C++中的list(2)//簡單復現list中的關鍵邏輯
前言
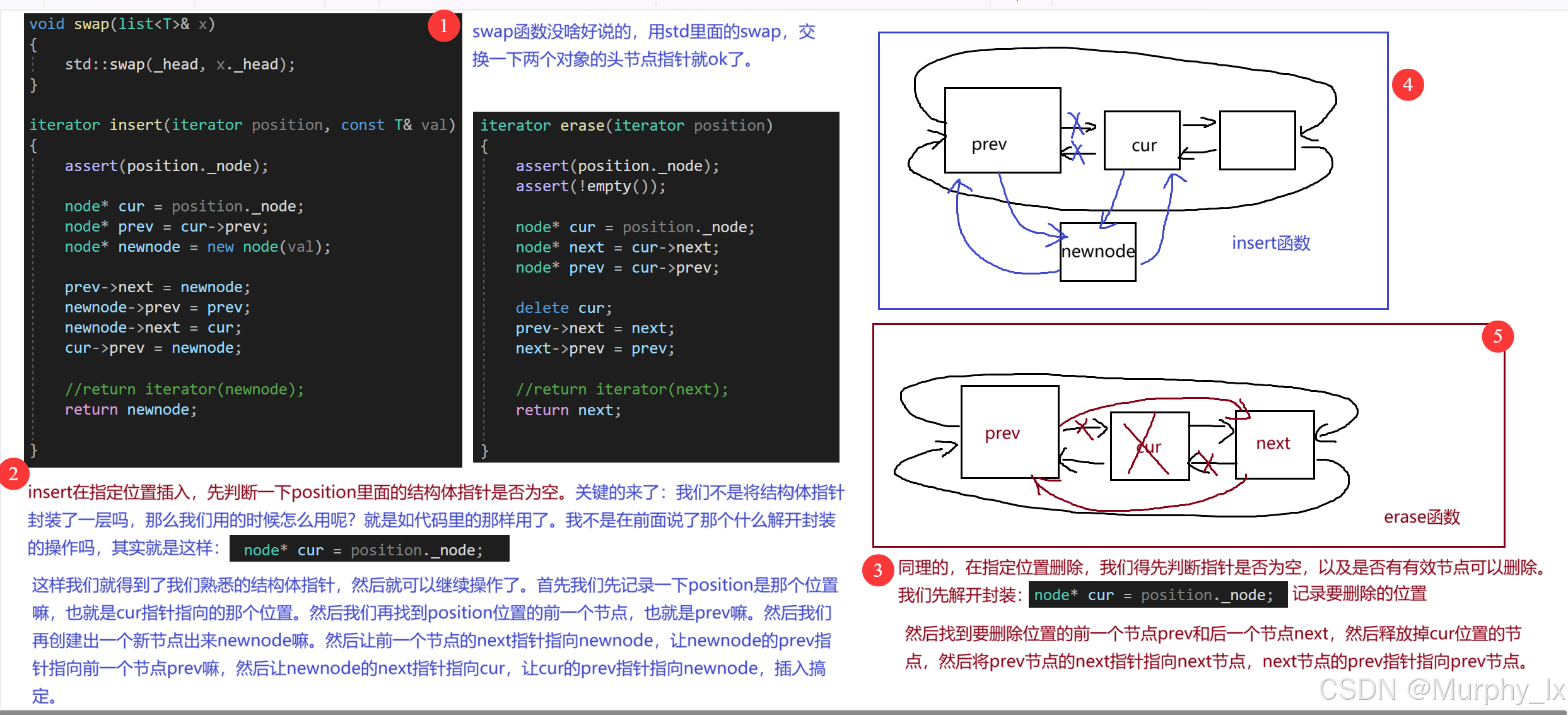
-
這一節的主要內容就是:簡單復現list中的關鍵邏輯。同樣的,我們這一節也是先粗略的看一眼源碼,結合源碼,邊理解邊復現。源碼我已經上傳到gitee,網址如下:Murphy/博客存檔,我們主要看的就是其中的
stl_list.h -
其次就是這一節是有難度的,但是難度很高嗎?也不是很高,我盡量捋順了給大家說清楚。這一節最主要的幾個知識點就是:模板、封裝、以及數據結構的邏輯。
自我梳理的邏輯
這一部分大家可看可不看,這是我自己梳理的一個邏輯過程,幫助我自己理解list的。大家感興趣可以看一下,當然也可以直接跳過這部分。
數據結構的邏輯
首先我們知道list容器是一個帶頭雙向循環鏈表。它和之前的string和vector不一樣。鏈表的底層空間是不連續的,是通過一個一個節點相連形成的。
string類實例化出來的對象實際上是一個字符串或者說字符數組,vector實例化出來的對象實際上就是一個數組,他們空間連續,且可以直接通過new來為數組開辟空間。而且string對象和vector對象中的數組就只是存儲目標數據。
而list類實例化出來的對象實際上是一個帶頭雙向循環鏈表。首先,鏈表不是數組,鏈表不能通過new來直接開辟空間。鏈表是由節點組成的,對鏈表的管理其實就是對節點的管理。節點的實現是通過結構體來實現的。因為每一個節點中存儲的數據不單純是一個目標數據,還有上一個節點的地址和下一個節點的地址,所以需要用到結構體。上面說過,鏈表是由節點組成的,對鏈表的管理其實就是對節點的管理,new無法直接為鏈表開辟空間,但是new可以為結構體開辟空間。
那么要實現一個list類,它其中的成員變量是什么呢?我們可以先借鑒string和vector,string類我們復現的時候它的成員變量是一個指針(指向數組的指針),一個有效元素個數,一個空間容量大小。因為數組底層空間連續,那么只要知道了首元素的地址(也就是指向數組的那個指針),那么就可以通過對指針進行加減訪問到每一個數據。
vector類復現的時候是有三個指針,分別指向數組首元素的地址,有效元素結束位置,數組空間結束位置。同樣的,最主要的就是數組首元素地址,因為知道首元素地址之后就可以訪問到別的元素。
到了list類,因為我們要實現帶頭的雙向循環鏈表,那么我們想通過一個簡單的成員變量就能找到全部成員,那么我們這里list類的成員變量應該就是:指向頭節點的指針。知道頭節點的位置之后,我們就可以通過頭節點中記錄的下一個節點的地址,找到下一個節點,以此類推,找到全部節點。
那么list類中的成員變量需要包含size(有效元素個數)和capacity(容量大小)嗎?
