?? 歡迎大家來到貝蒂大講堂??
🎈🎈養成好習慣,先贊后看哦~🎈🎈
所屬專欄:數據結構與算法
貝蒂的主頁:Betty’s blog
1. 堆的概念
堆(Heap)是計算機科學中一類特殊的數據結構。堆通常是一個可以被看作一棵完全二樹的數組對象,若滿足:
- 任意節點的值>=其子節點的值。則稱為大根堆。
- 任意節點的值<=其子節點的值。則稱為小根堆。


2. 堆的實現方式
雖然堆是一種特殊的二叉樹,它既可以用數組存儲也可以用鏈式存儲。但是考慮到其完全二叉樹的特性,我們最好采用數組存儲的方式,因為這樣既方便訪問,也并不會浪費格外的空間。

假設某個合法下標為i:
- 若雙親節點存在,下標為(i-1)/2。
- 若孩子節點存在,左孩子下標為2i+1,右孩子為2i+2。
3. 堆的功能
- 堆的初始化。
- 堆的插入。
- 堆的刪除。
- 獲取堆頂的元素。
- 堆的元素個數。
- 堆的判空。
- 輸出堆。
- 建堆。
- 銷毀堆。
4. 堆的聲明
因為我用數組實現堆,所以堆的聲明與順序表類似。
typedef int HpDataType;
typedef struct Heap
{HpDataType* a;//存儲數據int size;//大小int capacity;//容量
}Heap;
5. 堆的實現
5.1. 堆的初始化
5.1.1. 代碼實現
void HeapInit(Heap* hp)//堆的初始化
{assert(hp);hp->a = NULL;hp->size = hp->capacity = 0;
}
5.1.2. 復雜度分析
- 時間復雜度:沒有額外的時間消耗,時間復雜度為O(1)。
- 空間復雜度:沒有額外的空間消耗,空間復雜度為O(1)。
5.2. 堆的插入
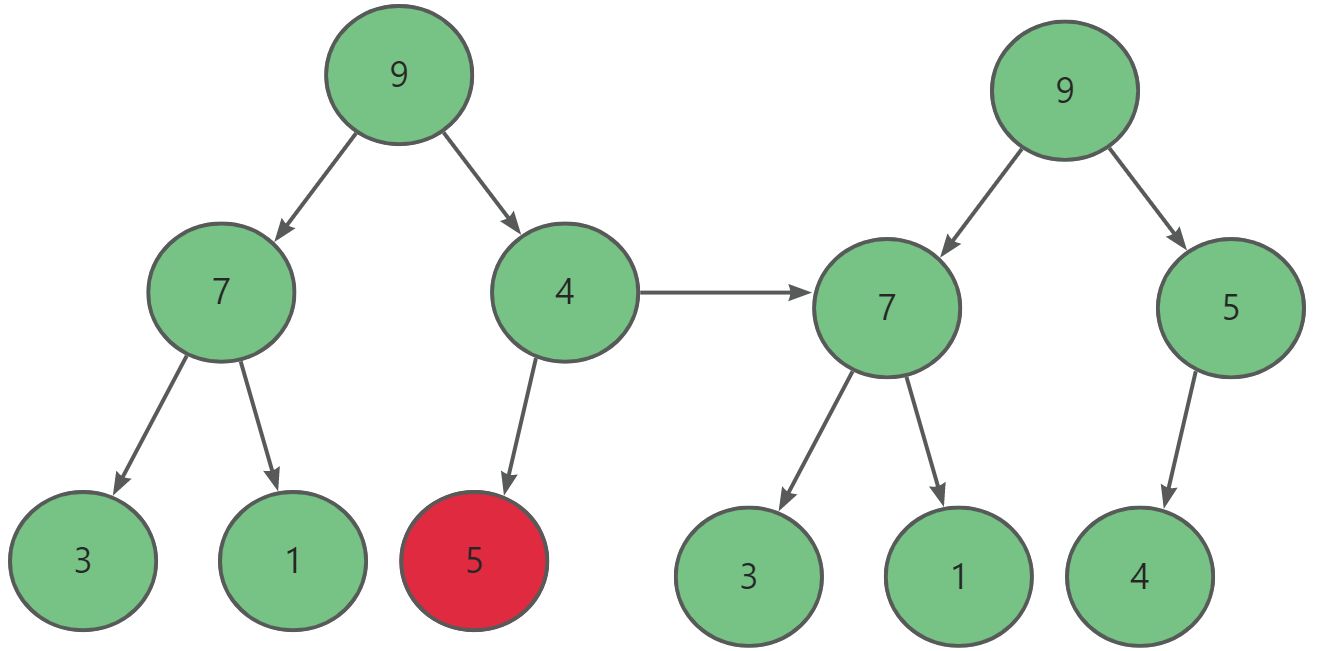
當我們堆進行插入時可能會破壞堆的原有結構,這時就需要我們對其進行向上調整。
5.2.1. 代碼實現
void AdjustUp(Heap* hp, int child)//向上調整
{int parent = (child - 1) / 2;while (child > 0){if (hp->a[child] > hp->a[parent]){swap(&hp->a[child], &hp->a[parent]);child = parent;parent = (child - 1) / 2;}else{break;}}
}
void HeapPush(Heap* hp, HpDataType x)//堆的插入
{assert(hp);if (hp->size == hp->capacity){int newCapacity = hp->capacity == 0 ? 4 : hp->capacity * 2;HpDataType* tmp = (HpDataType*)realloc(hp->a, newCapacity * sizeof(HpDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");exit(-1);}hp->a = tmp;hp->capacity = newCapacity;}hp->a[hp->size] = x;hp->size++;AdjustUp(hp, hp->size - 1);//向上調整
}
5.2.2. 復雜度分析
- 時間復雜度:假設有N個節點,高度為h,2h -1=N。至少調整log2(N+1)-1次,所以時間復雜度為logN。
- 空間復雜度:沒有開辟額外的空間,空間復雜度為O(1)。
5.3. 堆的刪除
堆的刪除是指刪除堆頂的數據,如果我們刪除堆頂元素并往前覆蓋就可能打亂原有的親緣關系。所以我們可以先將堆頂的元素與末尾元素交換,然后再進行向下調整·。

