目錄
可變參數
Collections工具類
Collections的常用靜態方法
實例演示
可變參數
可變參數
- 就是一種特殊形參,定義在方法、構造器的形參列表里,格式是:數據類型...參數名稱
可變參數的特點和好處
- 特點:可以不傳數據給它;可以傳一個或者同時傳多個數據給它;也可以傳一個數組給它。
- 好處:常常用來靈活的接收數據。
import java.util.Arrays;public class ParamTest {public static void main(String[] args) {test(); //不傳數據test(10); //傳輸一個數據test(10,20); //傳輸多個數據test(new int[]{10,20,30}); //傳輸一個數組}public static void test(int...nums){//可變參數在方法內部,本質就是一個數組System.out.println(nums.length);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));System.out.println("---------------------");}
}
運行結果:

可變參數的注意事項
- 可變參數在方法內部就是一個數組
- 一個形參列表中可變參數只能有一個
- 可變參數必須放在形參列表的最后面
Collections工具類
- 和Collection區分開來,Collections是一個用來操作集合的工具類。
Collections的常用靜態方法
| 方法名稱 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| public static<T> boolean addAll(Collection<? super T>c,T...elements) | 給集合批量添加元素 |
| public static void shuffle(List<?> list) | 打亂List集合中的元素順序 |
| public static<T> void sort(List<T>list) | 對List集合中的元素進行升序排序 |
| public static<T> void sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T>c) | 對List集合中元素,按照比較器對象指定的規則進行排序 |
實例演示
給集合批量添加元素、打亂List集合中的元素順序
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;public class CollectionsTest {public static void main(String[] args) {//1.public static<T> boolean addAll(Collection<? super T>c,T...elements)//給集合批量添加元素List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(names,"張三","王五","李四","張麻子");System.out.println(names);//2.public static void shuffle(List<?> list)//打亂List集合中的元素順序Collections.shuffle(names);System.out.println(names);}
}
運行結果:

排序部分一
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;public class CollectionsTest {public static void main(String[] args) {//3.public static<T> void sort(List<T>list)//對List集合中的元素進行升序排序List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(list,3,5,2);Collections.sort(list);System.out.println(list);}
}
運行結果:

當給對象排序時,就需要重寫對象內部的compareTo方法:
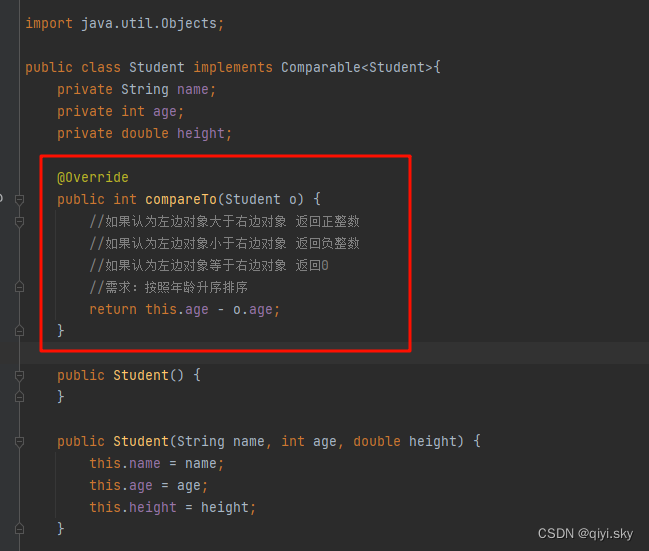
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;public class CollectionsTest {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();students.add(new Student("至尊寶",26,165.5));students.add(new Student("蜘蛛精",23,169.7));students.add(new Student("牛魔王",22,183.5));students.add(new Student("紫霞",22,169.8));Collections.sort(students); //自定義排序:按年齡升序排序System.out.println(students);}
}
運行結果:(輸出結果重寫了toString方法)

排序部分二
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;public class CollectionsTest {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();students.add(new Student("至尊寶",26,165.5));students.add(new Student("蜘蛛精",23,169.7));students.add(new Student("牛魔王",22,183.5));students.add(new Student("紫霞",22,169.8));//4.public static<T> void sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T>c)//對List集合中元素,按照比較器對象指定的規則進行排序Collections.sort(students, new Comparator<Student>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {return Double.compare(o1.getHeight(),o2.getHeight());}}); //如果兩種自定義排序都存在,則就近使用這個排序規則System.out.println(students);}
}
運行結果:

END
學習自:黑馬程序員——JavaSE課程
-- ABCDE開頭)







![[力扣題解] 200. 島嶼數量](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[力扣題解] 200. 島嶼數量)





)




