1. 核心功能
LossBasedBweV2是WebRTC Google Congestion Control (GoogCC) 算法套件中的第二代基于丟包的帶寬估計器。它的核心功能是:
帶寬估計: 根據網絡數據包的丟失情況,估算當前網絡路徑可用的帶寬上限。其核心假設是:當發送速率超過網絡容量時,將出現擁塞,表現為數據包丟失。通過分析丟包模式,它可以反向推斷出這個容量瓶頸。
狀態輸出: 不僅輸出一個帶寬估計值(
DataRate),還輸出一個狀態(LossBasedState)。這個狀態用于指導上層控制器(如GoogCCNetworkController)的行為,例如:kIncreasing/kIncreaseUsingPadding: 建議可以嘗試增加發送速率,后者暗示可以使用填充數據來探測。kDecreasing: 估計值正在因丟包而下降,應減少發送速率。kDelayBasedEstimate: 當前未處于丟包受限狀態,應優先使用基于延遲的估計結果。
多源信息融合: 它并非孤立工作,而是融合了多種信息源:
丟包信息: 主要輸入,來自
RTCP Receiver Reports或傳輸反饋。延遲基于估計值: 來自
DelayBasedBwe的另一個估計值,用作上限或候選值。確認速率: 當前網絡的吞吐量測量值,用作參考和下限。
配置參數: 通過字段試驗(Field Trials)提供大量可調參數,用于控制算法行為。
2. 核心算法原理
LossBasedBweV2的核心算法基于最大似然估計(Maximum Likelihood Estimation, MLE),其基本原理可以概括為:
建立丟包模型: 算法假設一個信道模型,其中包丟失概率由兩部分組成:
固有丟失(
inherent_loss): 代表與擁塞無關的隨機丟包(如無線鏈路錯誤)。擁塞丟失: 當發送速率(
sending_rate)超過信道的“丟包受限帶寬”(loss_limited_bandwidth)時,按一定比例((sending_rate - loss_limited_bandwidth) / sending_rate)產生額外丟包。
總的丟包概率函數為:loss_probability = inherent_loss + (1 - inherent_loss) * max(0, (sending_rate - loss_limited_bandwidth) / sending_rate)
定義似然函數: 給定一組觀測到的包接收/丟失情況,計算在這組信道參數(
inherent_loss,?loss_limited_bandwidth)下,觀察到這組結果的似然度(Likelihood)。似然度是模型參數的函數。最大化似然函數: 算法的目標是找到一組參數(
inherent_loss,?loss_limited_bandwidth),使得觀察到的數據的似然度最大。這組參數就是最可能產生當前觀測數據的信道狀態,其中的loss_limited_bandwidth就是最終的帶寬估計值。牛頓法優化: 為了高效地找到使似然函數最大化的參數,算法對
inherent_loss參數使用了牛頓法(Newton's Method)進行迭代優化。GetDerivatives()函數計算似然函數的一階和二階導數,NewtonsMethodUpdate()根據導數更新inherent_loss的值。高帶寬偏好: 為了防止算法在存在隨機丟包(高
inherent_loss)時過于保守,似然函數中引入了一個高帶寬偏置項(high_bandwidth_bias)。該項會隨著候選帶寬的增加而增加,從而讓算法更傾向于選擇高帶寬的估計,即使它需要假設一個更高的固有丟包率來解釋觀測到的丟包。GetHighBandwidthBias()和AdjustBiasFactor()負責計算這個偏置。
3. 關鍵數據結構
LossBasedBweV2::Config:作用: 包含所有可配置的實驗參數,通過字段試驗字符串(如
