在 C++ 標準庫中,有多種數據結構可用于組合多個值,每種結構都有其特定的設計目的和適用場景。以下是主要組合數據結構的分類解析:
一、核心組合數據結構
1. std::pair (C++98)
用途:存儲兩個相關值(鍵值對、坐標點等)
特點:
固定大小(只能包含兩個元素)
支持不同類型
支持比較操作(按 first 然后 second)
#include <utility>// 創建 pair
auto point = std::make_pair(10, 20);
std::pair<std::string, int> person{"Alice", 30};// 訪問元素
std::cout << "X: " << point.first << ", Y: " << point.second;
2. std::tuple (C++11)
用途:存儲固定數量的異構值(任意類型、任意數量)
特點:
類型安全的泛型結構
支持最多約 10 個元素(實現定義)
編譯時類型檢查
#include <tuple>// 創建 tuple
auto data = std::make_tuple(42, "Hello", 3.14);
std::tuple<int, std::string, double> record(1, "Alice", 95.5);// 訪問元素(編譯時索引)
auto id = std::get<0>(record);
auto name = std::get<1>(record);// C++17 結構化綁定
auto [id, name, score] = record;
3. std::array (C++11)
用途:固定大小的同質數組(棧分配)
特點:
替代傳統 C 風格數組
支持迭代器和標準容器操作
編譯時已知大小
#include <array>std::array<int, 5> numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};// 訪問元素
for (int n : numbers) {std::cout << n << " ";
}// 編譯時大小檢查
static_assert(numbers.size() == 5);
4. std::vector (C++98)
用途:動態大小的同質數組(堆分配)
特點:
最常用的順序容器
自動內存管理
隨機訪問 O(1)
尾部插入/刪除高效
#include <vector>std::vector<std::string> names = {"Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"};// 添加元素
names.push_back("David");// 訪問元素
std::cout << names[1]; // 輸出 "Bob"
二、高級組合結構
5. std::variant (C++17)
用途:類型安全的聯合體(存儲多個類型中的一個)
特點:
替代 union 的安全方案
值語義(非指針)
可包含復雜類型(字符串、容器等)
#include <variant>using Value = std::variant<int, double, std::string>;Value v1 = 42;
Value v2 = 3.14;
Value v3 = "Hello";// 訪問值
