本項目旨在利用計算機視覺技術和深度學習算法,實現對停車場車位狀態的實時自動識別。通過攝像頭監控停車場內部,系統能夠高效準確地辨認車位是否被占用,為車主提供實時的空閑車位信息,同時為停車場管理者提供智能化的車位管理工具。該系統結合了OpenCV的強大圖像處理能力與Keras的易用性,便于快速構建和部署。
技術棧:
- OpenCV:用于圖像的預處理,包括視頻捕獲、圖像處理(如灰度轉換、濾波、邊緣檢測等)以及ROI(感興趣區域)的選取,為深度學習模型提供高質量的輸入。
- Keras:基于TensorFlow的高級API,用于搭建和訓練深度學習模型。項目中,可能采用預訓練模型(如VGGNet、ResNet等)進行遷移學習,通過微調模型來適應車位識別任務,或者從零開始構建卷積神經網絡(CNN)模型進行車位狀態分類。
項目流程:
-
數據收集與預處理:首先,通過攝像頭錄制停車場視頻,從中截取包含車位的畫面,人工標注車位狀態(如空閑或占用)。接著,對圖像進行歸一化、增強等預處理,創建訓練和驗證數據集。
-
模型訓練:使用Keras構建深度學習模型,加載預處理后的數據集進行訓練。訓練過程中,可能涉及調整超參數、優化器選擇、損失函數配置等,以達到理想的分類性能。
-
模型驗證與優化:在驗證集上評估模型性能,根據準確率、召回率等指標調整模型結構或參數,進行模型優化。
-
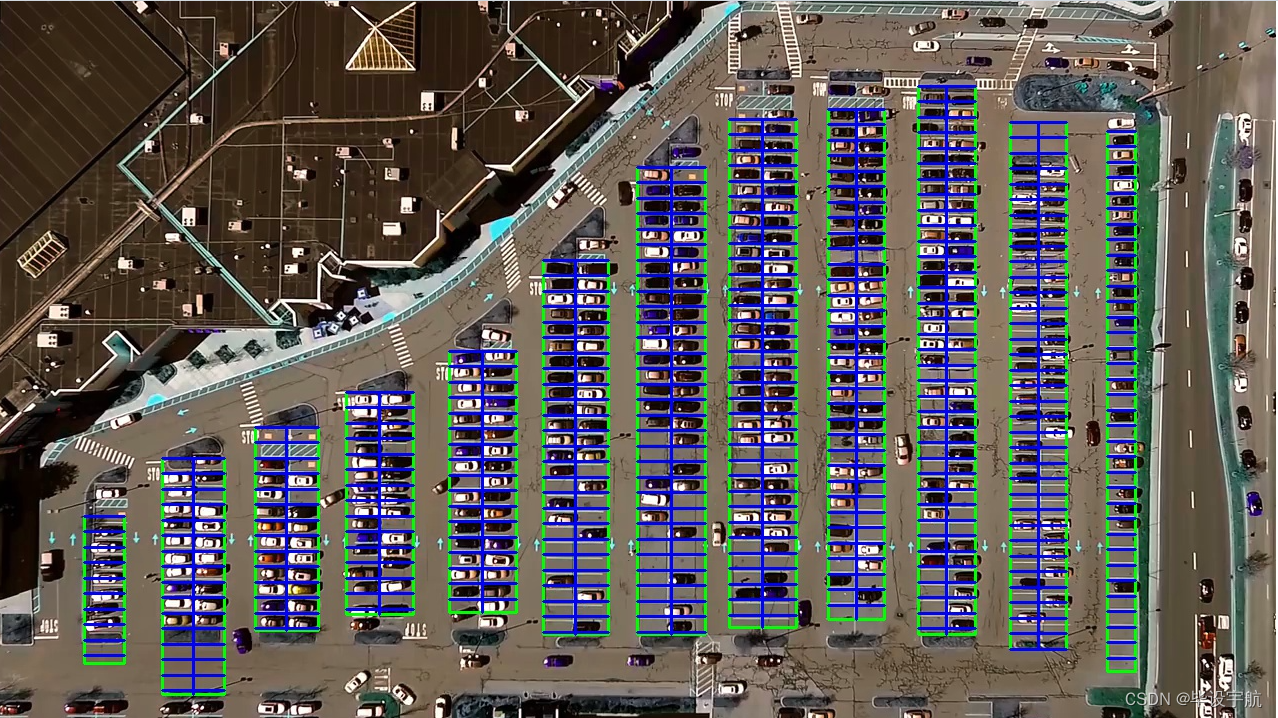
實時檢測與應用:將訓練好的模型集成到OpenCV中,實現實時視頻流處理。系統不斷捕獲停車場的視頻幀,進行圖像處理后,通過模型預測車位狀態。識別結果以可視化方式展示,如在視頻流中標記車位為空閑或占用,并可進一步集成到停車場管理系統,實現車位引導、計費等功能。
特色與優勢:
- 實時性:系統能夠實時監控車位狀態,及時更新信息,提高停車場的運營效率。
- 準確性:深度學習模型具有強大的特征學習能力,即使在復雜光照、遮擋等條件下也能保持較高識別準確率。
- 易部署與擴展:基于OpenCV和Keras的方案易于開發和調試,且模型可根據新數據持續優化,便于后續維護和功能升級。
- 智能化管理:為停車場管理者提供精準的車位占用情況,有助于優化停車資源分配,提升用戶體驗。
總結: 此項目通過融合OpenCV的圖像處理能力和Keras構建的深度學習模型,實現了對停車場車位狀態的自動識別,是智能交通系統和智慧城市應用中的一個重要組成部分,具有廣泛的應用前景和社會價值。
from __future__ import division # 改變 Python 2 中除法操作符 / 的默認行為,使其表現得像 Python 3 中的除法操作符,結果會保留小數部分
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 用于創建圖表和可視化數據的 Python 庫
import cv2
import os, glob # glob文件名匹配的模塊
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from keras.applications.imagenet_utils import preprocess_input
from keras.models import load_model
from keras.preprocessing import image
from Parking import Parking
import pickle # 序列化和反序列化對象的標準模塊cwd = os.getcwd() # 獲取當前工作目錄def img_process(test_images, park):# 過濾背景,低于lower_red和高于upper_red的部分分別編程0,lower_red~upper_red之間的值編程255# map 函數用于將一個函數應用到可迭代對象的每個元素,并返回結果# 通過 list 函數將其轉換為列表white_yellow_images = list(map(park.select_rgb_white_yellow,test_images))park.show_images(white_yellow_images)# 轉灰度圖gray_images = list(map(park.convert_gray_scale, white_yellow_images))park.show_images(gray_images)# 進行邊緣檢測edge_images = list(map(lambda image: park.detect_edges(image),gray_images))park.show_images(edge_images)# 根據需要設定屏蔽區域roi_images = list(map(park.select_region, edge_images))park.show_images(roi_images)# 霍夫變換,得出直線list_of_lines= list(map(park.hough_line, roi_images))# zip 函數來同時迭代 test_images 和 list_of_lines 中的元素line_images = []for image,lines in