那么很明顯是不需要的,首先鏈表的節點是按需開辟,當需要有一個新節點的時候直接創建一個就ok了,它不像數組那樣底層空間連續,開辟空間就一整塊的開,鏈表是有一個數據進來的時候開辟一個節點的空間。所以就不涉及到容量大小capacity的問題。size的存在其實主要是與capacity區別開,且方便判斷容量占用是否已滿,用處其實也不大,因為在鏈表中,全都是有效元素,它不像vector和string類中的數組,由于空間可能會有冗余,所以才會有有效元素和容量大小的概念。
所以list類是不需要size和capacity這兩個成員變量的,而且類里面也會提供size( )函數,所以size更沒必要存在了。
帶頭雙向循環鏈表是一個很不錯的數據結構,能極大的方便我們程序員管理數據。
封裝&&模板
在list中,我們就可以很明顯的感覺到C++的封裝和C++借助封裝和模板來實現泛型編程的思想。在這一節,你首先得明白list類是什么樣的,為什么是這樣,也就是上面剛剛說的數據結構的邏輯,然后便是封裝思想。封裝其實不是什么很高級的東西,但是它就是很有用。
這里的封裝主要體現在兩個地方,一方面是:類,一方面是:迭代器。list類其實就是對帶頭雙向循環鏈表的一個封裝,并且通過模板來實現存儲不同類型的數據。
C++借助類的封裝和模板,我們可以發現我們學習的容器在表面上都很相似,用法也十分相似。這其實就是封裝和模板的作用。首先我們學習容器的時候,可以發現C++提供的接口都很相似,用法相似,這能極大的幫助我們上手學習C++的容器。其次,當我們真正去實現C++的容器的時候又會發現它們的底層是不一樣的,這就帶來另一個好處就是,隱藏底層實現細節。
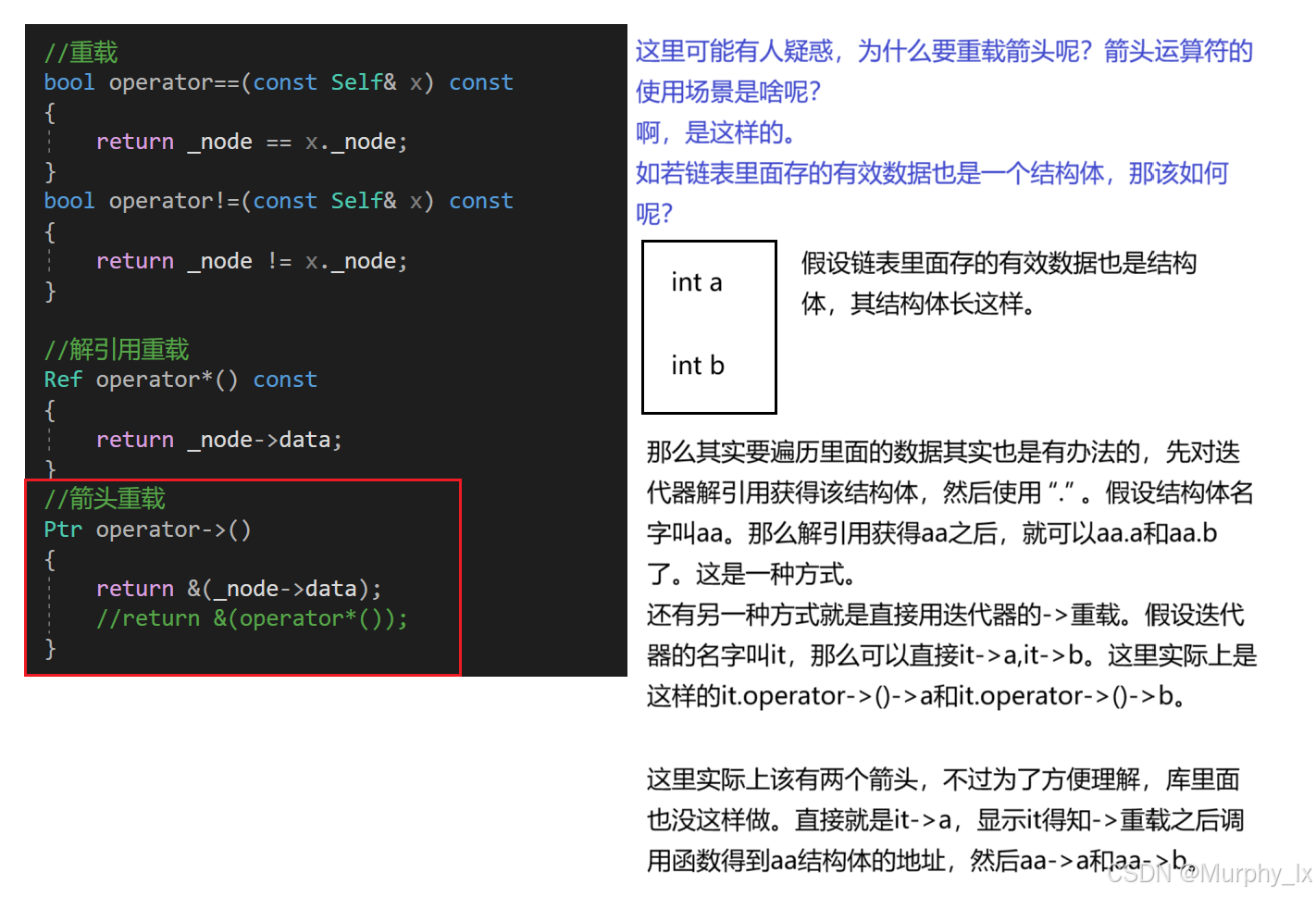
在這一節中,list類對帶頭雙向循環鏈表的封裝是比較容易理解的。但是迭代器對節點指針的封裝就比較難理解了。
一方面list的迭代器不同于我們前面學的string和vector,我們在學習vector和string的時候可能感覺他們的迭代器實現很簡單,不就是指針嘛。但是要知道,它們底層的物理空間是連續的,所以它們的原生指針(沒有經過封裝的指針)就是天然迭代器。只需要給它們的原生指針改個名字叫迭代器就行了。
那為什么底層物理空間連續的容器,它們的原生指針就能直接做迭代器呢?迭代器,迭代器,顧名思義,迭代,遍歷數據用的。這里我們就拿vector來舉例,當我們知道了首元素地址,也就是it=begin( )的時候,我們每對it進行一次++,it就會指向下一個元素。對it解引用就是數據本身。

但是,鏈表中節點的指針能直接當迭代器嗎?假設我們直接使用鏈表中節點的指針做迭代器。同樣是it=begin( ),當我們對it++的時候,it會指向什么地方?指向下一個節點嗎?很明顯,不一定。因為鏈表的底層物理空間不是連續的,所以對it++的時候(也就是對節點指針++)是無法準確的找到下一個節點的。
同樣,當我們對it解引用的時候,也就是*it,我們可以得到存儲的有效數據嗎?很明顯,也不行,為啥,因為it其實就是結構體指針,解引用之后就是結構體,結構體里面有前后節點的地址以及有效數據,我們無法直接通過對it解引用來獲得我們想要的有效數據。
之前我們學習vector和string的時候,都是直接把原生指針改個名,改成iterator直接用。現在不行了。我們直接對結構體指針改個名,無法實現我們想要的結果。
我們想要的是:當我們對迭代器加減的時候能準確的找到前后節點的位置,對迭代器解引用能直接獲得有效數據。
那么我們想實現這樣的功能,我們目前只能借助函數重載來實現(我也不知道還有什么辦法,我也才剛開始學)。
要知道所有的迭代器底層都是指針。我們要通過函數重載,使得迭代器的動作符合我們的要求。更改迭代器動作實質上就是更改結構體指針的動作邏輯,讓結構體指針++的時候不是傳統意義上的++,而是找到下一個節點的地址。
所以我們要對結構體指針的行為進行運算符重載來達到我們的目的。
但是,運算符重載的一個要求就是該類型是自定義類型,就好比如我們最開始學習的時候的時間類,我們可以使用運算符重載,使得時間類++是什么結果,–是什么結果。
所以,我們要對結構體指針進行封裝,封裝成一個自定義類型,然后在這個自定義類型里面,重載++和–和解引用等邏輯。
然后我們再對這個自定義類型改個名(iterator),這樣我們就得到我們想要的迭代器了。
那么這里其實就有兩層封裝,一層是對結構體指針進行封裝得到一個我們可以操作的自定義類型,一層是對自定義類型進行封裝成迭代器。
那么list容器整體的重難點我已經梳理完了,接下來代碼的講解中我也會結合的講。
源碼
這里我也給大家把源碼貼出來:
/*** Copyright (c) 1994* Hewlett-Packard Company** Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute and sell this software* and its documentation for any purpose is hereby granted without fee,* provided that the above copyright notice appear in all copies and* that both that copyright notice and this permission notice appear* in supporting documentation. Hewlett-Packard Company makes no* representations about the suitability of this software for any* purpose. It is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty.*** Copyright (c) 1996,1997* Silicon Graphics Computer Systems, Inc.** Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute and sell this software* and its documentation for any purpose is hereby granted without fee,* provided that the above copyright notice appear in all copies and* that both that copyright notice and this permission notice appear* in supporting documentation. Silicon Graphics makes no* representations about the suitability of this software for any* purpose. It is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty.*//* NOTE: This is an internal header file, included by other STL headers.* You should not attempt to use it directly.*/#ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_LIST_H
#define __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_LIST_H__STL_BEGIN_NAMESPACE#if defined(__sgi) && !defined(__GNUC__) && (_MIPS_SIM != _MIPS_SIM_ABI32)
#pragma set woff 1174
