Deep Learning-Driven Ultra-High-Definition Image Restoration: A Survey
Liyan Wang, Weixiang Zhou, Cong Wang, Kin-Man Lam, Zhixun Su, Jinshan Pan

Abstract
Ultra-high-definition (UHD) image restoration?? aims to specifically solve the problem of ??quality degradation in ultra-high-resolution images??. Recent advancements in this field are predominantly driven by ??deep learning-based innovations??, including enhancements in ??dataset construction??, ??network architecture??, ??sampling strategies??, ??prior knowledge integration??, and ??loss functions??. In this paper, we systematically review recent progress in ??UHD image restoration??, covering various aspects ranging from ??dataset construction?? to ??algorithm design??. This serves as a valuable resource for understanding ??state-of-the-art developments?? in the field. We begin by summarizing ??degradation models?? for various ??image restoration subproblems??, such as ??super-resolution??, ??low-light enhancement??, ??deblurring??, ??dehazing??, ??deraining??, and ??desnowing??, and emphasizing the ??unique challenges?? of their application to ??UHD image restoration??. We then highlight existing ??UHD benchmark datasets?? and organize the literature according to ??degradation types?? and ??dataset construction methods??. Following this, we showcase major milestones in ??deep learning-driven UHD image restoration??, reviewing the progression of ??restoration tasks??, ??technological developments??, and ??evaluations of existing methods??. We further propose a ??classification framework?? based on ??network architectures?? and ??sampling strategies??, helping to clearly organize existing methods. Finally, we share insights into the ??current research landscape?? and propose directions for ??further advancements??.
摘要??
??超高清(UHD)圖像修復??旨在針對性解決??超高分辨率圖像的質量退化問題??。該領域的最新進展主要由??基于深度學習的創新??驅動,包括??數據集構建??、??網絡架構設計??、??采樣策略優化??、??先驗知識融合??和??損失函數改進??等方面的增強。本文系統綜述了UHD圖像修復的最新進展,涵蓋??從數據集構建到算法設計的多個維度??,為理解該領域前沿發展提供了重要參考。我們首先總結了??多種圖像修復子問題??(如超分辨率、低光增強、去模糊、去霧、去雨、去雪等)的??退化模型??,并強調了其在UHD圖像修復中面臨的??獨特挑戰??;接著梳理了??現有UHD基準數據集??,并根據退化類型與數據集構建方法對文獻進行分類;隨后展現了??深度學習驅動的UHD圖像修復主要里程碑??,回顧了修復任務、技術發展與現有方法的評估進展;進一步提出基于??網絡架構??與??采樣策略的分類框架??,助力系統性組織現有方法;最后,針對當前研究現狀分享了見解并提出了未來發展方向的建議。
Introduction
Recently, with the rapid advancement of ??imaging and acquisition equipment??, ??ultra-high-definition (UHD) images?? featuring ??high pixel density?? and ??resolutions?? (e.g., 3,840 × 2,160 pixels or higher), become widely used in fields such as ??video streaming [1], [2]??, ??virtual reality [3]??, ??medical imaging [4]??, and ??satellite remote sensing [5], [6]??. This surge in applications has significantly heightened user demand for ??enhanced image clarity?? and ??detail performance??. However, ??hardware limitations??, ??restricted transmission bandwidth??, and ??challenging acquisition environments?? often impede the production of ??high-quality UHD images??. Common challenges include ??insufficient resolution?? and ??degradation factors?? such as ??blur??, ??rain??, ??snow??, ??haze??, ??low light??, etc. Fig. 1 illustrates examples of ??image degradation?? under different conditions, highlighting how these issues compromise ??image resolution?? and ??overall quality??. Consequently, ??UHD image restoration?? has emerged as a ??critical area of research?? within ??computer vision?? and ??image processing??.

