續接上一話:
目錄
一、ArrayList的使用(續)
1、ArrayList的擴容機制(續)
?五、ArrayList的相關練習
1、楊輝三角
2、簡單的洗牌算法
六、ArrayList的問題及思考
一、ArrayList的使用(續)
1、ArrayList的擴容機制(續)
????????ArrayList是一個動態類型的順序表,即:在插入元素的過程中會自動擴容。以下是ArrayList源碼中擴容方式:
Object[] elementData; // 存放元素的空間private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 默認空間private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; // 默認容量大小public boolean add(E e) {ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!elementData[size++] = e;return true;}private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));}private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);}return minCapacity;}private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {modCount++;// overflow-conscious codeif (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)grow(minCapacity);}private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;private void grow(int minCapacity) {// 獲取舊空間大小int oldCapacity = elementData.length;// 預計按照1.5倍方式擴容int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);// 如果用戶需要擴容大小 超過 原空間1.5倍,按照用戶所需大小擴容if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)newCapacity = minCapacity;// 如果需要擴容大小超過MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,重新計算容量大小if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);// 調用copyOf擴容elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);}private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {// 如果minCapacity小于0,拋出OutOfMemoryError異常if (minCapacity < 0)throw new OutOfMemoryError();return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;}總結:
(1)檢測是否真正需要擴容,如果是調用grow準備擴容
(2)預估需要庫容的大小
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 初步預估按照1.5倍大小擴容
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 如果用戶所需大小超過預估1.5倍大小,則按照用戶所需大小擴容
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 真正擴容之前檢測是否能擴容成功,防止太大導致擴容失敗
(3)使用copyOf進行擴容
?五、ArrayList的相關練習
1、楊輝三角
(118. 楊輝三角 - 力扣(LeetCode))
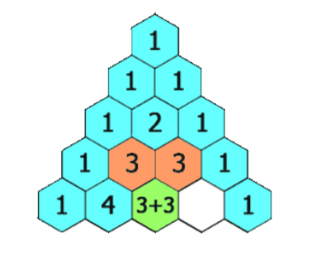
????????分析:
 ? ?
? ?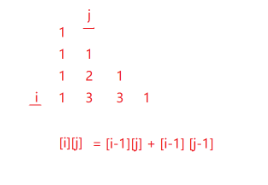
? ? ? ? 這里就是外側全是1,其他的分別是上面緊挨著的兩個的加和。但是,顯然我們不能像左圖一樣創建順序表,可以轉換成如右圖所示的樣式!!!如右圖,最外側都為1,若位置為(i,j),則[i][j] = [i-1][j] + [i-1][j-1]
? ? ? ? 因此,我們創建一個空列表ret,用來存儲所有的行(每行是一個整數列表)。
? ? ? ? 先處理第一行,元素為1;再循環生成一共numRows行,將每行的第一個元素添加為1。????????
? ? ? ? 利用上一行計算中間元素,最后添加上尾巴(1)。
class Solution {public static List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> list0 = new ArrayList<>();list0.add(1);ret.add(list0);//從第2行開始 進行求每個元素for (int i = 1; i < numRows; i++) {//處理第一個元素List<Integer> curRow = new ArrayList<>();curRow.add(1);//中間List<Integer> preRow = ret.get(i-1);for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {int val1 = preRow.get(j);int val2 = preRow.get(j-1);curRow.add(val1+val2);}//尾巴curRow.add(1);ret.add(curRow);}return ret;}
}2、簡單的洗牌算法
(一副新牌,四種花色(?,?,?,?),數值分別為1--13,經過一系列的洗牌之后,分別發給三個人每人5張(輪流抓牌),最后展示剩余牌和三人手里的牌)
public class Card {private String suit;//花色private int rank; //牌面值public Card(String suit, int rank) {this.suit = suit;this.rank = rank;}@Overridepublic String toString() {/*return "Card{" +"suit='" + suit + '\'' +", rank=" + rank +'}';*/return String.format("[%s %d]", suit, rank);}
}import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Random;public class CardDemo {public static final String[] suits = {"?","?","?","?"};//買來一副新牌public List<Card> buyCard() {List<Card> cardList = new ArrayList<>(52);for (int i = 1; i <= 13; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {int rank = i;String suit = suits[j];Card card = new Card(suit,rank);cardList.add(card);}}return cardList;}//洗牌public void shuffle(List<Card> cardList) {Random random = new Random();for (int i = cardList.size()-1; i > 0 ; i--) {int index = random.nextInt(i);swap(cardList,i,index);}}private void swap(List<Card> cardList,int i,int j) {/*Card tmp = cardList[i];cardList[i] = cardList[j];cardList[j] = tmp;*/Card tmp = cardList.get(i);cardList.set(i,cardList.get(j));cardList.set(j,tmp);}//分別發牌public List<List<Card>> play(List<Card> cardList) {List<Card> hand0 = new ArrayList<>();List<Card> hand1 = new ArrayList<>();List<Card> hand2 = new ArrayList<>();List<List<Card>> hand = new ArrayList<>();hand.add(hand0);hand.add(hand1);hand.add(hand2);for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {Card card = cardList.remove(0);//怎么把對應的牌 放到對應的人的手里面hand.get(j).add(card);}}return hand;}