#endiftemplate <class T>
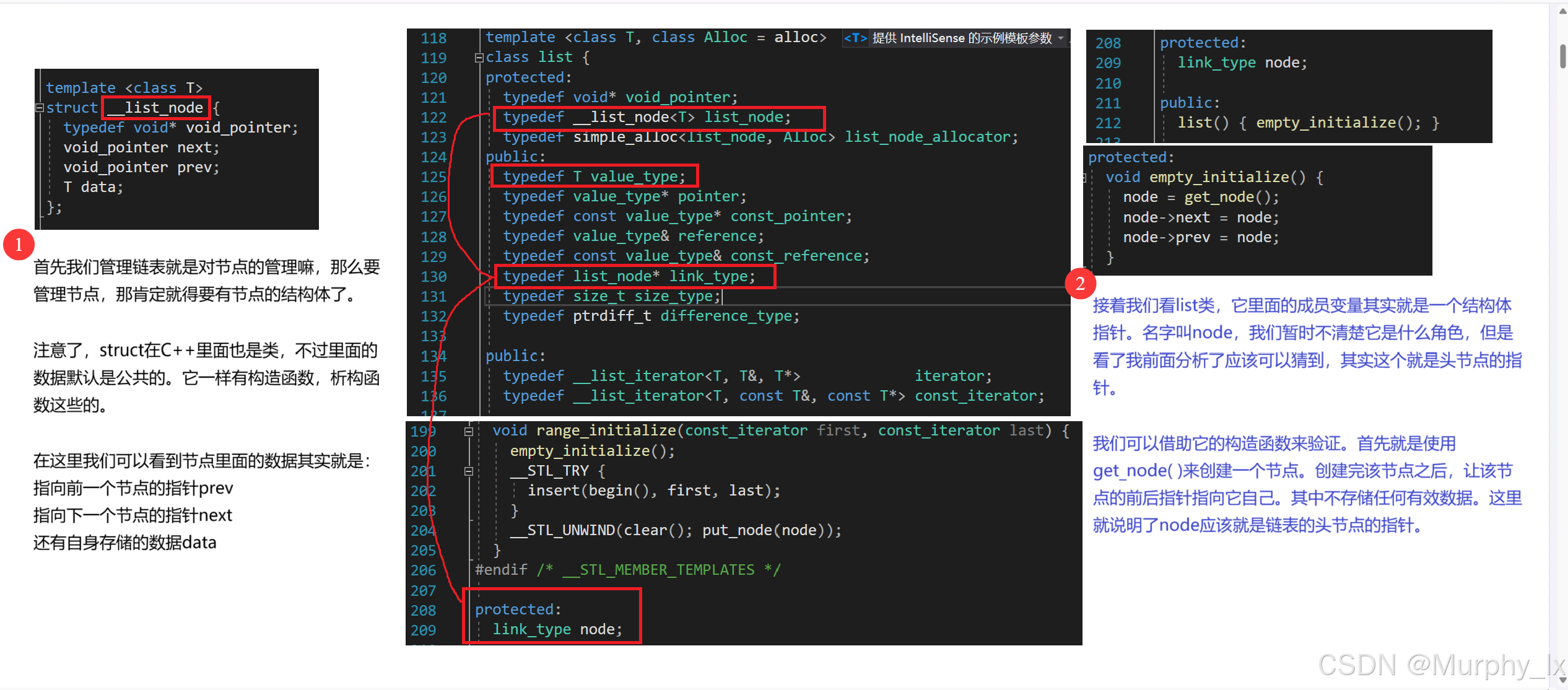
struct __list_node {typedef void* void_pointer;void_pointer next;void_pointer prev;T data;
};template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
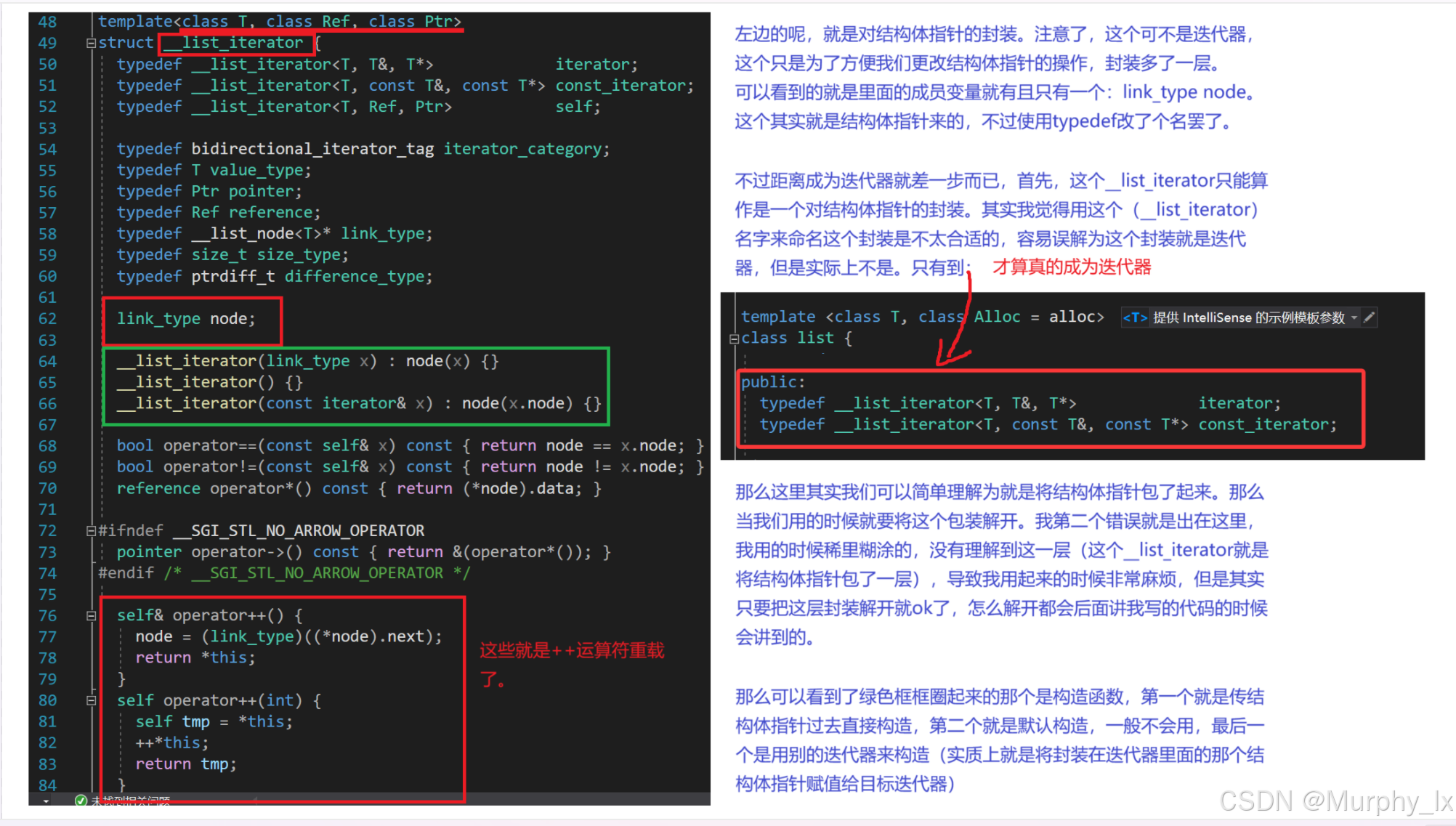
struct __list_iterator {typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;typedef bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category;typedef T value_type;typedef Ptr pointer;typedef Ref reference;typedef __list_node<T>* link_type;typedef size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;link_type node;__list_iterator(link_type x) : node(x) {}__list_iterator() {}__list_iterator(const iterator& x) : node(x.node) {}bool operator==(const self& x) const { return node == x.node; }bool operator!=(const self& x) const { return node != x.node; }reference operator*() const { return (*node).data; }#ifndef __SGI_STL_NO_ARROW_OPERATORpointer operator->() const { return &(operator*()); }
#endif /* __SGI_STL_NO_ARROW_OPERATOR */self& operator++() { node = (link_type)((*node).next);return *this;}self operator++(int) { self tmp = *this;++*this;return tmp;}self& operator--() { node = (link_type)((*node).prev);return *this;}self operator--(int) { self tmp = *this;--*this;return tmp;}
};#ifndef __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATIONtemplate <class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
inline bidirectional_iterator_tag
iterator_category(const __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr>&) {return bidirectional_iterator_tag();
}template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
inline T*
value_type(const __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr>&) {return 0;
}template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
inline ptrdiff_t*
distance_type(const __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr>&) {return 0;
}#endif /* __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION */template <class T, class Alloc = alloc>
class list {
protected:typedef void* void_pointer;typedef __list_node<T> list_node;typedef simple_alloc<list_node, Alloc> list_node_allocator;
public: typedef T value_type;typedef value_type* pointer;typedef const value_type* const_pointer;typedef value_type& reference;typedef const value_type& const_reference;typedef list_node* link_type;typedef size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;public:typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;#ifdef __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATIONtypedef reverse_iterator<const_iterator> const_reverse_iterator;typedef reverse_iterator<iterator> reverse_iterator;
#else /* __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION */typedef reverse_bidirectional_iterator<const_iterator, value_type,const_reference, difference_type>const_reverse_iterator;typedef reverse_bidirectional_iterator<iterator, value_type, reference,difference_type>reverse_iterator;
#endif /* __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION */protected:link_type get_node() { return list_node_allocator::allocate(); }void put_node(link_type p) { list_node_allocator::deallocate(p); }link_type create_node(const T& x) {link_type p = get_node();__STL_TRY {construct(&p->data, x);}__STL_UNWIND(put_node(p));return p;}void destroy_node(link_type p) {destroy(&p->data);put_node(p);}protected:void empty_initialize() { node = get_node();node->next = node;node->prev = node;}void fill_initialize(size_type n, const T& value) {empty_initialize();__STL_TRY {insert(begin(), n, value);}__STL_UNWIND(clear(); put_node(node));}#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATEStemplate <class InputIterator>void range_initialize(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) {empty_initialize();__STL_TRY {insert(begin(), first, last);}__STL_UNWIND(clear(); put_node(node));}
