標題【Java學習|黑馬筆記|Day20】
今天看的是黑馬程序員的《Java從入門到起飛》下部的95-118節,筆記包含IO流中的字節、字符緩沖流,轉換流,序列化流反序列化流,打印流,解壓縮流,常用工具包相關用法及練習

歡迎大家在評論區交流討論,一起學習共同進步🕵🏻?♀?
文章目錄
- 標題【Java學習|黑馬筆記|Day20】
- 10)上篇練習
- 1.拷貝一個文件夾,考慮子文件夾
- 2.文件加解密
- 3.修改文件中的數據
- 11)字節緩沖流
- 11.1)字節緩沖流拷貝文件(一次讀一個字節)
- 11.2)字節緩沖流拷貝文件(一次讀寫多個字節)
- 11.3)底層原理
- 12)字符緩沖流
- 13)練習
- 1.四種拷貝方式效率對比
- 2.恢復出師表的順序
- 3.控制軟件運行的次數
- 14)轉換流
- 14.1)練習
- 15)序列化流
- 16)反序列化流/對象操作輸入流
- 17)(反)序列化流的細節
- 18)練習
- 19)打印流
- 19.1)字節打印流
- 19.2)字符打印流
- 20.1)解壓縮流
- 20.2)壓縮流
- 21.1)常用工具包Commons-io
- 21.2)常用工具包-Hutool
接上篇
10)上篇練習
1.拷貝一個文件夾,考慮子文件夾
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1.數據源File src = new File("D:\\a\\bbb");//2.目的地File dest = new File("D:\\a\\aaa");copydir(src,dest);}private static void copydir(File src, File dest) throws IOException {dest.mkdir();//如果dest不存在就創建一個File[] files = src.listFiles();for (File file : files) {if(file.isFile()){FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(dest,file.getName()));byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];int len;while((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1){fos.write(bytes,0,len);}fos.close();fis.close();}else {copydir(file,new File(dest,file.getName()));}}}
}
2.文件加解密
加密:對原始文件的每一個字節數據進行更改,然后將更改后的數據存儲到新的文件中
解密:讀取加密之后的問價,按照加密的規則反向操作,編程原始文件
通過異或進行加解密
加密
//^異或 不同為true 一個數異或另一個數兩次結果是它本身
//1.創建對象關聯原始文件
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src\\1.jpg");
//2.創建對象關聯機密文件
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src\\ency.jpg");
//3.加密處理
int b;
while((b = fis.read()) != -1){fos.write(b ^ 2);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
解密
//4.解密FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src\\ency.jpg");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src\\redu.jpg");
