B. Meeting on the Line
題目: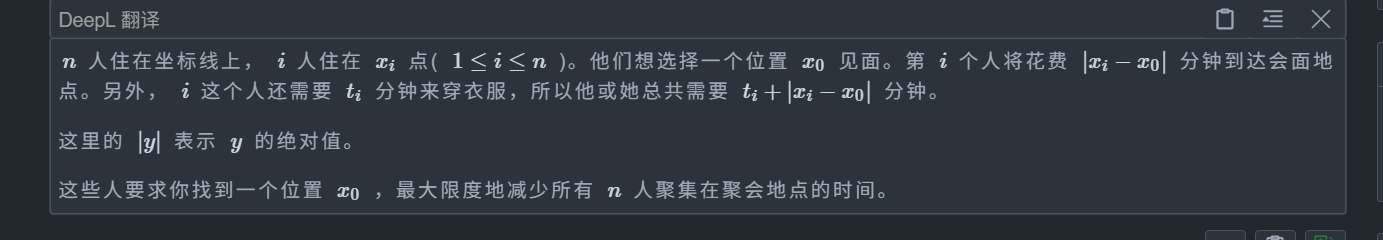
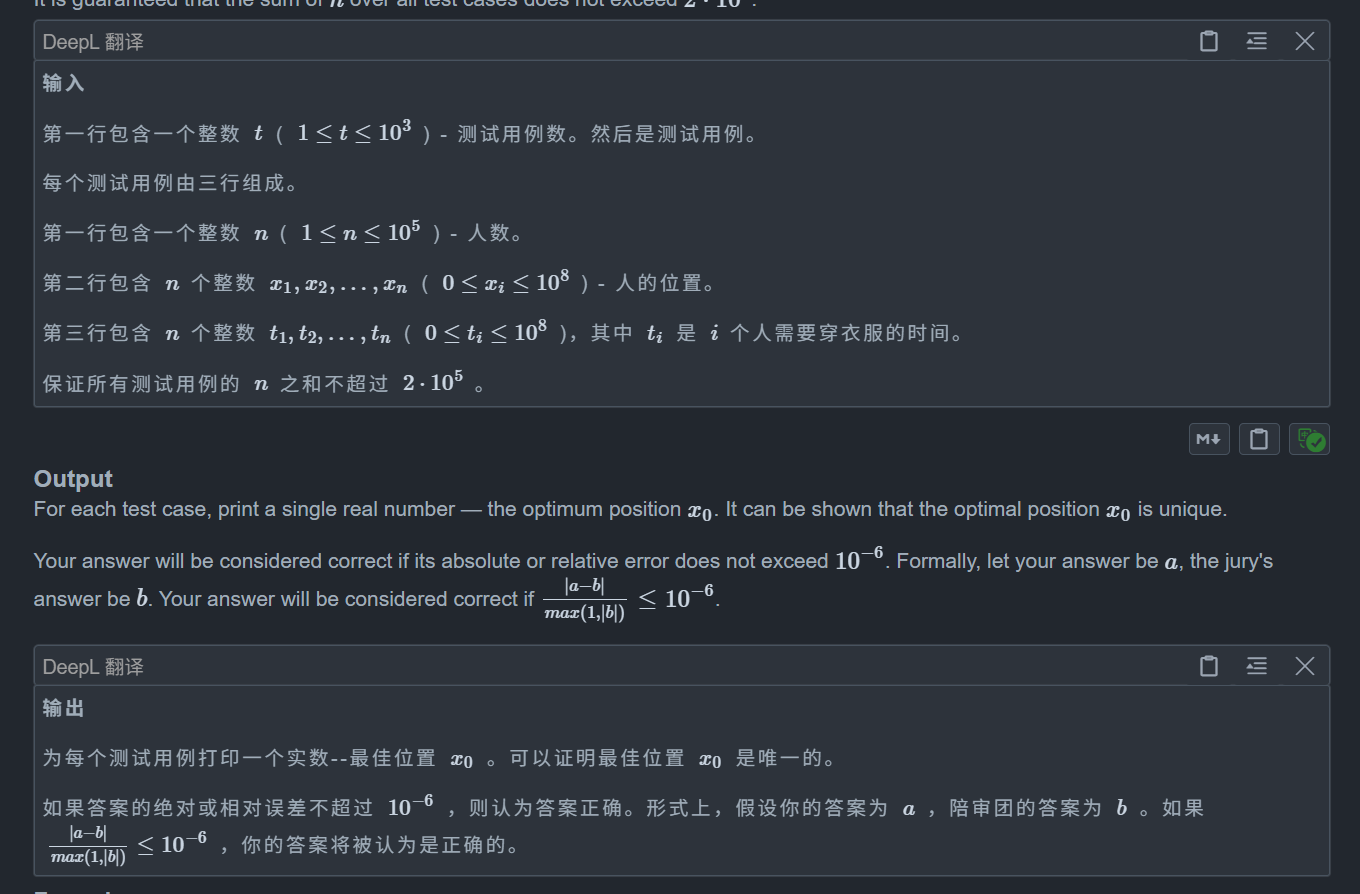 思路:
思路:
數形結合
首先考慮如果沒有 t 的影響該怎么寫
顯然我們就是讓最大時間最小化,那么顯然選擇最左端點和最右端點的中間值即可,即 (mi + mx) / 2,那么現在有了 t 該怎么辦
我們不妨考慮拆開絕對值,由 |a - b| = max(a-b, b-a) 可得原式 t - |x - x0| 拆解為
max(t - (x - x0), t - (x0 - x)) = max(t - x + x0, t + x - x0) = max(x0 - (x - t), (t + x) - x0)
我們令 x-t 和 t+x 為兩個新點,那么顯然 x-t 在 x0 左邊,t+x 在 x0 右邊,所以我們找到最大的右端點和最小的左端點即可,這就是我們上面的普通情況
除此之外,我們可以還能使用二分or三分
代碼:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES\n"
#define no cout << "NO\n"
mt19937 rnd(chrono::steady_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count());void solve()
{int n;cin >> n;vector<int> a(n + 1), t(n + 1);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> a[i];for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> t[i];int mx = -1e18, mi = 1e18;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){mx = max(mx, a[i] + t[i]);mi = min(mi, a[i] - t[i]);}double res = (mx + mi) * 1.0 / 2.0;printf("%.6lf\n", res);
}signed main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);int t = 1;cin >> t;while (t--){solve();}return 0;