#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */void range_initialize(const T* first, const T* last) {empty_initialize();__STL_TRY {insert(begin(), first, last);}__STL_UNWIND(clear(); put_node(node));}void range_initialize(const_iterator first, const_iterator last) {empty_initialize();__STL_TRY {insert(begin(), first, last);}__STL_UNWIND(clear(); put_node(node));}
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */protected:link_type node;public:list() { empty_initialize(); }iterator begin() { return (link_type)((*node).next); }const_iterator begin() const { return (link_type)((*node).next); }iterator end() { return node; }const_iterator end() const { return node; }reverse_iterator rbegin() { return reverse_iterator(end()); }const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const { return const_reverse_iterator(end()); }reverse_iterator rend() { return reverse_iterator(begin()); }const_reverse_iterator rend() const { return const_reverse_iterator(begin());} bool empty() const { return node->next == node; }size_type size() const {size_type result = 0;distance(begin(), end(), result);return result;}size_type max_size() const { return size_type(-1); }reference front() { return *begin(); }const_reference front() const { return *begin(); }reference back() { return *(--end()); }const_reference back() const { return *(--end()); }void swap(list<T, Alloc>& x) { __STD::swap(node, x.node); }iterator insert(iterator position, const T& x) {link_type tmp = create_node(x);tmp->next = position.node;tmp->prev = position.node->prev;(link_type(position.node->prev))->next = tmp;position.node->prev = tmp;return tmp;}iterator insert(iterator position) { return insert(position, T()); }
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATEStemplate <class InputIterator>void insert(iterator position, InputIterator first, InputIterator last);
#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */void insert(iterator position, const T* first, const T* last);void insert(iterator position,const_iterator first, const_iterator last);
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */void insert(iterator pos, size_type n, const T& x);void insert(iterator pos, int n, const T& x) {insert(pos, (size_type)n, x);}void insert(iterator pos, long n, const T& x) {insert(pos, (size_type)n, x);}void push_front(const T& x) { insert(begin(), x); }void push_back(const T& x) { insert(end(), x); }iterator erase(iterator position) {link_type next_node = link_type(position.node->next);link_type prev_node = link_type(position.node->prev);prev_node->next = next_node;next_node->prev = prev_node;destroy_node(position.node);return iterator(next_node);}iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last);void resize(size_type new_size, const T& x);void resize(size_type new_size) { resize(new_size, T()); }void clear();void pop_front() { erase(begin()); }void pop_back() { iterator tmp = end();erase(--tmp);}list(size_type n, const T& value) { fill_initialize(n, value); }list(int n, const