int b;
while((b = fis.read()) != -1){fos.write(b ^ 2);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
3.修改文件中的數據
排序文件中的數據
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileReader fr = new FileReader("src\\1.txt");StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();int ch;while ((ch = fr.read()) != -1) {sb.append((char)ch);}fr.close();String s = sb.toString();String[] arrStr = s.split("-");Arrays.sort(arrStr);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrStr));FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("src\\1.txt");for (int i = 0; i < arrStr.length; i++) {fw.write(arrStr[i]);if(i != arrStr.length-1){fw.write("-");}}fw.close();
}
11)字節緩沖流
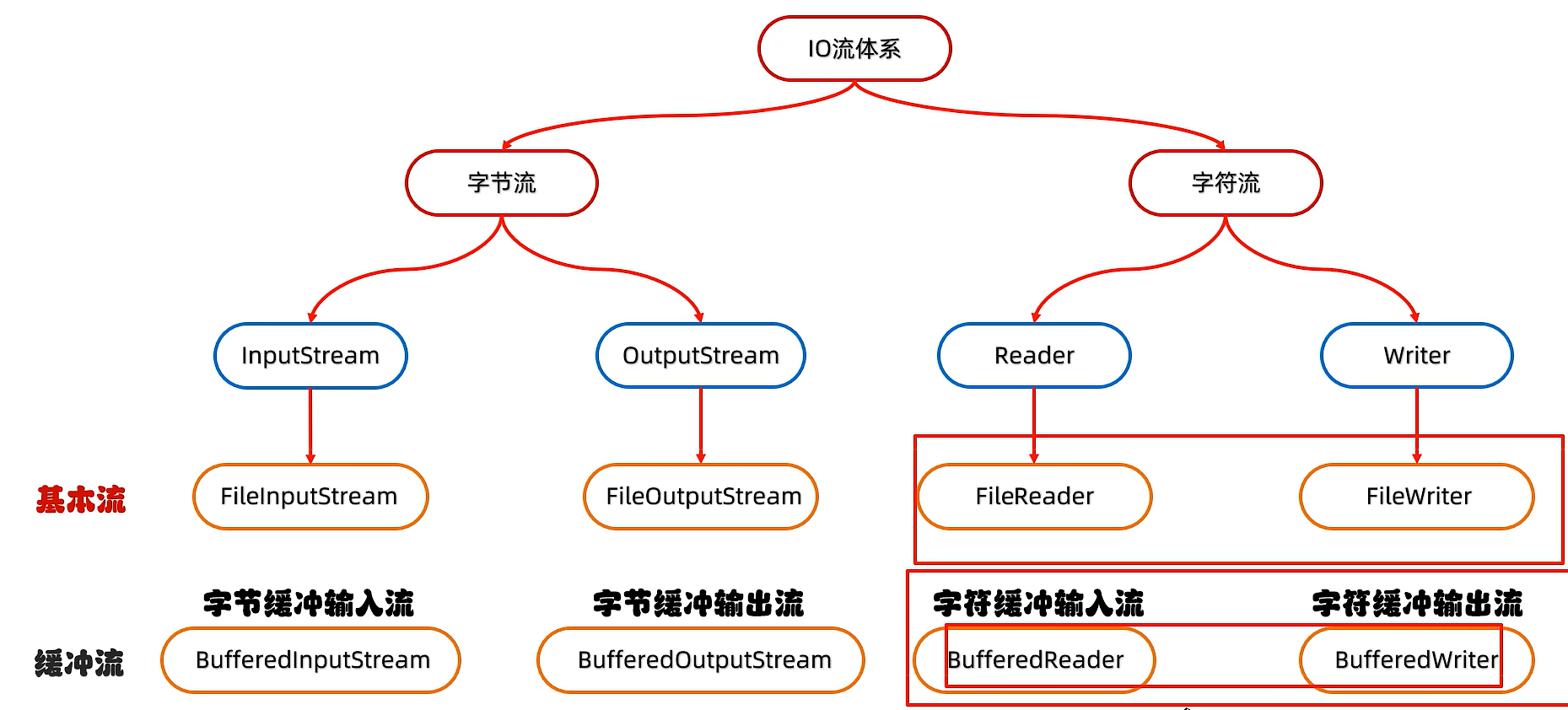
11.1)字節緩沖流拷貝文件(一次讀一個字節)
原理:底層自帶了長度為8192的緩沖區提高性能
| 方法名稱 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| public BufferedInputStream(InputStream is) | 把基本流包裝成高級流,提高讀取數據的性能 |
| public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream is) | 把基本流包裝成高級流,提高讀取數據的性能 |
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("src\\1.txt"));BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\copy.txt"));int b;while((b = bis.read()) != -1){bos.write(b);}bos.close();bis.close();}
}
11.2)字節緩沖流拷貝文件(一次讀寫多個字節)
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("src\\1.txt"));BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\copy.txt"));int len;byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];while((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1){bos.write(bytes,0,len);}bos.close();bis.close();}
}
11.3)底層原理
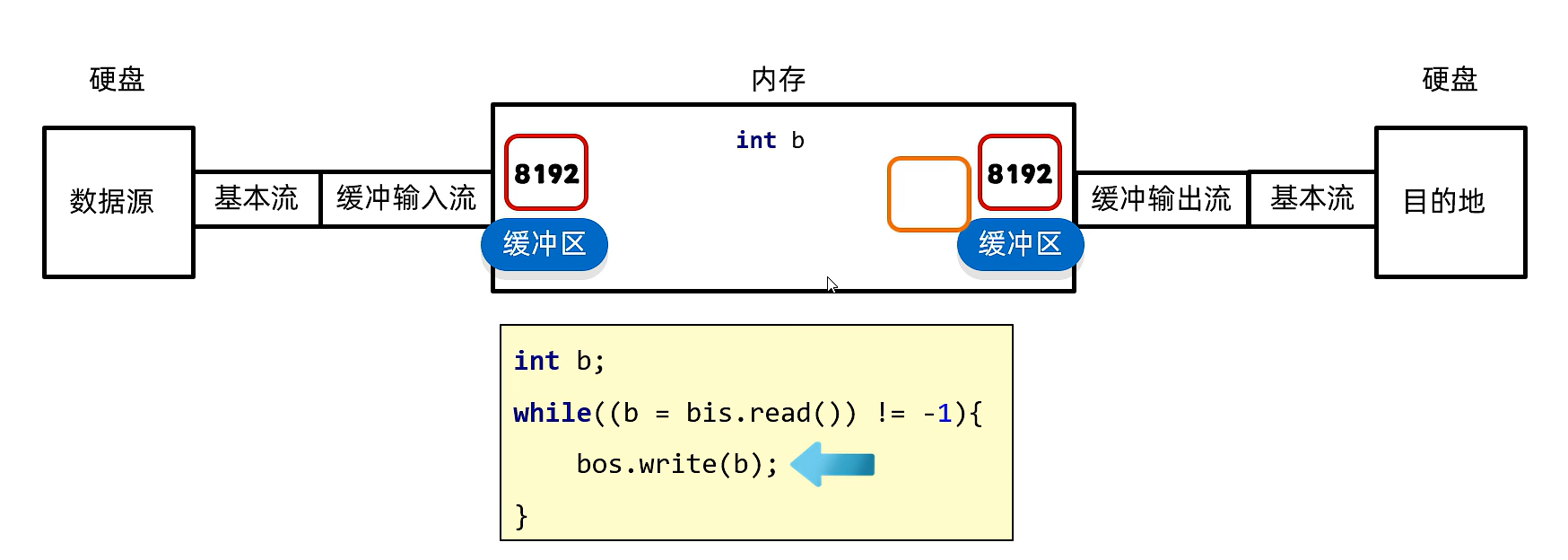
數據源通過基本流自動把數據加載到內存中的緩沖區,緩沖輸出流的緩沖區自動把數據傳給目的地,int b在兩緩沖區之間移動傳遞數據
為什么節省時間?
