一. 數據讀取
1.pd.to_csv & pd.read_csv
細節:
1.pd.read_csv 需要 ignore_index = True ?or ,index_col=0 ?否則會有列Unnamed0
2.pickle具有更快的讀取速度,與更小的體積。
讀取前N行(若不需獲取所有數據)
pd.read_csv(path, nrows =5)
pd.read_csv ? 只包含數據類型 strings, integers and floats,無datetime類似,datetime 會轉為object。
解決:parse_dates (如果為True,則僅解析index,若為列表,解析相對應字段)
headers = ['col1', 'col2', 'col3', 'col4']
dtypes = {'col1': 'str', 'col2': 'str', 'col3': 'str', 'col4': 'float'}
parse_dates = ['col1', 'col2']
pd.read_csv(file, sep='\t', header=None, names=headers, dtype=dtypes, parse_dates=parse_dates)2.pd.to_pkl & pd.read_pkl(推薦)
對象的序列化(serialization)與反序列化(deserialization)
pickle dump (pd.to_pickle)
with open(‘../pathname/source_object_name.pkl’, ‘wb’) as f:pickle.dump(object_name, f)Save:
a dataframe (df),
a matrix or array (X_train_sc),
a fitted model (rand_forest_1),
or anything else you want to save.
pickle load ? (pd.read_pickle)
with open(‘../pathname/source_object_name.pkl’, ‘rb’) as f:dest_object_name = pickle.load(f)pickle (python2 & python3)
? In python 2 there are 3 different protocols (0, 1, 2) and the default is 0.
? In python 3 there are 5 different protocols (0, 1, 2, 3, 4) and the default is 3.
在python3.8中多了protocols (5)
讀取方法:
# !pip3 install pickle5 import pickle5 as pickle
with open(path_to_protocol5, "rb") as fh: data = pickle.load(fh) # Could also save into a protocol-4 pickle from python 3.6
data.to_pickle(path_to_protocol4)3.pd.to_excel & pd.read_excel
pd.read_excel(path, sheet=None)
如果有多個sheet,想獲取sheet的名稱:
import pandas as pd
f = pd.ExcelFile('./data.xlsx')
f.sheet_names # 獲取工作表名稱data = pd.DataFrame()
for i in f.sheet_names:d = pd.read_excel('./data.xlsx', sheetname=i)4.pd.to_json & pd.read_json
其中有個參數:orient
Indication of expected JSON string format.
- Series:
- default is ‘index’
- allowed values are: {‘split’,’records’,’index’,’table’}.
- DataFrame:
- default is ‘columns’
- allowed values are: {‘split’, ‘records’, ‘index’, ‘columns’, ‘values’, ‘table’}.
- The format of the JSON string:
- ‘split’ : dict like {‘index’ -> [index], ‘columns’ -> [columns], ‘data’ -> [values]}
- ‘records’ : list like [{column -> value}, … , {column -> value}]
- ‘index’ : dict like {index -> {column -> value}}
- ‘columns’ : dict like {column -> {index -> value}}
- ‘values’ : just the values array
- ‘table’ : dict like {‘schema’: {schema}, ‘data’: {data}}
json_data = df_data.to_json(orient='index')
df_data = pd.read_json(json_data, orient='index)5.dict & pd.DataFrame
輸入:my_dict = {'i': 1, 'love': 2, 'you': 3}
期望輸出:my_df
0
i 1
love 2
you 3
如果字典里key和value是一一對應的,那么直接輸入
my_df = pd.DataFrame(my_dict)
會報錯“ValueError: If using all scalar values, you must pass an index”。
————————————————
解決方法如下:
1、使用DataFrame函數時指定字典的索引index
my_dict = {'i': 1, 'love': 2, 'you': 3}
my_df = pd.DataFrame(my_dict,index=[0]).T