近年來,隨著??成像與采集設備??的快速發展,具有??高像素密度??和??超高分辨率??(如3,840 × 2,160像素及以上)的??超高清(UHD)圖像??在視頻流媒體、虛擬現實、醫學影像、衛星遙感等領域廣泛應用。這一應用熱潮顯著提升了用戶對??圖像清晰度??與??細節表現??的需求。然而,??硬件限制??、??傳輸帶寬約束??以及??復雜采集環境??往往導致高質量UHD圖像難以生成,常見挑戰包括分辨率不足以及模糊、雨雪、霧霾、低光等退化因素。如圖1所示,不同條件下的圖像退化實例展示了這些問題如何損害圖像分辨率與整體質量。因此,??UHD圖像修復??已成為計算機視覺與圖像處理領域的??關鍵研究方向??。
UHD image restoration?? aims to recover ??high-quality UHD images?? from ??degraded inputs??, addressing various ??sub-problems??, such as ??UHD image super-resolution??, ??deblurring??, ??dehazing??, ??low-light image enhancement??, ??deraining??, and ??desnowing??. While ??deep learning-based image restoration methods [7]–[17]?? have achieved remarkable success on ??lower-resolution images?? (e.g., ??low-light image enhancement [18]–[20]??, ??dehazing [21], [22]??, ??desnowing [23], [24]??, ??deraining [25]–[28]??, and ??deblurring [29], [30]??) thanks to advances in techniques like ??convolutional neural networks (CNNs) [31], [32]?? and ??Transformers [33], [34]??, their effectiveness remains limited when applied to ??UHD image restoration??. This limitation stems from the fact that these models are often designed for ??low-resolution inputs?? and struggle to ??scale efficiently to UHD images??. In addition, ??UHD images?? inherently possess ??more intricate details??, a ??wider color gamut??, and a ??significantly larger number of pixels??, which pose ??unique computational challenges??. ?
UHD圖像修復旨在從退化輸入中恢復高質量的UHD圖像,涵蓋??超分辨率??、去模糊、去霧、低光增強、去雨、去雪等多種子問題。盡管基于深度學習的圖像修復方法在低分辨率圖像上(如低光增強、去霧、去雪、去雨、去模糊)憑借??卷積神經網絡(CNN)??與??Transformer等技術取得了顯著成功,但其在UHD圖像修復中的效果仍受限。這主要因為此類模型通常針對低分辨率輸入設計,難以高效擴展到UHD圖像。此外,UHD圖像本身包含??更精細的細節??、??更廣的色域??及??顯著增多的像素??,這帶來了??獨特的計算挑戰??。
Since the introduction of the ??first large-scale dataset for UHD image super-resolution reconstruction tasks [35]?? in 2021, a range of ??UHD image restoration methods?? and corresponding datasets have been developed. These include ??multi-guided bilateral learning?? for UHD image dehazing [36] with the ??4KID dataset??; ??multi-scale separable-patch integration networks?? for video deblurring [37] with the ??4DRK dataset??; the ??Transformer-based LLFormer [38]?? with the ??UHD-LOL dataset?? and the ??Fourier embedding network UHDFour [39]?? with the ??UHD-LL dataset?? for ??UHD low-light image enhancement??; and ??UHDformer [40]??, which explores ??feature transformation between high- and low-resolution??, with the ??UHD-Haze/UHD-Blur datasets?? for UHD image restoration. Additionally, the ??dual interaction prior-driven network UHDDIP [41]??, paired with the ??UHDSnow/UHD-Rain datasets??, addresses UHD image restoration.
These methods employ diverse strategies, including ??downsampling-enhancement-upsampling structure [37], [39], [41]–[48]??, ??encoder-decoder structures with stepwise up-downsampling [38], [49]–[51]??, and ??resampling-enhancement structures [52], [53]??. The evolution of network models has transitioned from ??CNNs [37], [39], [42], [49]?? (emphasizing ??local feature extraction??) to ??Transformer-based models [38], [41], [43], [48]?? (focusing on ??global modeling??), and most recently to ??Multilayer Perceptrons (MLPs) [44]–[47]?? and ??Mamba [50]?? (aiming to ??reduce computational overhead??). From 2021 to the present, approximately ??20 studies?? have explored ??deep learning-based UHD image restoration methods??. A concise summary of these developments is presented in ??Fig. 2??.

