支持)
set<int> st4({ 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 });set 支持正向和反向迭代遍歷,遍歷默認按照升序順序,因為底層是二叉搜索樹,迭代器遍歷走的中序;支持迭代器就意味著支持范圍 for,set 的 iterator 和 const_iterator 都不支持迭代器修改數據,修改關鍵字數據,破壞了底層搜索樹的結構。
set<int>::iterator it = st2.begin();
set<int>::reverse_iterator rit = st4.rbegin();while (it != st2.end())
{cout << *it << " ";it++;
}cout << endl;while (rit != st4.rend())
{cout << *rit << " ";rit++;
}cout << endl;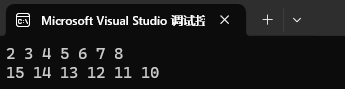
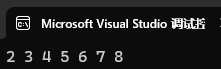
也是支持范圍 for 的。
for (auto e : st3)
{cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
2.4、set 的增刪查
set 的增刪查關注以下幾個接口即可:
增:
單個數據插入,如果已經存在則插入失敗。
![]()
這里的 value_type 其實就是把 T 封裝一下。
set<int> st1;
st1.insert(1);
st1.insert(2);
st1.insert(2);
st1.insert(4);
迭代器區間插入,已經在容器中存在的值不會插入。
![]()
vector<int> v({ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 });
set<int> st1({ 1, 2, 3 ,4 });
st1.insert(v.begin(), v.end());
列表插入,已經在容器中存在的值不會插入。
![]()
set<int> st1({ 1, 2, 3 ,4 });
st1.insert({3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8});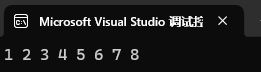
查:
查找 val,返回 val 所在的迭代器,沒有找到返回 end()。
![]()
set<int> st1({ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 });auto it = st1.find(4);
cout << *it << endl;
// 找不到就返回 end()
it = st1.find(0);
cout << *(--it) << endl;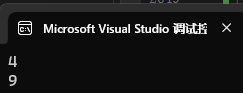
查找 val,返回 val 的個數(我們雖然 set 不能保存多個相同的數據,但是 multiset 則可以保存,這個接口主要就是給 multiset 使用的)。
![]()
set<int> st1({ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 });cout << st1.count(2) << endl;
cout << st1.count(0) << endl;
刪:
刪除一個迭代器位置的值。
![]()
set<int> st1({ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 });
set<int>::iterator it = st1.begin();
it++;
it++;
it++;st1.erase(it);for (auto e : st1)
{cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;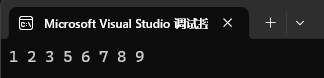
刪除 val,val 不存在返回 0,存在返回 1
![]()
set<int> st1({ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 });cout << st1.erase(5) << endl;
cout << st1.erase(100) << endl;for (auto e : st1)
{cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
