1、Collection接口遍歷元素—Iterator迭代器
看一下下面這張圖片:可以看出Collection接口有一個父接口Iterable,Iterable接口有一個iterator()方法,iterator()方法的類型是Iterator迭代器,實際上當我們使用方法時,返回的是一個Iterator對象,目的是實現元素的遍歷。
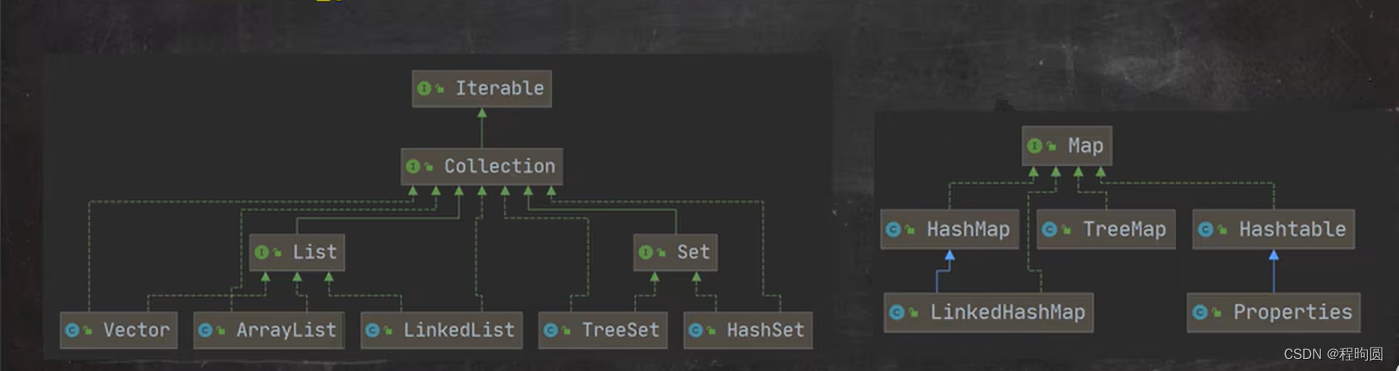
Iterator接口介紹
集合的迭代操作就是將集合中的元素逐個地遍歷取出來。?
-
iterator對象稱為迭代器,主要用于遍歷Collection集合中的元素。
-
所有實現了Collection接口集合類都有一個iterator()方法,用以返回一個實現了iterator接口的對象,既可以返回一個迭代器。
-
Iterator僅用于遍歷集合,Iterator本身并不存放對象。
Iterator接口的方法
Iterator接口的方法有hasNext()、next()、remove()。
注意:在調用iterator,next()方法之前必須要調用iterator.hasNext()進行檢測。如不調用,且下一條記錄無效,直接調用iterator.next()會拋出NoSuchElementWxception異常。
迭代器的執行原理
Iterator iterator= coll.iterator();//得到一個集合的迭代器
//hasNext():判斷是否還有下一個元素
while(iterator.hasNext()){
//next()作用:1、下移。2、將下移以后集合位置上的元素返回
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
原理實現
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;public class IteratorUse {@SuppressWarnings({"all"})public static void main(String[] args) {//由于接口不能直接被實例化,只有實現了接口的類才能被實例化,所以這里我們使用ArrayList//使用collection接口接收Collection collection = new ArrayList();//(1)普通輸出collection.add(new Book("三國演義","羅貫中",100.4));collection.add(new Book("紅樓夢","曹雪芹",87));collection.add(new Book("水滸傳","施耐庵",80.4));//System.out.println(collection);//[B00k{name='三國演義', author='羅貫中', price=100.4},// B00k{name='紅樓夢', author='曹雪芹', price=87.0},// B00k{name='水滸傳', author='施耐庵', price=80.4}]//(2)使用迭代器Iterator iterator = collection.iterator();//先得到collection對應的迭代器,使用while遍歷while(iterator.hasNext()){//返回下一個元素,類型是ObjectObject obj = iterator.next();System.out.println(obj);//B00k{name='三國演義', author='羅貫中', price=100.4}//B00k{name='紅樓夢', author='曹雪芹', price=87.0}//B00k{name='水滸傳', author='施耐庵', price=80.4}}}
}
class Book{private String name;private String author;private double price;public Book(String name, String author, double price) {this.name = name;this.author = author;this.price = price;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public String getAuthor() {return author;}public void setAuthor(String author) {this.author = author;}public double getPrice() {return price;}public void setPrice(double price) {this.price = price;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "B00k{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", author='" + author + '\'' +", price=" + price +'}';}
}2、Collection接口遍歷對象—for循環增強
增強for循環介紹
增強for循環,可以代替iterator迭代器。
特點:增強for就是簡化版的iterator,本質一樣。只能用于遍歷集合或數組。
基本語法:
for(元素類型 元素名?: 集合名或數組名){?
? ? 訪問元素;
}
案例演示:
集合中使用增強for循環:
package com.lwtstu6.practice3;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;public class IteratorUse {@SuppressWarnings({"all"})public static void main(String[] args) {//由于接口不能直接被實例化,只有實現了接口的類才能被實例化,所以這里我們使用ArrayList//使用collection接口接收Collection collection = new ArrayList();//(1)普通輸出collection.add(new Book("三國演義","羅貫中",100.4));collection.add(new Book("紅樓夢","曹雪芹",87));collection.add(new Book("水滸傳","施耐庵",80.4));//System.out.println(collection);//[B00k{name='三國演義', author='羅貫中', price=100.4},// B00k{name='紅樓夢', author='曹雪芹', price=87.0},// B00k{name='水滸傳', author='施耐庵', price=80.4}]//(2)使用增強for循環for(Object obj:collection){//把collection中的對象依次取出,并賦給obj,然后再輸出objSystem.out.println(obj);}//B00k{name='三國演義', author='羅貫中', price=100.4}//B00k{name='紅樓夢', author='曹雪芹', price=87.0}//B00k{name='水滸傳', author='施耐庵', price=80.4}}
}
class Book{private String name;private String author;private double price;public Book(String name, String author, double price) {this.name = name;this.author = author;this.price = price;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public String getAuthor() {return author;}public void setAuthor(String author) {this.author = author;}public double getPrice() {return price;}public void setPrice(double price) {this.price = price;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "B00k{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", author='" + author + '\'' +", price=" + price +'}';}
}直接在數組中使用增強for循環:
int[] nums = {1,8,19,76};
for(int i:num){
? ? ? ? System.out.println("i="+i);??
}
//輸出結果:
//1
//8
//19
//76
3、迭代器和增強for練習題
創建三個Dog{name,age}對象,放入到ArrayList中,賦給List引用,用迭代器和增強for循環兩種方式來遍歷,重寫Dog的toString 方法,輸出name和age.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;class Dog{private String name;private int age;public Dog(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Dog{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}public class CollectionExercise {public static void main(String[] args) {//由于接口不能直接被實例化,只有實現了接口的類才能被實例化。//這里使用list來接收,是因為ArrayList的實現類也有List接口。//創建流浪貓集合List list = new ArrayList();//創建流浪貓對象Dog dog1 = new Dog("小花",3);Dog dog2 = new Dog("小白",4);Dog dog3 = new Dog("小黑",7);//把流浪貓放到集合中list.add(dog1);list.add(dog2);list.add(dog3);//方式一使用迭代器遍歷數組輸出數據Iterator iterator = list.iterator();//獲取Iterator對象while(iterator.hasNext()){//判斷集合中是否存在下一個元素Dog ele = (Dog)iterator.next();//輸出集合中的元素System.out.println(ele);}System.out.println("--------------------");//方式二使用foreachfor (Object o :list) {System.out.println(o);}}
}
? ? ?

)




)



)



】JVM)
【附python實現代碼】)