自2021年首個面向??超高清(UHD)圖像超分辨率重建任務??的大規模數據集提出以來,一系列??UHD圖像修復方法??及對應數據集相繼涌現。例如:
- 基于??4KID數據集??的??多引導雙邊學習網絡??用于UHD圖像去霧;
- 基于??4DRK數據集??的??多尺度可分離補丁集成網絡??用于視頻去模糊;
- 基于??UHD-LOL數據集??的??Transformer架構LLFormer??,以及基于??UHD-LL數據集??的??傅里葉嵌入網絡UHDFour??用于UHD低光圖像增強;
- 基于??UHD-Haze/UHD-Blur數據集??的??UHDformer??,探索高低分辨率間的特征變換以實現UHD圖像修復;
- 結合??UHDSnow/UHD-Rain數據集??的??雙交互先驗驅動網絡UHDDIP??處理UHD圖像修復。
這些處理UHD圖像的方法采用了??多樣化策略??,包括:
- ??下采樣-增強-上采樣結構;
- ??分步上下采樣的編碼器-解碼器結構??;
- ??重采樣-增強結構??。
網絡模型的演進從??側重局部特征提取的CNN??,轉向??聚焦全局建模的Transformer??,再到近年旨在??降低計算開銷的MLP??與??Mamba。2021年至今,已有約20項研究探索??基于深度學習的UHD圖像修復方法??,其發展脈絡可簡要總結如圖2所示。
Although ??deep learning?? has dominated research on UHD image restoration, there is a lack of ??comprehensive and in-depth surveys?? on deep learning-based solutions. Therefore, our work ??systematically and comprehensively reviews?? the research in the field to provide a useful starting point for understanding ??major developments??, ??limitations of existing approaches??, and ??potential future research directions??. The main contributions of this paper are threefold:
? We conduct a ??systematic review?? of research progress in ??deep learning-based UHD image restoration??, covering ??problem definitions?? for various UHD restoration tasks, ??challenges??, the development of ??benchmark datasets??, and the ??improvements and limitations?? of existing methods.
? We propose an ??effective classification method?? for existing deep learning-based UHD image restoration methods and analyze ??representative benchmarks?? under different subtasks.
? Finally, we discuss the ??challenges faced by current deep learning methods?? and outline ??promising future directions??.
盡管深度學習主導了UHD圖像修復研究,但針對??基于深度學習的解決方案??仍缺乏全面且深入的綜述。因此,本文通過??系統性梳理與綜合分析??,為理解該領域的主要進展、現有方法的局限性及未來潛在研究方向提供參考。本文的主要貢獻包括以下三點:
- ??系統性綜述??:覆蓋各類UHD修復任務的??問題定義??、??挑戰??、??基準數據集發展??及現有方法的??改進與局限性??;
- ??分類與基準分析??:提出??基于深度學習的UHD圖像修復方法分類框架??,并在不同子任務下分析代表性基準;
- ??挑戰與未來方向??:探討當前深度學習方法面臨的挑戰,并展望??有潛力的研究方向??。
Challenges?
UHD images??, affected by the aforementioned degradation processes, pose ??unique challenges?? for restoration due to their ??ultra-high resolution?? and ??dense pixel characteristics??:
? ??High computational requirements??: Compared to ??high-definition (HD) images??, UHD images contain ??significantly more pixels??. Processing such ??large-scale feature maps?? demands ??substantial computational resources and storage??, necessitating ??advanced GPUs?? and ??high-performance hardware??.
? ??Difficulty in recovering details??: UHD images capture ??intricate details??, and degradation effects are ??more pronounced at high resolutions??. Although existing methods perform adequately with ??low-resolution images??, they often struggle to preserve ??fine structures?? in UHD images, resulting in ??texture loss?? or ??artifacts?? in the restoration output.
? ??Lack of training datasets??: Methods trained on ??low-resolution datasets?? cannot directly process UHD images, as they require ??large amounts of degraded-clear UHD image pairs?? for fine-tuning. However, most publicly available datasets are dominated by ??HD and lower-resolution images??, with a notable lack of ??datasets specialized for UHD scenarios??. This limitation significantly hinders the ??development and testing of algorithms??.
? ??Poor algorithm adaptability??: Many restoration algorithms are designed for ??low-resolution images?? and fail to ??scale effectively to UHD images??. Developing ??new algorithms?? that accommodate the ??distinct characteristics of UHD images?? is an urgent need.
受前述退化過程影響的??超高清(UHD)圖像??,因其??超高分辨率??與??密集像素特性??,在修復過程中面臨獨特挑戰:
- ??高計算需求??:相較于??高清(HD)圖像??,UHD圖像包含??顯著更多的像素??。處理此類??大規模特征圖??需消耗??大量計算資源與存儲空間??,必須依賴??高端GPU??及??高性能硬件?。
- ??細節恢復困難??:UHD圖像包含??精細細節??,且退化效應在高分辨率下更顯著。現有方法雖能處理??低分辨率圖像??,卻常難以有效保留UHD圖像的??細微結構??,導致修復結果出現??紋理丟失??或??偽影?。
- ??訓練數據匱乏??:基于??低分辨率數據集??訓練的方法無法直接處理UHD圖像,需??大量退化-清晰UHD圖像對??進行微調。然而,公開數據集以??HD及以下分辨率圖像為主??,??專為UHD場景設計的數據集嚴重不足??,極大阻礙??算法開發與測試?。
- ??算法適應性差??:多數修復算法針對??低分辨率圖像??設計,難以??有效擴展至UHD圖像??。亟需開發適應??UHD圖像特性??的新算法
Datasets
This section highlights the key benchmark datasets developed for UHD image restoration, categorized by the specific challenges they address.