刪除一段迭代器區間的值。
![]()
set<int> st1({ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 });st1.erase(++st1.begin(), --st1.end());for (auto e : st1)
{cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
我們的刪除方式和我們上一章節講解的二叉搜索樹一樣的刪除方式,所以有可能直接刪除銷毀,會導致我們的迭代器指向野指針,也有可能是交換,此時迭代器指向的內容變了,所以我們認為迭代器失效了。
我們的查詢除了 find 和 count 還有兩個之前沒有講過的函數 lower_bound 和 upper_bound。
lower_bound 的作用是返回 >= val 位置的迭代器。
![]()
set<int> st1({ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 });set<int>::iterator it = st1.lower_bound(4);while (it != st1.end())
{cout << *it << " ";++it;
}cout << endl;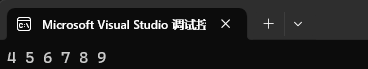
upper_bound 的作用是返回 > val 位置的迭代器。
![]()
set<int> st1({ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 });set<int>::iterator it = st1.upper_bound(4);while (it != st1.end())
{cout << *it << " ";++it;
}cout << endl;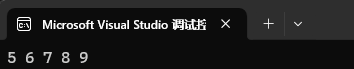
2.5、find 和 erase 使用樣例
由于我們的 set 的 find 接口返回的是一個迭代器,而 set 的 erase 支持迭代器刪除,所以我們就可以使用 find 去查找我們想要刪除的值,然后調用 erase 刪除。
int main()
{set<int> s = { 4,2,7,2,8,5,9 };int x;// 直接查找在利?迭代器刪除xcin >> x;auto pos = s.find(x);if (pos != s.end()){s.erase(pos);}else{cout << x << "不存在!" << endl;}for (auto e : s){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}2.6、multiset 和 set 的差異
multiset 和 set 使用基本完全類似,主要區別點在于 multiset 支持值冗余,那么 insert/find/count/erase 都圍繞著支持值冗余有所差異。
int main()
{// 相?set不同的是,multiset是排序,但是不去重multiset<int> s = { 4,2,7,2,4,8,4,5,4,9 };auto it = s.begin();while (it != s.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;// 相?set不同的是,x可能會存在多個,find查找中序的第?個int x;cin >> x;auto pos = s.find(x);while (pos != s.end() && *pos == x){cout << *pos << " ";++pos;}cout << endl;// 相?set不同的是,count會返回x的實際個數cout << s.count(x) << endl;// 相?set不同的是,erase給值時會刪除所有的xs.erase(x);for (auto e : s){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}三、map 系列的使用
3.1、map 和 multimap 參考文檔
我們大家可以打開參考文檔查看:map - C++ Reference;

3.2、map 類的介紹
map 的聲明如下,Key?就是 set 底層關鍵字的類型,T 就是 map 底層 value 的類型。
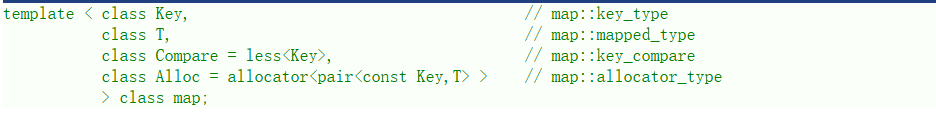