2、把字典dict轉為list后傳入DataFrame
my_dict = {'i': 1, 'love': 2, 'you': 3}
my_list = [my_dict]
my_df = pd.DataFrame(my_list).T
3、 使用DataFrame.from_dict函數
my_dict = {'i': 1, 'love': 2, 'you': 3}
my_df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(my_dict, orient='index')
二. 數據增刪改查
1.獲取數據or位置
- 已知列名or索引,求在所有列or索引中的位置
col_loc = df.columns.get_loc(col)
idx_loc = df.index.get_loc(idx)
已知在所有列or索引中的位置,求列名or索引
col_name = df.columns.columns[loc]
idx_name = df.index.index[loc] - Series獲取最大值最大值/位置
series_A.idxmax()
series_A.argxmax()
series_A.idxmin()
series_A.argxmin() - pandas獲取最大值最小值/位置
pd_A.stack().max()
pd_A.stack().idxmax()
pd_A.stack().min()
pd_A.stack().idxmin()
2.插入數據
插入列:
df.insert(loc, column, value, allow_duplicates=False)
# 例:
df.insert(0, 'datetime', times_list)# 默認插入到最后一列
df['datetime'] = times_list插入行
df = pd.concat([df_above,df_insertRow,df_below],ignore_index = True)2.字符串包含
df['name'].str.contains("ly")3. 索引排序sort_values, sort_index,set_index, reset_index
sort_values()
sort_index()
reset_index(drop=False)
在獲得新的index,原來的index變成數據列,保留下來。
不想保留原來的index,使用參數 drop=True,默認 False。
set_index()
注意:
很多會多nan值的操作,可能里邊有 參數fill_value,會很方便。
如:
pivot_table
reindex
對原始dataframe采用新的index。類似join的作用。
與pd.daterange常搭配用。
df.index = pd.to_datetime(df.index)
time_range = pd.date_range(dt_start, dt_end, freq='150s')
df = df.reindex(time_range)
df.fillna(method='ffill', inplace=True)
df.fillna(method='bfill', inplace=True)4. in / not in 篩選數據
篩選出某字段中值 in list的df。
錯誤寫法
data = data[data["idc"] in (["NA61","NA62"])]
data = data[data["idc"] not in (["NA61","NA62"])]
正確寫法
data = data[data["idc"].isin (["NA61","NA62"])
data = data[~data["idc"].isin (["NA61","NA62"])
5.多列中最大值組成新的一列
df['z']=df[['x','y']].max(axis=1)
6.找出每行最大的第n個值
def sort_value(column, n):
new_column = column.sort_values(ascending = False)
return new_column.iloc[n-1]
def nth_largest(df):
return df.apply(sort_value)
7.兩個DataFrame找交集,差集
交集:
intersected_df = pd.merge(df1, df2, how='inner')差集:
set_diff_df = pd.concat([df2, df1, df1]).drop_duplicates(keep=False)
print(set_diff_df)三. 數據轉換
0. df2str / str2df
def df2str(df):"""1.','連接每行數據,包括columns列。2.'|'聚合為長字符串。"""n = df.shape[0]df = df.astype(str)col_str_list = df.columns.astype(str)whole_str = ','.join(col_str_list)for i in range(n):row = df.iloc[i, :].valuesrow_str = ','.join(row)whole_str = '|'.join([whole_str, row_str])return whole_strdef str2df(whole_str):""""""row_list = whole_str.split('|')cols = row_list[0].split(',')row_data = []for row_str in row_list[1:]:row = row_str.split(',')row_data.append(row)df = pd.DataFrame(data=row_data, columns=cols)return df1.pivot/pivot_table
pd.pivot_table 后有multiIndex
取消:
pd_pivot.reset_index().rename_axis(None, axis=1)
unpivot:
df_unpivot = pd.melt(df, id_vars='col1', value_vars=['col2', 'col3', ...])