zip(test_images,list_of_lines):line_images.append(park.draw_lines(image,lines))park.show_images(line_images)rect_images = []rect_coords = [] # 列矩形for image,lines in zip(test_images, list_of_lines):# 過濾部分直線,對直線進行排序,得出每一列的起始點和終止點,并將列矩形畫出來new_image,rects = park.identify_blocks(image,lines)rect_images.append(new_image)rect_coords.append(rects)park.show_images(rect_images)delineated = []spot_pos = []for image,rects in zip(test_images, rect_coords):# 在圖上將停車位畫出來,并返回字典{坐標:車位序號}new_image,spot_dict = park.draw_parking(image,rects)delineated.append(new_image)spot_pos.append(spot_dict)park.show_images(delineated)final_spot_dict = spot_pos[1]print(len(final_spot_dict))with open('spot_dict.pickle','wb') as handle:pickle.dump(final_spot_dict,handle,property==pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)park.save_images_for_cnn(test_images[0],final_spot_dict)return final_spot_dictdef keras_model(weights_path):model = load_model(weights_path)return modeldef img_test(test_image,final_spot_dict,model,class_dictionary):for i in range (len(test_images)):predicted_images = park.predict_on_image(test_images[i],final_spot_dict,model,class_dictionary)def video_test(video_name,final_spot_dict,model,class_dictionary):name = video_namecap = cv2.VideoCapture(name)park.predict_on_video(name,final_spot_dict,model,class_dictionary,ret=True)if __name__ == '__main__':test_images = [plt.imread(path) for path in glob.glob('test_images/*.jpg')]weights_path = 'car1.h5'video_name = 'parking_video.mp4'class_dictionary = {}class_dictionary[0] = 'empty'class_dictionary[1] = 'occupied'park = Parking()park.show_image(test_images)final_spot_dict = img_process(test_images, park)model = keras_model(weights_path)img_test(test_images,final_spot_dict,model,class_dictionary)video_test(video_name,final_spot_dict,model,class_dictionary)
parking py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2
import os,glob
import numpy as npclass Parking:def show_images(self, images, cmap=None):cols = 2rows = (len(images) + 1)//cols # //為整除運算符plt.figure(figsize=(15,12)) # 創建一個圖形窗口,并指定其大小為 15x12 英寸for i,image in enumerate(images):plt.subplot(rows, cols, i+1) # 在當前圖形窗口中創建一個子圖,i+1 是因為子圖的編號是從 1 開始的# 檢查圖像的維度,如果圖像是二維的(灰度圖像),則將顏色映射設置為灰度,否則保持傳入的 cmap 參數不變cmap = 'gray' if len(image.shape)==2 else cmapplt.imshow(image, cmap=cmap)plt.xticks([]) # 去除 x 軸和 y 