類設計原則:
- 單一職責原則(Single?Responsibility?Principle,SRP):實現類要職責單一
- 開閉原則(Open?Close?Principle,OCP):對擴展開放,對修改關閉
- 里氏替換原則(Liskov?Substitution?Principle,LSP):不要破壞繼承體系
- 接口隔離原則(Interface?Segregation?Principle,ISP):設計接口的時候要精簡單一
- 依賴倒置原則(Dependence?Inversion?Principle,DIP):面向接口編程
- 迪米特法則(Law?Of?Demeter):降低耦合
1. 類設計原則
(1)單一職責原則
(Single?Responsibility?Principle,SRP)
原則定義:應該有且僅有一個原因引起類的變更
原則描述:
- 問題由來:類T負責兩個不同的職責,即職責P1,職責P2。當由于職責P1需求發生改變而需要修改類T時,有可能會導致原本運行正常的職責P2功能發生故障
- 解決方案:遵循單一職責原則。分別建立兩個類T1、T2,使T1完成職責P1功能,T2完成職責P2功能。這樣,當修改類T1、T2時,不會使P1、P2相互影響

使用單一職責原則之前:?
public interface IHuman {//身高void setShengao(double height);double getShengao();//體重void setTizhong(double weight);double getTizhong();//吃飯boolean chiFan(boolean hungry);//上網boolean shangWang(boolean silly);
}public class Human implements IHuman {private double height;private double weight;@Overridepublic double getShengao() { return height;}@Overridepublic double getTizhong() {return weight;}@Overridepublic void setShengao(double height) {this.height = height;}@Overridepublic void setTizhong(double weight) {this.weight = weight;}@Overridepublic boolean chiFan(boolean hungry) {if(hungry){System.out.println("去吃火鍋...");return true;}return false;}@Overridepublic boolean shangWang(boolean silly) {if(silly){System.out.println("好無聊啊,上會網...");return true;}return false;}}?使用單一職責原則之后:
public interface IHumanBO {//身高void setShengao(double height);double getShengao();//體重void setTizhong(double weight);double getTizhong();
}public interface IHumanBL {//吃飯boolean chiFan(boolean hungry);//上網boolean shangWang(boolean silly);
}public class HumanBO implements IHumanBO {private double height;private double weight;@Overridepublic double getShengao() { return height;}@Overridepublic double getTizhong() {return weight;}@Overridepublic void setShengao(double height) {this.height = height;}@Overridepublic void setTizhong(double weight) {this.weight = weight;}}public class HumanBL implements IHumanBL {@Overridepublic boolean chiFan(boolean hungry) {if(hungry){System.out.println("去吃火鍋...");return true;}return false;}@Overridepublic boolean shangWang(boolean silly) {if(silly){System.out.println("好無聊啊,上會網...");return true;}return false;}}(2)開閉原則
(Open?Close?Principle,OCP)
原則定義:一個軟件實體如類、模塊和函數應該對擴展開放,對修改關閉
原則描述:
- 問題由來:對軟件原有代碼進行修改時,可能會給舊代碼中引入錯誤
- 解決方案:當軟件需要變化時,盡量通過擴展軟件實體的行為來實現變化,而不是通過修改已有的代碼來實現變化
?

使用開閉原則前:?
public interface IFindGirl {//年齡public int getAge();//姓名public String getName();
}public class FindGirl implements IFindGirl {private String name;private int age;public FindGirl(String name, int age){this.name = name;this.age = age;}@Overridepublic int getAge() {return age;}@Overridepublic String getName() {return name;}
}public class Main {private final static ArrayList<IFindGirl> girls = new ArrayList<IFindGirl>();//靜態初始化塊static{girls.add(new FindGirl("A",23));girls.add(new FindGirl("B",33));girls.add(new FindGirl("C",19));}public static void main(String args[]){for(IFindGirl girl:girls){System.out.println("姓名:"+girl.getName()+" 年齡:"+girl.getAge());}}
}?使用開閉原則后:
public interface IFindGirl {//年齡public int getAge();//姓名public String getName();
}public interface IForeigner extends IFindGirl {//國籍public String getCountry();
}public class ForeignerGirl implements IForeigner {private String name;private int age;private String country;public ForeignerGirl(String name, int age, String country){this.name = name;this.age = age;this.country = country;}@Overridepublic String getCountry() {return country;}@Overridepublic int getAge() {return age;}@Overridepublic String getName() {return name;}}public class Main {private final static ArrayList<IForeigner> girls = new ArrayList<IForeigner>();static{girls.add(new ForeignerGirl("A",23, "USA"));girls.add(new ForeignerGirl("B",33, "Japan"));girls.add(new ForeignerGirl("C",19, "England"));}//靜態初始化塊public static void main(String args[]){System.out.println("----------美女在這里----------");for(IForeigner girl:girls){System.out.println("姓名:"+girl.getName()+" 年齡:"+girl.getAge() + " 國籍:"+girl.getCountry());}}
}(3)里氏替換原則
(Liskov?Substitution?Principle,LSP)
繼承的三大問題:
①?代碼侵入性:只要繼承,就必須擁有父類的所有屬性和方法
② 降低代碼的靈活性:子類必須擁有父類的屬性和方法,讓子類自由的世界中多了些約束
③?增強耦合性:當父類的常量、變量和方法被修改時,必須要考慮子類的修改,而且在缺乏規范的環境下,這種修改可能帶來非常糟糕的結果:大片的代碼需要重構
原則定義:所有引用基類的地方必須能透明地使用其子類的對象
原則描述:
- 問題由來:有一功能P1,由類A完成。現需要將功能P1進行擴展,擴展后的功能為P,其中P由原有功能P1與新功能P2組成。新功能P2由類A的子類B來完成,則子類B在完成新功能P2的同時,有可能會導致原有功能P1發生故障
- 解決方案:當使用繼承時,遵循里氏替換原則。類B繼承類A時,除添加新的方法完成新增功能P2外,盡量不要重寫父類A的方法,也盡量不要重載父類A的方法
?
輸入:
public class Father {public Collection say(HashMap map) {//HashMapSystem.out.println("父類被執行...");return map.values();}
}public class Son extends Father {//方法輸入參數類型public Collection say(Map map){System.out.println("子類被執行...");return map.values();}
}public class Home {public static void main(String args[]){invoke();}public static void invoke(){//父類存在的地方,子類就應該能夠存在Father f = new Father();Son s = new Son();HashMap hashMap = new HashMap(); Map map = new HashMap();//HashMap是Map的子類f.say(hashMap);s.say(map);}
}運行結果:

輸出:
public abstract class Father {public abstract Map say();
}public class Son extends Father {@Overridepublic HashMap say() {HashMap h = new HashMap();h.put("h", "執行子類...");return h;}}public class Home {public static void main(String args[]){invoke();}public static void invoke(){Father f = new Son();System.out.println(f.say());}
}運行結果:
![]()
代碼示例要點:當子類覆蓋或實現父類的方法時,方法的前置條件(即方法的形參)要比父類方法的輸入參數更寬松;當子類的方法實現父類的抽象方法時,方法的后置條件(即方法的返回值)要比父類更嚴格
實現注意點:子類的所有方法必須在父類中聲明,或子類必須實現父類中聲明的所有方法;盡量把父類設計為抽象類或者接口,讓子類繼承父類或實現父接口,并實現在父類中聲明的方法;盡量避免子類重寫父類的方法
?
(4)接口隔離原則
(Interface?Segregation?Principle,ISP)
原則定義:客戶端不應該依賴它不需要的接口;一個類對另一個類的依賴應該建立在最小的接口上
原則描述:
- 問題由來:類A通過接口I依賴類B,類C通過接口I依賴類D,如果接口I對于類A和類B來說不是最小接口,則類B和類D必須去實現他們不需要的方法
- 解決方案:將臃腫的接口I拆分為獨立的幾個接口,類A和類C分別與他們需要的接口建立依賴關系
?
public interface IPrettyGirl {//長相好public void greatLooks();//好身材public void greatFigure();//氣質佳public void greatTemperament();
}public class PrettyGirl implements IPrettyGirl {private String name;//構造函數,美女名字public PrettyGirl(String name){this.name = name;}//好身材@Overridepublic void greatFigure() {System.out.println(name+":身材非常好");}//好長相@Overridepublic void greatLooks() {System.out.println(name+":長相非常好");}//好氣質@Overridepublic void greatTemperament() {System.out.println(name+":氣質非常好");}}public abstract class AMan {protected IPrettyGirl prettyGirl;public AMan(IPrettyGirl prettyGirl){this.prettyGirl = prettyGirl;}//帥哥開始找美女啦public abstract void findGirl();
}public class Man extends AMan {public Man(IPrettyGirl prettyGirl) {super(prettyGirl);}@Overridepublic void findGirl() {System.out.println("美女在這里:----------------------");super.prettyGirl.greatLooks();super.prettyGirl.greatFigure();super.prettyGirl.greatTemperament();}}public class Main {public static void main(String args[]){IPrettyGirl jiajia = new PrettyGirl("佳佳");AMan man = new Man(jiajia);man.findGirl();}
}運行結果:

(5)依賴倒置原則
(Dependence?Inversion?Principle,DIP)
原則定義:高層模塊不應該依賴低層模塊,二者都應該依賴其抽象;抽象不應該依賴細節,細節應該依賴抽象
原則描述:
- 問題由來:類A直接依賴類B,假如要將類A改為依賴類C,則必須通過修改類A的代碼來達成。直接修改類A,會給程序帶來不必要的風險
- 解決方案:將類A修改為依賴接口I,類B和類C各自實現接口I,類A通過接口I間接與類B或者類C發生聯系,則會大大降低修改類A的幾率
?