Approaches
This section presents a comprehensive and systematic review of existing deep learning-based UHD image restoration methods. This review covers various tasks, including super-resolution reconstruction, low-light image enhancement, dehazing, deblurring, deraining, and desnowing.



Technical
In this section, we examine the evolution of deep learningbased UHD image restoration methods, focusing on three critical aspects:
- network architecture
- sampling strategy
- loss function
1. Network Architectures
??Existing UHD image restoration models?? employ a variety of ??advanced network architectures??, including ??convolutional neural networks (CNNs) [31]??, ??UNet [62]??, ??pyramid networks [63]??, ??multilayer perceptrons (MLPs) [64]??, ??Transformers [33]??, and ??Mamba [65]??. These architectures provide ??different processing methods?? and ??technical support?? for UHD image restoration tasks. To systematically analyze their ??characteristics?? and ??application scenarios??, we categorize existing models into three forms based on ??UHD image processing methods??:
- ??Downsampling-enhancement-upsampling structure??,
- ??Encoder-decoder structure with stepwise up-downsampling??,
- ??Resampling-enhancement structure??.
現有UHD圖像修復模型??
現有模型采用多種??先進網絡架構??,包括:
- ??卷積神經網絡(CNNs)??
- ??UNet??
- ??金字塔網絡??
- ??多層感知機(MLPs)
- ??Transformer??
- ??Mamba??
這些架構為UHD圖像修復任務提供??差異化處理方法??與??技術支持??。為系統分析其??特性??與??應用場景??,依據??UHD圖像處理方法??將現有模型分為三類:
- ??下采樣-增強-上采樣結構??
- ??分步上下采樣的編碼器-解碼器結構??
- ??重采樣-增強結構
1.1 Downsampling-Enhancement-Upsampling

Figure 4??: Summary of the ??downsampling-enhancement-upsampling structure?? for UHD image restoration. (a) The ??single-branch downsampling-enhancement-upsampling architecture?? focuses on the design of ??enhancement networks in the low-resolution space??, utilizing some popular architectures such as ??CNN, UNet, MLP, and Transformer??. (b) The ??dual-branch downsampling-enhancement-upsampling architecture?? explores the ??correlation between high- and low-resolution features?? or incorporates ??additional prior information?? to guide the reconstruction process.
1.1 ??下采樣-增強-上采樣結構??
??圖4??總結了用于??超高清(UHD)圖像恢復??的??下采樣-增強-上采樣結構??。(a) ??單分支下采樣-增強-上采樣架構??側重于在??低分辨率空間??中設計??增強網絡??,采用流行架構如??CNN、UNet、MLP和Transformer??。(b) ??雙分支下采樣-增強-上采樣架構??探索??高分辨率與低分辨率特征之間的相關性??,或融入??額外先驗信息??以指導重建過程。

Figure 5??: Overview of ??dual branch frameworks?? under the ??downsampling-enhancement-upsampling structure??. ??DMixer [45]?? ??upsamples low-resolution features?? and ??merges them with high-resolution features?? for reconstruction. ??UDR-Mixer [47]?? ??feeds high-resolution features into the low-resolution branch?? to facilitate reconstruction. ??UHDformer [43]?? ??transforms features from high to low resolution?? and ??enhances high-resolution reconstruction through concatenation??. ??UHDDIP [41]?? ??extracts gradient and normal priors in the low-resolution space?? to ??interact with low-resolution features??, ??guiding high-resolution reconstruction??.
圖 5?? 總結了??下采樣-增強-上采樣結構??下的??雙分支框架??。??DMixer 上采樣低分辨率特征??并將其??與高分辨率特征融合??以進行重建。??UDR-Mixer?? ??將高分辨率特征輸入低分辨率分支??以促進重建。??UHDformer 將特征從高分辨率轉換為低分辨率??,并通過??拼接增強高分辨率重建??。??UHDDIP?在低分辨率空間中提取梯度和法線先驗??,以??與低分辨率特征交互??,??指導高分辨率重建??。
1.2 Encoder-Decoder with Stepwise Up-downsampling