WebRTC-Bwe-LossBasedBweV2)解析而來。這些參數控制著算法的幾乎所有方面,包括觀察窗口大小、候選因子、牛頓法迭代次數、各種閾值和開關等。其有效性由IsConfigValid()函數驗證。重要性: 使得算法行為高度可調,便于A/B測試和算法迭代。
LossBasedBweV2::ChannelParameters:作用: 表示信道模型的一個候選參數集。
loss_limited_bandwidth: 待評估的帶寬估計值。inherent_loss: 對應的固有丟包率估計。
重要性: MLE優化過程的核心操作對象。
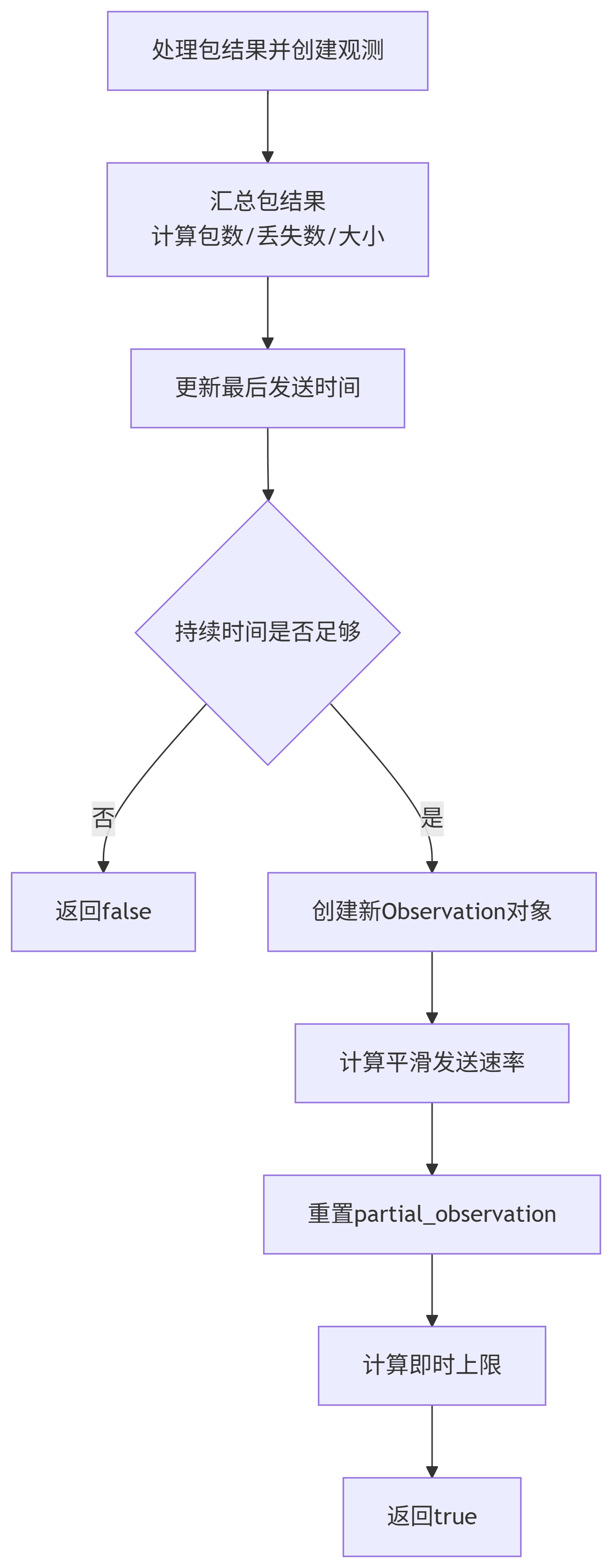
LossBasedBweV2::Observation:作用: 存儲一個時間窗口內的丟包觀測結果。由多次
UpdateBandwidthEstimate調用中積累的PacketResult匯總而成,直到持續時間滿足observation_duration_lower_bound。num_packets,?num_lost_packets,?num_received_packetssize,?lost_size?(字節數,use_byte_loss_rate為true時使用)sending_rate: 該觀測窗口內的平均發送速率(經過平滑處理)。id: 觀測的唯一ID,用于時間加權。
重要性: 是似然計算的基礎數據單元。
LossBasedBweV2::Result:作用: 算法的輸出結果。
bandwidth_estimate: 最終計算出的基于丟包的帶寬估計值。state: 估計器的狀態(Increasing/Decreasing/DelayBasedEstimate),用于指導擁塞控制行為。
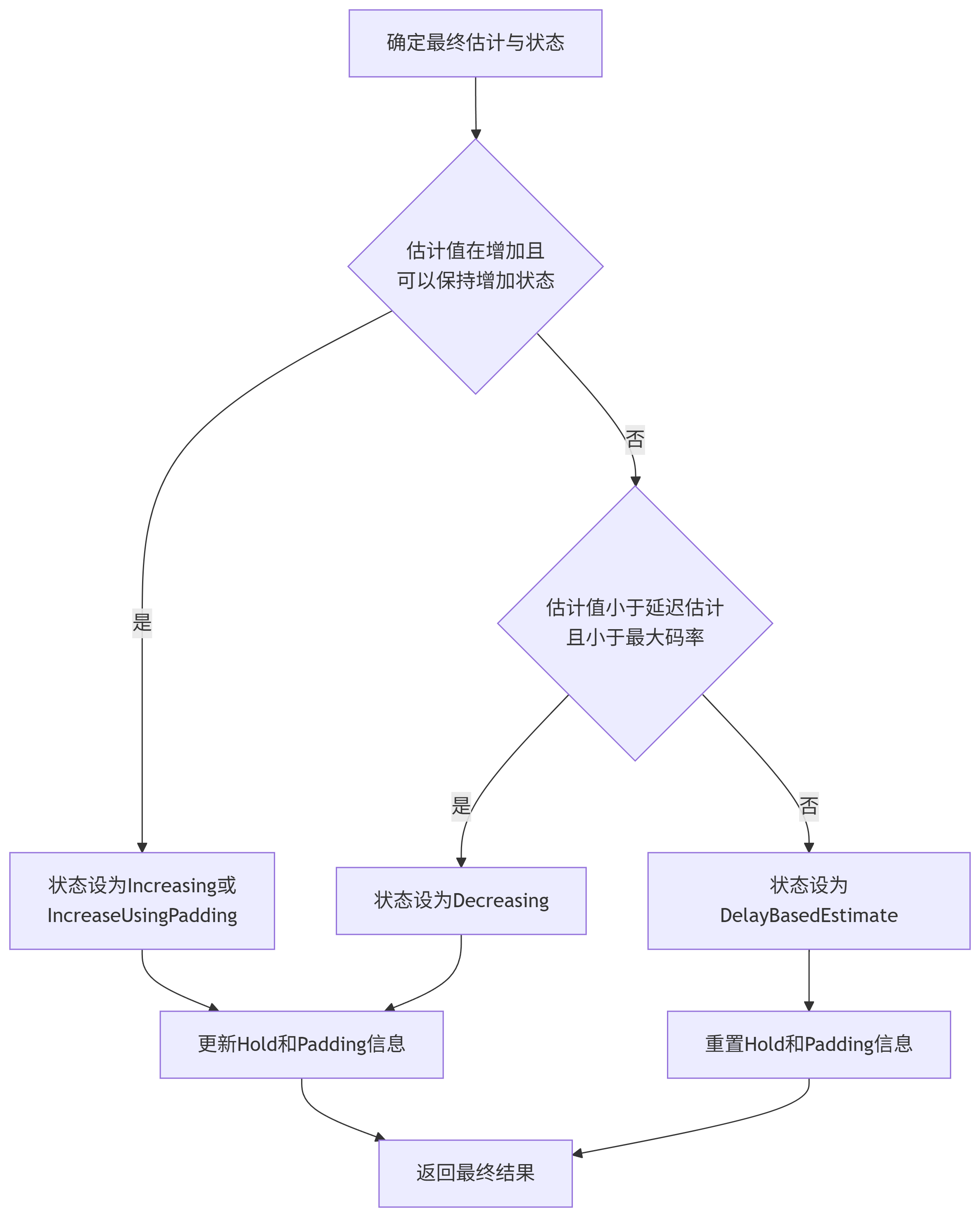
HoldInfo?和?PaddingInfo:作用: 用于實現狀態保持(Hold)和填充(Padding)邏輯。
HoldInfo: 在估計減少后,暫時限制估計值的增長幅度和持續時間,避免過快回升再次引發丟包。PaddingInfo: 當狀態為kIncreaseUsingPadding時,記錄用于判斷是否持續進行填充探測的速率和時間戳。
重要性: 這些是增強算法穩定性和主動探測能力的機制。
4. 核心方法詳解
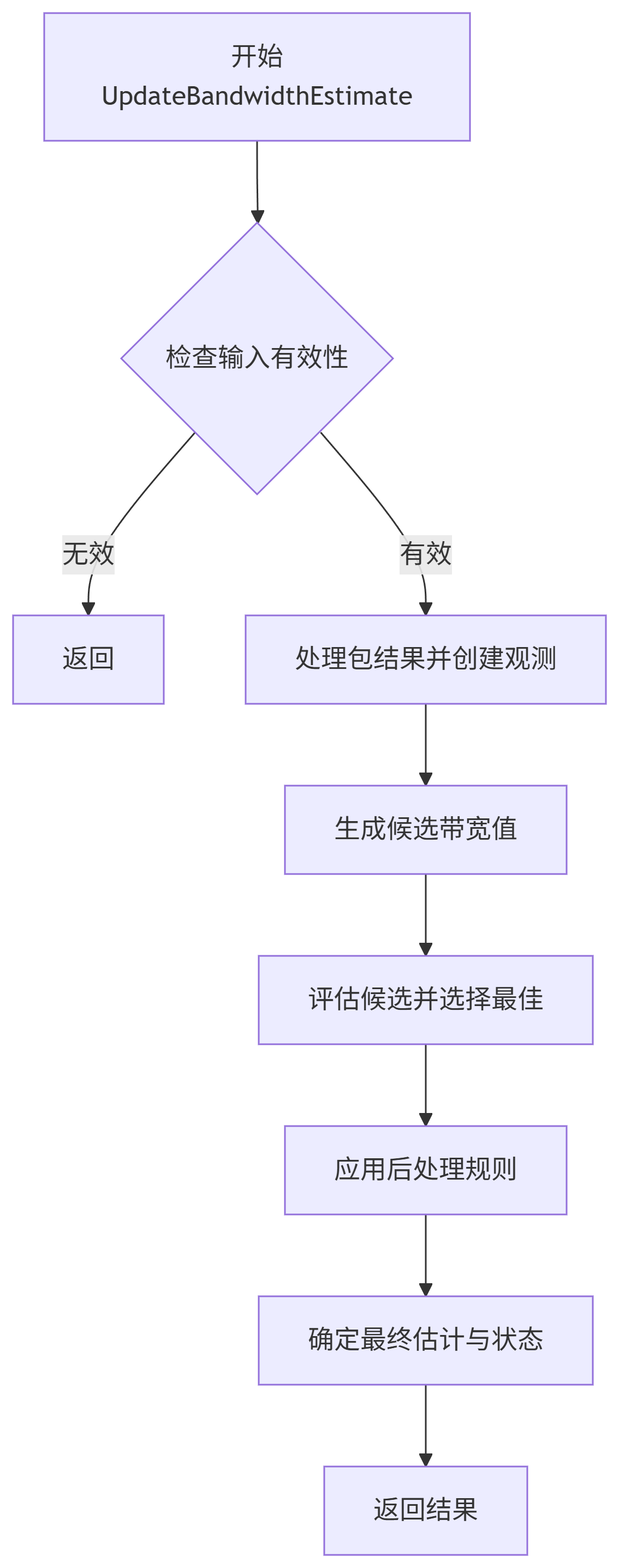
UpdateBandwidthEstimate:入口方法。接收新的包反饋信息(
packet_results)、當前的延遲估計值(delay_based_estimate)和是否在應用限制區域(in_alr)的標志。流程:
更新觀測值: 調用
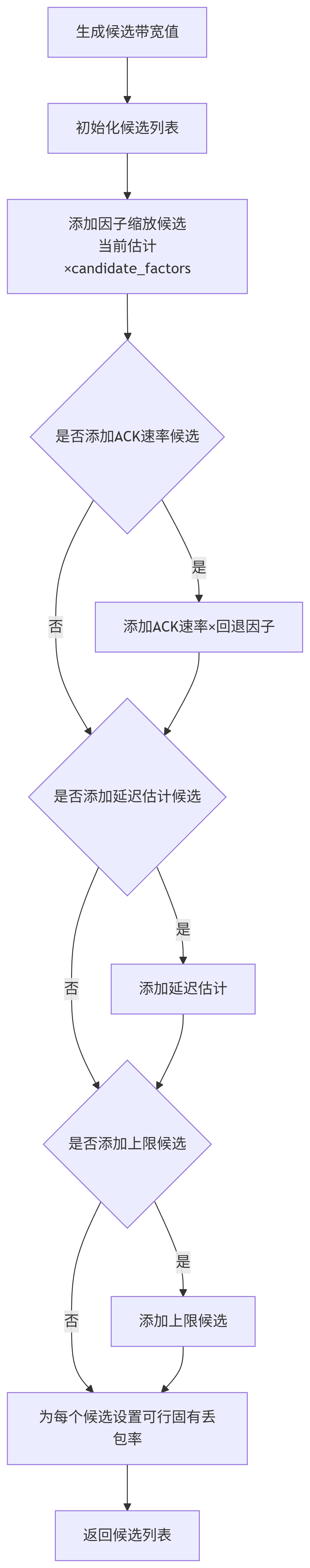
PushBackObservation將新的包結果匯總到當前部分觀測中,如果持續時間足夠,則創建一個新的Observation并加入環形緩沖區。生成候選: 調用
GetCandidates生成一組待評估的ChannelParameters候選。候選來自:當前估計乘以配置的
candidate_factors(如1.02, 1.0, 0.95)。確認速率(
acknowledged_bitrate_)。延遲估計值(
delay_based_estimate_)。即時上限(
GetInstantUpperBound(),在ALR狀態下)。
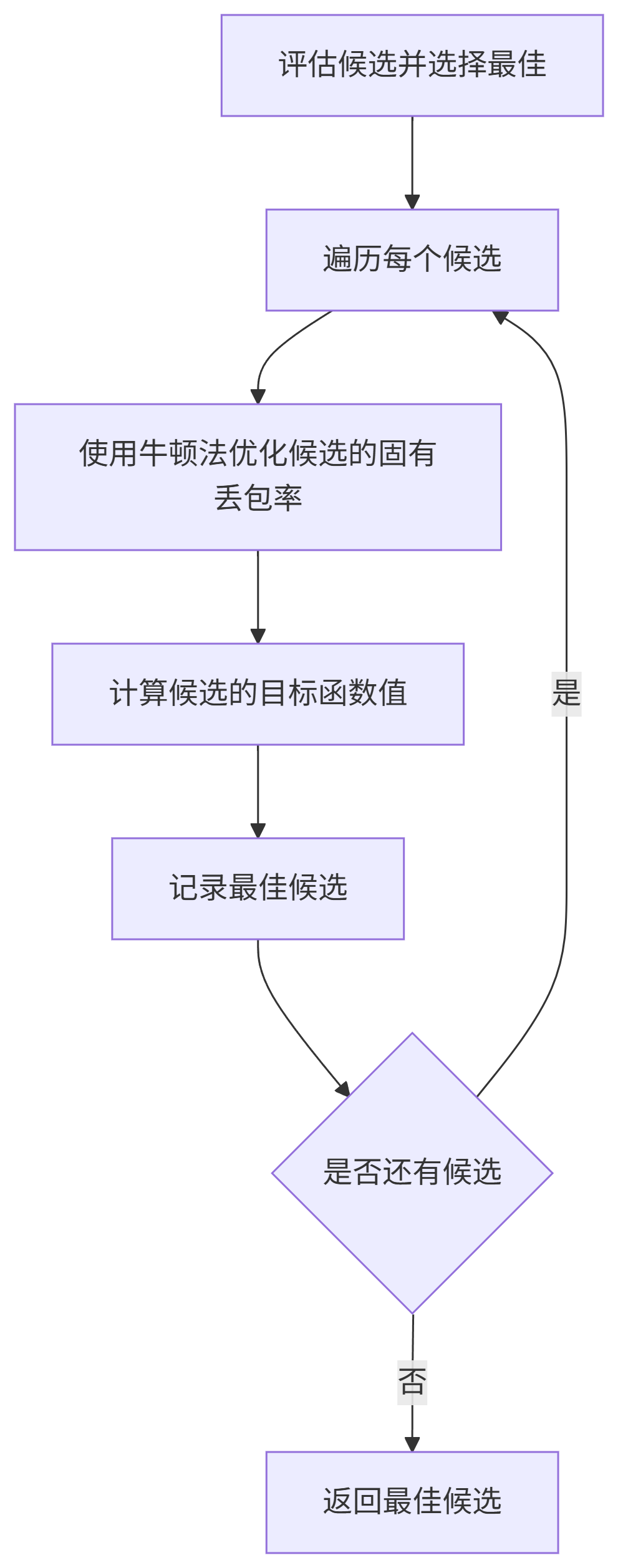
評估候選: 對每個候選,使用牛頓法優化其
inherent_loss(NewtonsMethodUpdate),然后計算其似然函數值加上高帶寬偏置后的目標函數值(GetObjective)。選擇最佳候選: 選擇目標函數值最大的候選作為
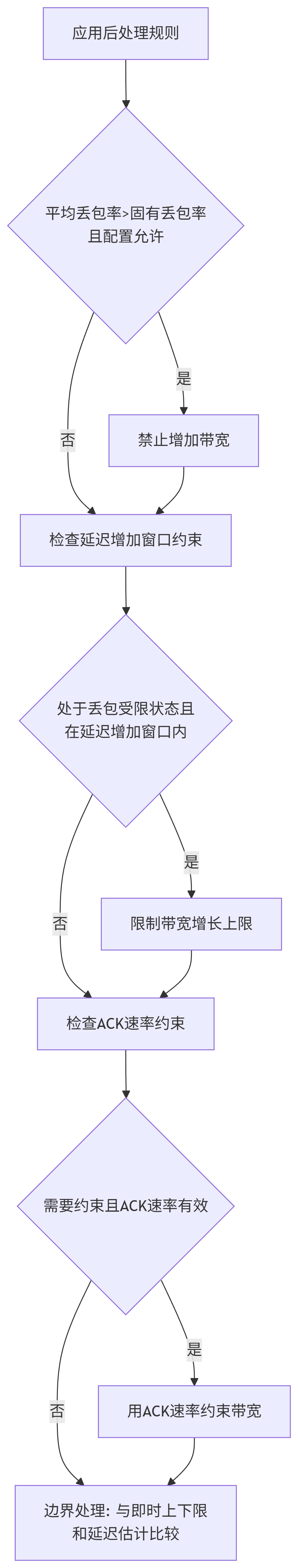
best_candidate。應用約束和規則:
平均丟失檢查: 如果平均上報丟包率大于最佳候選的固有丟包率,可能禁止增加(