因為在內存當中操作速度非常快,int b來回傳遞的速度可以忽略不計
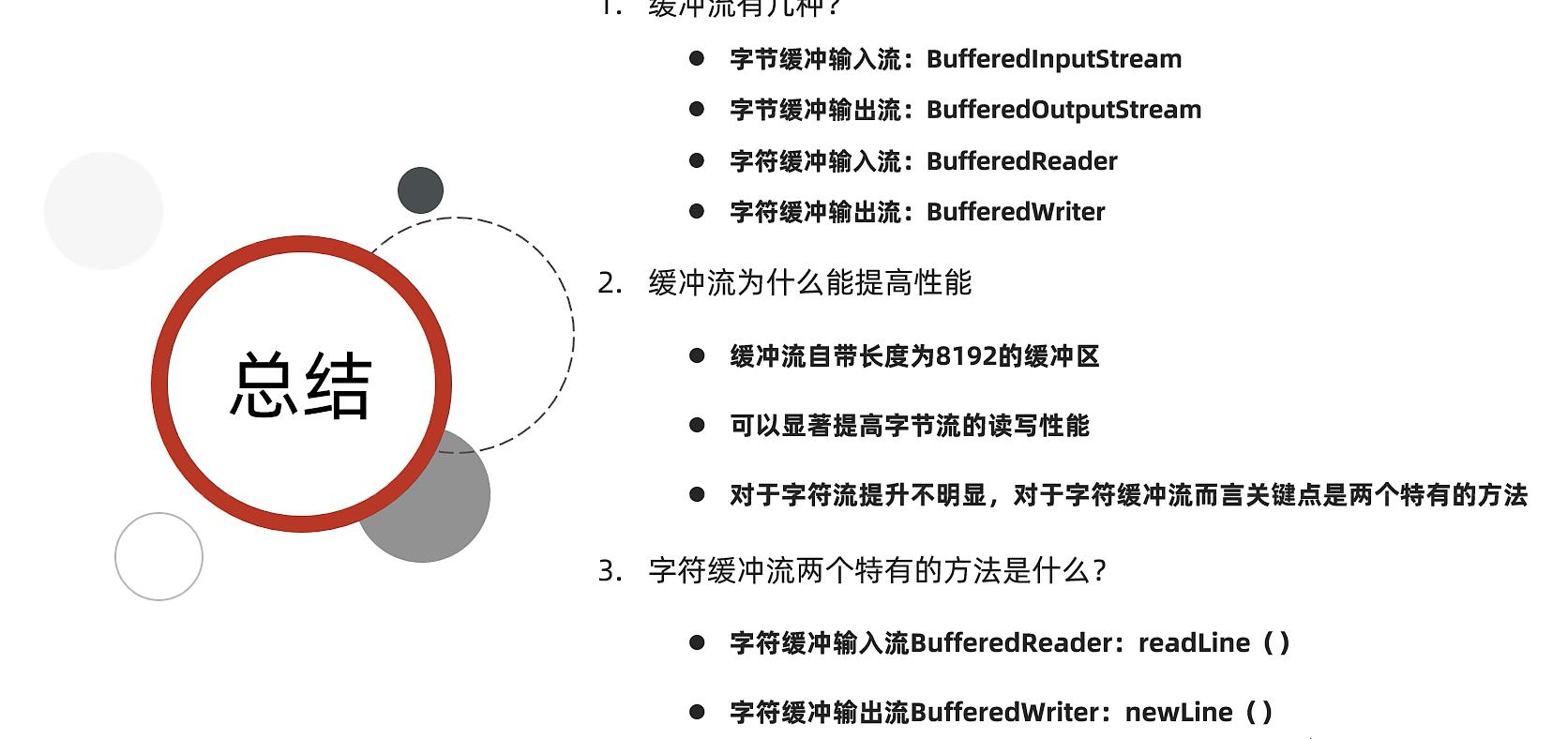
12)字符緩沖流
| 方法名稱 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| public BufferedReader(Reader r) | 把基本流包裝成高級流,提高讀取數據的性能 |
| public BufferedWriter(Writer r) | 把基本流包裝成高級流,提高讀取數據的性能 |
字符緩沖流特有方法
| 字符緩沖輸入流特有方法 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| public String readLine() | 讀取一行數據,如果沒有數據可讀了會返回null |
| 字符緩沖輸出流特有方法 | 說明跨平臺的換行 |
|---|---|
| public void newLine() | 讀取一行數據,如果沒有數據可讀了會返回null |
字符緩沖輸出流
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//創建對象BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src\\1.txt"));//讀取數據//readLine細節:在讀取時讀取一整行讀到回車換行結束,// 但是不會把回車換行讀到內存中String line;while((line = br.readLine()) != null){System.out.println(line);}//釋放資源br.close();}
}
字符緩沖輸入流
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//創建對象BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("src\\2.txt"));//讀取數據bw.write("123456789");bw.newLine();//釋放資源bw.close();}
}
總結
13)練習
1.四種拷貝方式效率對比
字節基本流一次讀一個字節
字節基本流一次讀一個字節數組
字節緩沖流一次讀一個字節
字節緩沖流一個讀一個字節數組
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {long start = System.currentTimeMillis();//method1(); //method2();method3();//method4();long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println((end - start) / 1000.0 + "秒");}private static void method4() throws IOException {BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("src\\1.txt"));BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\2.txt"));int len;byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {bos.write(bytes);}bos.close();bis.close();}private static void method3() throws IOException {BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("src\\1.txt"));BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\2.txt"));int b;while ((b = bis.read()) != -1) {bos.write(b);}bos.close();bis.close();}private static void method2() throws IOException {FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src\\1.txt");FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src\\2.txt");int len;byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) {fos.write(len);}fos.close();fis.close();}private static void method1() throws IOException {FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src\\1.txt");FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src\\2.txt");int b;while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) {fos.write(b);}fos.close();fis.close();}}
2.恢復出師表的順序
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\\BaiduNetdiskDownload\\csb.txt"));String line;ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();while((line = br.readLine()) != null){list.add(line);}br.close();Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<String>() {@Overridepublic int compare(String o1, String o2) {//獲取o1、o2序號return Integer.parseInt(o1.split("\\.")[0]) - Integer.parseInt(o2.split("\\.")[0]);}});BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\\BaiduNetdiskDownload\\csbnew.txt"));for (String s : list) {bw.write(s);bw.newLine();}bw.close();}
}
3.控制軟件運行的次數

public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//定義一個計數器保存在本地文件中,程序停止數據不會消失//1.讀取文件的數字count//原則:IO隨用隨建,不用就關閉BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src\\count.txt"));String line = br.readLine();br.close();int count = Integer.parseInt(line);count++;//又運行一次//2.判斷 > 3 不能運行if(count <= 3){System.out.println("歡迎使用,第" + count + "次免費");}else {System.out.println("只能免費使用三次,請注冊會員");}//bw創建在用的時候,如果創建到br下會清空文件使程序出錯BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("src\\count.txt"));bw.write(count + "");//把數字轉換成字符bw.close();}
}
14)轉換流
字符流和字節流之間的橋梁
InputStreamReader 將 字節流 轉換為 字符流,并可以指定字符編碼(如 UTF-8、GBK 等)來正確解析字節。
OutputStreamWriter 將 字符流寫入到字節流中,并可以指定字符編碼(如 UTF-8、GBK 等)。
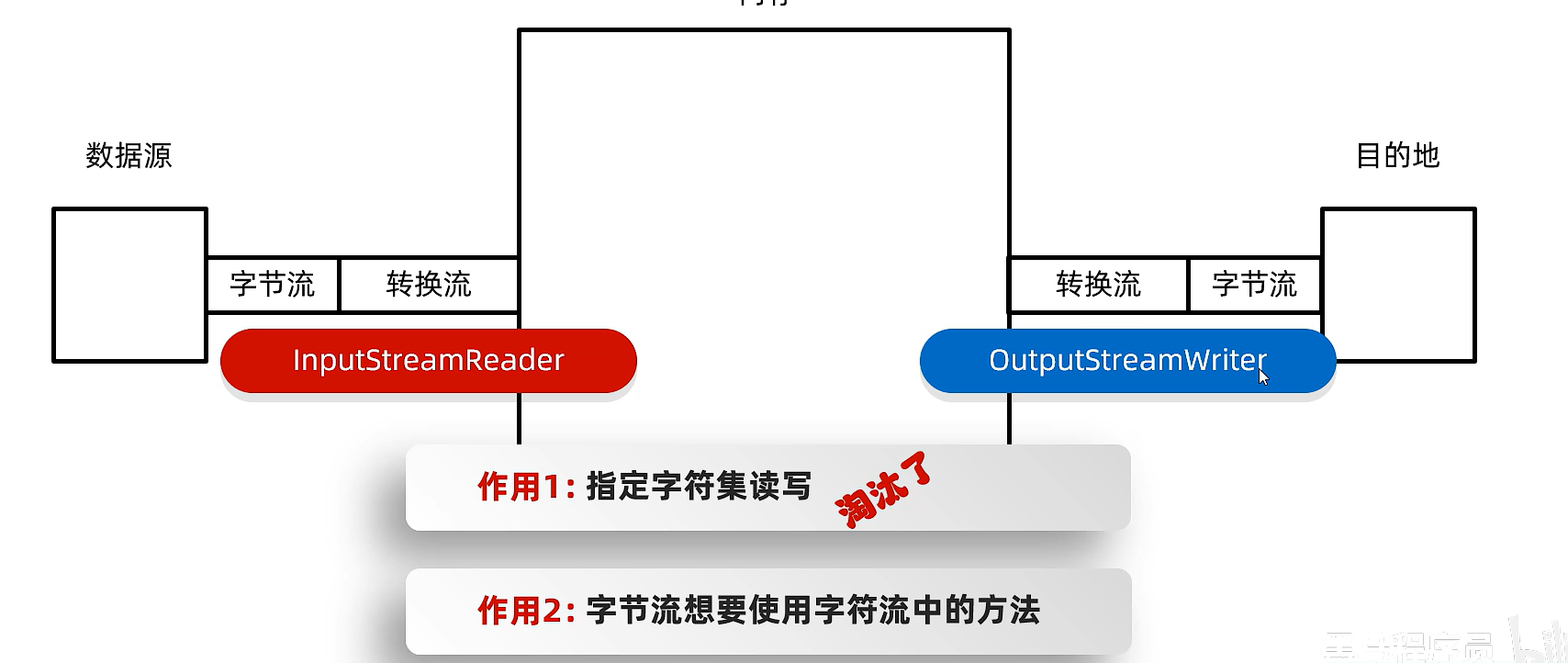