set 默認要求 Key 支持小于比較,如果不支持或者需要的話可以自行實現仿函數傳給第二個模板參數,map 底層存儲數據的內存是從空間配置器申請的。一般情況下,我們都不需要傳后兩個模板參數。map 底層是用紅黑樹實現的,增刪查改的效率是 O(logN),迭代器遍歷是走的中序,所以是按 key 有序順序遍歷的。
3.3、pair 類型介紹
![]()
這里的 pair 是一個類模板,它里面有兩個成員,分別是 first 和 second。

我們如果把 key 傳給 T1 ,value 傳給 T2 的話,那 first 就對應 key,second 就對應 value。
我們可以來看看它的底層實現。
typedef pair<const Key, T> value_type;template <class T1, class T2>
struct pair
{typedef T1 first_type;typedef T2 second_type;T1 first;T2 second;pair() : first(T1()), second(T2()){}pair(const T1& a, const T2& b) : first(a), second(b){}template<class U, class V>pair(const pair<U, V>& pr) : first(pr.first), second(pr.second){}
};template <class T1, class T2>
inline pair<T1, T2> make_pair(T1 x, T2 y)
{return (pair<T1, T2>(x, y));
}map 底層的紅黑樹結點中的數據,使用 pair<Key, T> 存儲鍵值對數據。
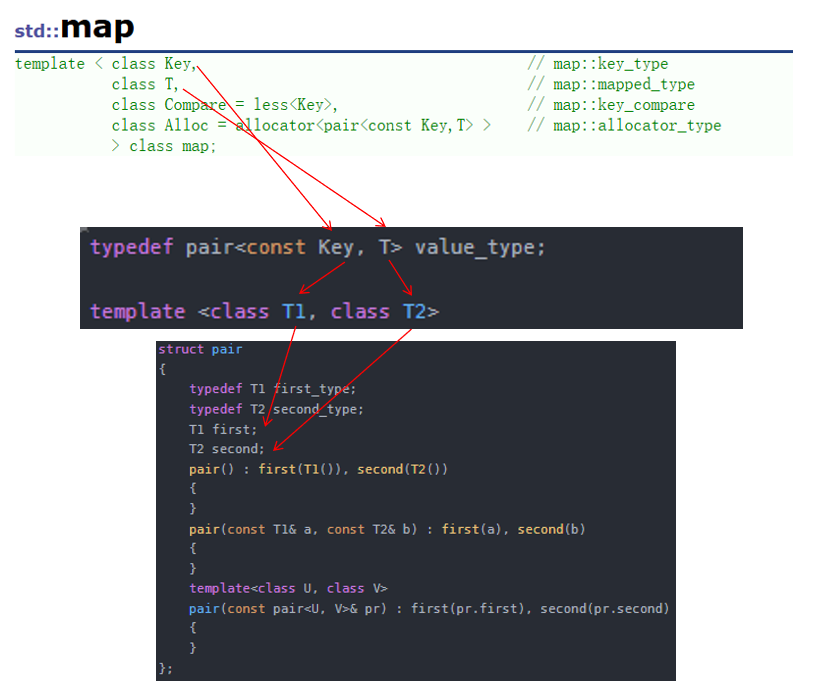
我們上一章節實現 key/value 是創建了兩個值,這里只不過是把這兩個值放在一個結構里面封裝起來了罷了。
3.4、map 的構造和迭代器
map 的構造我們關注以下幾個接口即可。
1、無參默認構造

map<int, int> mp1;2、迭代器區間構造

vector<pair<int, int>> v({ {1,1}, {2, 2}, {3, 3}, {4, 4}, {5, 5} });
map<int, int> mp2(v.begin() + 1, v.end() - 1);3、拷貝構造
![]()
map<int, int> mp3(mp2);4、列表構造
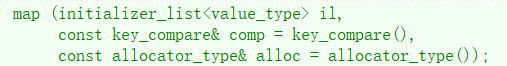
map<int, int> mp4({ {10, 10}, {11, 11}, {12, 12}, {13, 13}, {14, 14} });map 的支持正向和反向迭代遍歷,遍歷默認按 key 的升序順序,因為底層是?叉搜索樹,迭代器遍歷?的中序;?持迭代器就意味著?持范圍 for,map 支持修改 value 數據,不?持修改 key 數據,修改關鍵字數據,破壞了底層搜索樹的結構。
map<int, int>::iterator it = mp2.begin();
map<int, int>::reverse_iterator rit = mp2.rbegin();while (it != mp2.end())
{cout << it->first << " " << it->second << endl;++it;
}
cout << endl;while (rit != mp2.rend())
{cout << it->first << " " << it->second << endl;++it;
}
cout << endl;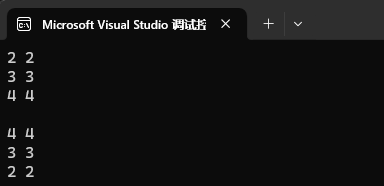
我們這里因為 map 中存儲的是一個 pair 結構,而 pair 沒有重載流輸入和流輸出,所以此時我們就得自己去實現我們的輸入和輸出,而 pair 中就兩個數據,first 和 second。我們可以使用
(*it).first、(*it).second,或者直接使用箭頭即可。
當然也是支持范圍 for 的。
for (auto e : mp4)
{cout << e.first << " " << e.second << endl;
}cout << endl;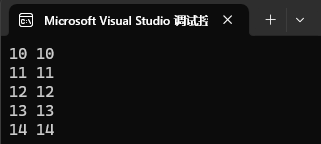
也可以試著修改 value。
map<int, int>::iterator it = mp2.begin();while (it != mp2.end())
{cout << it->first << " " << it->second << endl;++it;
}
cout << endl;it = mp2.begin();while (it != mp2.end())