Figure 6??: Summary of the ??Encoder-Decoder structure with stepwise up-downsampling?? for UHD image restoration. ??UHDVD [37]?? and ??LapDehazeNet [49]?? progressively downsample the input image based on ??separable-patch and Laplace pyramid architectures?? to encode features respectively, while ??LLFormer [38]?? and ??Wave-Mamba [50]?? reduce the scale of potential features with ??stepwise?? and adopt the core components of the ??Axis-based Transformer block?? and the ??Low-Frequency State Space Block (LFSS Block)?? for restoration, respectively.
1.2 ??帶逐步上下采樣的編碼器-解碼器結構??
??圖 6?? 總結了用于??UHD圖像恢復??的??帶逐步上下采樣的編碼器-解碼器結構??。??UHDVD 和 ??LapDehazeNet 分別基于??可分離塊(separable-patch)和拉普拉斯金字塔架構??逐步下采樣輸入圖像以編碼特征;而 ??LLFormer?和 ??Wave-Mamba?通過??逐步方式??降低潛在特征尺度,并分別采用??基于軸向的Transformer塊??和??低頻狀態空間塊(LFSS Block)?? 作為核心組件進行恢復。
1.3 Resampling-Enhancement

Figure 7??: Summary of the ??resampling-enhancement structure?? for UHD image restoration. Unlike previous methods that rely on ??uniform, content-agnostic downsampling?? (represented by the gray arrows), (a) a ??non-uniform sampling enhancement network (NSEN) [52]??, which incorporates two core designs: 1) ??content-guided downsampling?? to generate ??detail-preserving low-resolution images??, and 2) ??invertible pixel alignment?? that computes inverse functions to remove distortions induced during the downsampling process; and (b) a ??learning model-aware resampling (LMAR) [53]??, which focuses on obtaining ??compensated low-resolution features?? from UHD input images guided by ??model knowledge??. These features are fed into the ??enhancer??, along with original low-resolution features, and are subsequently ??upsampled to UHD results??.
1.3 ??重采樣-增強結構??
??圖 7?? 總結了用于??UHD圖像恢復??的??重采樣-增強結構??。與依賴??均勻、內容無關下采樣??(灰色箭頭表示)的傳統方法不同,(a) ??非均勻采樣增強網絡(NSEN)包含兩大核心設計:1) ??內容引導下采樣??以生成??保留細節的低分辨率圖像??;2) ??可逆像素對齊??,通過計算逆函數消除下采樣過程中的失真。(b) ??學習模型感知重采樣(LMAR)專注于從UHD輸入圖像中獲取??模型知識引導的補償低分辨率特征??。這些特征與原始低分辨率特征一同輸入??增強器??,最終??上采樣為UHD結果??。
2 Sampling Strategy
在現有超高清(UHD)圖像修復框架中,??三種主要采樣策略??被廣泛采用:
- ??高倍率上下采樣??(如4×、8×、16×、32×),常用方法包括??雙三次插值??、??雙線性插值??和??PixelUnshuffle??。這些方法雖能減少計算負擔,但??高倍率下導致顯著信息丟失??,影響修復質量(例如,PixelUnshuffle在PSNR/SSIM指標最優,但雙線性插值在LPIPS更優)。
- ??逐步上下采樣??(如從2×降至16×),通常集成于??編碼器-解碼器結構??以提取多尺度特征。然而,??下采樣程度增加會不可逆損傷圖像質量??,后續上采樣難以恢復。
- ??內容相關重采樣??,通過??自適應調整采樣率??解決上述問題。例如:
- ??小波變換??避免關鍵信息丟失,
- ??Min-p采樣??保留高置信度特征并丟棄次要特征,
- ??非均勻下采樣器??根據圖像細節豐富度動態采樣,
- ??模型感知重采樣(LMAR)?? 利用模型知識定制采樣,兼容現有插值方法且無需重新訓練增強網絡。
??核心挑戰??在于??平衡計算效率與信息保留??,高倍率采樣雖高效但犧牲細節,而內容相關策略通過智能優化(如動態采樣和模型驅動)提升魯棒性。
3 Loss Functions
1) Pixel-Level Loss
- 𝐿1 loss (Mean Squared Error, MAE)
- 𝐿2 loss (Mean Squared Error, MSE)
- 𝑆𝑚𝑜𝑜𝑡?𝐿1 loss [66]
- 𝐶?𝑎𝑟𝑏𝑜𝑛𝑛𝑖𝑒𝑟 loss
- 𝑇𝑉 (Total Variation) loss
2)𝑆𝑆𝐼𝑀 loss [67]?
3)Frequency-Domain Loss?[68]
4)Perceptual loss [69]
5)Adversarial loss [70]

