堆:
- 此處堆為二叉樹的應用,不是計算機中用于管理動態內存的堆。
- 形狀是完全二叉樹。
- 堆分兩種:最大堆,最小堆。
- 最大堆:每個節點比子樹所有節點的數值都大,根節點為最大值。
- 最小堆:每個節點比子樹所有節點的數值都小,根節點為最小值。
- 左右節點的數值沒有順序要求,但有左子節點才能有右子節點。
- 一般用數組實現堆。最小堆可以實現優先隊列。
注:完全二叉樹:每個節點最多2個節點,倒數第二層級(含)之前層級的所有節點都有元素,最后一層級從左到右依次有元素(中間不能斷)。
子樹:節點及其所有子節點形成子樹。(即節點,左右子節點,左右子節點的左右子節點,。。。)
根節點:沒有父節點。
兄弟節點:其父節點是同一個節點。
| 節點 | 索引號(根節點為0) |
|---|---|
| 節點 | x |
| 父節點 | (x-1)// 2 |
| 左兄弟節點(右節點才有) | x - 1 |
| 右兄弟節點(左節點才有) | x + 1 |
| 左子節點 | 2x + 1 |
| 右子節點 | 2x + 2 |
C語言實現:(使用數組實現最小堆)
創建堆(結構體數據類型):記錄數組地址和元素個數
// 堆(結構體數據類型)
typedef struct Heap
{int *p; // 記錄數組地址int n; // 記錄元素個數
} Heap; // 別名?(函數)堆初始化:
// 堆初始化
void init(Heap *heap, int length)
{heap->p = (int *)malloc(length * sizeof(int)); // 分配內存空間if(heap->p == NULL){perror("Memory allocation failed");exit(-1);}heap->n = 0; // 元素個數,初始化為0
}?創建堆變量,并初始化
Heap heap; // 創建堆變量
init(&heap, 8); // 設置數組最大元素個數為8添加元素:
1、先在末尾添加元素。
2、(向上調整)與父節點比較大小,若小于父節點,與父節點交換位置,直到開頭位置(根節點,數組第一個元素)。
(注:子節點索引號為x,父節點索引號為(x-1)//2)
void add(Heap *heap, int data) // add a element to the heap
{// 往末尾添加元素heap->p[heap->n] = data;// (向上調整) 與父節點比較,小于父節點的值,與父節點交換位置int cur = heap->n;while(cur > 0){int parent = ceil((cur - 1) / 2);if(heap->p[parent] > data){heap->p[cur] = heap->p[parent];heap->p[parent] = data;cur = parent;}else break;}// 每添加一個元素,元素個數+1heap->n++;
}刪除(根節點):
1、記錄根節點(數組第一個元素)和末尾節點(數組最后一個元素)。
2、末尾節點的值換到根節點位置,元素個數-1。
3、(向下調整)從根節點開始,依次與左右子節點比較大小,數值小的是父節點,直到比對到末尾。
(注:父節點索引號為x,左子節點索引號為2x+1,右子節點索引號為2x+2)
int delete(Heap *heap) // delete root from the heap
{if(heap->n == 0) return -1; // 空樹heap->n--; // 每刪除一次根節點,元素個數-1int root = heap->p[0], enddata = heap->p[heap->n];heap->p[0] = enddata; // 末尾元素換到第一個位置// (向下調整) 與左右子節點比較,若子節點小,與較小子節點交換位置int cur = 0;while(cur <= heap->n){int left = cur * 2 + 1, right = cur * 2 + 2, minchild;if(left > heap->n) break; // 沒有左子節點if(right > heap->n) minchild = left; // 沒有右子節點,有左子節點else // 左右子節點都有的情況{// 左右子節點比較,找到較小子節點if(heap->p[right] < heap->p[left]) minchild = right;else minchild = left;// 父節點與較小子節點比較,若子節點小,與子節點交換位置if(heap->p[minchild] < enddata){heap->p[cur] = heap->p[minchild];heap->p[minchild] = enddata;cur = minchild;}else break;}}return root;
}獲取根節點:(數組第一個元素)
int getroot(Heap *heap) // get the root from the heap
{if(heap->n == 0){printf("Empty heap\n");exit(-1);}return heap->p[0];
}遍歷堆:(類似廣度遍歷二叉樹)
每個節點比子樹的所有節點都小,但左右節點沒有順序要求。
void traverse(Heap *heap) // show element one by one (like breadth traverse the tree)
{if(heap->n == 0) return ;printf("elements(%d): ", heap->n);for(int k = 0; k < heap->n; k++){printf("%d ", heap->p[k]);}printf("\n");
}清空堆:
釋放數組內存空間,指向數組的指針指向NULL,元素個數為0。
void clear(Heap *heap) // clear the heap (free memory space of the array)
{free(heap->p); // 釋放數組內存空間heap->p = NULL; // 指針指向NULL,避免野指針heap->n = 0; // 元素個數為0
}?
完整代碼:(heap.c)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdlib.h>/* structure */
typedef struct Heap
{int *p; // memory address of the heap (array)int n; // the number of the heap
} Heap;/* function prototype */