使用依賴倒置原則前:
public class Noodles {//吃面條public void eat(){System.out.println("吃面條...");}
}public class Human {public void cook(Noodles noodles){noodles.eat();}
}public class Main {public static void main(String args[]){Human human = new Human();Noodles food = new Noodles();human.cook(food);}
}
使用依賴倒置原則后:
public interface IFood {public void eat();
}public class Noodles implements IFood {@Overridepublic void eat() {System.out.println("吃面條...");}}public class Rice implements IFood {@Overridepublic void eat() {System.out.println("吃米飯(終于吃上米飯了)...");}
}public interface IHuman {//這樣就會做很多飯菜了public void cook(IFood food);
}public class Human implements IHuman {@Overridepublic void cook(IFood food) {food.eat();}}public class Main {public static void main(String args[]){IHuman human = new Human();//實例化米飯,可以吃米飯了IFood rice = new Rice();//吃面條IFood noodles = new Noodles();human.cook(noodles);human.cook(rice);}
}
?
(6)迪米特法則
(Law?Of?Demeter)
原則定義:一個對象應該對其他對象保持最少的了解
原則描述:
- 問題由來:類與類之間的關系越密切,耦合度越大,當一個類發生改變時,對另一個類的影響也越大
- 解決方案:盡量降低類與類之間的耦合
?
使用迪米特法則之前:
public class Inmates {public void weAreFriend(){System.out.println("獄友說:我們是獄友...");}
}public class Prisoners {private Inmates inmates = new Inmates();public Inmates helpEachOther(){System.out.println("家人說:你和獄友之間應該互相幫助...");return inmates;}
}public class Family {//家人探望犯人public void visitPrisoner(Prisoners prisoners){//家人希望犯人與獄友互幫互助Inmates inmates = prisoners.helpEachOther();//獄友說,我們是盟友inmates.weAreFriend();}
}public class Main {public static void main(String args[]) {Family family = new Family();family.visitPrisoner(new Prisoners());}
}運行結果:

使用迪米特法則之后:
public class Inmates {public void weAreFriend(){System.out.println("我們是獄友...");}
}public class Prisoners {private Inmates inmates = new Inmates();public Inmates helpEachOther(){System.out.println("犯人和獄友之間應該互相幫助...");System.out.print("犯人說:");inmates.weAreFriend();return inmates;}
}public class Family {public void visitPrisoner(Prisoners prisoners){System.out.print("家人說:");prisoners.helpEachOther();}
}public class Main {public static void main(String args[]){Family family = new Family();family.visitPrisoner(new Prisoners());}
}運行結果:

DDD中的聚合概念是迪米特法則的典型應用方式
注意事項:
- 在類的結構設計上,每一個類都應當盡量降低成員的訪問權限
- 在類的設計上,只要有可能,一個類應當設計成不變類
- 在對其他類的引用上,一個對象對其它對象的引用應當降到最低
- 盡量降低類的訪問權限
- 謹慎使用序列化功能
- 不要暴露類成員,而應該提供相應的訪問器(屬性)
2. 設計模式
創建型模式:工廠方法、抽象工廠、單例、原型、建造者
結構型模式:代理、橋接、裝飾者、享元/蠅量、適配器、組合、門面
行為型模式:模板方法、策略、責任鏈、命令、狀態、觀察者、中介者、迭代器、訪問者、備忘錄、解釋器
(1)工廠方法
???法是?種創建型設計模式,它提供了在?類中創建對象的接口,但允許?類改變將要創建的對象的類型。???法(Factory Method)的核??標是解耦對象創建與使?邏輯。
場景:

問題:

① 直接依賴具體實現
LogisticsManager直接通過new Truck()硬編碼創建對象,客戶端代碼與Truck類強耦合。新增Ship類時必須修改transportCargo方法的邏輯。
② 違反開閉原則
每添加一種新的運輸工具,例如Ship或Airplane,都需要:
- 修改transportCargo方法,新增條件分支;
- 引入對其他具體類的依賴;
- 導致核心業務邏輯頻繁變更。
③ 條件分支泛濫
if-else或switch語句擴散到多個位置(例如支付方式、日志記錄等其他模塊重復出現類似代碼),維護成本指數級增長。
④ 代碼重復風險
若其他模塊(如計費系統)也需要根據運輸類型創建對象,必須重復編寫相同的條件分支邏輯,系統復雜度失控。
解決:
子類可以修改工廠方法返回的對象類型:

所有產品都必須使用同一接口:
?
完整類圖:

說明:
① 實現關系:Truck / Ship 實現 Transport接口
② 繼承關系:RoadLogistics / SeaLogistics繼承Logistics抽象類
③? 依賴關系:Logistics依賴Transport接口(虛線箭頭)
核心優勢:
① 快速擴展能力:新增空運只需要添加AirLogistics類和Plane產品類,零/少修改現有代碼
② 核心業務穩定:planDelivery()模板方法與運輸工具實現完全解耦?
③ 統一接口調用:客戶端通過Logistics基類操作所有物流類型,符合里氏替換原則(在使用集成的過程中,子類可以完全替換掉父類,并且軟件的功能不受到影響,這個原則是保證代碼的健壯性和可擴展性的重要原則之一)
// 抽象產品接口:所有運輸工具必須實現此接口
interface Transport {void deliver();
}// 具體產品實現:卡車類
class Truck implements Transport {@Overridepublic void deliver() {System.out.println("陸地運輸:卡車配送");}
}// 具體產品實現:船舶類
class Ship implements Transport {@Overridepublic void deliver() {System.out.println("海運:船舶配送");}
}// 抽象工廠類(核心工廠方法)
abstract class Logistics {// 模板方法:組合核心邏輯與工廠方法public void planDelivery() {Transport transport = createTransport();transport.deliver();}// 工廠方法聲明:延遲具體運輸工具創建到子類public abstract Transport createTransport();
}// 具體工廠類:陸地物流
class RoadLogistics extends Logistics {@Overridepublic Transport createTransport() {return new Truck(); // 無需判讀條件的直接構造}
}// 具體工廠類:海洋物流
class SeaLogistics extends Logistics {@Overridepublic Transport createTransport() {return new Ship();}
}// 客戶端調用示例
public class FactoryMethod {public static void main(String[] args) {FactoryMethod client = new FactoryMethod();client.clientMethod("road");}public void clientMethod(String logisticsType) {Logistics logistics;// 通過簡單映射選擇具體工廠if ("road".equals(logisticsType)) {logistics = new RoadLogistics();} else {logistics = new SeaLogistics();}// 統一調用接口(核心業務邏輯無需修改)logistics.planDelivery();}
}// 優化
// 創建對象注冊表
class LogisticsRegistry {private static Map<String, Supplier<Logistics>> registry = new HashMap<>();static {registry.put("road", RoadLogistics::new); // 配置化綁定, 可以從配置文件中加載registry.put("sea", SeaLogistics::new);}public static Logistics getLogistics(String type) {return registry.getOrDefault(type, SeaLogistics::new).get();}
}// 客戶端無需任何條件判斷
class ClientV2 {public void clientMethod(String logisticsType) {Logistics logistics = LogisticsRegistry.getLogistics(logisticsType);logistics.planDelivery();}
}?總結:

(2)抽象工廠
抽象??是?種創建型設計模式,可以?成相關對象系列,??需指定它們的具體類。
場景:


問題:

① 風格一致性失控:客戶端直接創建不同風格的對象(現代椅子+維多利亞沙發)

結果:客戶收到風格沖突的家具套裝
② 對象創建硬編碼:每當新增風格時(如新增ArtDeco),強制修改所有客戶端代碼

③ 產品族管理實效:缺乏統一約束機制,易出現類型錯誤

解決:

// 接口約束產品規格interface Chair {void sit();
}interface Sofa {void lieDown();
}interface CoffeeTable {void placeItem();
}
// 確保現代系列組件統一class ModernChair implements Chair {@Overridepublic void sit() {System.out.println("Modern chair designed seating");}
}class ModernSofa implements Sofa {@Overridepublic void lieDown() {System.out.println("Modern sofa clean lines design");}
}class ModernCoffeeTable implements CoffeeTable {@Overridepublic void placeItem() {System.out.println("Modern geometric table surfaces");}
}// 保證維多利亞風格一致性class VictorianChair implements Chair {@Overridepublic void sit() {System.out.println("Classic carved wood chair");}
}class VictorianSofa implements Sofa {@Overridepublic void lieDown() {System.out.println("Antique fabric sofa");}
}class VictorianCoffeeTable implements CoffeeTable {@Overridepublic void placeItem() {System.out.println("Ornate marble-top table");}
}interface FurnitureFactory {Chair createChair();Sofa createSofa();CoffeeTable createCoffeeTable();
}// 現代風格產品線工廠class ModernFactory implements FurnitureFactory {@Overridepublic Chair createChair() {return new ModernChair();}@Overridepublic Sofa createSofa() {return new ModernSofa();}@Overridepublic CoffeeTable createCoffeeTable() {return new ModernCoffeeTable();}
}// 維多利亞風格產品線工廠class VictorianFactory implements FurnitureFactory {@Overridepublic Chair createChair() {return new VictorianChair();}@Overridepublic Sofa createSofa() {return new VictorianSofa();}@Overridepublic CoffeeTable createCoffeeTable() {return new VictorianCoffeeTable();}
}class FurnitureStore {private FurnitureFactory factory;// 動態綁定具體工廠public FurnitureStore(FurnitureFactory factory) {this.factory = factory;}public void showcaseSet() {Chair chair = factory.createChair();Sofa sofa = factory.createSofa();CoffeeTable table = factory.createCoffeeTable();System.out.println("展示完整風格套件:");chair.sit();sofa.lieDown();table.placeItem();}
}public class AbstractFactory {public static void main(String[] args) {// 創建現代風格商店FurnitureStore modernStore = new FurnitureStore(new ModernFactory());modernStore.showcaseSet();// 創建維多利亞風格商店FurnitureStore victorianStore = new FurnitureStore(new VictorianFactory());victorianStore.showcaseSet();}
}總結:

?
(3)建造者
Builder是?種創建型設計模式,可讓你逐步構建復雜對象。該模式允許你使?相同的構造代碼?成對象的不同類型和表示形式。
場景:

問題:
問題1:
class IssueHouse1 {// 基礎參數protected int wallCount;protected boolean hasDoor;// 擴展參數(部分子類不使用)protected boolean hasSwimmingPool;protected boolean hasGarage;protected boolean hasGarden;// 分層構造函數(引發參數冗余)public IssueHouse1(int wallCount, boolean hasDoor) {this.wallCount = wallCount;this.hasDoor = hasDoor;}// 參數爆炸式重載(違反單一職責原則)public IssueHouse1(int wallCount, boolean hasDoor, boolean hasSwimmingPool) {this(wallCount, hasDoor);this.hasSwimmingPool = hasSwimmingPool;}public IssueHouse1(int wallCount, boolean hasDoor,boolean hasSwimmingPool, boolean hasGarage) {this(wallCount, hasDoor, hasSwimmingPool);this.hasGarage = hasGarage;}// 更多構造函數組合...public IssueHouse1(int wallCount, boolean hasDoor,boolean hasSwimmingPool, boolean hasGarage, boolean aaa) {this(wallCount, hasDoor, hasSwimmingPool);this.hasGarage = hasGarage;}
}// 基礎房屋(必須調用父類構造傳遞無效參數)
class BasicHouse extends IssueHouse1 {public BasicHouse() {super(4, true, false, false); // 強制填寫無用參數}
}// 帶泳池房屋
class HouseWithSwimmingPool extends IssueHouse1 {public HouseWithSwimmingPool() {super(4, true, true, false);}
}// 帶車庫房屋
class HouseWithGarage extends IssueHouse1 {public HouseWithGarage() {super(4, true, false, true);}
}// 混合組合場景需創建新子類(類數量激增)
class LuxuryHouse extends IssueHouse1 {public LuxuryHouse() {super(6, true, true, true, true); // 需要修改父類構造函數簽名}
}public class NoBuilder1 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 類型強制轉換問題IssueHouse1 basic = new BasicHouse();IssueHouse1 luxury = new LuxuryHouse();// 新增類型無法動態組合(需預定義所有子類)boolean needHeatedPool = true;if(needHeatedPool) {// 必須創建新的HeatedPoolHouse子類}}
}問題2:
class IssueHouse2 {// 核心參數private int wallCount;private int doorCount;// 可選設施private boolean hasSwimmingPool; // 90%場景無用參數private boolean hasSolarPanels;private boolean hasUndergroundBunker;// 裝飾參數private String roofMaterial;private String wallPaintColor;private boolean hasLandscaping;// 電器系統private boolean hasSmartHomeSystem;private boolean hasCentralAir;/*** 萬能的構造函數(包含18個參數)* @param wallCount 墻體數量(必須)* @param doorCount 門數量(必須)* @param hasSwimmingPool 泳池存在性(90%為false)* @param solarPanels 太陽能板(特殊設施)* ...其他參數省略...*/public IssueHouse2(int wallCount,int doorCount,boolean hasSwimmingPool,boolean hasSolarPanels,boolean hasUndergroundBunker,String roofMaterial,String wallPaintColor,boolean hasLandscaping,boolean hasSmartHomeSystem,boolean hasCentralAir// ...還有8個額外參數...) {this.wallCount = wallCount;this.doorCount = doorCount;this.hasSwimmingPool = hasSwimmingPool; // 參數浪費this.hasSolarPanels = hasSolarPanels;// ...剩余參數初始化邏輯...}
}// 客戶端被迫填寫無用參數
public class NoBuilder2 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 基礎住宅實例化(需要填寫7個默認false)IssueHouse2 basicHouse = new IssueHouse2(4, 1,false, false, false, // 泳池/太陽能/地堡"Asphalt", "White", false, false, false);// 豪華住宅調用(所有參數必須顯式指定)[^3]IssueHouse2 mansion = new IssueHouse2(12, 6,true, true, true,"Slate", "Ivory", true,true, true// ...仍需補全所有參數...);}
}
解決:
① Builder核心接口定義
② 產品類(簡化結構)
③ 具體建造者實現
④ 導演類(統一建造流程)
⑤ 客戶端調用模式
// Product類代表復雜對象
class House {private String wallMaterial;private int doors;private int windows;private String roofType;private boolean hasSwimmingPool;public void setWallMaterial(String material) { /*...*/ } // 墻體材料設置public void setDoors(int count) { /*...*/ }public void setWindows(int count) { /*...*/ }public void setRoofType(String type) { /*...*/ }public void setSwimmingPool(boolean has) { /*...*/ } // 可選游泳池配置
}// Builder接口定義建造步驟
interface HouseBuilder {void reset();void buildWalls();void buildDoors(int count); // 參數化建造方法void buildWindows(int count);void buildRoof(String type);void buildSwimmingPool();House getResult();
}// 石頭房屋建造者
class StoneHouseBuilder implements HouseBuilder {private House house = new House();@Overridepublic void reset() {this.house = new House(); // 重置構建狀態}@Overridepublic void buildWalls() { // 實現具體建造邏輯house.setWallMaterial("花崗巖");}@Overridepublic void buildDoors(int count) {}@Overridepublic void buildWindows(int count) {}@Overridepublic void buildRoof(String type) { // 參數化方法示例house.setRoofType(type + "石質屋頂");}@Overridepublic void buildSwimmingPool() { // 實現可選配置house.setSwimmingPool(true);}@Overridepublic House getResult() {return null;}// 其他方法實現...
}// 木屋建造者
class WoodHouseBuilder implements HouseBuilder {@Overridepublic void reset() {}@Overridepublic void buildWalls() {}@Overridepublic void buildDoors(int count) {}@Overridepublic void buildWindows(int count) {}@Overridepublic void buildRoof(String type) {}@Overridepublic void buildSwimmingPool() {}@Overridepublic House getResult() {return null;} /* 類似實現 */ }// 可擴展第三類建造者(例如現代玻璃房屋)
class ModernHouseBuilder implements HouseBuilder {private House currentHouse = new House();@Overridepublic void reset() {}@Overridepublic void buildWalls() {currentHouse.setWallMaterial("鋼化玻璃");}@Overridepublic void buildDoors(int count) {}@Overridepublic void buildWindows(int count) {}@Overridepublic void buildRoof(String type) {currentHouse.setRoofType("透明生態屋頂");}@Overridepublic void buildSwimmingPool() {}@Overridepublic House getResult() {return null;}
}// Director控制建造流程
class ConstructionDirector { // 封裝常見建造方案public void constructFamilyHouse(HouseBuilder builder) {builder.reset();builder.buildWalls();builder.buildDoors(3); // 標準流程步驟builder.buildWindows(6);builder.buildRoof("斜頂");}public void constructLuxuryVilla(HouseBuilder builder) {builder.reset();builder.buildWalls();builder.buildDoors(5);builder.buildWindows(10);builder.buildRoof("平頂");builder.buildSwimmingPool(); // 添加可選設施}
}// Client使用示例
public class Builder {public static void main(String[] args) {ConstructionDirector director = new ConstructionDirector();// 建造石頭別墅HouseBuilder stoneBuilder = new StoneHouseBuilder();director.constructLuxuryVilla(stoneBuilder); // 調用導演建造邏輯House stoneVilla = stoneBuilder.getResult(); // 獲取產品// 建造木屋HouseBuilder woodBuilder = new WoodHouseBuilder();woodBuilder.buildSwimmingPool(); // 客戶端自定義步驟director.constructFamilyHouse(woodBuilder);House woodHouse = woodBuilder.getResult();}
}總結:

(4)原型
原型是?種創建型設計模式,它允許你復制現有對象,?不使你的代碼依賴于它們的類。
場景:

示例:

abstract class Shape implements Cloneable {protected int xCoord;protected int yCoord;protected String fillColor;// 基礎構造方法public Shape() {this.xCoord = 0;this.yCoord = 0;this.fillColor = "#FFFFFF"; // 默認填充顏色}// 原型構造方法(拷貝構造核心)protected Shape(Shape prototype) {this.xCoord = prototype.xCoord; // 坐標克隆this.yCoord = prototype.yCoord; // 實現位置復制this.fillColor = prototype.fillColor; // 顏色屬性繼承}public void setPosition(int x , int y) {this.xCoord = x;this.yCoord = y;}public void move(int x , int y) {this.xCoord = x;this.yCoord = y;}public void setColor(String color) {this.fillColor = color;}public abstract Shape clone();
}class Rectangle extends Shape {private int width;private int height;public Rectangle(Rectangle source) {super(source); // 調用父類拷貝構造this.width = source.width; // 特有屬性復制this.height = source.height; // 包括寬高參數}public Rectangle(int w, int h) {this.width = w;this.height = h;}@Overridepublic Rectangle clone() { // 返回具體子類類型return new Rectangle(this); // 原型引導構造}
}class Circle extends Shape {private int radius;public Circle(Circle source) {super(source); // 父類屬性初始化this.radius = source.radius; // 半徑參數拷貝}public Circle(int r) {this.radius = r;}public void setRadius(int r) {this.radius = r; // 半徑獨立可變}@Overridepublic Circle clone() {return new Circle(this); // 生成新實例}
}public class Prototype {public static void main(String[] args) {Shape prototype = new Circle(10);prototype.setPosition(15, 20);prototype.setColor("#FFA500");// 快速生成克隆體Shape clonedCircle = prototype.clone(); // 無需知道具體類型clonedCircle.move(5, 5); // 獲得獨立坐標// 構造矩形原型Shape rectProto = new Rectangle(100,200);Shape clonedRect = rectProto.clone(); // 完美復制屬性}
}總結:

(5)單例
單例是?種創建型設計模式,它可以確保?個類只有?個實例,同時為該實例提供全局訪問點。
問題:
① 確保?個類只有?個實例
② 為該實例提供全局訪問點
解決:所有Singleton的實現都有以下兩個共同的步驟:
① 將默認構造函數設置為私有,以防止其他對象使用new帶有Singleton類的運算符;
② 創建一個充當構造函數的靜態方法。在底層,此方法調用私有構造函數來創建一個對象并將其保存在靜態字段中,對此方法的所有后續調用都會返回緩存的對象。
示例:數據庫連接
重構前:

重構后:
public class Singleton {
}
public class Database {private static volatile Database instance;private Connection connection;// 私有化構造并建立物理連接private Database() {this.connection = DriverManager.getConnection(JDBC_URL); // 真實連接建立}// 雙重檢查鎖定實現線程安全public static Database getInstance() {if (instance == null) {synchronized (Database.class) {if (instance == null) {instance = new Database();}}}return instance;}// 統一入口方法(可擴展緩存邏輯)public ResultSet query(String sql) {return connection.createStatement().executeQuery(sql); // 所有SQL通過單連接執行}
}總結:

(6)適配器
使接口不兼容的類實現協同?作,通過引入中間層將客戶端接口轉換為服務端接口標準。典型場景如整合第三?類庫或遺留系統時保持代碼兼容。
場景:

問題:
① 接口不匹配:客戶端調用規則與現有服務類接口無法直接通信(如XML接口需轉JSON請求)
② 保護現有代碼:無法修改第三方/遺留代碼的接口,實現時避免侵入性改造(例如封閉系統或缺乏源碼)
解決:
① 適配器實現了一個與現有對象之一兼容的接口
② 使用這個接口,現有的對象可以安全地調用適配器的方法
③ 接收到調用后,適配器將請求傳遞給第二個對象,但采用第二個對象期望的格式和順序

定義客戶端協議接口,強制適配器實現該約定:

適配器持有服務實例引用,委托調用并進行數據轉換:

總結:

?
(7)橋接器
橋接器是?種結構型設計模式,可將?個?類或?系列緊密相關的類拆分為抽象和實現兩個獨? 的層次結構,從?能在開發時分別使?。
問題:

解決:

示例:

/* 實現層級:設備接口規范 */
interface Device {// 狀態檢測基礎方法boolean isEnabled();void enable(); // Device接口定義void disable();// 媒體控制方法int getVolume();void setVolume(int percent);int getChannel();void setChannel(int channel);
}/* 具體設備實現 */
class Tv implements Device { // TV實現private boolean on = false;private int volume = 50;private int channel = 1;public boolean isEnabled() { return on; }public void enable() { on = true; } // TV特有啟動過程public void disable() { on = false; }public int getVolume() { return volume; }public void setVolume(int percent) {volume = Math.max(0, Math.min(100, percent));}public int getChannel() { return channel; }public void setChannel(int ch) {channel = Math.max(1, ch);}
}class Radio implements Device { // Radio實現private boolean active = false;private int level = 30;public boolean isEnabled() { return active; }public void enable() { active = true; }public void disable() { active = false; }public int getVolume() { return level; }public void setVolume(int percent) {level = (percent > 100) ? 100 : Math.max(0, percent);}public int getChannel() { return 0; } // 收音機無頻道public void setChannel(int ch) {} // 空實現
}/* 抽象層級:遙控器抽象 */
class RemoteControl {// 持有實現層對象的引用(關鍵結構)protected Device device;public RemoteControl(Device device) {this.device = device;}// 電源切換核心邏輯public void togglePower() {if (device.isEnabled()) {device.disable();} else {device.enable();}}public void volumeUp() {device.setVolume(device.getVolume() + 10);}public void volumeDown() {device.setVolume(device.getVolume() - 10);}public void channelUp() {device.setChannel(device.getChannel() + 1);}public void channelDown() {device.setChannel(device.getChannel() - 1);}
}/* 擴展抽象:高級遙控器(擴展功能) */
class AdvancedRemoteControl extends RemoteControl {public AdvancedRemoteControl(Device device) {super(device);}public void mute() { // 新增靜音功能device.setVolume(0); // 通過接口操作設備}
}// 客戶端使用示例
public class Bridge {public static void main(String[] args) {Device tv = new Tv();RemoteControl basicRemote = new RemoteControl(tv);basicRemote.togglePower(); // 開啟電視Device radio = new Radio();AdvancedRemoteControl advancedRemote = new AdvancedRemoteControl(radio);advancedRemote.mute(); // 設置靜音}
}總結:

(8)組合模式
組合模式是?種結構型設計模式,你可以使?它將對象組合成樹狀結構,并且能像使?獨?對象?樣使?它們。組合模式以遞歸方式處理對象樹中的所有項目。
問題:

解決:

public class Composite {
}
/* 組合元素基類(公共接口) */
interface OrderComponent {double calculatePrice(); // 核心計算方法定義
}/* 商品項實現類 */
class ProductItem implements OrderComponent {private double unitPrice;private int quantity;public ProductItem(double price, int qty) {this.unitPrice = price;this.quantity = qty;}@Overridepublic double calculatePrice() {return unitPrice * quantity; // 基本商品價格計算邏輯}
}/* 組合容器(有包裝附加費) */
class CompositeBox implements OrderComponent {private List<OrderComponent> contents = new ArrayList<>();private double packagingFee;public CompositeBox(double fee) {this.packagingFee = fee; // 包裝費擴展}public void add(OrderComponent item) {contents.add(item);}@Overridepublic double calculatePrice() {double total = packagingFee; // 包裝費基數for (OrderComponent item : contents) {// 遞歸計算嵌套內容(樹形結構處理)total += item.calculatePrice();}return total;}
}// 使用示例(典型場景)
class Client {public static void main(String[] args) {// 創建基礎商品OrderComponent phone = new ProductItem(2999.0, 2);OrderComponent earphone = new ProductItem(199.0, 1);// 構建禮品套裝盒子(含子包裝)CompositeBox giftBox = new CompositeBox(50.0);giftBox.add(new ProductItem(399.0, 1)); // 贈品數據線giftBox.add(earphone);// 主訂單容器(包含嵌套包裝)CompositeBox mainOrder = new CompositeBox(20.0);mainOrder.add(phone);mainOrder.add(giftBox);System.out.println("總金額:" + mainOrder.calculatePrice());}
}
總結:

(9)裝飾者
裝飾是?種結構型設計模式,允許你通過將對象放?包含?為的特殊封裝對象中來為原對象綁定新的?為。
場景:程序可以使用通知器類向預定義的郵箱發送重要事件通知:

每種通知類型都將作為通知器的一個子類得以實現:

問題:

解決:

// 抽象構件 - 通知接口
interface Notification {void send(String message);
}// 具體構件 - 短信通知
class SMSNotification implements Notification {@Overridepublic void send(String message) {System.out.println("發送短信通知:" + message);}
}// 具體構件 - 微信通知
class WeChatNotification implements Notification {@Overridepublic void send(String message) {System.out.println("發送微信通知:" + message);}
}// 具體構件 - 郵件通知
class EmailNotification implements Notification {@Overridepublic void send(String message) {System.out.println("發送郵件通知:" + message);}
}// 具體構件 - 系統通知
class SystemNotification implements Notification {@Overridepublic void send(String message) {System.out.println("發送系統通知:" + message);}
}// 裝飾器 - 抽象裝飾器類
abstract class NotificationDecorator implements Notification {protected Notification notification;public NotificationDecorator(Notification notification) {this.notification = notification;}@Overridepublic void send(String message) {notification.send(message);}
}// 具體裝飾器 - 短信通知裝飾器
class SMSNotificationDecorator extends NotificationDecorator {public SMSNotificationDecorator(Notification notification) {super(notification);}@Overridepublic void send(String message) {super.send(message);sendSMS(message);}private void sendSMS(String message) {System.out.println("額外發送短信通知:" + message);}
}// 具體裝飾器 - 微信通知裝飾器
class WeChatNotificationDecorator extends NotificationDecorator {public WeChatNotificationDecorator(Notification notification) {super(notification);}@Overridepublic void send(String message) {super.send(message);sendWeChat(message);}private void sendWeChat(String message) {System.out.println("額外發送微信通知:" + message);}
}public class Decorator {public static void main(String[] args) {// 創建基礎通知對象Notification notification = new SystemNotification();// 使用裝飾器動態添加短信通知和微信通知notification = new SMSNotificationDecorator(notification);notification = new WeChatNotificationDecorator(notification);// 發送通知notification.send("您有新的消息,請注意查收!");// 輸出:// 發送系統通知:您有新的消息,請注意查收!// 額外發送短信通知:您有新的消息,請注意查收!// 額外發送微信通知:您有新的消息,請注意查收!}
}
總結:

(10)外觀/門面模式
外觀是?種結構型設計模式,能為程序庫、框架或其他復雜類提供?個簡單的接口。
問題:如果必須在代碼中使用某個復雜的庫或框架中的眾多對象,正常情況下,需要負責所有對象的初始化工作、管理其依賴關系并按照正確的順序執行方法等。最終,程序中類的業務邏輯將與第三方類的實現細節緊密耦合,使得理解和維護代碼的工作很難進行。
示例:

// 視頻文件抽象(第三方類模擬)
class VideoFile {private String filename;public VideoFile(String name) {this.filename = name;}public String getCodecType() {// 偽代碼提取類型邏輯return filename.contains(".ogg") ? "ogg" : "unknown";}
}// 編解碼抽象
interface CompressionCodec {}
class MPEG4CompressionCodec implements CompressionCodec {} // MP4編解碼
class OggCompressionCodec implements CompressionCodec {} // Ogg編解碼// 編解碼工廠實現(提取邏輯)
class CodecFactory {public static CompressionCodec extract(VideoFile file) {String type = file.getCodecType();return type.equals("ogg") ? new OggCompressionCodec() : null;}
}// 碼率處理組件(轉換邏輯)
class BitrateReader {public static VideoFile read(String filename, CompressionCodec codec) {System.out.println("解碼原始文件: " + filename);return new VideoFile(filename);}public static VideoFile convert(VideoFile buffer, CompressionCodec codec) {System.out.println("轉換編碼格式: " + codec.getClass().getSimpleName());return new VideoFile(buffer + "_converted");}
}// 音頻混合組件(后處理步驟)
class AudioMixer {public VideoFile fix(VideoFile result) {System.out.println("標準化音頻軌道");return new VideoFile(result + "_mixed");}
}/* 核心外觀類(完整轉換流程封裝) */
class VideoConverter {public File convert(String filename, String format) {VideoFile file = new VideoFile(filename);CompressionCodec sourceCodec = CodecFactory.extract(file); // 源編碼識別// 目標編碼選擇(條件分支)CompressionCodec destinationCodec;if (format.equalsIgnoreCase("mp4")) {destinationCodec = new MPEG4CompressionCodec();} else {destinationCodec = new OggCompressionCodec();}// 轉換處理鏈條(標準流程)VideoFile buffer = BitrateReader.read(filename, sourceCodec);VideoFile intermediateResult = BitrateReader.convert(buffer, destinationCodec);VideoFile finalResult = new AudioMixer().fix(intermediateResult);return new File(finalResult.toString());}
}// 客戶端調用(典型使用示例)
public class Facade {public static void main(String[] args) {VideoConverter converter = new VideoConverter();File mp4File = converter.convert("presentation.ogg", "mp4");
// mp4File.save();}
}
總結:

(11)享元/蠅量
享元是?種結構型設計模式,它摒棄了在每個對象中保存所有數據的?式,通過共享多個對 象所共有的相同狀態,讓你能在有限的內存容量中載?更多對象。
場景:

解決:外部狀態存儲;享元與不可變性;享元工廠



public class Flyweight {
}
// 粒子內在狀態(游戲特效屬性)
final class ParticleType {private final String color; // 不可變特征private final String sprite;private final String effectType;public ParticleType(String color, String sprite, String effectType) {this.color = color;this.sprite = sprite;this.effectType = effectType;}public void render(String position, double velocity) {System.out.printf("繪制%s特效: 位置%s | 速度%.1fm/s | 材質[%s]%n",effectType, position, velocity, sprite);}
}// 粒子外在狀態載體
class Particle {private double x, y;private double velocity;private final ParticleType type; // 共享引用public Particle(double x, double y, double v, ParticleType type) {this.x = x;this.y = y;this.velocity = v;this.type = type;}public void display() {type.render(String.format("(%.1f, %.1f)", x, y), velocity);}
}// 享元工廠
class ParticleFactory {private static final Map<String, ParticleType> pool = new HashMap<>();public static ParticleType getType(String color, String sprite, String effect) {String key = color + "_" + sprite + "_" + effect;// 池化檢測邏輯(資料5的核心機制)[^5]if (!pool.containsKey(key)) {pool.put(key, new ParticleType(color, sprite, effect));}return pool.get(key);}
}// 粒子系統管理
class ParticleSystem {private List<Particle> particles = new ArrayList<>();public void addParticle(double x, double y, double v,String color, String sprite, String effect) {ParticleType type = ParticleFactory.getType(color, sprite, effect);particles.add(new Particle(x, y, v, type));}public void simulate() {particles.forEach(Particle::display);}
}// 運行示例(參照[資料4]的客戶端調用方式)[^4]
class GameEngine {public static void main(String[] args) {ParticleSystem system = new ParticleSystem();// 添加火焰粒子system.addParticle(10.5, 20.3, 5.2, "橙紅", "fire_tex", "火焰");system.addParticle(15.1, 18.7, 4.8, "橙紅", "fire_tex", "火焰");// 添加冰雪粒子system.addParticle(30.0, 50.0, 2.1, "冰藍", "snow_tex", "冰霜");system.simulate();}
}總結:

(12)代理
代理是?種結構型設計模式,讓你能夠提供對象的替代品或其占位符。代理控制著對于原對象的訪問,并允許在 將請求提交給對象前后進??些處理。
問題:數據庫查詢有可能會非常緩慢。

解決:代理將自己偽裝成數據庫對象,可在客戶端或實際數據庫對象不知情的情況下處理延遲初始化和緩存查詢結果的工作。

核心設計要點:
① 代理類與現實服務實現相同接口
② 第一次查詢延遲初始化真實連接(虛擬代理模式)
③ 哈希表緩存重復查詢結果(緩存優化)
④ 客戶端代碼不需感知代理存在(透明訪問)
public class Proxy {
}
// 服務接口
interface Database {String executeQuery(String sql);
}// 真實服務對象
class RealDatabase implements Database {public RealDatabase() {initializeConnection(); // 耗時的連接初始化}private void initializeConnection() {System.out.println("正在建立數據庫連接...");}@Overridepublic String executeQuery(String sql) {System.out.println("執行真實查詢: " + sql);return "結果數據"; // 示例返回值}
}// 代理類(延遲加載和緩存)
class DatabaseProxy implements Database {private RealDatabase realDatabase;private Map<String, String> cache = new HashMap<>(); // 查詢結果緩存@Overridepublic String executeQuery(String sql) {// 延遲初始化(虛擬代理模式)if (realDatabase == null) {realDatabase = new RealDatabase();}// 結果緩存邏輯(緩存代理)if (cache.containsKey(sql)) {System.out.println("[Proxy] 返回緩存結果: " + sql);return cache.get(sql);}String result = realDatabase.executeQuery(sql);cache.put(sql, result);return result;}
}// 客戶端交互
class Application {public static void main(String[] args) {Database proxy = new DatabaseProxy();// 第一次查詢觸發真實連接System.out.println(proxy.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM users"));// 重復查詢使用緩存System.out.println(proxy.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM users"));// 新查詢繼續代理System.out.println(proxy.executeQuery("SELECT COUNT(*) FROM products"));}
}總結:
?
(13)責任鏈
責任鏈是?種?為設計模式,允許你將請求沿著處理者鏈進?發送。收到請求后,每個處理者均可對請 求進?處理,或將其傳遞給鏈上的下個處理者。
問題:

解決:處理者依次排列,組成一條鏈

核心改進點:
① 解耦檢查邏輯:每個安全檢查獨立成類,通過setNext組合鏈式結構
② 動態擴展性:新增日志檢查僅需創建LogHandler并插入鏈中任意位置
③ 復用性增強:在PaymentService中可重用UserAuthHandler而不用重復驗證代碼
public class ChainOfResponse {
}class AuthException extends RuntimeException {private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;public AuthException(String msg) {super(msg);}}class PermissionException extends RuntimeException {private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;public PermissionException(String msg) {super(msg);}}
// Handler接口定義處理契約
interface Handler {void handle(Request request) throws AuthException;
}// BaseHandler實現鏈式傳遞邏輯
abstract class BaseHandler implements Handler {private Handler next;public BaseHandler setNext(Handler next) {this.next = next;return this;}protected void passToNext(Request request) throws AuthException {if (next != null) next.handle(request); // 核心鏈式調用邏輯[^1]}
}// 具體處理者1:用戶認證
class UserAuthHandler extends BaseHandler {@Overridepublic void handle(Request request) throws AuthException {int userId = 0; // request.getUserId()if (!validateUser(userId)) {throw new AuthException("用戶未登錄");}passToNext(request); // 驗證成功移交后續處理}private boolean validateUser(int userId) {return true;}
}// 具體處理者2:權限校驗
class PermissionHandler extends BaseHandler {@Overridepublic void handle(Request request) throws AuthException {int userId = 0; // request.getUserId()if (!checkAdminPermission(userId)) {throw new PermissionException("權限不足");}passToNext(request);}private boolean checkAdminPermission(int userId){return false;}
}// Client動態組合處理鏈
class OrderService {private Handler chain;public OrderService() {this.chain = new UserAuthHandler().setNext(new PermissionHandler()); // 靈活配置處理順序}public void createOrder(Request request) {chain.handle(request); // 統一入口觸發處理鏈// 執行業務邏輯...}
}總結:

(14)命令
命令是?種?為設計模式, 它可將請求轉換為?個包 含與請求相關的所有信息的獨?對象。該轉換讓你 能根據不同的請求將方法參數化、延遲請求執?或將其放?隊列中,且能實現可撤銷操作。
問題:

解決:

public class CommandCode {
}
// 1.Receiver 編輯器核心
class Editor {private StringBuilder content = new StringBuilder();public String getSelection() {return content.toString(); // 實際應按選區范圍獲取}public void deleteSelection() {content.setLength(0); // 清空選區}public void replaceSelection(String text) {content.replace(0, content.length(), text); // 替換選區}public String getContent() {return content.toString();}
}// 2.Command 接口層
interface Command {void execute();
}// 3.具體命令實現
class CopyCommand implements Command {private Editor editor;private String clipboard; // 仿系統剪貼板public CopyCommand(Editor editor) {this.editor = editor;}@Overridepublic void execute() {clipboard = editor.getSelection(); // 獲取選區存入剪貼板}
}class PasteCommand implements Command {private Editor editor;private String clipboard;public PasteCommand(Editor editor, String clipboard) {this.editor = editor;this.clipboard = clipboard;}@Overridepublic void execute() {editor.replaceSelection(clipboard); // 用剪貼板內容覆蓋選區}
}// 4.Invoker觸發器
class Toolbar {private Command command;public void setCommand(Command cmd) { // 動態綁定命令this.command = cmd;}public void onClick() {if(command != null) command.execute();}
}// 5.Client組裝結構
class App {public static void main(String[] args) {// 創建核心模塊Editor doc = new Editor();doc.replaceSelection("Hello");// 建立命令紐帶Toolbar copyBtn = new Toolbar();copyBtn.setCommand(new CopyCommand(doc)); // 綁定復制行為Toolbar pasteBtn = new Toolbar();pasteBtn.setCommand(new PasteCommand(doc, "World")); // 粘貼命令攜帶參數// 用戶點擊按鈕時copyBtn.onClick(); // 將Hello存入剪貼板pasteBtn.onClick(); // 文檔內容變為World}
}總結:

(15)迭代器
迭代器是?種?為設計模式,讓你能在不暴露集合底層表現形式(列表、棧和樹等)的情況下遍歷集合中所有的元素。
場景:

解決:

// 1.Iterator接口 (定義遍歷標準)
interface TreeIterator<T> {boolean hasNext();T next();
}// 2.Concrete Iterator(實現廣度優先遍歷)
class BfsIterator implements TreeIterator<TreeNode> {private Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();public BfsIterator(TreeNode root) {if(root != null) queue.add(root);}public boolean hasNext() { // 判斷是否有下一節點return !queue.isEmpty();}public TreeNode next() { // 按層遍歷樹節點TreeNode current = queue.poll();for(TreeNode child : current.getChildren()) {queue.add(child);}return current;}
}// 3.Collection接口(樹結構抽象)
interface TreeCollection {TreeIterator<TreeNode> createBfsIterator(); // 創建特定迭代器
}// 4.Concrete Collection(樹節點實現)
class TreeNode implements TreeCollection {private String data;private List<TreeNode> children = new ArrayList<>();public TreeNode(String data) {this.data = data;}public void addChild(TreeNode node) {children.add(node);}public List<TreeNode> getChildren() {return children;}public TreeIterator<TreeNode> createBfsIterator() {return new BfsIterator(this); // 自身作為遍歷起點}public String getData() {return this.data;}
}// 5.Client使用示例
public class Iterator {public static void main(String[] args) {/* 構建樹結構:A/ \B C/ \D E*/TreeNode root = new TreeNode("A");TreeNode nodeB = new TreeNode("B");TreeNode nodeC = new TreeNode("C");root.addChild(nodeB);root.addChild(nodeC);nodeC.addChild(new TreeNode("D"));nodeC.addChild(new TreeNode("E"));// 獲取BFS迭代器TreeIterator<TreeNode> iterator = root.createBfsIterator();// 遍歷樹節點while(iterator.hasNext()) {System.out.println(iterator.next().getData());// 依次輸出 A → B → C → D → E}}
}
總結:

(16)中介者
中介者是?種?為設計模式, 能讓你減少對象之間混亂?序的依賴關系。該模式會限制對象之間 的直接交互,迫使它們通過?個中介者對象進?合作。
問題:

解決:

① 解耦組件:各組件僅依賴中介對象,無直接關聯
② 集中控制:表單驗證邏輯統一在validateForm()處理
③ 擴展靈活:新增密碼強度校驗組件時不影響現有結構
// 1.Mediator接口
interface DialogMediator {void notify(Component sender, String event); // 統一事件通知口[^2]
}// 2.Concrete Mediator(登錄對話框)
class LoginDialogMediator implements DialogMediator {private CheckBox rememberMeBox; // ComponentAprivate TextBox usernameTextBox; // ComponentBprivate TextBox passwordTextBox; // ComponentCprivate Button submitButton; // ComponentDpublic LoginDialogMediator() {// 組件在中介內創建并建立雙向引用[^5]rememberMeBox = new CheckBox(this);usernameTextBox = new TextBox(this);passwordTextBox = new TextBox(this);submitButton = new Button(this);}@Overridepublic void notify(Component sender, String event) {if (sender == rememberMeBox && event.equals("check")) {toggleRememberMeConfig();} else if ((sender == usernameTextBox || sender == passwordTextBox)&& event.equals("keypress")) {validateForm(); // 實時校驗表單[^3]} else if (sender == submitButton && event.equals("click")) {handleSubmit();}}private void toggleRememberMeConfig() {System.out.println("記住密碼配置更改:" + rememberMeBox.isChecked());}private void validateForm() {boolean isValid = !usernameTextBox.getText().isEmpty() &&passwordTextBox.getText().length() >= 6;submitButton.setEnabled(isValid); // 聯合控制按鈕狀態[^3]}private void handleSubmit() {System.out.println("提交用戶:" + usernameTextBox.getText());}
}// 3.Components實現
abstract class Component {protected DialogMediator dialog; // 持中介引用public Component(DialogMediator dialog) {this.dialog = dialog;}public abstract void triggerEvent(String event);
}class CheckBox extends Component { // ComponentAprivate boolean checked;public CheckBox(DialogMediator dialog) { super(dialog); }public void toggle() {checked = !checked;dialog.notify(this, "check"); // 通知中介[^2]}public boolean isChecked() { return checked; }@Overridepublic void triggerEvent(String event) { toggle(); }
}class TextBox extends Component { // ComponentB/Cprivate String text = "";public TextBox(DialogMediator dialog) { super(dialog); }public void input(String text) {this.text = text;dialog.notify(this, "keypress"); // 實時反饋輸入[^2]}public String getText() { return text; }@Overridepublic void triggerEvent(String event) { input(event); }
}class Button extends Component { // ComponentDprivate boolean enabled = false;public Button(DialogMediator dialog) { super(dialog); }public void click() {if(enabled) dialog.notify(this, "click");}public void setEnabled(boolean state) {enabled = state;System.out.println("按鈕狀態:" + (state?"可用":"禁用"));}@Overridepublic void triggerEvent(String event) { click(); }
}// 4.Client使用
public class Mediator {public static void main(String[] args) {LoginDialogMediator dialog = new LoginDialogMediator();/* 模擬用戶交互流程dialog.getUsernameTextBox().triggerEvent("john"); // 輸入用戶名dialog.getPasswordTextBox().triggerEvent("123456"); // 輸入密碼dialog.getSubmitButton().triggerEvent("click"); // 成功提交dialog.getRememberMeBox().triggerEvent("check"); // 切換"記住我"dialog.getPasswordTextBox().triggerEvent("123"); // 觸發按鈕禁用*/}
}總結:

(17)備忘錄
備忘錄是?種?為設計模式,允許在不暴露對象實現細節的情況下保存和恢復對象之前的狀態。
問題:

解決:

關鍵實現要點:
① 嚴格封裝:Memento的構造器和訪問方法僅對Originator可見
② 狀態融合:Originator內部維護狀態恢復邏輯
③ 歷史管理:Caretaker用棧結構實現撤銷機制
④ 數據安全:Memento對象不可變,確保快照完整性
// Originator:文本編輯器核心類
class TextEditor {private String content; // 當前編輯內容private int cursorPosition; // 光標位置public void type(String words) {content = (content == null) ? words : content.substring(0, cursorPosition)+ words + content.substring(cursorPosition);cursorPosition += words.length();}public void setCursor(int position) {cursorPosition = Math.min(position, content.length());}public String getContent(){return this.content;}// 創建備忘錄public EditorMemento createMemento() {return new EditorMemento(content, cursorPosition);}// 從備忘錄恢復public void restoreFromMemento(EditorMemento memento) {this.content = memento.getSavedContent();this.cursorPosition = memento.getSavedCursorPosition();}// Memento作為內部類(封裝狀態細節)public static class EditorMemento {private final String content;private final int cursorPosition;private EditorMemento(String content, int cursor) { // 僅Originator可創建實例this.content = content;this.cursorPosition = cursor;}private String getSavedContent() { return content; } // 包權限訪問private int getSavedCursorPosition() { return cursorPosition; }}
}// Caretaker:歷史記錄管理器
class History {private final Stack<TextEditor.EditorMemento> mementos = new Stack<>();public void save(TextEditor.EditorMemento memento) {mementos.push(memento); // 保存狀態快照}public TextEditor.EditorMemento undo() {mementos.pop(); // 移除當前狀態return mementos.peek(); // 返回前一次狀態}
}// Client使用示例
public class Memento {public static void main(String[] args) {TextEditor editor = new TextEditor();History history = new History();// 第一次輸入并保存editor.type("Hello");history.save(editor.createMemento());// 第二次輸入并保存editor.type(" World");history.save(editor.createMemento());// 執行撤銷操作(狀態退回第一次保存點)editor.restoreFromMemento(history.undo());System.out.println(editor.getContent()); // 輸出 "Hello"}
}總結:

(18)觀察者
觀察者是?種?為設計模式, 允許你定義?種訂閱機制,可在對象事件發?時通知多個“觀察”該對象的其他對象。
問題:前往商店和發送垃圾郵件

解決:

關鍵實現說明:
① IPhoneStore作為具體發布者,實現訂閱管理和產品到貨通知
② 通過接口解耦使得新訂閱者類型可以擴展而不影響發布者
③ 客戶端通過subscribe() / unsubscribe() 動態維護訂閱列表
// Publisher 接口
interface StorePublisher {void subscribe(CustomerSubscriber subscriber);void unsubscribe(CustomerSubscriber subscriber);void notifySubscribers(String product);
}// 具體 Publisher 類
class IPhoneStore implements StorePublisher {private List<CustomerSubscriber> customers = new ArrayList<>();@Overridepublic void subscribe(CustomerSubscriber subscriber) {customers.add(subscriber);}@Overridepublic void unsubscribe(CustomerSubscriber subscriber) {customers.remove(subscriber);}@Overridepublic void notifySubscribers(String product) { // 觸發所有訂閱者更新 [^1]for (CustomerSubscriber customer : customers) {customer.update(product);}}public void restockProduct(String product) {System.out.println("新品到貨:" + product);notifySubscribers(product);}
}// Subscriber 接口 [^4]
interface CustomerSubscriber {void update(String product);
}// 具體 Subscriber 類
class PremiumCustomer implements CustomerSubscriber {private String name;public PremiumCustomer(String name) {this.name = name;}@Overridepublic void update(String product) { // 實現標準通知接口System.out.println("[尊享客戶]" + name + ",您關注的" + product + "已到店");}
}// Client 客戶端配置 [^6]
public class Observer {public static void main(String[] args) {IPhoneStore store = new IPhoneStore();CustomerSubscriber alice = new PremiumCustomer("Alice");CustomerSubscriber bob = new PremiumCustomer("Bob");// 動態添加訂閱 [^3]store.subscribe(alice);store.subscribe(bob);// 模擬到貨事件store.restockProduct("iPhone15");// 動態移除訂閱store.unsubscribe(bob);store.restockProduct("iPhone15 Pro");}
}
總結:

(19)狀態
狀態是?種?為設計模式,讓你能在?個對象的內部狀態變化時改變其?為,使其看上去就像改 變了??所屬的類?樣。
問題:

解決:

關鍵優化點:
① 狀態自管理:每個具體狀態類自行控制下一步狀態轉換
② 上下文訪問:通過傳遞文檔引用獲取當前用戶角色(簡化私有字段訪問)
③ 可擴展性:新增狀態只需要創建類并實現接口,無需修改現有代碼
④ 消除條件邏輯:完全移除switch / case結構,使用多臺分發
// Context 類
class DemoDocument {private DocumentState currentState;private String currentUserRole;public DemoDocument() {this.currentState = new DraftState(); // 初始化為草稿狀態}// 設置當前用戶角色public void setCurrentUserRole(String role) {this.currentUserRole = role;}public String getCurrentUserRole() {return this.currentUserRole;}// 狀態轉移方法void transitionTo(DocumentState state) { // 支持狀態自我轉換this.currentState = state;}// 發布入口方法public void publish() {currentState.handlePublish(this); // 委托給當前狀態處理}
}// State 接口
interface DocumentState {void handlePublish(DemoDocument context); // 參數傳遞上下文引用
}// 具體狀態實現
class DraftState implements DocumentState {@Overridepublic void handlePublish(DemoDocument doc) { // 草稿狀態轉審核System.out.println("提交文檔進入審核狀態");doc.transitionTo(new ModerationState()); // 狀態自我轉換}
}class ModerationState implements DocumentState {@Overridepublic void handlePublish(DemoDocument doc) { // 根據管理員權限處理if ("admin".equals(doc.getCurrentUserRole())) { // 獲取上下文中的角色信息System.out.println("管理員發布文檔");doc.transitionTo(new PublishedState());} else {System.out.println("非管理員無法發布");}}
}class PublishedState implements DocumentState {@Overridepublic void handlePublish(DemoDocument doc) { // 終態不處理System.out.println("文檔已發布,無法重復操作");}
}// Client(客戶端)
public class State {public static void main(String[] args) {DemoDocument doc = new DemoDocument();// 測試普通用戶場景doc.setCurrentUserRole("user");doc.publish(); // Draft → Moderationdoc.publish(); // 保留Moderation// 測試管理員場景doc.setCurrentUserRole("admin");doc.publish(); // Moderation → Published// 檢查終態穩定性doc.publish(); // 保持Published狀態}
}
總結:

(20)策略
策略是?種?為設計模式,它能讓你定義?系列算法,并將每種算法分別放?獨?的類中, 以使算法的對象能夠相互替換。
問題:

解決:

關鍵實現細節說明:
① 策略切換機制:通過setStrategy方法動態綁定策略對象
② 算法封裝:每個具體策略類自行實現路徑生成算法
③ 正交擴展:新增導覽策略無需修改現有代碼(如可添加BicycleStrategy)
④ 接口統一:所有策略實現相同的buildRoute方法簽名
// Strategy 接口
interface NavigationStrategy {List<String> buildRoute(String start, String end); // 路由算法接口
}// 具體策略實現
class WalkingStrategy implements NavigationStrategy {@Overridepublic List<String> buildRoute(String start, String end) { // 步行策略return Arrays.asList(start, "→ Central Park", "→ 5th Ave", end); // 步行路線}
}class BusTourStrategy implements NavigationStrategy {@Overridepublic List<String> buildRoute(String start, String end) { // 巴士路線策略return Arrays.asList(start, "→ Bus Stop A", "→ Bus Terminal", end); // 公交路線}
}class HelicopterStrategy implements NavigationStrategy {@Overridepublic List<String> buildRoute(String start, String end) { // 飛行路線策略return Arrays.asList(start, "→ Airport", "→ "+end+" Airspace", end); // 空中路線}
}// 上下文類
class TourGuide {private NavigationStrategy strategy;public void setStrategy(NavigationStrategy strategy) { // 運行時切換策略this.strategy = strategy;}public void showRoute(String start, String end) { // 統一入口方法if(strategy == null) {System.out.println("請先選擇導覽策略");return;}List<String> checkpoints = strategy.buildRoute(start, end); // 委托策略執行System.out.println("建議路線:");checkpoints.forEach(point -> System.out.println("? " + point));}
}// 客戶端示例
public class Strategy {public static void main(String[] args) {TourGuide app = new TourGuide();Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("請選擇導覽模式:\n1.步行 2.巴士 3.直升機");int choice = input.nextInt(); // 動態選擇策略switch(choice) {case 1:app.setStrategy(new WalkingStrategy()); // 綁定步行策略break;case 2:app.setStrategy(new BusTourStrategy());break;case 3:app.setStrategy(new HelicopterStrategy());break;default:throw new IllegalArgumentException("無效選擇");}app.showRoute("時代廣場", "自由女神像"); // 執行所選策略}
}
總結:

(21)模版方法
模板?法是?種?為設計模式,它在超類中定義了?個算法的框架,允許?類在不修改結構的情況下重寫算 法的特定步驟。
問題:數據挖掘類中包含許多重復代碼。

解決:

關鍵優化點:
① 固定流程:不可重寫的processDocument()確保流程一致
② 職責分離:各子類僅需實現格式相關解析邏輯
③ 擴展能力:通過鉤子方法實現可選擴展(如CSV格式驗證)
public class TemplateMethod {
}
// 抽象類定義模板方法
abstract class DataMiner {// 模板方法(不可被覆蓋)[^2]public final void processDocument() {openDocument();extractRawData();parseData(); // 抽象步驟[^1]analyzeData(); // 通用實現generateReport(); // Hook方法[^6]}// 文檔打開基礎實現protected void openDocument() {System.out.println("打開文檔...");}// 數據抽取基礎實現protected void extractRawData() {System.out.println("抽取原始數據...");}// 解析算法必須子類實現[^1]protected abstract void parseData();// 通用分析實現protected void analyzeData() {System.out.println("執行數據聚類分析...");}/* 鉤子方法(可選覆蓋)[^6] */protected void generateReport() {System.out.println("生成基礎統計報表");}
}// 具體子類實現
class PDFDataMiner extends DataMiner {@Overrideprotected void parseData() { // 實現特定解析邏輯System.out.println("解析PDF版式結構");System.out.println("提取PDF文本流");}
}class CSVDataMiner extends DataMiner {@Overrideprotected void parseData() {System.out.println("識別CSV分隔符");System.out.println("映射CSV字段");}@Overrideprotected void generateReport() { // 自定義Hook實現[^6]super.generateReport();System.out.println("追加CSV格式驗證結果");}
}// 客戶端調用示例
class Client {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("處理PDF文檔:");DataMiner pdfProcessor = new PDFDataMiner();pdfProcessor.processDocument(); // 執行完整流程[^1]System.out.println("\n處理CSV文檔:");DataMiner csvProcessor = new CSVDataMiner();csvProcessor.processDocument();}
}總結:

(22)訪問者
訪問者是?種?為設計模式,它能將算法與其所作?的對象隔離開來。
場景:
 解決:
解決:

模式核心實現要點:
① 雙分派機制:通過element.accept() 調用visitor特定方法
② 開放擴展:新增數據操作只需要添加訪問者類
③ 數據結構穩定:元素類無需修改即可支持新業務邏輯
// Visitor 接口定義地理信息操作規范
interface GeoVisitor {void visitCity(CityElement city); // 城市節點訪問接口void visitIndustry(IndustryElement industry); // 工業區訪問接口void visitSightseeing(SightseeingElement sight); // 景區訪問接口
}// 具象訪問者(統計信息導出)
class StatisticsExporter implements GeoVisitor {@Overridepublic void visitCity(CityElement city) { // 處理城市數據System.out.printf("統計城市[%s]: 人口%d萬 | ",city.getName(), city.getPopulation()); // 訪問節點屬性System.out.println("GDP " + city.getGdp() + "億元");}@Overridepublic void visitIndustry(IndustryElement industry) { // 處理工業區System.out.printf("工業區評估: %s 類型 | 占地面積%.1f平方公里\n",industry.getIndustryType(), industry.getArea());}@Overridepublic void visitSightseeing(SightseeingElement sight) { // 處理景點System.out.printf("景點分級: %s(%dA景區)\n",sight.getLandmark(), sight.getRating());}
}// 地理元素抽象接口(使用雙分派機制)
interface GeoElement {void accept(GeoVisitor visitor); // 關鍵接收方法
}// 城市實體類
class CityElement implements GeoElement {private String name;private int population;private double gdp;public CityElement(String name, int pop, double gdp) { }@Overridepublic void accept(GeoVisitor visitor) { // 雙分派入口visitor.visitCity(this);}public String getName() {return name;}public int getPopulation() {return population;}public double getGdp() {return gdp;}
}// 工業園區實體類
class IndustryElement implements GeoElement {private String industryType;private double area;public IndustryElement(String type, double area) { }@Overridepublic void accept(GeoVisitor visitor) {visitor.visitIndustry(this); // 調用工業區專門方法}public String getIndustryType() {return industryType;}public double getArea() {return area;}
}// 旅游景區實體類
class SightseeingElement implements GeoElement {private String landmark;private int rating;public SightseeingElement(String name, int stars) { }@Overridepublic void accept(GeoVisitor visitor) {visitor.visitSightseeing(this); // 調用景區處理邏輯}public String getLandmark() {return landmark;}public int getRating() {return rating;}
}// 客戶端使用
public class Visitor {public static void main(String[] args) {// 構建地理數據模型(復雜對象結構)List<GeoElement> geoGraph = Arrays.asList(new CityElement("上海", 2487, 43214),new IndustryElement("化工", 58.3),new SightseeingElement("外灘", 5));// 應用統計訪問者GeoVisitor exporter = new StatisticsExporter();geoGraph.forEach(element -> element.accept(exporter)); // 統一訪問入口}
}
總結:

(23)解釋器
解釋器設計模式提供了?種解釋和評估語?中的句?或表達式的?法。因為場景?較單?,所以 放在最后來講。此模式定義了?種語?語法,以及?個可以解析和執?表達式的解釋器。
優點:
① 可擴展性:解釋器模式允許通過創建新的表達式類來添加新的語法規則或語言結構,這使得它靈活且可擴展,以適應新的語言特性。
② 關注點分離:該模式將解釋邏輯與語言表達式分離。每個表達式類專注于解釋其特定的語法規則,從而提高代碼的模塊化和可維護性。
③ 簡化的語法表示:解釋器模式使用面向對象的類和遞歸算法提供了一種清晰簡潔的方式來表示復雜的語法。
④ 易于實現新的解釋器:該模式提供了一種為不同語言或領域特定語言(DSL)創建解釋器的結構化方法。
public class Interpretor {
}
// Abstract Expression
interface Expression {int interpret(Context context);
}
// Terminal Expressions
class NumberExpression implements Expression {private int number;public NumberExpression(int number) {this.number = number;}@Overridepublic int interpret(Context context) {return number;}
}
class AddExpression implements Expression {private Expression leftExpression;private Expression rightExpression;public AddExpression(Expression leftExpression, Expression rightExpression) {this.leftExpression = leftExpression;this.rightExpression = rightExpression;}@Overridepublic int interpret(Context context) {return leftExpression.interpret(context) + rightExpression.interpret(context);}
}
// Context
class Context {// Additional context information, if needed
}
// Client
public class Application {public static void main(String[] args) {// Create the expression: (2 + 3) + 4Expression expression = new AddExpression(new AddExpression(new NumberExpression(2), new NumberExpression(3)),new NumberExpression(4));// Create the context, if neededContext context = new Context();// Interpret the expressionint result = expression.interpret(context);System.out.println("Result: " + result); // Output: Result: 9}
}總結:
3. API設計方法
API設計的需求:分布式環境下的組件交互;自定義的工具服務/組件/框架;人人都在設計API
API設計的價值:API是對功能和組件內部實現的抽象;利用API避免了解第三方組件的細節;API用戶交流和溝通
(1)靜態工廠代替構造器
靜態工廠有名稱:valueOf/getInstance/newType/…
不需要每次調用時都創建一個新對象:緩存實例重復利用
可以返回任何子類型對象:更大的靈活性

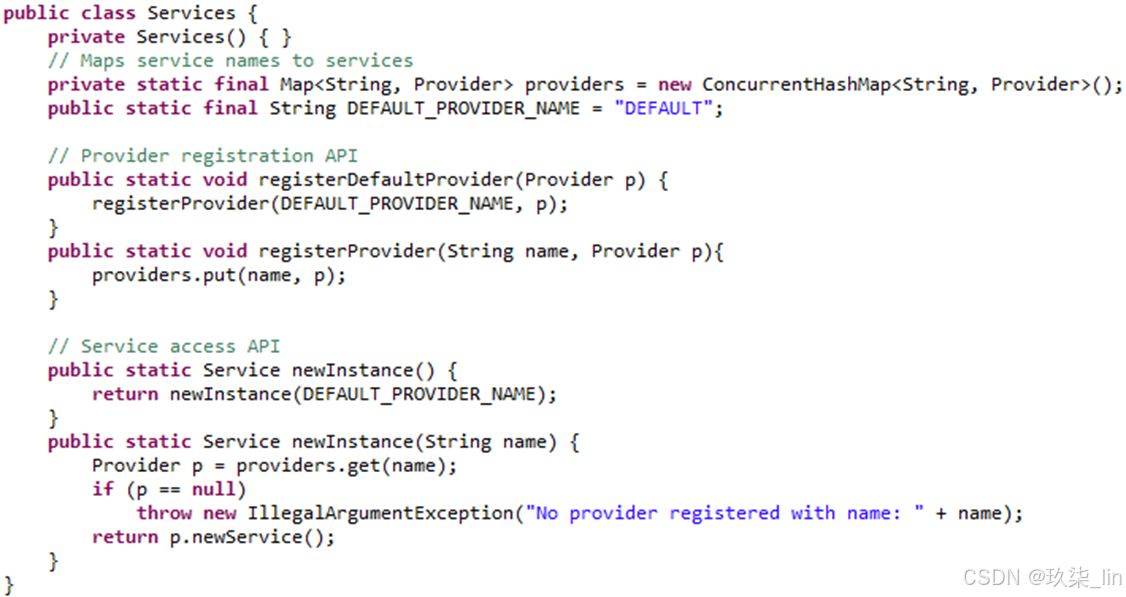
(2)使用Builder替代多個構造器
場景:當構造器需要一些必選參數、又需要大量可選參數時
解決方案:① 多個構造器或靜態工廠;②?API使用代碼難以編寫和閱讀
更好的解決方案:① Builder設計模式;②?鏈式API

(3)使可訪問性最小化
基本原則:API公開的內容越少越好
實踐:
- 方法優于字段
- getter:計算;數據延遲加載;同步訪問
- setter:數據合法性校驗;發送字段變更通知
- 應對API的潛在變動
- 工廠方法優于構造函數
- 讓所有內容不可修改
- 避免濫用setter方法
- API中getter應遠遠多于setter
- 很多setter操作應該封裝到上下文內部進行
- 很多setter公開給所有開發人員調用時沒有必要的
- 很多setter方法通可以過getter方法獲取結果:setVisible/isVisible
(4)使可變性最小化
- 原則:
- 不要提供任何會修改對象狀態的方法
- 保證類不會被擴展
- 所有域都是final
- 所有域都是私有的
- 確保對于任何可變組件的互斥訪問
- 不可變對象的特點:
- 線程安全,不要求同步
- 每個值都需要一個實例變量
(5)檢查參數的有效性
- fast-fail:應該在發生錯誤之后盡快檢測出錯誤
- 方法和構造器需要限制參數值:
- 拋出異常
- 異常轉譯
- 使用斷言(Assertion)

(6)謹慎設計方法簽名
- 選擇方法的名稱:中文->英文/通用術語/統一風格
- 不要過于追求便利的方法
- 避免過長的參數:分解方法/幫助類/Builder模式;參數類型中盡量使用接口而非類
?
(7)慎用重載和可變參數
重載:里氏替換原則;保守做法(不要設計兩個具有相同參數數量的重載方法)
可變參數:API中盡量不要使用可變參數
(8)返回零長度的數組或集合
習慣的做法:

更好的做法:

4. 組件設計原則
(1)無環依賴原則
認為在組件之間不應該存在循環依賴關系。通過將系統劃分為不同的可發布組件,對某一個組件的修改所產生的影響不應該擴展到其他組件
(2)穩定抽象原則
認為組件的抽象程度應該與其穩定程度保持一致。即一個穩定的組件應該也是抽象的,這樣該組件的穩定性就不會無法擴展。另一方面,一個不穩定的組件應該是具體的,因為他的不穩定性使其內部代碼更易于修改
(3)穩定依賴原則
認為被依賴者應該比依賴者更穩定。一個好的設計中的組件之間的依賴應該朝著穩定的方向進行。一個組件只應該依賴那些比自己更穩定的組件
組件穩定性度量:I = Ce / (Ca + Ce)
- I代表Instability,即不穩定性,它的值處于[0,1]之間
- Ce代表離心耦合(Efferent Coupling),表示被該組件依賴的外部組件的數量
- Ca代表向心耦合(Afferent Coupling),表示依賴該組件的外部組件數量
?
組件抽象度度量:A = AC / (AC + CC)
- A代表抽象度(Abstractness)
- AC(Abstract Class)表示組件中抽象類的數量
- CC(Concrete Class)表示組件中非抽象類的總和
?
一個系統中多數的組件位于依賴鏈的中間,也就是說它們即具備一定的穩定性也表現出一定的抽象度。如果一個組件的穩定度和抽象度都是1,意味著該組件里面全是抽象類且沒有任何組件依賴它,那么這個組件就沒有任何用處。相反,如果一個組件穩定度和抽象度都是0,那么意味著這個組件不斷在變化,不具備維護性,這也是我們不想設計的組件。所以,在穩定度和抽象度之間應該保持一種平衡,這條平衡線有一個專業的名稱,即主序列(Main Sequence)
?


 WebSocket+語音播報功能實現(來訂單+催單))





 錯誤)






)