T& value) { fill_initialize(n, value); }list(long n, const T& value) { fill_initialize(n, value); }explicit list(size_type n) { fill_initialize(n, T()); }#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATEStemplate <class InputIterator>list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) {range_initialize(first, last);}#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */list(const T* first, const T* last) { range_initialize(first, last); }list(const_iterator first, const_iterator last) {range_initialize(first, last);}
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */list(const list<T, Alloc>& x) {range_initialize(x.begin(), x.end());}~list() {clear();put_node(node);}list<T, Alloc>& operator=(const list<T, Alloc>& x);protected:void transfer(iterator position, iterator first, iterator last) {if (position != last) {(*(link_type((*last.node).prev))).next = position.node;(*(link_type((*first.node).prev))).next = last.node;(*(link_type((*position.node).prev))).next = first.node; link_type tmp = link_type((*position.node).prev);(*position.node).prev = (*last.node).prev;(*last.node).prev = (*first.node).prev; (*first.node).prev = tmp;}}public:void splice(iterator position, list& x) {if (!x.empty()) transfer(position, x.begin(), x.end());}void splice(iterator position, list&, iterator i) {iterator j = i;++j;if (position == i || position == j) return;transfer(position, i, j);}void splice(iterator position, list&, iterator first, iterator last) {if (first != last) transfer(position, first, last);}void remove(const T& value);void unique();void merge(list& x);void reverse();void sort();#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATEStemplate <class Predicate> void remove_if(Predicate);template <class BinaryPredicate> void unique(BinaryPredicate);template <class StrictWeakOrdering> void merge(list&, StrictWeakOrdering);template <class StrictWeakOrdering> void sort(StrictWeakOrdering);
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */friend bool operator== __STL_NULL_TMPL_ARGS (const list& x, const list& y);
};template <class T, class Alloc>
inline bool operator==(const list<T,Alloc>& x, const list<T,Alloc>& y) {typedef typename list<T,Alloc>::link_type link_type;link_type e1 = x.node;link_type e2 = y.node;link_type n1 = (link_type) e1->next;link_type n2 = (link_type) e2->next;for ( ; n1 != e1 && n2 != e2 ;n1 = (link_type) n1->next, n2 = (link_type) n2->next)if (n1->data != n2->data)return false;return n1 == e1 && n2 == e2;
}template <class T, class Alloc>
inline bool operator<(const list<T, Alloc>& x, const list<T, Alloc>& y) {return lexicographical_compare(x.begin(), x.end(), y.begin(), y.end());
}#ifdef __STL_FUNCTION_TMPL_PARTIAL_ORDERtemplate <class T, class Alloc>
inline void swap(list<T, Alloc>& x, list<T, Alloc>& y) {x.swap(y);
}#endif /* __STL_FUNCTION_TMPL_PARTIAL_ORDER */#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATEStemplate <class T, class Alloc> template <class InputIterator>
void list<T, Alloc>::insert(iterator position,InputIterator first, InputIterator last) {for ( ; first != last; ++first)insert(position, *first);
}#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */template <class T, class Alloc>
void list<T, Alloc>::insert(iterator position, const T* first, const T* last) {for ( ; first != last; ++first)insert(position, *first);
}template <class T, class Alloc>