void init(Heap *, int); // heap initialization
void add(Heap *, int); // add a element to the heap
int delete(Heap *); // delete root from the heap
int getroot(Heap *); // get the root from the heap
void traverse(Heap *); // show element one by one (likely breadth traverse the tree)
void clear(Heap *); // clear the heap (free memory space of the array)/* main function */
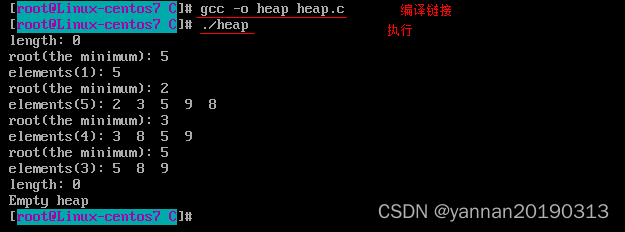
int main(void)
{Heap heap;init(&heap, 8);printf("length: %d\n", heap.n);add(&heap, 5); printf("root(the minimum): %d\n", getroot(&heap));traverse(&heap);add(&heap, 8); add(&heap, 3); add(&heap, 9); add(&heap, 2);printf("root(the minimum): %d\n", getroot(&heap));traverse(&heap);delete(&heap); printf("root(the minimum): %d\n", getroot(&heap));traverse(&heap);delete(&heap); printf("root(the minimum): %d\n", getroot(&heap));traverse(&heap);clear(&heap);printf("length: %d\n", heap.n);printf("root(the minimum): %d\n", getroot(&heap));return 0;
}/* subfunction */
void init(Heap *heap, int length) // heap initialization
{heap->p = (int *)malloc(length * sizeof(int));if(heap->p == NULL){perror("Memory allocation failed");exit(-1);}heap->n = 0;
}void add(Heap *heap, int data) // add a element to the heap
{// add a element to the end of the heapheap->p[heap->n] = data;// (adjust up) compair with parent,if smaller than parent, change the positionint cur = heap->n;while(cur > 0){int parent = ceil((cur - 1) / 2);if(heap->p[parent] > data){heap->p[cur] = heap->p[parent];heap->p[parent] = data;cur = parent;}else break;}heap->n++;
}int delete(Heap *heap) // delete root from the heap
{if(heap->n == 0) return -1;heap->n--;int root = heap->p[0], enddata = heap->p[heap->n];heap->p[0] = enddata; // put the last element to the first position// (adjust down) compair with left and right child, minimun is parentint cur = 0;while(cur <= heap->n){int left = cur * 2 + 1, right = cur * 2 + 2, minchild;if(left > heap->n) break; // no left childif(right > heap->n) minchild = left; // have left child, no right childelse // have left child and right child{// compair left child and right child, find smaller oneif(heap->p[right] < heap->p[left]) minchild = right;else minchild = left;// smaller child compair with parent,if child is the smallest, changeif(heap->p[minchild] < enddata){heap->p[cur] = heap->p[minchild];heap->p[minchild] = enddata;cur = minchild;}else break;}}return root;
}int getroot(Heap *heap) // get the root from the heap
{if(heap->n == 0){printf("Empty heap\n");exit(-1);}return heap->p[0];
}void traverse(Heap *heap) // show element one by one (like breadth traverse the tree)
{if(heap->n == 0) return ;printf("elements(%d): ", heap->n);for(int k = 0; k < heap->n; k++){printf("%d ", heap->p[k]);}printf("\n");
}void clear(Heap *heap) // clear the heap (free memory space of the array)
{free(heap->p);heap->p = NULL;heap->n = 0;
}編譯鏈接: gcc -o heap heap.c
執行可執行文件:?./heap
?









申請的字典的類型是什么?)


:事件、文件)



:JVM虛擬機運行時棧幀結構)