}C1. Sheikh (Easy version)
題目:
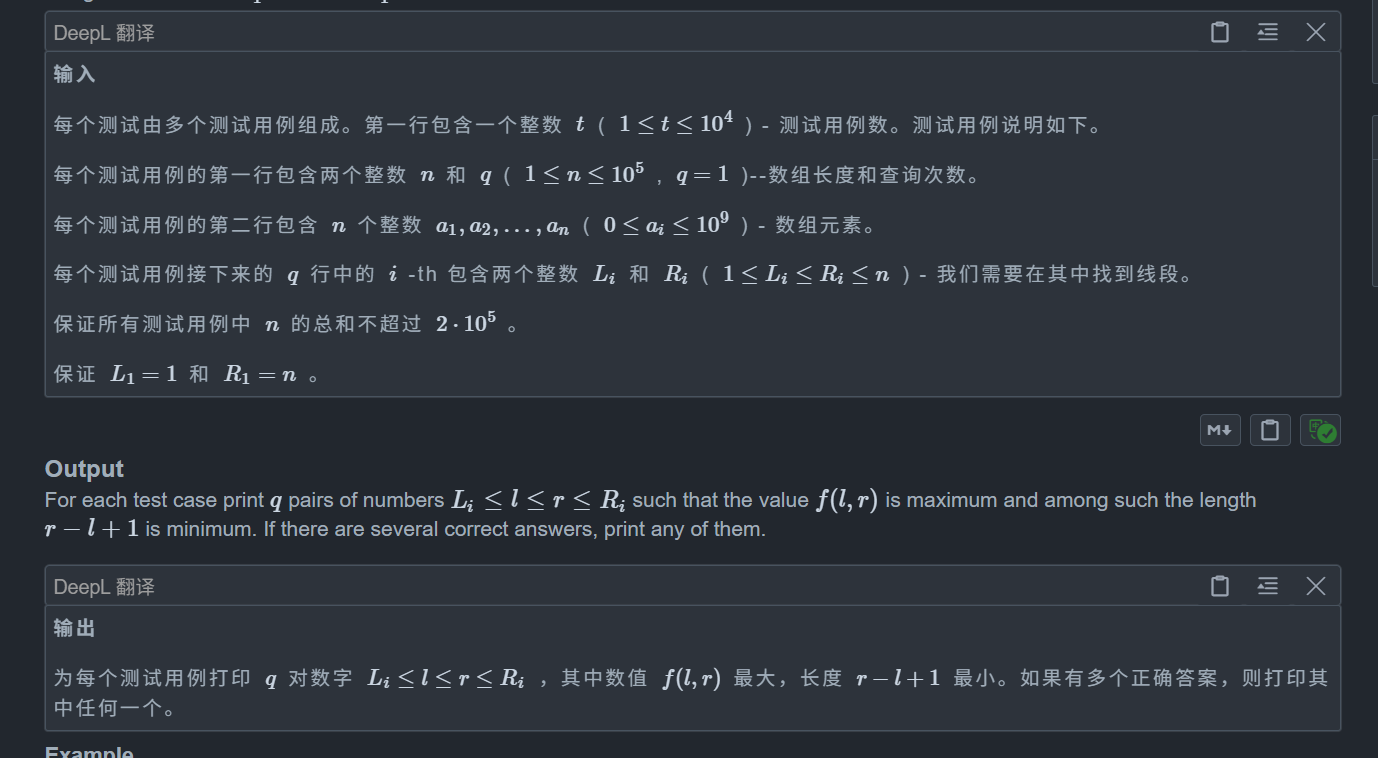 思路:
思路:
異或性質
這題看似無從下手,但是我們關鍵點在于發現異或的性質,不難發現一個特點,異或是不帶進位的加法,那么對于任意 x,y,我們都有 x+y >= x ^ y,這是顯然的
那么我們就豁然開朗了,既然 x+y >= x ^ y,那么對于一個區間我們肯定是多加數的,因為 x+y - x^y >= 0 恒成立,所以多加顯然是不劣的
那么最大值顯然就是選取整個區間,但是題目讓我們輸出最小的長度,所以考慮如何最小
顯然由上訴結論可知,我們區間長度越長,那么值就越大,這是單調的,所以我們考慮二分區間長度,我們枚舉每一個左端點,然后二分最大長度即可
特別注意預處理前綴和即可,還有越界問題
代碼:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES\n"
#define no cout << "NO\n"
mt19937 rnd(chrono::steady_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count());void solve()
{int n,q;cin >> n >> q;vector<int> a(n+1),sum(n+1,0),sumxor(n+1,0);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){cin >> a[i];sum[i] = sum[i-1] + a[i];sumxor[i] = sumxor[i-1] ^ a[i];}cin >> q >> q;int mx = sum[n] - sumxor[n];auto check = [&](int l,int len)->int{int r = min(l + len - 1,n);int nmx = (sum[r] - sum[l-1]) - (sumxor[r] ^ sumxor[l-1]);return nmx >= mx;};int le = 1e18;int mxl = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){int l = 1,r = 1e18;while (l+1 < r){int mid = l+r >> 