not_increase_if_inherent_loss_less_than_average_loss)。延遲增加窗口: 在剛減少帶寬后的一段時間(
delayed_increase_window)內,限制增長上限(bandwidth_limit_in_current_window)。確認速率約束: 在丟包受限狀態下,如果估計要增加,則其上限受
acknowledged_bitrate_乘以一個因子約束。
最終邊界處理: 將最佳候選的帶寬與即時下限(
GetInstantLowerBound,主要來自確認速率)、即時上限(GetInstantUpperBound,基于平均丟包率計算)和延遲估計值進行比對,得到最終的bounded_bandwidth_estimate。狀態機更新: 根據最終估計值的變化、與延遲估計的關系以及Hold/Padding的狀態,決定新的
LossBasedState。更新內部狀態: 設置
current_best_estimate_、loss_based_result_、last_hold_info_、last_padding_info_等。
GetCandidates:根據配置和當前狀態,生成一系列帶寬候選值,然后為每個帶寬值創建一個
ChannelParameters結構體,并為其設置一個可行的初始inherent_loss(GetFeasibleInherentLoss)。
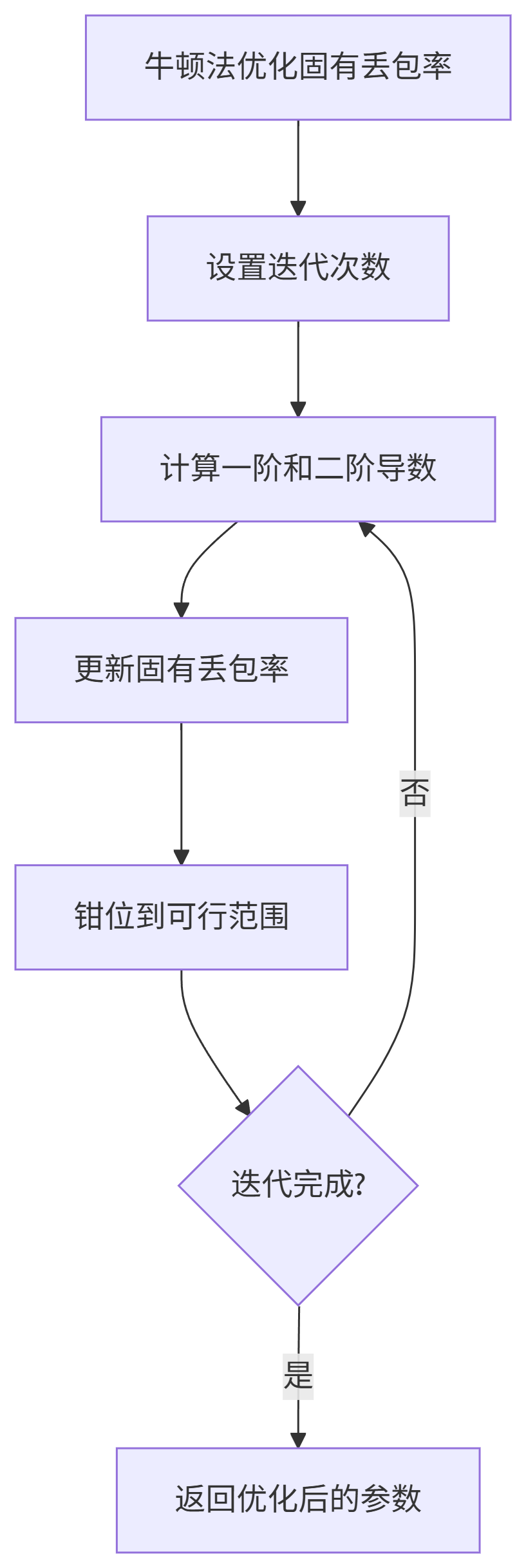
GetDerivatives?和?NewtonsMethodUpdate:MLE優化的核心。
GetDerivatives計算當前參數下似然函數對inherent_loss的一階和二階導數。NewtonsMethodUpdate根據牛頓迭代公式?inherent_loss -= step_size * (first_derivative / second_derivative)?更新參數,并將結果鉗位到可行范圍內?[inherent_loss_lower_bound, GetInherentLossUpperBound]。
GetObjective:計算候選參數的目標函數值,即對數似然值 + 高帶寬偏置。算法目標是最大化該函數。
GetInstantUpperBound?和?CalculateInstantUpperBound:基于近期平均丟包率計算一個帶寬上限。其模型為:
instant_upper_bound = bandwidth_balance / (average_loss - loss_offset)。如果平均丟包率很低,這個上限會很高(max_bitrate_),丟包率越高,這個上限越低。
GetInstantLowerBound?和?CalculateInstantLowerBound:計算帶寬下限,通常取
max(min_bitrate_, acknowledged_bitrate_ * factor)。確保估計值不會低于當前網絡的實際吞吐量太多。
5. 設計亮點
基于模型的MLE方法: 相比于簡單的丟包閾值法(如
SendSideBandwidthEstimation中使用的),V2版本采用了更嚴謹的概率模型和優化方法,理論上能更準確地反映網絡狀態。靈活可配置性: 通過大量的字段試驗參數暴露了算法的核心旋鈕,使得算法可以快速迭代和調優,無需修改代碼。
多候選評估: 不是只做一次優化,而是生成多個候選點并評估,避免陷入局部最優,并能融合其他估計源(如延遲估計、確認速率)。
狀態機與控制邏輯: 輸出的
State為上層控制器提供了豐富的語義信息,使得擁塞控制策略可以更精細,例如區分“可用填充數據探測”的增加和普通增加。時間加權: 對觀測窗口內的歷史數據使用指數衰減加權(
temporal_weights_),更重視近期的網絡狀況。Hold機制: 在帶寬下降后引入一個“冷靜期”,防止估計過快反彈,提高穩定性。
區分包丟失率和字節丟失率: 通過