{++it->second;cout << it->first << " " << it->second << endl;++it;
}
cout << endl;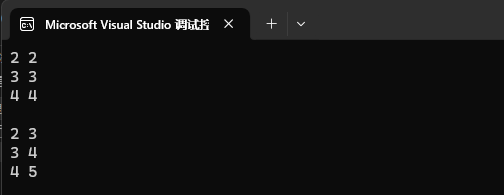
3.5、map 的增刪查
map 的增刪查關注以下幾個接口即可:
map 增的接口,插入的 pair 鍵值對數據,跟 set 所有不同,但是查和刪的接口只用關鍵字 key 跟set 是完全類似的,不過 find 返回 iterator,不僅僅可以確認 key 在不在,還找到 key 映射的 value,同時通過迭代還可以修改 value。
增:
1、單個數據插入,如果已經 key 存在則插?失敗,key 存在相等 value 不相等也會插?失敗。
![]()
map<int, int> mp1;
pair<int, int> kv1 = { 3, 2 };
pair<int, int> kv2 = { 4, 1 };mp1.insert(pair<int, int>( 1, 1 ));
mp1.insert(pair<int, int>( 2, 1 ));
mp1.insert(pair<int, int>( 2, 1 ));
mp1.insert(pair<int, int>( 3, 1 ));
mp1.insert(kv1);
mp1.insert(kv2);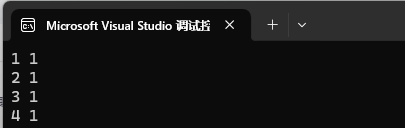
我們的 pair 就和對象一樣直接調用即可。只輸出了 4 個值,只要 key 相同就只會插入第一次出現的那個 key/value。但是我們這樣調用十分的麻煩,不是特別方便,所以我們引入了一個make_pair。
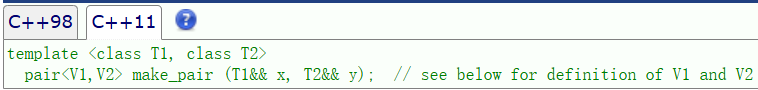
有了這個類型,我們可以直接把 key 和 value 傳給 map, 它會自動推導類型,推導成功后構造一個 pair 進行返回。

map<int, int> mp1;
mp1.insert(make_pair(1, 1));
mp1.insert(make_pair(2, 1));
mp1.insert(make_pair(2, 1));
mp1.insert(make_pair(3, 1));
mp1.insert(make_pair(3, 2));
mp1.insert(make_pair(4, 1));C++11 后支持多參數的隱式類型轉換,此時我們便支持這種方式了。
map<int, int> mp1;
mp1.insert({ 1, 1 });
mp1.insert({ 2, 1 });
mp1.insert({ 2, 1 });
mp1.insert({ 3, 1 });
mp1.insert({ 3, 2 });
mp1.insert({ 4, 1 });2、列表插入,已經在容器中存在的值不會插入。
![]()
map<int, int> mp1;
mp1.insert({ {1, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 3}, {2, 3}, {3, 3}, {4, 3} });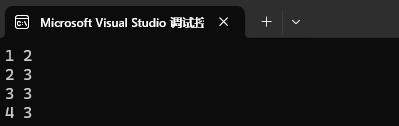
3、迭代器區間插入,已經在容器中存在的值不會插入。
![]()
map<int, int> mp1;
mp1.insert({ {1, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 3}, {2, 3}, {3, 3}, {4, 3} });
vector<pair<int, int>> v({ {1, 3}, {10, 2}, {3, 7}, {5, 10}, {100, 1} });
mp1.insert(v.begin(), v.end());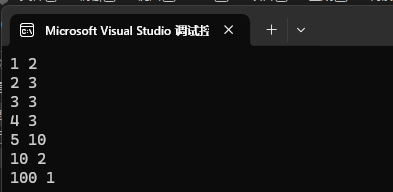
查:
1、查找k,返回k所在的迭代器,沒有找到返回end()。
![]()
map<int, int> mp1;
mp1.insert({ {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 4}, {4, 5}, {5, 6}, {6, 7} });auto it1 = mp1.find(2);
cout << it1->first << " " << it1->second << endl;
auto it2 = mp1.find(9);
it2--;
cout << it2->first << " " << it2->second << endl;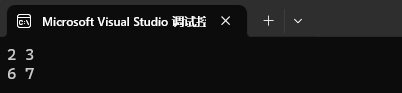
2、查找k,返回k的個數。