void list<T, Alloc>::insert(iterator position,const_iterator first, const_iterator last) {for ( ; first != last; ++first)insert(position, *first);
}#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */template <class T, class Alloc>
void list<T, Alloc>::insert(iterator position, size_type n, const T& x) {for ( ; n > 0; --n)insert(position, x);
}template <class T, class Alloc>
list<T,Alloc>::iterator list<T, Alloc>::erase(iterator first, iterator last) {while (first != last) erase(first++);return last;
}template <class T, class Alloc>
void list<T, Alloc>::resize(size_type new_size, const T& x)
{iterator i = begin();size_type len = 0;for ( ; i != end() && len < new_size; ++i, ++len);if (len == new_size)erase(i, end());else // i == end()insert(end(), new_size - len, x);
}template <class T, class Alloc>
void list<T, Alloc>::clear()
{link_type cur = (link_type) node->next;while (cur != node) {link_type tmp = cur;cur = (link_type) cur->next;destroy_node(tmp);}node->next = node;node->prev = node;
}template <class T, class Alloc>
list<T, Alloc>& list<T, Alloc>::operator=(const list<T, Alloc>& x) {if (this != &x) {iterator first1 = begin();iterator last1 = end();const_iterator first2 = x.begin();const_iterator last2 = x.end();while (first1 != last1 && first2 != last2) *first1++ = *first2++;if (first2 == last2)erase(first1, last1);elseinsert(last1, first2, last2);}return *this;
}template <class T, class Alloc>
void list<T, Alloc>::remove(const T& value) {iterator first = begin();iterator last = end();while (first != last) {iterator next = first;++next;if (*first == value) erase(first);first = next;}
}template <class T, class Alloc>
void list<T, Alloc>::unique() {iterator first = begin();iterator last = end();if (first == last) return;iterator next = first;while (++next != last) {if (*first == *next)erase(next);elsefirst = next;next = first;}
}template <class T, class Alloc>
void list<T, Alloc>::merge(list<T, Alloc>& x) {iterator first1 = begin();iterator last1 = end();iterator first2 = x.begin();iterator last2 = x.end();while (first1 != last1 && first2 != last2)if (*first2 < *first1) {iterator next = first2;transfer(first1, first2, ++next);first2 = next;}else++first1;if (first2 != last2) transfer(last1, first2, last2);
}template <class T, class Alloc>
void list<T, Alloc>::reverse() {if (node->next == node || link_type(node->next)->next == node) return;iterator first = begin();++first;while (first != end()) {iterator old = first;++first;transfer(begin(), old, first);}
} template <class T, class Alloc>
void list<T, Alloc>::sort() {if (node->next == node || link_type(node->next)->next == node) return;list<T, Alloc> carry;list<T, Alloc> counter[64];int fill = 0;while (!empty()) {carry.splice(carry.begin(), *this, begin());int i = 0;while(i < fill && !counter[i].empty()) {counter[i].merge(carry);carry.swap(counter[i++]);}carry.swap(counter[i]); if (i == fill) ++fill;} for (int i = 1; i < fill; ++i) counter[i].merge(counter[i-1]);swap(counter[fill-1]);
}#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATEStemplate <class T, class Alloc> template <class Predicate>
void list<T, Alloc>::remove_if(Predicate pred) {iterator first = begin();iterator last = end();while (first != last) {iterator next = first;++next;if (pred(*first)) erase(first);first = next;}
}template <class T, class Alloc> template <class BinaryPredicate>
void list<T, Alloc>::unique(BinaryPredicate binary_pred) {iterator first = begin();iterator last = end();if (first == last) return;iterator next = first;while (++next != last) {if (binary_pred(*first, *next))erase(next);elsefirst = next;next = first;}