use_byte_loss_rate開關,可以選擇是基于包計數還是基于字節計數來計算丟包率,以適應不同的場景。
6. 典型工作流程
初始化: 創建
LossBasedBweV2對象,通過字段試驗解析并驗證配置(CreateConfig,?IsConfigValid)。初始化觀察窗口、權重向量等。初始狀態為未就緒。設置初始值: 通常由上層控制器調用
SetBandwidthEstimate或通過UpdateBandwidthEstimate傳入的第一個delay_based_estimate來設置初始帶寬估計。持續更新:
上層控制器定期(如每次收到傳輸反饋時)調用
UpdateBandwidthEstimate。該方法匯總包反饋,形成觀測點。
生成多個候選帶寬值。
對每個候選,優化其固有丟包率,并計算目標函數。
選擇最佳候選。
應用各種約束和規則(Hold、ACK速率約束等)得到最終估計。
根據最終估計值的變化和與其他估計值的關系,更新狀態機。
返回
Result(帶寬+狀態)。
控制決策: 上層控制器(如
GoogCCNetworkController)根據返回的Result中的state和bandwidth_estimate,結合其他模塊(如延遲基于BWE、探測器)的輸出,最終決定目標碼率、是否發起探測等控制命令。
7. LossBasedBweV2 核心算法流程圖
7.1.總體流程圖
7.2.處理包結果并創建觀測
7.3.生成候選帶寬值
7.4.評估候選并選擇最佳
7.5.應用后處理規則
7.6.確定最終估計與狀態
7.7.牛頓法優化過程
8.核心算法精解
void LossBasedBweV2::UpdateBandwidthEstimate(rtc::ArrayView<const PacketResult> packet_results,DataRate delay_based_estimate,bool in_alr) {// 存儲延遲基于的帶寬估計值,用于后續比較和約束delay_based_estimate_ = delay_based_estimate;// 檢查估計器是否已啟用if (!IsEnabled()) {RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING) << "The estimator must be enabled before it can be used.";return;}// 檢查是否有包結果數據if (packet_results.empty()) {RTC_LOG(LS_VERBOSE) << "The estimate cannot be updated without any loss statistics.";return;}// 處理包結果并創建觀測數據if (!PushBackObservation(packet_results)) {return;}// 如果當前最佳估計尚未初始化,使用延遲基于的估計進行初始化if (!IsValid(current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth)) {if (!IsValid(delay_based_estimate)) {RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING) << "The delay based estimate must be finite: " << ToString(delay_based_estimate);return;}current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth = delay_based_estimate;loss_based_result_ = {.bandwidth_estimate = delay_based_estimate,.state = LossBasedState::kDelayBasedEstimate};}// 初始化最佳候選為當前最佳估計ChannelParameters best_candidate = current_best_estimate_;double objective_max = std::numeric_limits<double>::lowest();// 生成并評估所有候選帶寬值for (ChannelParameters candidate : GetCandidates(in_alr)) {// 使用牛頓法優化候選的固有丟包率參數NewtonsMethodUpdate(candidate);// 計算候選的目標函數值const double candidate_objective = GetObjective(candidate);// 選擇目標函數值最大的候選if (candidate_objective > objective_max) {objective_max = candidate_objective;best_candidate = candidate;}}// 如果估計值減少了,記錄減少時間if (best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth <current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth) {last_time_estimate_reduced_ = last_send_time_most_recent_observation_;}// 如果平均丟包率大于當前固有丟包率,且配置允許,禁止增加估計值if (GetAverageReportedLossRatio() > best_candidate.inherent_loss &&config_->not_increase_if_inherent_loss_less_than_average_loss &¤t_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth <best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth) {best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth =current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth;}// 如果處于丟包受限狀態,應用額外的約束if (IsInLossLimitedState()) {// 在延遲增加窗口內限制估計值的增長if (recovering_after_loss_timestamp_.IsFinite() &&recovering_after_loss_timestamp_ + config_->delayed_increase_window >last_send_time_most_recent_observation_ &&best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth >bandwidth_limit_in_current_window_) {best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth =bandwidth_limit_in_current_window_;}// 檢查估計是否在丟包受限狀態下增加bool increasing_when_loss_limited = IsEstimateIncreasingWhenLossLimited(/*old_estimate=*/current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth,/*new_estimate=*/best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth);// 