軸的刻度標簽plt.yticks([])plt.tight_layout(pad=0,h_pad=0,w_pad=0) # 調整子圖之間的間距plt.show()def cv_show(self, name, img):cv2.imshow(name, img)cv2.waitKey(0)cv2.destroyAllWindows()def select_rgb_white_yellow(self,image):# 過濾掉背景lower = np.uint8([120,120,120])upper = np.uint8([255,255,255])# 低于lower_red和高于upper_red的部分分別編程0,lower_red~upper_red之間的值編程255,相當于過濾背景white_mask = cv2.inRange(image,lower,upper)self.cv_show('white_mask',white_mask)# 與操作masked = cv2.bitwise_and(image, image, mask=white_mask)self.cv_show('masked',masked)return maskeddef convert_gray_scale(selfself,image):return cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# 提取圖像中的邊緣信息# 返回的是一個二值圖像,其中邊緣點被標記為白色(255),而非邊緣點被標記為黑色(0)def detect_edges(self, image, low_threshole=50, high_threshold=200):return cv2.Canny(image, low_threshole, high_threshold)def filter_region(self, image, vertices):# 剔除掉不需要的地方mask = np.zeros_like(image) # 創建和原圖一樣大的圖,置零if len(mask.shape)==2: # 是否為一張灰度圖cv2.fillPoly(mask, vertices, 255) # 使用頂點vertices在mask上填充多邊形,并置為255白色self.cv_show('mask',mask)return cv2.bitwise_and(image,mask)def select_region(self, image):# 手動選擇區域# 首先,通過頂點定義多邊形。rows, cols = image.shape[:2] # h和wpt_1 = [cols*0.05, rows*0.09]pt_2 = [cols*0.05, rows*0.70]pt_3 = [cols*0.30, rows*0.55]pt_4 = [cols*0.6, rows*0.15]pt_5 = [cols*0.90, rows*0.15]pt_6 = [cols*0.90, rows*0.90]vertices = np.array([[pt_1, pt_2, pt_3, pt_4, pt_5, pt_6]],dtype=np.int32)point_img = image.copy()point_img = cv2.cvtColor(point_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)for point in vertices[0]:cv2.circle(point_img,(point[0], point[1]), 10, (0,0,255), 4)self.cv_show('point_img',point_img)return self.filter_region(image, vertices)# 霍夫變換,得出直線def hough_line(self,image):# 檢測輸入圖像中的直線,并返回檢測到的直線的端點坐標# 輸入的圖像需要是邊緣檢測后的結果# minLineLength(線的最短長度,比這個短的都被忽略)和MaxLineCap(兩條直線之間的最大間隔,小于辭職,認為是一條直線)# rho以像素為單位的距離分辨率,通常設置為 1 像素# thrta角度精度# threshod直線交點數量閾值。只有累加器中某個點的投票數高于此閾值,才被認為是一條直線。return cv2.HoughLinesP(image, rho=0.1, thrta=np.pi/10, threshold=15,minLineLength=9,maxLineGap=4)# 過濾霍夫變換檢測到的直線def draw_lines(self, image, lines, color=[255,0,0], thickness=2, make_copy=True):if make_copy:image = np.copy(image)cleaned = []for line in lines:for x1,y1,x2,y2 in line:if abs(y2-y1) <= 1 and abs(x2-x1) >= 25 and abs(x2-x1) <= 55:cleaned.append((x1,y1,x2,y2))cv2.line(image, (x1,y1), (x2,y2), color, thickness)print(" No