}import java.util.*;
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {CardDemo cardDemo = new CardDemo();//1. 買52張牌List<Card> cardList = cardDemo.buyCard();System.out.println("剛買回來的牌:");System.out.println(cardList);//2. 洗牌cardDemo.shuffle(cardList);System.out.println("洗過的牌:");System.out.println(cardList);//3. 3個人每個人輪流發牌5張List<List<Card>> ret = cardDemo.play(cardList);for (int i = 0; i < ret.size(); i++) {System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"個人的牌:"+ret.get(i));}System.out.println("剩下的牌:");System.out.println(cardList);}運行程序可以得到類似的運行結果:
剛買回來的牌:
[[? 1], [? 2], [? 3], [? 4], [? 5], [? 6], [? 7], [? 8], [? 9], [? 10], [? 11], [? 12], [? 13], [? 1], [? 2], [? 3], [? 4], [? 5], [? 6], [? 7],
[? 8], [? 9], [? 10], [? 11], [? 12], [? 13], [? 1], [? 2], [? 3], [? 4], [? 5], [? 6], [? 7], [? 8], [? 9], [? 10], [? 11], [? 12], [?
13], [? 1], [? 2], [? 3], [? 4], [? 5], [? 6], [? 7], [? 8], [? 9], [? 10], [? 11], [? 12], [? 13]]
洗過的牌:
[[? 11], [? 6], [? 13], [? 10], [? 13], [? 2], [? 1], [? 9], [? 12], [? 5], [? 8], [? 6], [? 3], [? 5], [? 1], [? 6], [? 13], [? 12], [? 12],
[? 5], [? 4], [? 3], [? 7], [? 3], [? 2], [? 1], [? 2], [? 4], [? 8], [? 10], [? 11], [? 10], [? 7], [? 9], [? 4], [? 8], [? 7], [? 8], [? 9], [?
12], [? 11], [? 11], [? 10], [? 5], [? 13], [? 9], [? 7], [? 6], [? 4], [? 2], [? 1], [? 3]]
第1個人的牌:[[? 11], [? 10], [? 1], [? 5], [? 3]]
第2個人的牌:[[? 6], [? 13], [? 9], [? 8], [? 5]]
第3個人的牌:[[? 13], [? 2], [? 12], [? 6], [? 1]]
剩下的牌:
[[? 6], [? 13], [? 12], [? 12], [? 5], [? 4], [? 3], [? 7], [? 3], [? 2], [? 1], [? 2], [? 4], [? 8], [? 10], [? 11], [? 10], [? 7], [? 9], [?
4], [? 8], [? 7], [? 8], [? 9], [? 12], [? 11], [? 11], [? 10], [? 5], [? 13], [? 9], [? 7], [? 6], [? 4], [? 2], [? 1], [? 3]]六、ArrayList的問題及思考
1. ArrayList底層使用連續的空間,任意位置插入或刪除元素時,需要將該位置后序元素整體往前或者往后搬 移,故時間復雜度為O(N)
解決方案:
????????使用LinkedList:鏈表結構插入刪除時間復雜度為O(1)
????????分段數組:將大數組分成多個小數組塊
????????樹狀數組:使用樹形結構維護數據
鏈表+數組組合(Unrolled Linked List)
class Chunk {private static final int CHUNK_SIZE = 64;private Object[] data;private int size;private Chunk next;// 插入刪除只在當前chunk內搬移數據// 大大減少數據移動量
}2. 增容需要申請新空間,拷貝數據,釋放舊空間。會有不小的消耗。
解決方案:
????????預分配策略:根據業務場景預估容量
????????增量式擴容:每次只擴容部分空間
????????內存池技術:預先申請大塊內存
????????使用鏈表結構:完全避免擴容問題
3. 增容一般是呈2倍的增長,勢必會有一定的空間浪費。例如當前容量為100,滿了以后增容到200,我們再繼 續插入了5個數據,后面沒有數據插入了,那么就浪費了95個數據空間。
解決方案:
????????更合理的擴容因子:1.5倍或其他經驗值
????????縮容機制:當空間利用率低于閾值時自動縮容
????????彈性數組:動態調整容量
????????內存碎片整理:定期整理內存空間
彈性數組(彈性擴容因子)
class ElasticArrayList<T> {private static final double GROW_FACTOR = 1.5;private static final double SHRINK_THRESHOLD = 0.3;private Object[] elementData;private int size;// 根據使用情況動態調整擴容因子private int calculateNewCapacity(int minCapacity) {if (size < 1000) return (int)(size * 1.8);else if (size < 10000) return (int)(size * 1.5);else return (int)(size * 1.2);}// 自動縮容機制public void trimToUsage() {if (size < elementData.length * SHRINK_THRESHOLD) {elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);}}
}![[Vid-LLM] docs | 視頻理解任務](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Vid-LLM] docs | 視頻理解任務)

![[Java惡補day51] 46. 全排列](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Java惡補day51] 46. 全排列)



)







-理解筆記3)