eg:利用轉換流按照指定字符編碼讀取
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//法一(已淘汰)InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("D:\\a\\1.txt"),"GBK");int ch;while((ch = isr.read()) != -1){System.out.print((char)ch);}isr.close();//法二:用FileReaderFileReader fr = new FileReader("D:\\a\\1.txt", Charset.forName("GBK"));int ch1;while((ch1 = fr.read()) != -1){System.out.print((char)ch1);}fr.close();}
}
14.1)練習
利用字節流讀取文件中的數據,每次讀一行
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("D:\\a\\1.txt")));String str = br.readLine();System.out.println(str);br.close();}
}
15)序列化流
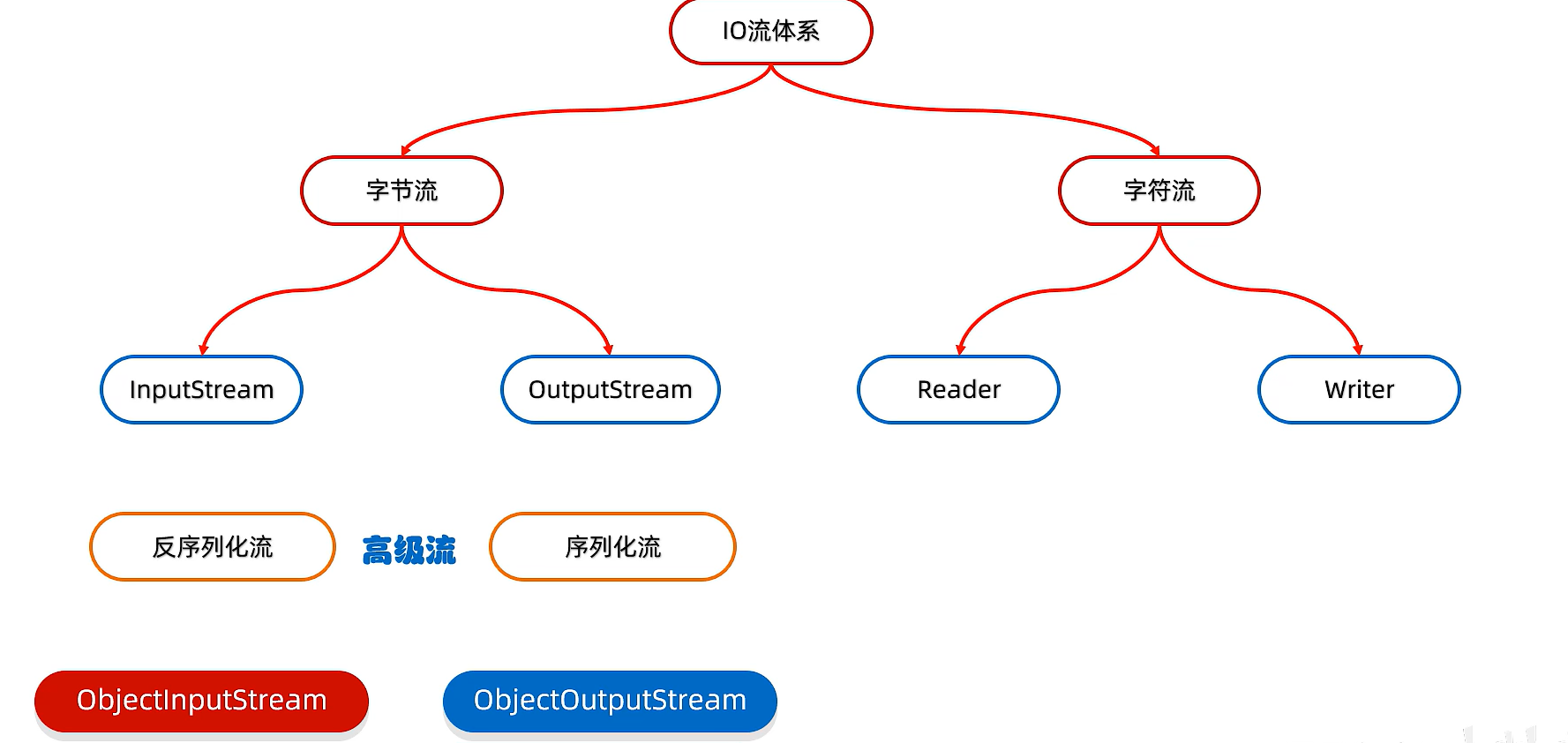
序列化流/對象操作輸出流:可以把Java中的對象寫到本地文件中
| 構造方法 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| public ObjectOutputStream(OubtputStream out) | 把基本流包裝成高級流 |
| 成員方法 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| public final void writeObject(Object obj) | 把對象序列化寫出到文件中 |
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {Student stu = new Student("zs",23);//創建序列化流對象ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\1.txt"));//細節:使用對象輸出流保存到文件時會出現NotSerializableException異常// 解決方案:需要讓Javabean類實現Serializable接口//寫出數據oos.writeObject(stu);//關閉資源oos.close();}
}
//Serializable接口里沒有抽象方法,是標記型接口
//一旦實現了找個接口表示當前的Student類可以被序列化
public class Student implements Serializable {private String name;private int age;//......}
16)反序列化流/對象操作輸入流
可以把序列化到本地文件中的對象讀取到程序中來
| 構造方法 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| public ObjectInputStream(InputStream out) | 把基本流升級為高級流 |
| 成員方法 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| public Object readObject() | 把序列化到本地的對象讀取到程序中 |
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {//創建對象ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("src//1.txt"));//讀取數據Student o = (Student)ois.readObject();//返回值類型是Object 可以強轉成Student//打印對象System.out.println(o);//釋放資源ois.close();}
}
17)(反)序列化流的細節