2.join/merge/concat
- merge方法主要基于兩個dataframe的共同列進行合并;
- join方法主要基于兩個dataframe的索引進行合并;
- concat方法是對series或dataframe進行行拼接或列拼接。
DataFrame數據的合并與拼接(merge、join、concat)
3.多行合并為一行
df = df.groupby(['姓名','年齡'])['愛好'].apply(lambda x: ','.join(x))注:這個匿名函數相當于聚合函數。
3. apply
一列生成一列
df[col].apply(lambda x: x+1)多列生成一列(實際上是在行上進行apply)
df.apply(lambda row: row[col1] + row[col2], axis=1)4. 拆分一行為多行 (explode)
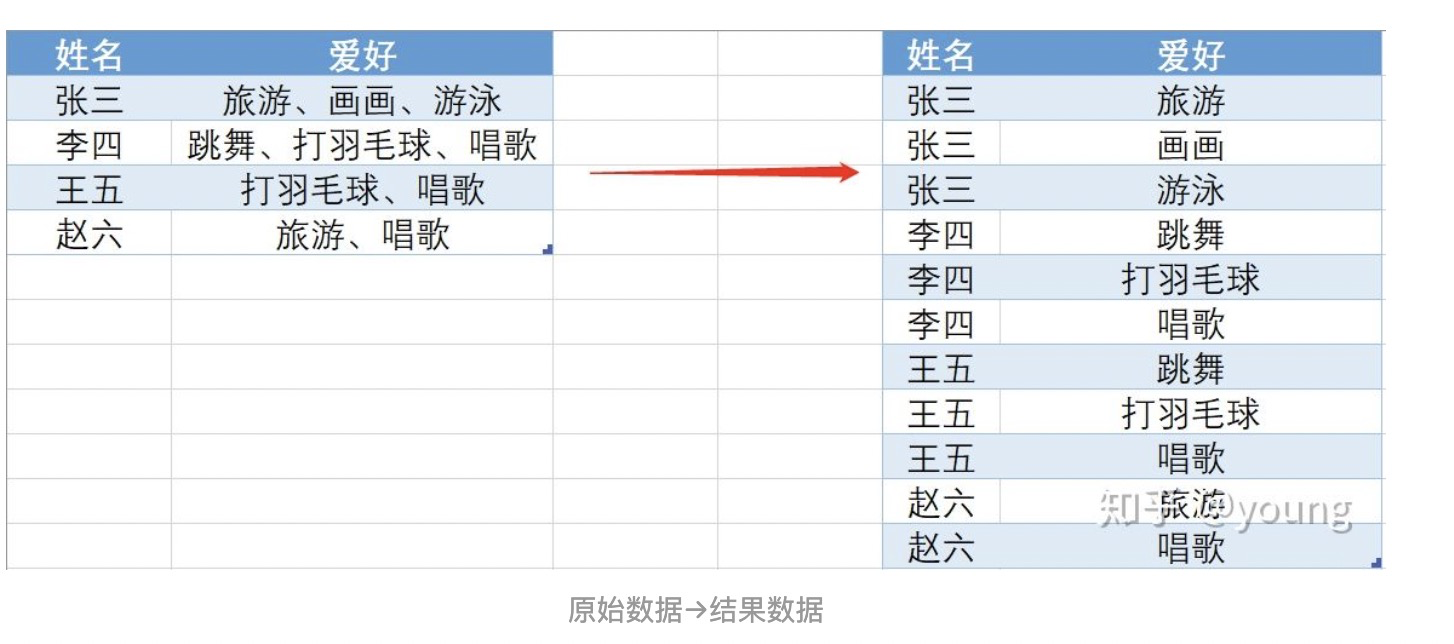
方法一:
##一、讀數據
df=pd.read_excel('一行變多行.xlsx')
#二、把“愛好”字段拆分,分為多列
df_name=df['愛好'].str.split('、',expand=True)
#三、把行轉列成列
df_name=df_name.stack()
#四、重置索引,并刪除多于的索引
df_name = df_name.reset_index(level=1,drop=True)
#五、與原始數據合并
df_name.name='df_name1'
df_new = df.drop(['愛好'], axis=1).join(df_name)
df_new方法二:
#一、先將‘愛好’字段拆分
df['愛好']=df['愛好'].map(lambda x:x.split(','))
#二、然后直接調用explode()方法
df_new=df.explode('愛好')5. groupby agg
groupby之后記著reset_index,會變得顯示正常。
pandas.core.groupby.DataFrameGroupBy.agg — pandas 0.23.1 documentation
四. 時間datetime相關
pd.to_datetime()
可以直接對字符串轉為datetime格式,而不需要用內置函數datetime.datetime
date_time = pd.to_datetime('2020-06-15')pd.Timedelta('1D')
可直接與datetime格式 相加減,而不需要用內置函數datetime.timedelta
unit: str, default ‘ns’
Denote the unit of the input, if input is an integer.