std::visit([](auto&& arg) {std::cout << arg;
}, v3);// 檢查當前類型
if (std::holds_alternative<int>(v1)) {std::cout << "Integer: " << std::get<int>(v1);
}
6. std::any (C++17)
用途:存儲任意類型的單個值
特點:
類似腳本語言的動態類型
運行時類型檢查
需要顯式類型轉換
#include <any>std::any data;
data = 42; // 存儲 int
data = std::string("Hello"); // 替換為 string// 安全訪問
try {std::string s = std::any_cast<std::string>(data);
} catch (const std::bad_any_cast& e) {std::cerr << "Wrong type: " << e.what();
}
7. std::optional (C++17)
用途:表示可選值(可能有值或為空)
特點:
替代指針或特殊值(如 -1)表示缺失值
明確表達"可能有值"的語義
避免空指針異常
#include <optional>std::optional<int> findValue(const std::vector<int>& vec, int target) {for (int v : vec) {if (v == target) return v;}return std::nullopt; // 空值
}// 使用
auto result = findValue({1,2,3}, 2);
if (result) {std::cout << "Found: " << *result;
} else {std::cout << "Not found";
}
三、復合數據結構
8. 嵌套容器
用途:創建多維或復雜數據結構
常見組合:
// 二維數組
std::vector<std::vector<int>> matrix = {{1, 2, 3},{4, 5, 6}
};// 字典列表
std::map<std::string, std::vector<double>> studentGrades = {{"Alice", {95.5, 88.0}},{"Bob", {78.5, 92.0}}
};// 元組集合
std::set<std::tuple<int, int, int>> uniquePoints;
9. 結構體綁定
用途:組合相關數據字段
特點:
優于 std::pair/std::tuple 的語義清晰性
支持成員函數和自定義行為
struct Person {std::string name;int age;std::vector<std::string> hobbies;
};Person alice{"Alice", 30, {"Reading", "Hiking"}};// C++17 結構化綁定
auto [name, age, hobbies] = alice;
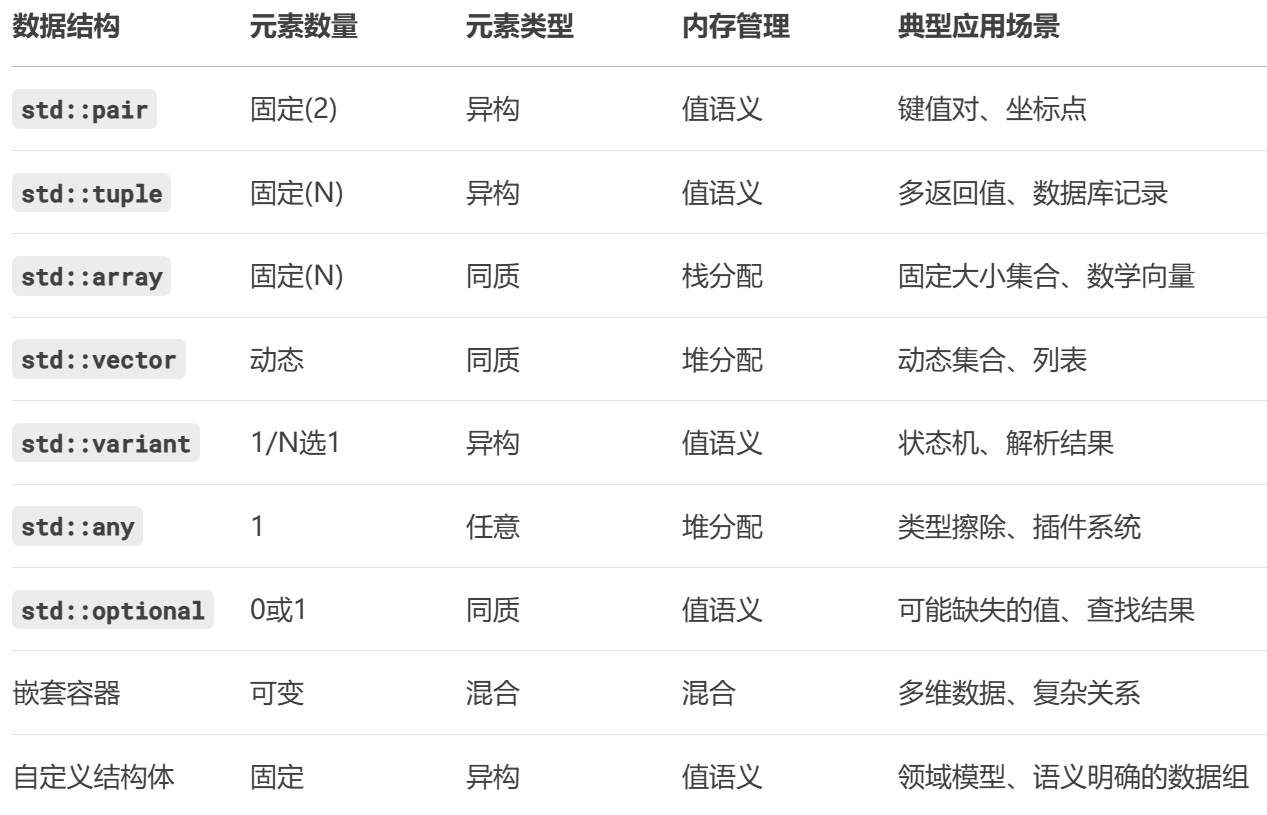
四、數據結構對比指南
模擬實現)


,110. 字符串接龍(卡碼網),105. 有向圖的完全聯通(卡碼網))
詳解)




)


,視頻保存在指定位置)






)