如果估計在增加且確認速率有效,使用確認速率約束估計值if (increasing_when_loss_limited && IsValid(acknowledged_bitrate_)) {double rampup_factor = config_->bandwidth_rampup_upper_bound_factor;// 如果在保持狀態下,使用不同的增長因子if (IsValid(last_hold_info_.rate) &&acknowledged_bitrate_ <config_->bandwidth_rampup_hold_threshold * last_hold_info_.rate) {rampup_factor = config_->bandwidth_rampup_upper_bound_factor_in_hold;}// 應用確認速率約束best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth =std::max(current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth,std::min(best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth,rampup_factor * (*acknowledged_bitrate_)));// 如果狀態為減少但估計值未變,稍微增加以確保狀態切換if (loss_based_result_.state == LossBasedState::kDecreasing &&best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth ==current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth) {best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth =current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth +DataRate::BitsPerSec(1);}}}// 應用最終邊界約束DataRate bounded_bandwidth_estimate = DataRate::PlusInfinity();if (IsValid(delay_based_estimate_)) {bounded_bandwidth_estimate =std::max(GetInstantLowerBound(),std::min({best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth,GetInstantUpperBound(), delay_based_estimate_}));} else {bounded_bandwidth_estimate = std::max(GetInstantLowerBound(), std::min(best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth,GetInstantUpperBound()));}// 如果配置要求約束最佳候選,并且約束后的估計小于最佳候選,重置估計if (config_->bound_best_candidate &&bounded_bandwidth_estimate < best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth) {RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Resetting