Possible values:
? ‘W’, ‘D’, ‘T’, ‘S’, ‘L’, ‘U’, or ‘N’
? ‘days’ or ‘day’
? ‘hours’, ‘hour’, ‘hr’, or ‘h’
? ‘minutes’, ‘minute’, ‘min’, or ‘m’
? ‘seconds’, ‘second’, or ‘sec’
? ‘milliseconds’, ‘millisecond’, ‘millis’, or ‘milli’
? ‘microseconds’, ‘microsecond’, ‘micros’, or ‘micro’
? ‘nanoseconds’, ‘nanosecond’, ‘nanos’, ‘nano’, or ‘ns’.date_end = data_time + pd.Timedelta(1,'D')unix_time <-> datetime
'1643558400' -> '2022-01-31 00:00:00'
注意:直接以下邊方式,和系統自帶datetime會有8個小時的時差。
1. 如果單位為s
df['date'] = pd.to_datetime(df['date'], unit='s')1. 如果單位為ms
df['date'] = pd.to_datetime(df['date'], unit='ms')
系統自帶
1. 如果單位為s
df['date'] = df.unix_time.apply(lambda x: datetime.fromtimestamp(int(x))) 1. 如果單位為ms
df['date'] = df.unix_time.apply(lambda x: datetime.fromtimestamp(int(x/1000)))
datetime -> unix_time
'2022-01-31 00:00:00' -> '1643558400'. # 這個是正常的,沒誤差
df['unix_time'] = df['date_time'].apply(lambda x: pd.to_datetime(x).strftime('%s'))或者
df['unix_time'] = df['date_time'].apply(lambda x: datetime.strptime(x, '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S').timestamp()*1000)Timestamp
此外,在pandas中,還有一種Timestamp格式。轉化容易出錯:
在ODPS中,為 datetime 格式,下載到本地為 Timestamp :
alarm_time: Timestamp('2023-02-13 14:52:00')# .timestamp()的方式 直接轉化
alarm_time.timestamp(): 1676299920 --有誤
datetime.fromtimestamp(int(1676299920)): datetime(2023, 2, 13, 22, 52) --時間+8h# .timestamp()的方式 設置時區
alarm_time.tz_localize('Asia/Shanghai').timestamp(): 1676271120
datetime.fromtimestamp(int(1676271120)): datetime(2023, 2, 13, 14, 52) --正常
# Pandas中 tz_localize 和 tz_convert函數,前者用于將時間戳轉換為本地時間,而后者可以用于任意時區的轉換。# .strftime的方式 直接轉化
alarm_time.strftime('%s'): '1676271120' --正常,不過是string
datetime.fromtimestamp('1676271120'): datetime(2023, 2, 13, 14, 52) --正常此外:如果對Timestamp格式先求str,然后轉為datetime格式,以上兩種方式都可正常運行
alarm_time = str(alarm_time)
alarm_time = datetime.strptime(alarm_time, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")pd.date_range()
按指定間隔,生成時間序列
time_range = pd.date_range(start=start_date, end=end_date, freq='5min')*這里start_date/end_date可以為 string or datetime-like
*這里的time_range是DatetimeIndex格式。
這里經常與df.reindex()搭配使用。
DatetimeIndex to str_list
date_list = time_range.format()
或者
date_list = [datetime.strftime(x,'%F') for x in time_range]
或者
date_list = [x.strftime('%F') for x in time_range]Sample
df_feat.index = pd.DatetimeIndex(df_feat.index)
df_feat_res = df_feat.resample('5min').mean()8.rolling
DataFrame.rolling(window, min_periods=None, center=False, win_type=None, on=None, axis=0, closed=None)
window:?也可以省略不寫。表示時間窗的大小,注意有兩種形式(int or offset)。如果使用int,則數值表示計算統計量的觀測值的數量即向前幾個數據。如果是offset類型,表示時間窗的大小。offset詳解
min_periods:每個窗口最少包含的觀測值數量,小于這個值的窗口結果為NA。值可以是int,默認None。offset情況下,默認為1。
center:?把窗口的標簽設置為居中。布爾型,默認False,居右