![]()
map<int, int> mp1;
mp1.insert({ {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 4}, {4, 5}, {5, 6}, {6, 7} });auto it1 = mp1.count(2);
cout << it1 << endl;
auto it2 = mp1.count(9);
cout << it2 << endl;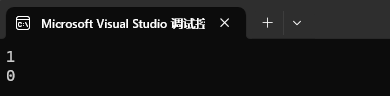
刪:
1、刪除?個迭代器位置的值。
![]()
map<int, int> mp1;
mp1.insert({ {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 4}, {4, 5}, {5, 6}, {6, 7} });map<int, int>::iterator it = mp1.begin();
it++;
it++;
it++;
mp1.erase(it);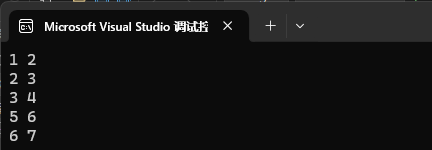
2、刪除k,k存在返回0,存在返回1。
![]()
map<int, int> mp1;
mp1.insert({ {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 4}, {4, 5}, {5, 6}, {6, 7} });cout << mp1.erase(2) << endl;
cout << mp1.erase(100) << endl;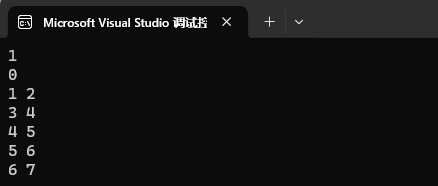
3、刪除?段迭代器區間的值。
![]()
map<int, int> mp1;
mp1.insert({ {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 4}, {4, 5}, {5, 6}, {6, 7} });mp1.erase(++mp1.begin(), --mp1.end());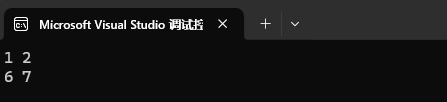
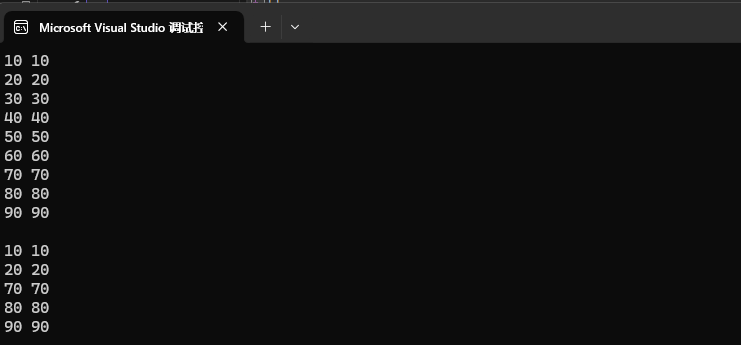
我們 map 也有 lower_bound 和 upper_bound 這兩個接口。和我們的 set 的功能是一樣的,也是比較 key,查找大于或大于等于 key 的所有值。


int main()
{map<int, int> mp;for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)mp.insert({ i * 10, 1 }); // 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90for (auto e : mp){cout << e.first << " " << e.first << endl;}cout << endl;// 實現查找到的[itlow,itup)包含[30, 60]區間// 返回 >= 30auto itlow = mp.lower_bound(30);// 返回 > 60auto itup = mp.upper_bound(60);// 刪除這段區間的值mp.erase(itlow, itup);for (auto e : mp){cout << e.first << " " << e.first << endl;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
3.6、map 的數據修改
- 前?我提到 map 支持修改 mapped_type 數據,不支持修改 key 數據,修改關鍵字數據,破壞了底層搜索樹的結構。
- map 第?個支持修改的方式是通過迭代器,迭代器遍歷時或者 find 返回 key 所在的 iterator 修改,map 還有?個?常重要的修改接口 operator[ ],但是 operator[ ] 不僅僅支持修改,還?持插?數據和查找數據,所以他是?個多功能復合接口。
- 需要注意從內部實現?度,map 這?把我們傳統說的 value 值,給的是 T 類型,typedef 為mapped_type。? value_type 是紅?樹結點中存儲的 pair 鍵值對值。?常使?我們還是習慣將這?的 T 映射值叫做 value。
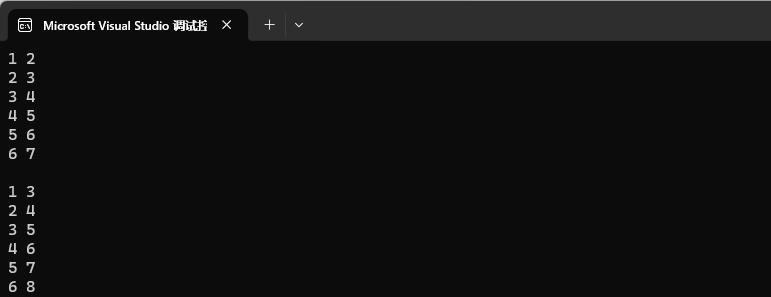
我們迭代器修改只能對 pair 的第二個值 value 進行修改,不能對第一個值進行修改。
int main()