創建一個對象的序列化流后,又修改對象的成員變量會報錯,報錯原因:文件中的版本號跟Javabean的版本號不匹配
處理方法:固定版本號
public static Student implements Serializable{private static final long 版本號 = 1L;private Stirng name;private int age;private String address;
}
18)練習
讀寫多個對象,個數不確定
//序列化流
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {Student s1 = new Student("zs",23);Student s2 = new Student("ls",24);Student s3 = new Student("ww",25);ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(s1);list.add(s2);list.add(s3);ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\1.txt"));oos.writeObject(list);oos.close();}
}
//反序列化流
public class T2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("src\\1.txt"));ArrayList<Student> list = (ArrayList<Student>) ois.readObject();for (Student student : list) {System.out.println(student);}ois.close();}
}
19)打印流
分類:PrintStream字節打印流,PrintWriter字符打印流
特點:
- 打印流只操作文件目的地,不操作數據源
- 特有的寫出方法,數據原樣寫出 eg:打印97 文件中97
19.1)字節打印流
| 構造方法 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| public PrintStream(OutputStream/File/String) | 灌流字節輸出流/文件/文件路徑 |
| public PrintStream(String fileName,Charset charset) | 指定字符編碼 |
| public PrintStream(OutputStream out,bollean autoFlush) | 自動刷新 |
| public PrintStream(OutputStream out,boolean autoFlush,String encoding) | 指定字符編碼且自動刷新 |
字節流底層沒有緩沖區,開不開自動刷新都一樣
| 成員方法 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| public void write(int b) | 將指定的字節寫出 |
| public void println(Xxx xx) | 特有:打印任意數據,自動刷新,自動換行 |
| public void print(Xxx xx) | 特有:打印任意數據,不換行 |
| public void printf(String format,Object…args) | 特有:帶有占位符的打印語句,不換行 |
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\1.txt"),true,Charset.forName("UTF-8"));ps.println(97);//寫出+自動刷新+自動換行
ps.print(true);
ps.printf(" %s 1 %s","a","b");ps.close();
//占位符
//%n 換行
//%c 大寫
//%b boolean類型的
//%d 小數的占位符
19.2)字符打印流
| 構造方法 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| public PrintWrite(Write/File/String) | 關聯字節輸出流/文件/文件路徑 |