loss based BWE to " << bounded_bandwidth_estimate.kbps()<< "due to loss. Avg loss rate: " << GetAverageReportedLossRatio();current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth = bounded_bandwidth_estimate;current_best_estimate_.inherent_loss = 0;} else {current_best_estimate_ = best_candidate;// 確保估計不低于確認速率的下限if (config_->lower_bound_by_acked_rate_factor > 0.0) {current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth =std::max(current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth,GetInstantLowerBound());}}// 處理保持狀態下的估計約束if (loss_based_result_.state == LossBasedState::kDecreasing &&last_hold_info_.timestamp > last_send_time_most_recent_observation_ &&bounded_bandwidth_estimate < delay_based_estimate_) {// 確保確認速率是保持速率的下限if (config_->lower_bound_by_acked_rate_factor > 0.0) {last_hold_info_.rate =std::max(GetInstantLowerBound(), last_hold_info_.rate);}// 帶寬估計不允許超過保持速率loss_based_result_.bandwidth_estimate =std::min(last_hold_info_.rate, bounded_bandwidth_estimate);return;}// 確定最終狀態if (IsEstimateIncreasingWhenLossLimited(/*old_estimate=*/loss_based_result_.bandwidth_estimate,/*new_estimate=*/bounded_bandwidth_estimate) &&CanKeepIncreasingState(bounded_bandwidth_estimate) &&bounded_bandwidth_estimate < delay_based_estimate_ &&bounded_bandwidth_estimate < max_bitrate_) {// 設置增加狀態,可能使用填充數據進行探測if (config_->padding_duration > TimeDelta::Zero() &&bounded_bandwidth_estimate > last_padding_info_.padding_rate) {last_padding_info_.padding_rate = bounded_bandwidth_estimate;last_padding_info_.padding_timestamp =last_send_time_most_recent_observation_;}loss_based_result_.state = config_->padding_duration > TimeDelta::Zero()? LossBasedState::kIncreaseUsingPadding: LossBasedState::kIncreasing;} else if (bounded_bandwidth_estimate < delay_based_estimate_ &&bounded_bandwidth_estimate < max_bitrate_) {// 設置減少狀態if (loss_based_result_.state != LossBasedState::kDecreasing &&config_->hold_duration_factor > 0) {RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << this << " " << "Switch to HOLD. Bounded BWE: "<< bounded_bandwidth_estimate.kbps()<< ", duration: " << last_hold_info_.duration.ms();last_hold_info_ = {.timestamp = last_send_time_most_recent_observation_ +last_hold_info_.duration,.duration =std::min(kMaxHoldDuration, last_hold_info_.duration *config_->hold_duration_factor),.rate = bounded_bandwidth_estimate};}last_padding_info_ = PaddingInfo();loss_based_result_.state = LossBasedState::kDecreasing;} else {// 重置保持和填充信息,使用延遲基于的估計last_hold_info_ = {.timestamp = Timestamp::MinusInfinity(),.duration = kInitHoldDuration,.rate = DataRate::PlusInfinity()};last_padding_info_ = PaddingInfo();loss_based_result_.state = LossBasedState::kDelayBasedEstimate;}// 設置最終帶寬估計值loss_based_result_.bandwidth_estimate = bounded_bandwidth_estimate;// 更新延遲增加窗口和帶寬限制if (IsInLossLimitedState() &&(recovering_after_loss_timestamp_.IsInfinite() ||recovering_after_loss_timestamp_ + config_->delayed_increase_window <last_send_time_most_recent_observation_)) {bandwidth_limit_in_current_window_ =std::max(kCongestionControllerMinBitrate,current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth *config_->max_increase_factor);recovering_after_loss_timestamp_ = last_send_time_most_recent_observation_;}
}LossBasedBweV2是WebRCC中一個設計復雜、高度可配置的第二代基于丟包的帶寬估計器。它采用最大似然估計原理,結合了信道模型、優化算法、多源信息融合和狀態機邏輯,旨在更準確、更穩定地從丟包事件中推斷網絡帶寬,并為擁塞控制決策提供豐富的依據。






系統詳細操作配置教程)

概述:組成、發展、性能、體系結構等)




)