{map<int, int> mp1;mp1.insert({ {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 4}, {4, 5}, {5, 6}, {6, 7} });for (auto e : mp1){cout << e.first << " " << e.second << endl;}cout << endl;map<int, int>::iterator it = mp1.begin();while (it != mp1.end()){(it->second)++;cout << it->first << " " << it->second << endl;it++;}return 0;
}
我們 operator[ ] 函數,如果 [ ] 中的 key 值存在的話,那就是修改。
map<int, int> mp1;
mp1.insert({ {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 4}, {4, 5}, {5, 6}, {6, 7} });mp1[2] = 200;
mp1[3] = 300;
mp1[4] = 400;
mp1[5] = 500;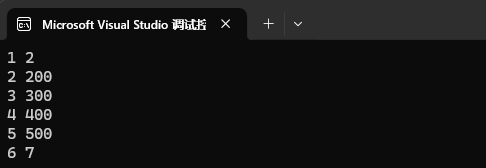
如果 [ ] 中的 key 值不存在的話,那就是插入。
map<int, int> mp1;
mp1.insert({ {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 4}, {4, 5}, {5, 6}, {6, 7} });mp1[10] = 2;
mp1[20] = 3;
mp1[30] = 4;
mp1[40] = 5;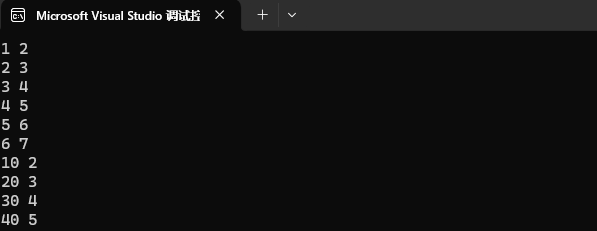
3.7、map 的迭代器和 [ ] 功能樣例
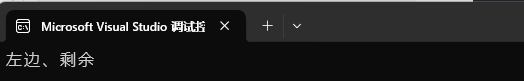
1、
using namespace std;
int main()
{map<string, string> dict;dict.insert(make_pair("sort", "排序"));// key不存在->插? {"insert", string()}dict["insert"];// 插?+修改dict["left"] = "左邊";// 修改dict["left"] = "左邊、剩余";// key存在->查找cout << dict["left"] << endl;return 0;
}
2、
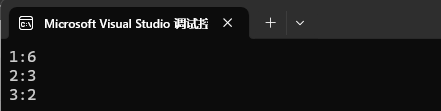
int main()
{// 利?find和iterator修改功能,統計數字出現的次數string arr[] = { "1", "2", "1", "2", "1", "1", "2","1", "3", "1", "3" };map<string, int> countmap;for (const auto& str : arr){// 先查找數字在不在map中// 1、不在,說明數字第?次出現,則插?{數字, 1}// 2、在,則查找到的節點中數字對應的次數++auto ret = countmap.find(str);if (ret == countmap.end()){countmap.insert({ str, 1 });}else{ret->second++;}}for (const auto& e : countmap){cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
3.8、multimap 和 map 的差異
multimap 和 map 的使用基本完全類似,主要區別點在于 multimap 支持關鍵值 key 冗余,那insert/find/count/erase 都圍繞著支持關鍵值 key 冗余有所差異,這?跟 set 和 multiset 完全?樣,比如 find 時,有多個 key,返回中序第?個。其次就是 multimap 不支持 [ ],因為支持 key 冗余, [ ] 就只能支持插入了,不能支持修改。
總結
以上便是 map/set 的主要內容學習,在看的時候可以和上一章節的內容進行結合,因為 map/set 的底層的主體就是二叉搜索樹,我們可以通過對上一章節的了解來更加深刻的理解我們 map/set 的各種接口的實現。下一章節將會講解我們的 map/set 的模擬實現,我們下一章節再見。
🎇堅持到這里已經很厲害啦,辛苦啦🎇
? ? ? ? ?
づ?ど





)
從語言模型到通用智能體)




刀具分配問題詳解)


哨兵模式與集群模式有何區別?)