Evaluation
1 Evaluation Metrics
1.1 Full-Reference Metrics
PSNR. Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) [71]?
SSIM. Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) [67]?
MAE/MSE. Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and Mean Squared Error (MSE)?
LPIPS. LPIPS [72] assesses perceptual similarity by calculating the distance between feature representations in a neural network. This deep learning-based metric approximates human judgment of image quality. Lower LPIPS values correspond to higher perceptual similarity.
全參考指標??
- ??PSNR??(峰值信噪比)[71]:衡量修復圖像與真實圖像之間的信噪比,值越高表示質量越接近真實圖像。
- ??SSIM??(結構相似性指數)[67]:通過亮度、對比度和結構相似性綜合評估圖像質量,值越接近1表示修復效果越好。
- ??MAE/MSE??(平均絕對誤差/均方誤差):直接計算像素級差異,MAE值越小表示誤差越低,MSE值越小表示修復精度越高。
- ??LPIPS??(基于學習的感知相似性指標)[72]:利用神經網絡提取特征的距離評估??感知相似性??,更貼近人類對圖像質量的判斷。??LPIPS值越低??,表示感知質量越接近真實圖像。
1.2 No-Reference Metrics
NIQE. The primary purpose of Natural Image Quality Evaluator (NIQE) [75] is to assess an image’s naturalness based on statistical models of natural scenes. It determines how visually natural and realistic an image appears without requiring reference images. Lower NIQE scores indicate more natural and realistic images.
MUSIQ. Multi-scale Image Quality (MUSIQ) [76] evaluates image quality by analyzing contrast preservation across multiple scales. It focuses on the preservation of fine details and textures in the image after processing. Higher MUSIQ values signify better image quality.
PI. Perceptual Index (PI) combines two metrics, MAE and NIQE, to evaluate image perceptual quality. It emphasizes both aesthetic appeal and naturalness. A lower PI score reflects better perceptual quality.
?無參考指標??
- ??NIQE??(自然圖像質量評估器)[75]:基于自然場景的統計模型評估圖像的??自然性??,無需參考圖像。??NIQE值越低??,表示圖像越接近真實自然場景。
- ??MUSIQ??(多尺度圖像質量評估)[76]:通過??多尺度對比度分析??衡量細節和紋理的保留程度。??MUSIQ值越高??,表示圖像質量越好。
- ??PI??(感知指數):結合??MAE與NIQE??,綜合評價圖像的??美學吸引力??和??自然性??。??PI值越低??,表示感知質量越優。
2 Comparision Results

--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------

--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------

--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
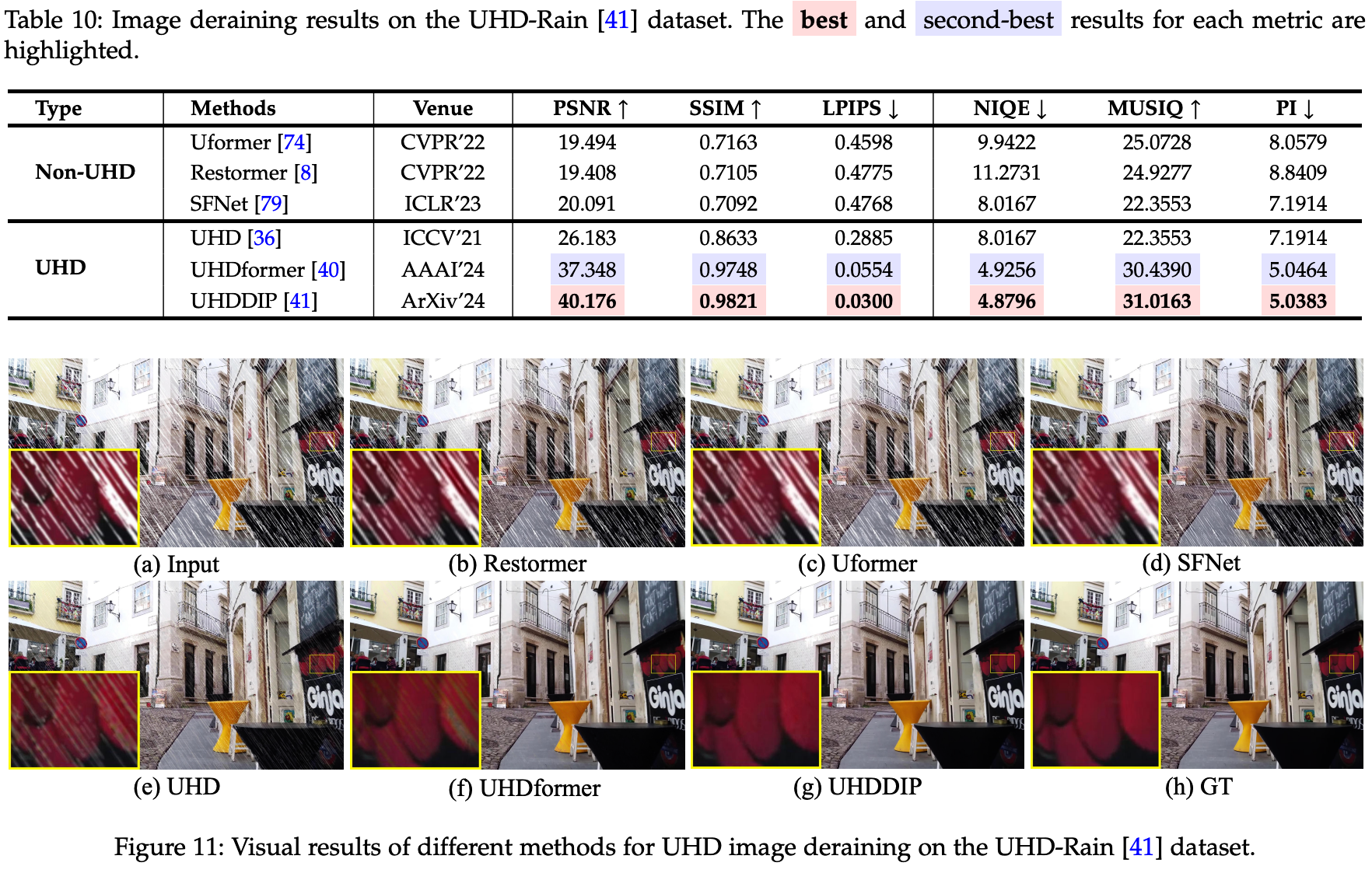
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------