# 滑動聚合
s = [1,2,3,5,6,10,12,14,12,30]
pd.Series(s).rolling(window=3).mean()# 如果index是datetime形式,也可以直接滑窗
df_w_sum = df_trian.rolling('7D').sum()9.resample
重采樣。僅對時間序列。
index = pd.date_range('1/1/2000', periods=9, freq='T')
series = pd.Series(range(9), index=index)# 下采樣
s.resample('3T').sum() # 分鐘
s.resample('H').sum() # 小時
s.resample('M').sum()
s.resample('W').mean()# 上采樣
s.resample('D').asfreq()10.fill 插值
可配合resample使用。
ffill 空值取前面的值
bfill 空值取后面的值
interpolate 線性取值五.繪圖plot
df.plot()
使用DataFrame的plot方法繪制圖像會按照數據的每一列繪制一條曲線,默認按照列columns的名稱在適當的位置展示圖例,比matplotlib繪制節省時間,且DataFrame格式的數據更規范,方便向量化及計算。
參數詳解:(參考:pandas.DataFrame.plot( )參數詳解 - BobPong - 博客園)
DataFrame.plot(x=None, y=None, kind='line', ax=None, subplots=False, sharex=None,sharey=False, layout=None, figsize=None, use_index=True, title=None, grid=None,legend=True, style=None, logx=False, logy=False, loglog=False, xticks=None,yticks=None, xlim=None, ylim=None, rot=None, fontsize=None, colormap=None,position=0.5, table=False, yerr=None, xerr=None, stacked=True/False,sort_columns=False, secondary_y=False, mark_right=True, **kwds)說明
x : label or position, default None #指數據列的標簽或位置參數
y : label, position or list of label, positions, default None
kind : str#繪圖類型
‘line’ : line plot (default)#折線圖
‘bar’ : vertical bar plot#條形圖。stacked為True時為堆疊的柱狀圖
‘barh’ : horizontal bar plot#橫向條形圖
‘hist’ : histogram#直方圖(數值頻率分布)
‘box’ : boxplot#箱型圖
‘kde’ : Kernel Density Estimation plot#密度圖,主要對柱狀圖添加Kernel 概率密度線
‘density’ : same as ‘kde’
‘area’ : area plot#與x軸所圍區域圖(面積圖)。Stacked=True時,每列必須全部為正或負值,stacked=False時,對數據沒有要求
‘pie’ : pie plot#餅圖。數值必須為正值,需指定Y軸或者subplots=True
‘scatter’ : scatter plot#散點圖。需指定X軸Y軸
‘hexbin’ : hexbin plot#蜂巢圖。需指定X軸Y軸
ax : matplotlib axes object, default None#子圖(axes, 也可以理解成坐標軸) 要在其上進行繪制的matplotlib subplot對象。如果沒有設置,則使用當前matplotlib subplot其中,變量和函數通過改變figure和axes中的元素(例如:title,label,點和線等等)一起描述figure和axes,也就是在畫布上繪圖。
# ax可以這樣直接畫兩條線
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 1)
axs.plot(t, s1, t, s2)subplots : boolean, default False#是否對列分別作子圖
較常用:
layout : tuple (rows, columns) for the layout of subplots#子圖的行列布局
figsize : a tuple (width, height) in inches#圖片尺寸大小
title : string#圖片的標題用字符串 Title to use for the plot
grid : boolean, default None#圖片是否有網格
legend : False/True/’reverse’#子圖的圖例 (默認為True)
style : list or dict#對每列折線圖設置線的類型
xticks : sequence#設置x軸刻度值,序列形式(比如列表)
yticks : sequence#設置y軸刻度,序列形式(比如列表)
xlim : float/2-tuple/list#設置坐標軸的范圍。數值(最小值),列表或元組(區間范圍)
ylim : float/2-tuple/list
rot : int, default None#設置軸標簽(軸刻度)的顯示旋轉度數
fontsize : int, default None#設置軸刻度的字體大小
模版一
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 9), dpi = 80)
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)# 或