}template <class T, class Alloc> template <class StrictWeakOrdering>
void list<T, Alloc>::merge(list<T, Alloc>& x, StrictWeakOrdering comp) {iterator first1 = begin();iterator last1 = end();iterator first2 = x.begin();iterator last2 = x.end();while (first1 != last1 && first2 != last2)if (comp(*first2, *first1)) {iterator next = first2;transfer(first1, first2, ++next);first2 = next;}else++first1;if (first2 != last2) transfer(last1, first2, last2);
}template <class T, class Alloc> template <class StrictWeakOrdering>
void list<T, Alloc>::sort(StrictWeakOrdering comp) {if (node->next == node || link_type(node->next)->next == node) return;list<T, Alloc> carry;list<T, Alloc> counter[64];int fill = 0;while (!empty()) {carry.splice(carry.begin(), *this, begin());int i = 0;while(i < fill && !counter[i].empty()) {counter[i].merge(carry, comp);carry.swap(counter[i++]);}carry.swap(counter[i]); if (i == fill) ++fill;} for (int i = 1; i < fill; ++i) counter[i].merge(counter[i-1], comp);swap(counter[fill-1]);
}#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */#if defined(__sgi) && !defined(__GNUC__) && (_MIPS_SIM != _MIPS_SIM_ABI32)
#pragma reset woff 1174
#endif__STL_END_NAMESPACE #endif /* __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_LIST_H */// Local Variables:
// mode:C++
// End:觀察源碼

看到這里,也該到我們自己動手寫一個出來了,我先把我的代碼貼出來給大家:
復現源碼
list.h
#pragma once
#include<cassert>namespace lx
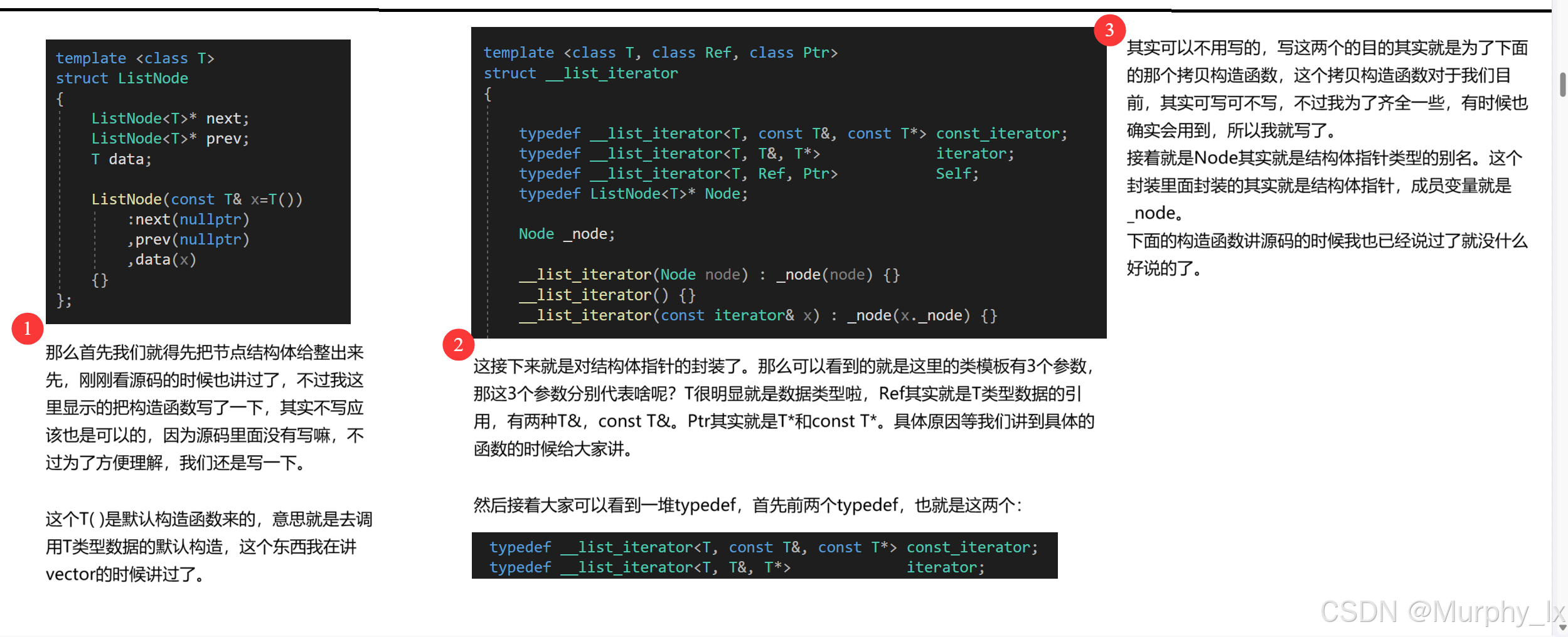
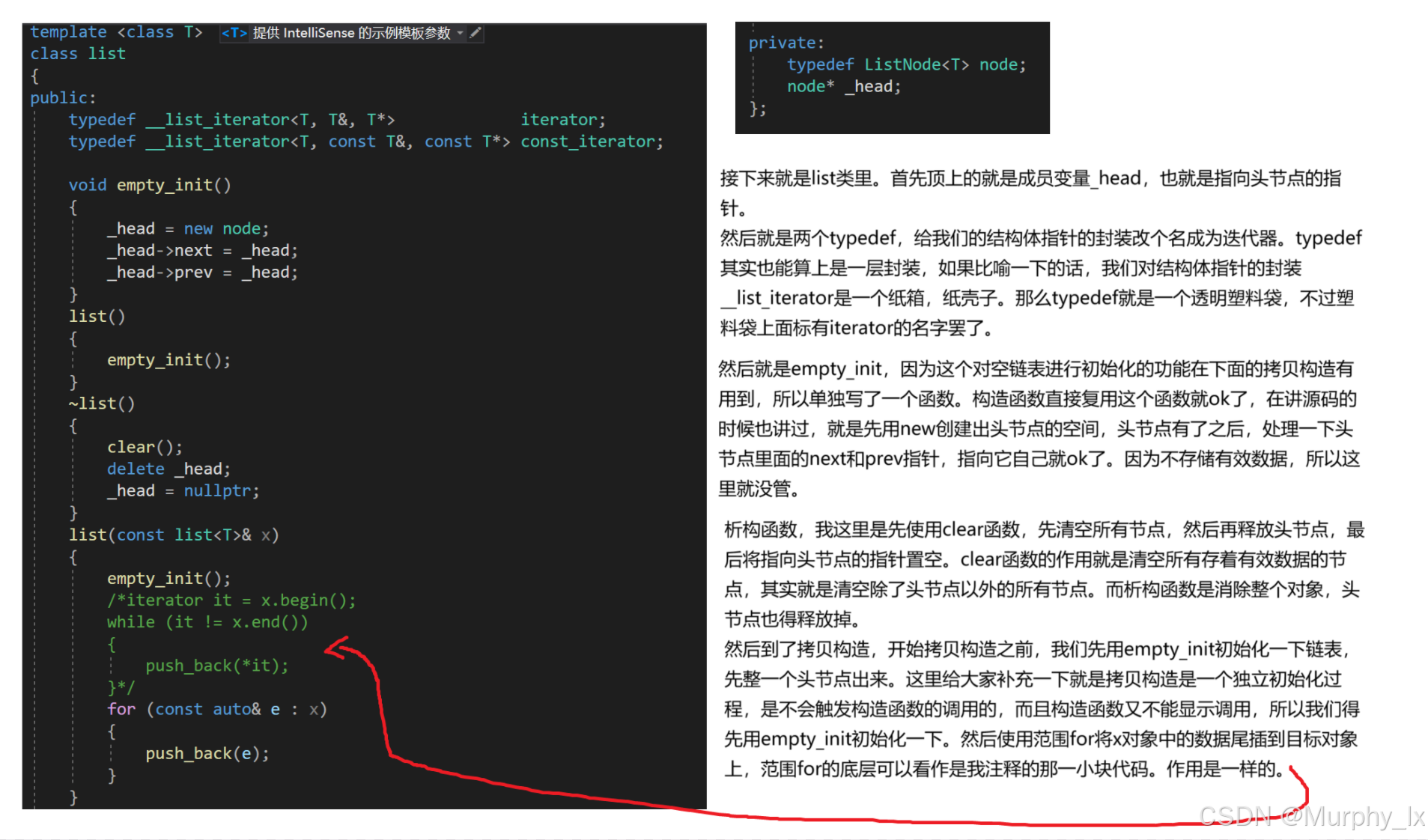
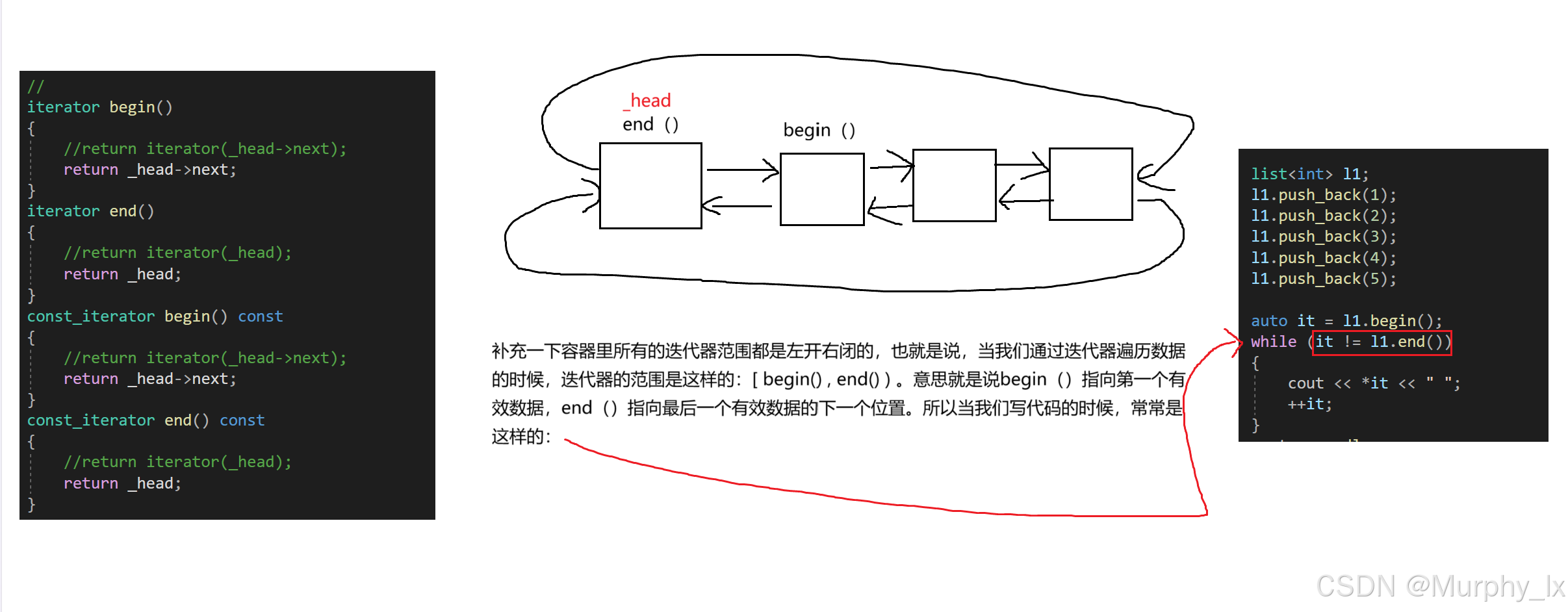
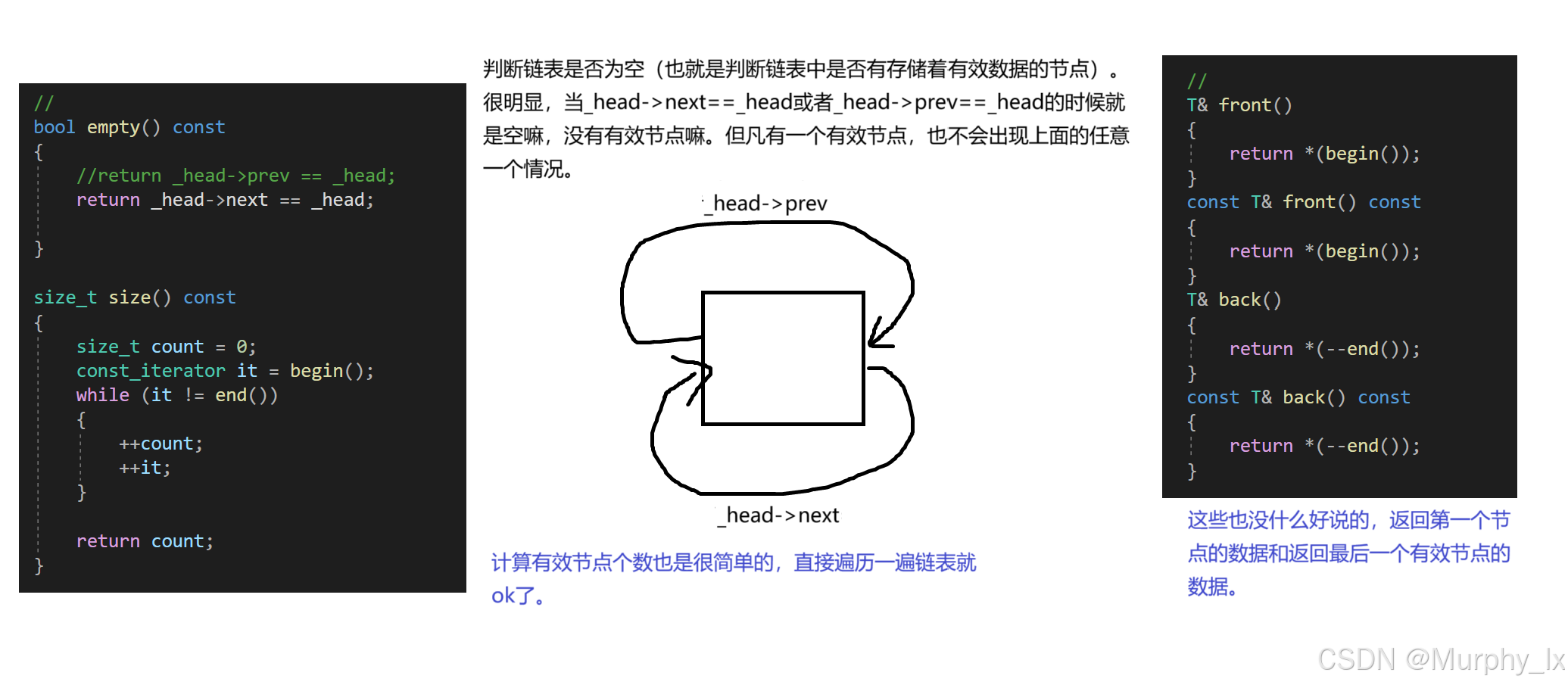
{template <class T>struct ListNode{ListNode<T>* next;ListNode<T>* prev;T data;ListNode(const T& x=T()):next(nullptr),prev(nullptr),data(x){}};template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct __list_iterator{typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;typedef ListNode<T>* Node;Node _node;__list_iterator(Node node) : _node(node) {}__list_iterator() {}__list_iterator(const iterator& x) : _node(x._node) {}//重載bool operator==(const Self& x) const{return _node == x._node;}bool operator!=(const Self& x) const{return _node != x._node;}//解引用重載Ref operator*() const{return _node->data;}//箭頭重載Ptr operator->(){return &(_node->data);//return &(operator*());}//前置++Self& operator++(){_node = _node->next;return *this;}//后置++Self operator++(int){Self tmp = *this;++ *this;return tmp;}//前置--Self& operator--(){_node = _node->prev;return *this;}//后置--Self operator--(int){Self tmp = *this;-- *this;return tmp;}};template <class T>class list{public:typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;void empty_init(){_head = new node;_head->next = _head;_head->prev = _head;}list(){empty_init();}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}list(const list<T>& x){empty_init();/*iterator it = x.begin();while (it != x.end()){push_back(*it);}*/for (const auto& e : x){push_back(e);}}/*list<T>& operator=(const list<T>& x){if (this != &x){clear();for (const auto& e : x){push_back(e);}}return *this;}*/list<T>& operator=(list<T> x){swap(x);return *this;}//iterator begin(){//return iterator(_head->next);return _head->next;}iterator end(){//return iterator(_head);return _head;}const_iterator begin() const{//return iterator(_head->next);return _head->next;}const_iterator end() const{//return iterator(_head);return _head;}//bool empty() const{//return _head->prev == _head;return _head->next == _head;}size_t size() const{size_t count = 0;const_iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){++count;++it;}return count;}//T& front(){return *(begin());}const T& front() const{return *(begin());}T& back(){return *(--end());}const T& back() const{return *(--end());}//void swap(list<T>& x){std::swap(_head, x._head);}iterator insert(iterator position, const T& val){assert(position._node);node* cur = position._node;node* prev = cur->prev;node* newnode = new node(val);prev->next = newnode;newnode->prev = prev;newnode->next = cur;cur->prev = newnode;//return iterator(newnode);return newnode;}iterator erase(iterator position){assert(position._node);assert(!empty());node* cur = position._node;node* next = cur->next;node* prev = cur->prev;delete cur;prev->next = next;next->prev = prev;//return iterator(next);return next;}void push_back(const T& val){node* tail = _head->prev;node* newnode = new node(val);tail->next = newnode;newnode->prev = tail;newnode->next = _head;_head->prev = newnode;}/*void push_back(const T& val){insert(end(), val);}*/void push_front(const T& val){node* cur = begin()._node;node* newnode = new node(val);_head->next = newnode;newnode->prev = _head;newnode->next = cur;cur->prev = newnode;}/*void push_front(const T& val){insert(begin(), val);}*/void pop_back(){assert(!empty());node* cur = _head->prev;node* prev = cur->prev;delete cur;prev->next = _head;_head->prev = prev;}/*void pop_back(){erase(--end());}*/void pop_front(){assert(!empty());node* cur = begin()._node;node* next = cur->next;delete cur;_head->next = next;next->prev = _head;}/*void pop_front(){erase(begin());}*/void resize(size_t n, T val = T()){if (n != size()){if (n > size()){size_t len = n - size();for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++){push_back(val);}}else{size_t len = size() - n;for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++){pop_back();}}} }void clear(){assert(!empty());iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it=erase(it);}}private:typedef ListNode<T> node;node* _head;};}
test.cpp//測試使用
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;#include"list.h"namespace lx
{void test1(){list<int> l1;l1.push_back(1);l1.push_back(2);l1.push_back(3);l1.push_back(4);l1.push_back(5);auto it = l1.begin();while (it != l1.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;//////l1.push_front(11);l1.push_front(22);l1.push_front(33);l1.push_front(44);it = l1.begin();while (it != l1.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;/////l1.pop_front();l1.pop_front();l1.pop_front();l1.pop_front();it = l1.begin();while (it != l1.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;/////l1.pop_back();l1.pop_back();l1.pop_back();l1.pop_back();it = l1.begin();while (it != l1.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;l1.resize(7, 99);it = l1.begin();while (it != l1.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;l1.resize(1);it = l1.begin();while (it != l1.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;}
}int main()
{lx::test1();return 0;
}
復現代碼講解
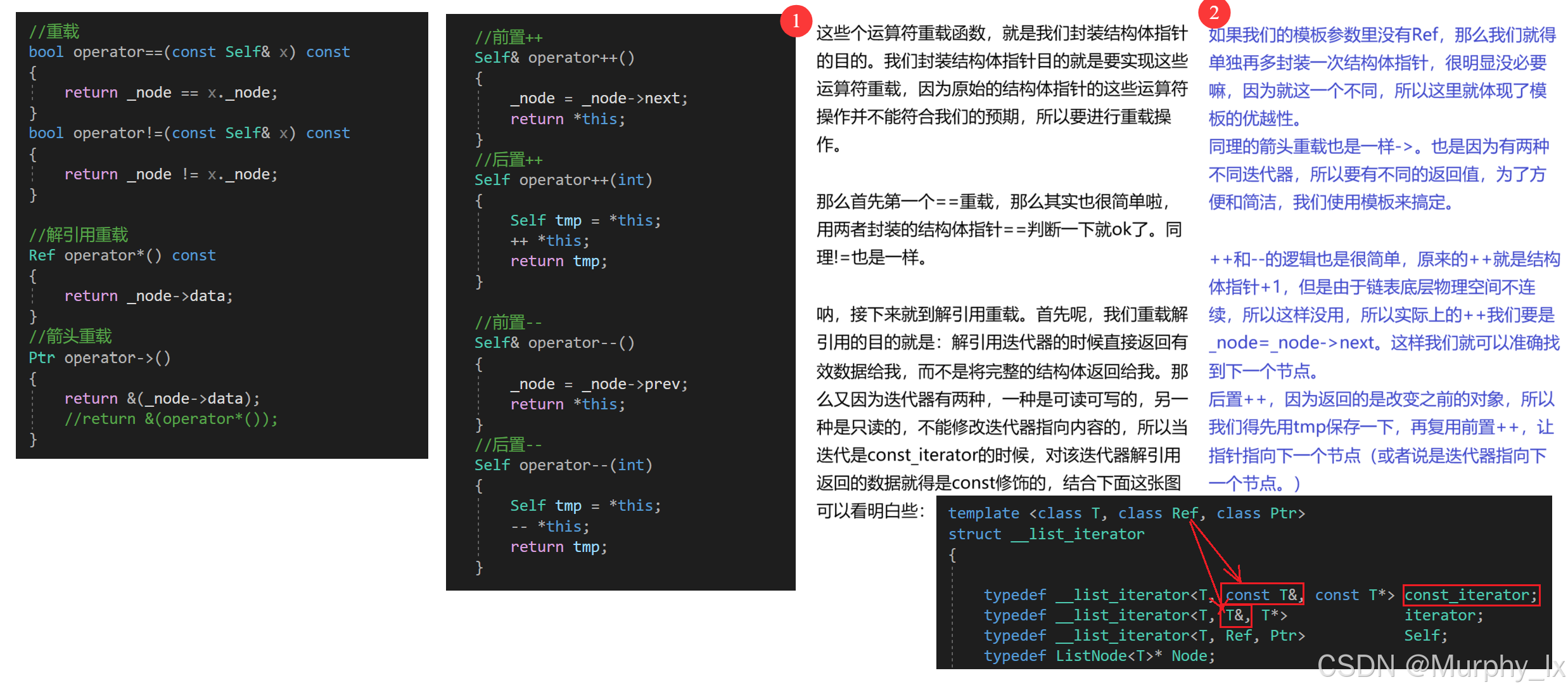

后續的什么push_back(插入邏輯和insert一樣,畫畫圖就能明白)昂和resize呀,clear昂,都很簡單了的,看代碼完全能看懂的。(注釋掉的代碼表示的是另一種方法。)
這里簡單說一下resize的作用:分為兩種,當n大于原來的size()的時候,就是插入n-size()個節點。n小于原來的size()的時候就是刪除size()-n個節點,也就是復用push_back和pop_back兩個函數。

:Python 的基本數據類型——復數)


:Python 的基本數據類型——浮點數)




_位運算優化)