| public PrintWrite(String fileName,Charset charset) | 指定字符編碼 |
| public PrintWrite(Write w,boolean autoFlush) | 自動刷新 |
| public PrintWrite(OutputStream out,bollean autoFlush,Charset charset) | 指定字符編碼且自動刷新 |
字符流底層有緩沖區,相應自動刷新需要開啟
| 成員方法 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| public void write(int b) | 將指定的字節寫出 |
| public void println(Xxx xx) | 特有:打印任意數據,自動刷新,自動換行 |
| public void print(Xxx xx) | 特有:打印任意數據,不換行 |
| public void printf(String format,Object…args) | 特有:帶有占位符的打印語句,不換行 |
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("src\\1.txt"),true);
pw.println("a");
pw.print("b");
pw.printf(" %s 1 %s","a","b");pw.close();
打印流的應用場景
//獲取打印流的對象,此打印流在虛擬機,不能關閉,在系統中唯一啟動時由虛擬機創建默認指向控制臺//特殊的打印流,系統中的標準輸出流PrintStream ps = System.out;//調用打印輸出流的println寫出數據自動換行自動刷新ps.println("123");ps.close();System.out.println("asd");//關閉后sout也不能打印了20.1)解壓縮流
解壓本質:把每一個ZipEntry按照層級拷貝到本地另一個文件夾中
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1.創建一個File表示要解壓的壓縮包File src = new File("D:\\a\\1.zip");//2.創建一個File表示是解壓的目的地File dest = new File("D:\\a");//調用方法unzip(src, dest);}public static void unzip(File src,File dest) throws IOException {//創建一個解壓縮流用來讀取壓縮包中的數據ZipInputStream zip = new ZipInputStream(new FileInputStream(src));//獲取壓縮包里每一個zipEntry對象ZipEntry entry;//getNextEntry可以獲取壓縮包里的所有文件文件夾while((entry = zip.getNextEntry()) != null) {System.out.println(entry);//如果是文件夾需要再dest創建一個同樣的文件夾//如果是文件拷貝到dest中if(entry.isDirectory()) {File file = new File(dest, entry.toString());file.mkdirs();//創建多層目錄}else {FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(dest, entry.toString()));int b;while((b=zip.read()) != -1) {fos.write(b);}fos.close();//表示壓縮包中的一個文件處理完畢了}}zip.close();}
}
20.2)壓縮流
壓縮單個文件