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16,9), dpi= 80) df.plot(ax=ax, grid=True, fontsize=16, ylim=None, legend=True)
plt.tick_params(axis='x', labelsize=16)
plt.tick_params(axis='y', labelsize=16)
plt.xlabel('collect_time', fontsize=16)
plt.ylabel('ylabel', fontsize=16)
plt.legend(loc='upper right', title='location', fontsize='x-large',) #shadow=True,)
plt.savefig('figure0.png', dpi=150)
# plt.show()模版二(推薦)
1)首先定義畫圖的畫布
2)然后定義子圖ax
3)然后加plt的各種設置。
3)用 ax.plot( )函數或者 df.plot(ax = ax)
4)plt.show()
5) plt.close() : close the figure
? ??plt.clf() : clear the figure
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16,9), dpi = 80)
ax= fig.add_subplot(行,列,位置標)
df.plot(ax = ax) # 或ax.plot( )
plt.show()
plt.clf() # 或 plt.close()雙y軸圖
pandas 自帶(需在一個dataframe里的兩列):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16,9), dpi= 80)
df.plot(ax=ax, grid=True, fontsize=16, y=['col1','col2'], secondary_y=['col2'])pandas 常規(兩個series, x軸長度必須相等):
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots(figsize=(16,9), dpi= 80) ax1.set_xlabel('Same X for different Y')
ax1.set_ylabel('Y1')
ax1.set_title("Double Y axis")ax1.plot(df1.index, df1.values, color='red')
# df1.plot(ax=ax1, color='red')ax2 = ax1.twinx() # this is the important function
ax2.set_ylabel('Y2')ax2.plot(df1.index, df2.values, color='blue')
# df2.plot(ax=ax2, color='blue')
多subplot圖
(1)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 9), dpi = 80)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(2,1,1)
x = pd_cold_mean_new.index
ax1.plot(x, pd_cold_mean_new.values, color='red')
ax1.set_xlabel('time')
ax1.set_ylabel('cold')
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(2,1,2)
ax2.plot(x, pd_it_mean.values, color='blue')
ax2.set_xlabel('time')
ax2.set_ylabel('it')(2)
如果存在多個子圖,直接df.plot() 會畫在一個ax上。
如果想畫在多個ax上,直接用參數 subplots=True,而且不用指定分為多少個子圖
pandas 自帶
df.plot(subplots=True)六、Excel插入圖片
def save_to_excel(file_name,category_name,point_name,df_result,patten = ''):imgsize = (1280*2 / 4, 720*2 / 4)# 創建一個新的工作簿wb = openpyxl.Workbook()ws = wb.activews.column_dimensions['B'].width = imgsize[0] * 0.14# 添加表頭ws.append(['device_tag', 'Image','llm_check','check'])# # 添加數據與圖片df_result = df_result.sort_values('device_tag')for i,[name, image_path,str_check] in enumerate(df_result.values):cell = ws[f'A{i+2}']cell.value = nameif image_path:img = Image(image_path) # 縮放圖片img.width, img.height = imgsizews.add_image(img, f'B{i+2}') # 圖片 插入 A1 的位置上ws.row_dimensions[i+2].height = imgsize[1] * 0.78 # 修改列第1行的寬cell = ws[f'C{i+2}']cell.value = str_check# 保存為 Excel 文件wb.save(f'result/{file_name}/{category_name}_{point_name}_{patten}.xlsx'))
如何分析MySQL的鎖等待問題?)



)









馮諾依曼體系結構,操作系統與系統調用和庫函數概念)
——言語理解與表達、判斷推理(強化訓練))