3 Computational Complexity

Future
1.???Effective Processing Paradigm??
As previously discussed, current ??UHD image restoration methods?? predominantly follow two main processing paradigms: ??the downsampling-enhancement-upsampling?? and ??the encoder-decoder with stepwise up-downsampling??. These paradigms aim to ??reduce computational costs?? by employing high magnification or stepwise downsampling; however, a significant drawback is ??the information loss?? which degrades overall restoration quality. Although some researchers have attempted to avoid information loss through ??wavelet transforms?? [50], ??the connection with the augmentation network?? has not been considered, and its effectiveness requires further improvement. Additionally, advancements in ??learning model-aware resampling methods?? [53] have shown potential for ??preserving feature consistency?? between UHD image inputs and their corresponding low-resolution inputs ??without requiring retraining?? of the enhancement network. Thus, exploring ??the intrinsic connection between resampling and enhancement networks?? is a potential research direction for developing ??more effective processing paradigms??.
高效處理范式??
如前所述,當前??UHD圖像修復方法??主要遵循兩種處理范式:??下采樣-增強-上采樣??和??分階段上下采樣的編碼器-解碼器結構??。這些范式通過采用高倍率或分步下采樣來??降低計算成本??,但其顯著缺點是??信息丟失??導致修復質量下降。盡管已有研究者嘗試通過??小波變換??[50]避免信息丟失,但未考慮??與增強網絡的關聯??,且其效果仍需改進。此外,??模型感知重采樣方法??[53]的最新進展展現了潛力,能夠在??無需重新訓練增強網絡??的前提下,保持UHD圖像輸入與其對應低分辨率輸入之間的??特征一致性??。因此,探索??重采樣操作與增強網絡的內在關聯??是開發??更高效處理范式??的潛在研究方向。
2 ??Lightweight Network Design??
Existing ??deep learning models?? face significant ??computational challenges??, which limit their application in UHD image restoration tasks. Current restoration methods, ranging from ??traditional CNNs?? to advanced ??Transformer architectures??, demand ??substantial computational power??, making them heavily reliant on ??high-end GPUs??. Although some networks have been proposed to reduce these complexities through ??MLPs?? and novel ??Mamba frameworks??, they fall short of enabling ??direct implementation on mobile devices??. Consequently, future research should prioritize the development of ??lightweight network architectures?? that balance ??performance and efficiency??, enabling broader applicability across ??diverse devices??.
輕量化網絡設計??
現有??深度學習模型??面臨顯著的??計算挑戰??,限制了其在UHD圖像修復任務中的應用。當前修復方法(從??傳統CNN??到先進的??Transformer架構??)需要??大量計算資源??,嚴重依賴??高端GPU??。盡管已有網絡通過??MLP??和新型??Mamba框架??嘗試降低復雜度,但仍無法實現??在移動設備上直接部署??。因此,未來研究需優先開發??輕量化網絡架構??,平衡??性能與效率??,從而擴大其??跨多樣化設備的適用性??。
3 ??Developing Real-World Benchmark Datasets??
As shown in Table 1, except for the ??UHD-LL dataset?? [39], most existing benchmark datasets are ??artificially synthesized??. Although the data shortage in UHD image restoration has been temporarily alleviated, a significant gap remains between ??synthetic images?? and ??real-world degraded images??. Models trained on synthetic images often perform well on synthetic test samples but exhibit ??poor performance on real-world images??. For this reason, it is imperative to develop ??large-scale paired training datasets?? comprising ??real-world UHD images??.