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1.創建File對象表示要壓縮的文件File src = new File("D:\\a\\1.txt");//2.創建File對象表示壓縮包的位置File dest = new File("D:\\a\\");//調用方法toZip(src,dest);}public static void toZip(File src, File dest) throws IOException {//1.創建壓縮流關聯壓縮包ZipOutputStream zos = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File(dest,"a.zip")));//2.把ZipEntry對象表示壓縮包里每一個對象ZipEntry entry = new ZipEntry("a.txt");//3.把對象放到壓縮包里zos.putNextEntry(entry);//4.把src文件中的數據寫到壓縮包中FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(src);int b;while((b = fis.read()) != -1) {zos.write(b);}fis.close();zos.closeEntry();zos.close();}
}
壓縮整個文件夾
public class T1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1.創建File對象表示要壓縮的文件File src = new File("D:\\a\\aaa");//2.創建File對象表示元素包的父級目錄File destParent = src.getParentFile();//3.創建File對象表示壓縮包的位置File dest = new File( destParent,src.getName() +".zip");//4.創建壓縮流關聯壓縮包ZipOutputStream zos = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest));//5.獲取src里面的每一個文件,變成ZipEntry對象放到壓縮包中toZip(src,zos,src.getName());zos.close();}public static void toZip(File src, ZipOutputStream zos,String name) throws IOException {//1.進入src文件夾File[] files = src.listFiles();for (File file : files) {if(file.isFile()){//變成ZipEntry對象放到壓縮包ZipEntry entry = new ZipEntry(name + "\\" + file.getName());zos.putNextEntry(entry);//讀取文件中的數據寫到壓縮包FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);int b;while((b = fis.read()) != -1){zos.write(b);}fis.close();zos.closeEntry();}else {toZip(file,zos,name + "\\"+file.getName());}}}
}
21.1)常用工具包Commons-io
是一組IO操作的開源工具包
作業:提高IO流的開發效率
使用步驟:
- 在項目中創建一個文件夾:
lib - 將
jar包復制粘貼到lib文件夾 - 右鍵點擊
jar包,選擇Add as Library -> 點擊OK - 在類中導包使用
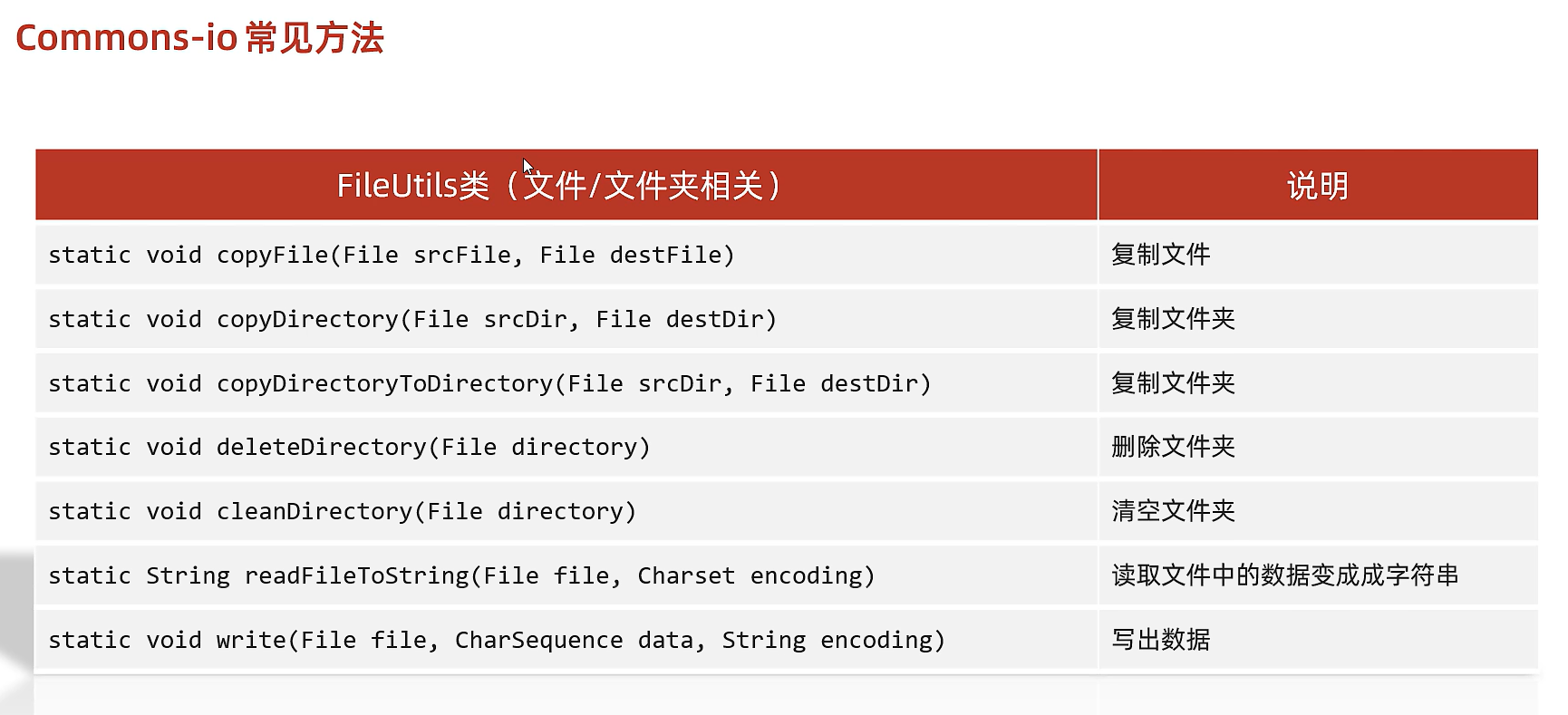

eg
File src = new File("src\\1.txt");
File dest = new File("src\\2.txt");
FileUtils.copyFile(src,dest);
21.2)常用工具包-Hutool
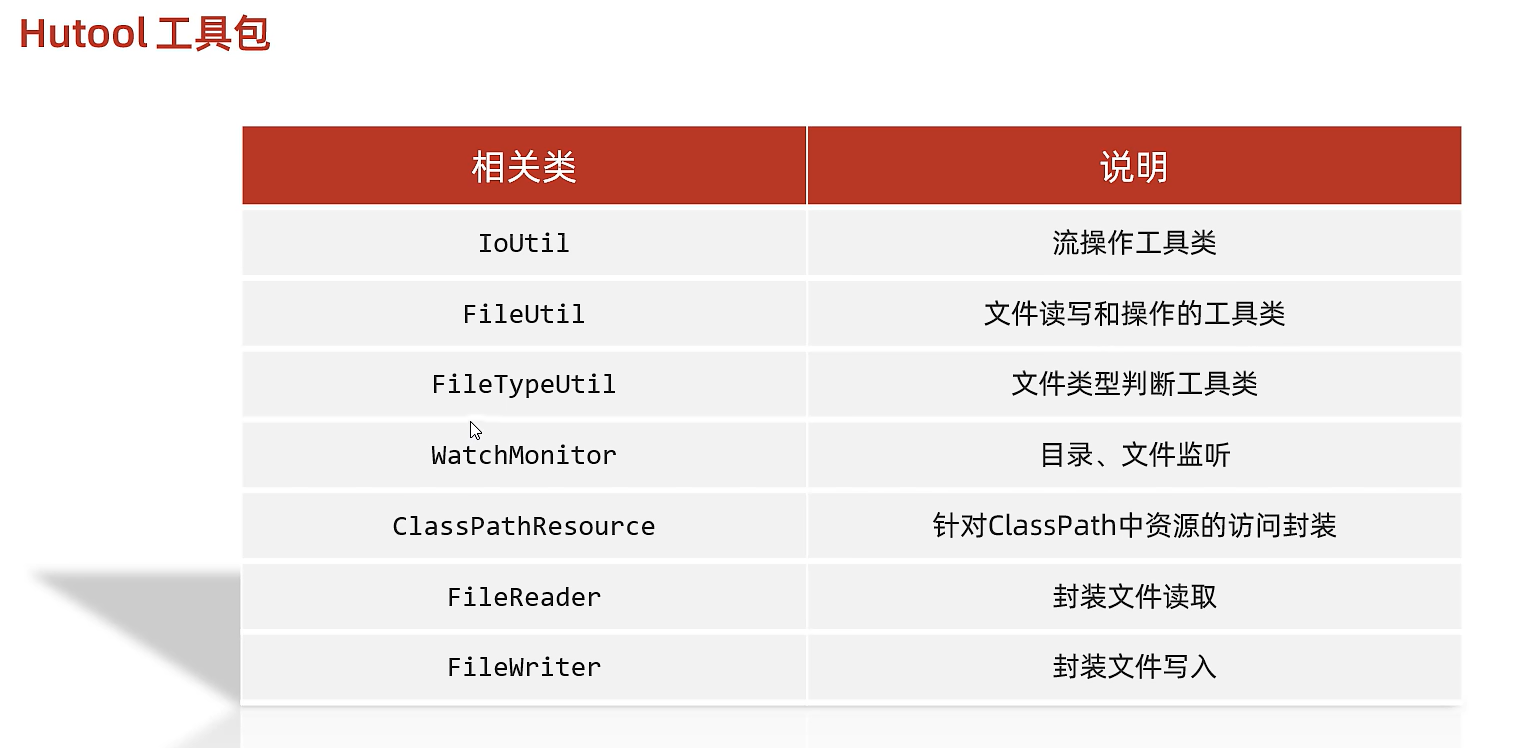
(筆記內容主要基于黑馬程序員的課程講解,旨在加深理解和便于日后復習)

希望這篇筆記能對大家的學習有所幫助,有啥不對的地方歡迎大佬們在評論區


 219. 存在重復元素 II (哈希表))



)







分布式事務)




)