1;if(check(i,mid)){r = mid;}else{l = mid;}}int templen = 0;if(check(i,l)) templen = l;else templen = r;if(templen < le){le = templen;mxl = i;}}cout << mxl << " " << mxl + le - 1 << endl;
}signed main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);int t = 1;cin >> t;while (t--){solve();}return 0;
}E. Guess the Cycle Size
題目:
 思路:
思路:
隨機數據的特征
注意到題目數據隨機,那么可以考慮稍微暴力的做法
我們假設對于 a,b 點對進行詢問,如果 a,b 和 b,a 的詢問結果不同,那么顯然二者相加就是答案
但是由于 a,b 和 b,a 的詢問結果不同,因此我們要多次判斷,可以發現 50 次內基本上不可能會錯,如果擔心錯的話可以在代碼結尾加上 while(1) 使得其超時,因為TLE 會重測 3 次,3 次全錯肯定不可能
最后特別注意特判 -1 情況即可
代碼:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES\n"
#define no cout << "NO\n"
mt19937 rnd(chrono::steady_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count());void solve()
{int ans1, ans2;for (int i = 2; i <= 1e18; i++){cout << "? " << 1 << " " << i << endl;cin >> ans1;if (ans1 == -1){cout << "! " << i - 1 << endl;return;}cout << "? " << i << " " << 1 << endl;cin >> ans2; if(ans1 != ans2){cout << "! " << ans1 + ans2 << endl;return;} }while (1);
}signed main()
{int t = 1;while (t--){solve();}return 0;
}




)







)


 詳細指南)