開發真實世界基準數據集??
如表1所示,除??UHD-LL數據集??外,現有基準數據集多為??人工合成??。盡管UHD圖像修復領域的數據短缺問題暫時緩解,但??合成圖像??與??真實世界退化圖像??之間仍存在顯著差距。基于合成數據訓練的模型在合成測試樣本上表現良好,但對??真實世界圖像的修復效果較差??。因此,亟需構建包含??真實世界UHD圖像??的??大規模成對訓練數據集??。
4. ??Using Image Priors??
Current UHD image restoration networks predominantly focus on ??learning intrinsic features??; however, ??the incorporation of image priors?? plays a pivotal role in enhancing image quality. For instance, ??UHDDIP?? [41] incorporates ??gradient and normal priors?? into its model design, significantly improving ??structural integrity?? and ??detail preservation?? of restored images. This demonstrates the potential of leveraging image priors to guide the restoration process. Further exploration of ??alternative image priors?? opens promising avenues for advancing UHD image restoration methodologies.
利用圖像先驗??
當前的UHD圖像修復網絡主要關注??學習圖像固有特征??,但??圖像先驗的融合??對提升修復質量至關重要。例如,??UHDDIP??在模型設計中融入了??梯度和法向先驗??,顯著提高了修復圖像的??結構完整性??和??細節保留能力??。這證明了利用先驗信息引導修復過程的潛力。進一步探索??其他類型的圖像先驗??,將為UHD圖像修復方法的創新提供機遇。
5. ??Specialized Evaluation Metrics??
Most image quality evaluation metrics, such as ??PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS??, are designed for ??standard-resolution images?? and reflect image quality to a certain extent. However, the ??high-resolution characteristics?? of UHD images place greater demands on ??detail restoration?? and ??subjective visual perception??. For example, the perceived quality of an image may be affected by ??local detail in different areas??, which may not be evident in low-resolution images. Therefore, it is crucial to develop ??evaluation indicators specifically tailored for UHD images??. These metrics should accurately reflect the unique requirements of UHD images in terms of ??detail representation?? and ??overall sensory quality??.
專用評估指標??
大多數圖像質量評估指標(如??PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS??)針對??標準分辨率圖像??設計,僅能部分反映圖像質量。然而,UHD圖像的??高分辨率特性??對??細節修復??和??主觀視覺體驗??提出了更高要求。例如,圖像感知質量可能受??不同區域局部細節??的影響,而此類現象在低分辨率圖像中并不明顯。因此,需開發??專門針對UHD圖像的評估指標??,以準確反映其在??細節還原??與??整體感官質量??上的獨特需求。
6. ??UHD Images with Multiple Degradations??
Current UHD image restoration algorithms are usually designed to address ??a single type of degradation??. However, in practical applications, UHD images are often affected by ??a combination of degradation factors??, leaving the need for ??mixed degradation processing?? largely unresolved. It is worth noting that ??SimpleIR?? [48] is the first to propose ??an all-in-one restoration method?? for UHD images. While ??all-in-one image restoration methods?? have shown significant progress on low-resolution images using ??prompt learning?? and ??dynamic network technologies??, these techniques have not yet been applied to ??UHD images??.
多退化類型UHD圖像修復??
現有UHD圖像修復算法通常針對??單一退化類型??設計。然而,實際應用中UHD圖像常受??多種退化因素共同影響??,導致??混合退化處理需求??尚未解決。值得注意的是,??SimpleIR首次提出了??面向UHD圖像的一體化修復方法??。盡管通過??提示學習??和??動態網絡技術??,一體化修復方法已在低分辨率圖像中取得顯著進展,但這些技術尚未在??UHD圖像??中應用。



