lines detected: ", len(cleaned))return image# 過濾部分直線,對直線進行排序,得出每一列的起始點和終止點,并將列矩形畫出來def identify_blocks(self, image, lines, make_copy=True):if make_copy:new_image = np.copy(image)# step1: 過濾部分直線cleaned = []for line in lines:for x1,y1,x2,y2 in line:if abs(y2-y1) <= 1 and abs(x2-x1) >= 25 and abs(x2-x1)<= 55:cleaned.append((x1,y1,x2,y2))# step2: 對直線按照 起始點的x和y坐標 進行排序import operator # 可以使用其中的各種函數來進行操作,例如比較、算術list1 = sorted(cleaned, key=operator.itemgetter(0,1)) # 從列表的每個元素中獲取索引為0和1的值,然后將這些值用作排序的依據# step3: 找到多個列,相當于每列是一排車clusters = {} # 列數:對應該列有哪些車位線dIndex = 0clus_dist = 10for i in range(len(list1) - 1):distance = abs(list1[i+1][0] - list1[i][0]) # 根據前后兩組車位線的x1距離if distance <= clus_dist:if not dIndex in clusters.keys(): clusters[dIndex] = []clusters[dIndex].append(list1[i])clusters[dIndex].append(list1[i + 1])else:dIndex += 1# step4: 得到每一列的四個坐標rects = {} # 每一列的四個角的坐標i = 0for key in clusters:all_list = clusters[key]# 將列表 all_list 轉換為一個集合set,去重# {(10, 20, 30, 40), (20, 30, 40, 50)} 轉為 [(10, 20, 30, 40), (20, 30, 40, 50)]cleaned = list(set(all_list))if len(cleaned) > 5:cleaned = sorted(cleaned, key=lambda tup: tup[1]) # 按y1進行排序avg_y1 = cleaned[0][1] # 第一條線段的起始點 y 坐標avg_y2 = cleaned[-1][1] # 最后一條線段的起始點 y 坐標,即整個區域的上下邊界avg_x1 = 0avg_x2 = 0for tup in cleaned: # 累加起始點和結束點的 x 坐標avg_x1 += tup[0]avg_x2 += tup[2]avg_x1 = avg_x1/len(cleaned) # 取平均起始點和結束點x坐標值avg_x2 = avg_x2/len(cleaned)rects[i] = (avg_x1, avg_y1,avg_x2,avg_y2)i += 1print("Num Parking Lanes:", len(rects))# step5: 把列矩形畫出來buff = 7for key in rects:tup_topLeft = (int(rects[key][0] - buff), int(rects[key][1])) # x1-buff, y1tup_botRight = (int(rects[key][2] + buff), int(rects[key][3])) # x2+buff, y2cv2.rectangle(new_image, tup_topLeft, tup_botRight,(0,255,0),3)return new_image,rects# 在圖上將停車位畫出來,并返回字典{坐標:車位序號}def draw_parking(self, image, rects, make_copy=True, color=[255,0,0], thickness=2, save=True):if make_copy:new_image = np.copy(image)gap = 15.5 # 一個車位大致高度spot_dict = {} # 字典:一個車位對應一個位置tot_spots = 0 # 總車位# 微調adj_y1 = {0: 20, 1: -10, 2: 0, 3: -11, 4: 28, 5: 5, 6: -15, 7: -15, 8: -10, 9: -30, 10: 9, 11: -32}adj_y2 = {0: 30, 1: 50, 2: 15, 3: 10, 4: -15, 5: 15, 6: 15, 7: -20, 8: 15, 9: 15, 10: 0, 11: 30}adj_x1 = {0: -8, 1: -15, 2: -15, 3: -15, 4: -15, 5: -15, 6: -15, 7: -15, 8: -10, 9: -10, 10: -10, 11: 0}adj_x2 = {0: 0, 1: 15, 2: 15, 3: 15, 4: 15, 5: 15, 6: 15, 7: 15, 8: 10, 9: 10, 10: 10, 11: 0}for key in rects:tup = rects[key]x1 = int(tup[0] + adj_x1[key])x2 = int(tup[2] + adj_x2[key])y1 = int(tup[1] + adj_y1[key])y2 = int(tup[3] + adj_y2[key])cv2.rectangle(new_image,(x1,y1), (x2,y2), (0,255,0), 2)num_splits = int(abs(y2-y1)//gap) # 一列總共有多少個車位for i in range (0,num_splits+1): # 畫車位框y = int(y1 + i*gap)cv2.rectangle(new_image, (x1,y), (x2,y2), (0,255,0), 2)if key > 0 and key < len(rects)-1:# 豎直線x = int((x1+x2)/2)cv2.line(new_image,(x,y1),(x,y2),color,thickness)# 計算數量if key == 0 or key == (len(rects) - 1): # 對于第一列和最后一列(只有一排車位)tot_spots += num_splits + 1else:tot_spots += 2*(num_splits + 1) # 一列有兩排車位# 字典對應好if key == 0 or key == (len(rects) - 1): # 對于第一列和最后一列(只有一排車位)for i in range(0, num_splits+1):cur_len = len(spot_dict)y = int(y1 + i*gap)spot_dict[(x1,y,x2,y+gap)] = cur_len + 1else:for i in range(0, num_splits+1):cur_len = len(spot_dict)y = int(y1 + i*gap)x = int((x1+x2)/2)spot_dict[(x1,y,x,y+gap)] = cur_len + 1spot_dict[(x,y,x2,y+gap)] = cur_len + 2print("total parking spaces: ", tot_spots, cur_len)if save:filename = 'with_parking.jpg'cv2.imwrite(filename, new_image)return new_image, spot_dict# 根據傳入的起始點和終止點坐標列表畫框def assign_spots_map(self, image, spot_dict, make_copy= True, color=[255,0,0], thickness=2):if make_copy:new_image = np.copy(image)for spot in spot_dict.keys():(x1,y1,x2,y2) = spotcv2.rectangle(new_image,(int(x1),int(y1)), (int(x2),int(y2)), color, thickness)return new_image# 遍歷字典{坐標,車位號}在圖片中截取對應坐標的圖像,按車位號保存下來def save_images_for_cnn(self, image, spot_dict, folder_name= 'cnn_data'):for spot in spot_dict.keys():(x1,y1,x2,y2) = spot(x1,y1,x2,y2) = (int(x1),int(y1),int(x2),int(y2))# 裁剪spot_img= image[y1:y2, x1:x2]spot_img = cv2.resize(spot_img, (0,0), fx=2.0, fy=2.0)spot_id = spot_dict[spot]filename = 'spot' + str(spot_id) + '.jpg'print(spot_img.shape, filename, (x1,x2,y1,y2))cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(folder_name, filename), spot_img)# 將圖像進行歸一化,并將其轉換成一個符合深度學習模型輸入要求的四維張量,進行訓練def make_prediction(self, image, model, class_dictionary):# 預處理img = image/255. # 將圖像的像素值歸一化到 [0, 1] 的范圍內# 將圖像轉換成一個四維張量image = np.expend_dims(img, axis = 0)# 將圖片調用keras算法進行預測class_predicted = model.predict(image) # 得出預測結果inID = np.argmax(class_predicted[0]) # 找到數組中最大值所在的索引label = class_dictionary[inID]return labeldef predict_on_image(self, image, spot_dict, model, class_dictionary,make_copy=True, color=[0,255,0], alpha=0.5):if make_copy:new_image = np.copy(image)overlay = np.copy(image)self.cv_show('new_image',new_image)cnt_empty = 0all_spots = 0for spot in spot_dict.keys():all_spots += 1(x1, y1, x2, y2) = spot(x1, y1, x2, y2) = (int(x1), int(y1), int(x2), int(y2))spot_img = image[y1:y2, x1:x2]spot_img = cv2.resize(spot_img, (48,48))label = self.make_prediction(spot_img, model, class_dictionary)if label== 'empty':cv2.rectangle(overlay, (int(x1), int(y1)), (int(x2), int(y2)), color, -1)cnt_empty += 1cv2.addWeighted(overlay, alpha, new_image, 1-alpha, 0, new_image)cv2.putText(new_image, "Available: %d spots" %cnt_empty, (30,95),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,0.7,(255,255,255),2)cv2.putText(new_image, "Total: %d spots" %all_spots, (30,125),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7,(255,255,255),2)save = Falseif save:filename = 'with_parking.jpg'cv2.imwrite(filename, new_image)self.cv_show('new_image',new_image)return new_imagedef predict_on_video(self, video_name, final_spot_dict, model, class_dictionary, ret=True):cap= cv2.VideoCapture(video_name)count = 0while ret:ret, image = cap.read()count += 1if count == 5:count == 0new_image = np.copy(image)overlay = np.copy(image)cnt_empty = 0all_spots = 0color = [0,255,0]alpha = 0.5for spot in final_spot_dict.keys():all_spots += 1(x1,y1,x2,y2) = spot(x1,y1,x2,y2) = (int(x1), int(y1), int(x2), int(y2))spot_img = image[y1:y2, x1:x2]spot_img = cv2.resize(spot_img, (48,48))label = self.make_prediction(spot_img, model, class_dictionary)if label == 'empty':cv2.rectangle(overlay, (int(x1),int(y1)), (int(x2),int(y2)), color, -1)cnt_empty += 1cv2.addWeighted(overlay, alpha, new_image, 1-alpha, 0, new_image)cv2.putText(new_image,"Available: %d spots" % cnt_empty,(30,95),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (255,255,255),2)cv2.putText(new_image, "Total: %d spots" %all_spots, (30,125),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (255,255,255), 2)cv2.imshow('frame',new_image)# 檢測用戶是否按下了 'q' 鍵if cv2.waitKey(10) & 0xFF == ord('q'): # 通過 & 0xFF 操作,可以確保只獲取ASCII碼的最后一個字節breakcv2.destroyWindow()cap.release()



】)














 Popover 的content有個modal,關不掉了)