5.3.1. 代碼實現
void swap(HpDataType* x1, HpDataType* x2)
{HpDataType tmp = *x1;*x1 = *x2;*x2 = tmp;
}
void
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent)//向下調整
{int child = parent * 2 + 1;//默認左孩子更大while (child < n){ if (child + 1 < n && a[child + 1]> a[child]){++child;//右孩子}if (a[child] > a[parent]){swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;}else {break;}}
}void HeapPop(Heap* hp)//刪除堆頂元素
{assert(hp);assert(hp->size > 0);swap(&hp->a[0], &hp->a[hp->size - 1]);hp->size--;//刪除最后一個數據AdjustDown(hp->a, hp->size, 0);//向下調整
}
5.3.2. 復雜度分析
- 時間復雜度:假設有N個節點,高度為h,2h -1=N。至少調整log2(N+1)-1次,所以時間復雜度為logN。
- 空間復雜度:沒有開辟額外的空間,空間復雜度為O(1)。
5.4. 獲取堆頂元素
5.4.1. 代碼實現
HpDataType HeapTop(Heap* hp)//獲取堆頂元素
{assert(hp);assert(hp->size > 0);return hp->a[0];
}
5.4.2. 復雜度分析
- 時間復雜度:沒有額外的時間消耗,時間復雜度為O(1)。
- 空間復雜度:沒有額外的空間消耗,空間復雜度為O(1)。
5.5. 獲取堆的元素個數
5.5.1. 代碼實現
size_t HeapSize(Heap* hp)//堆的大小
{assert(hp);return hp->size;
}
5.5.2. 復雜度分析
- 時間復雜度:沒有額外的時間消耗,時間復雜度為O(1)。
- 空間復雜度:沒有額外的空間消耗,空間復雜度為O(1)。
5.6. 判斷堆是否為空
5.6.1. 代碼實現
bool HeapEmpty(Heap* hp)//判斷堆是否為空
{assert(hp);return hp->size == 0;
}
5.6.2. 復雜度分析
- 時間復雜度:沒有額外的時間消耗,時間復雜度為O(1)。
- 空間復雜度:沒有額外的空間消耗,空間復雜度為O(1)。
5.7. 輸出堆
5.7.1. 代碼實現
void HeapDisplay(Heap* hp)//堆的打印
{for (int i = 0; i < hp->size; ++i){printf("%d ", hp->a[i]);}printf("\n");
}
5.7.2. 復雜度分析
- 時間復雜度:遍歷整個數組,時間復雜度為O(N)。
- 空間復雜度:沒有額外的空間消耗,空間復雜度為O(1)。
5.8. 建堆
5.8.1. 代碼實現
void HeapCreatUp(Heap* hp,HpDataType* arr,int n)//向上調整建堆
{assert(hp && arr);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){HeapPush(hp, arr[i]);}
}
void HeapCreatDown(Heap* hp, HpDataType* arr, int n)//向下調整建堆
{assert(hp && arr);HpDataType* tmp = (HpDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HpDataType) * n);if (tmp == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}hp->a = tmp;memcpy(hp->a, arr, sizeof(HpDataType) * n);hp->size = n;hp->capacity = n;for (int i = ((n - 1) - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)//從最后一個元素開始{AdjustDown(hp->a, n, i);}
}
5.8.2. 復雜度分析
假設高度為h,節點個數為N。如果是向上調整建堆:

F ( N ) = 2 1 × 1 + 2 2 × 2 + . . . + 2 h ? 1 × ( h ? 1 ) 2 F ( N ) = 2 2 × 1 + 2 3 × 2 + . . . + 2 h ? 1 × ( h ? 1 ) + 2 h × ( h ? 1 ) 2 F ( N ) ? F ( N ) = ? 2 1 ? 2 2 ? 2 3 ? . . . 2 h ? 1 + 2 h × ( h ? 1 ) = ? 2 h + 2 ? 2 h + 2 h × h F ( N ) = 2 h × ( h ? 2 ) + 2 , N = 2 h ? 1 F ( N ) = ( N + 1 ) × ( l o g 2 ( N + 1 ) ? 2 ) + 2 F(N)=2^1×1+2^2×2+...+2^{h-1}×(h-1)\\ 2F(N)=2^2×1+2^3×2+...+2^{h-1}×(h-1)+2^h×(h-1)\\ 2F(N)-F(N)=-2^1-2^2-2^3-...2^{h-1}+2^h×(h-1)=-2^h+2-2^h+2^h×h\\ F(N)=2^h×(h-2)+2,N=2^h-1\\ F(N)=(N+1)×(log2(N+1)-2)+2 F(N)=21×1+22×2+...+2h?1×(h?1)2F(N)=22×1+23×2+...+2h?1×(h?1)+2h×(h?1)2F(N)?F(N)=?21?22?23?...2h?1+2h×(h?1)=?2h+2?2h+2h×hF(N)=2h×(h?2)+2,N=2h?1F(N)=(N+1)×(log2(N+1)?2)+2
如果是向下調整建堆:
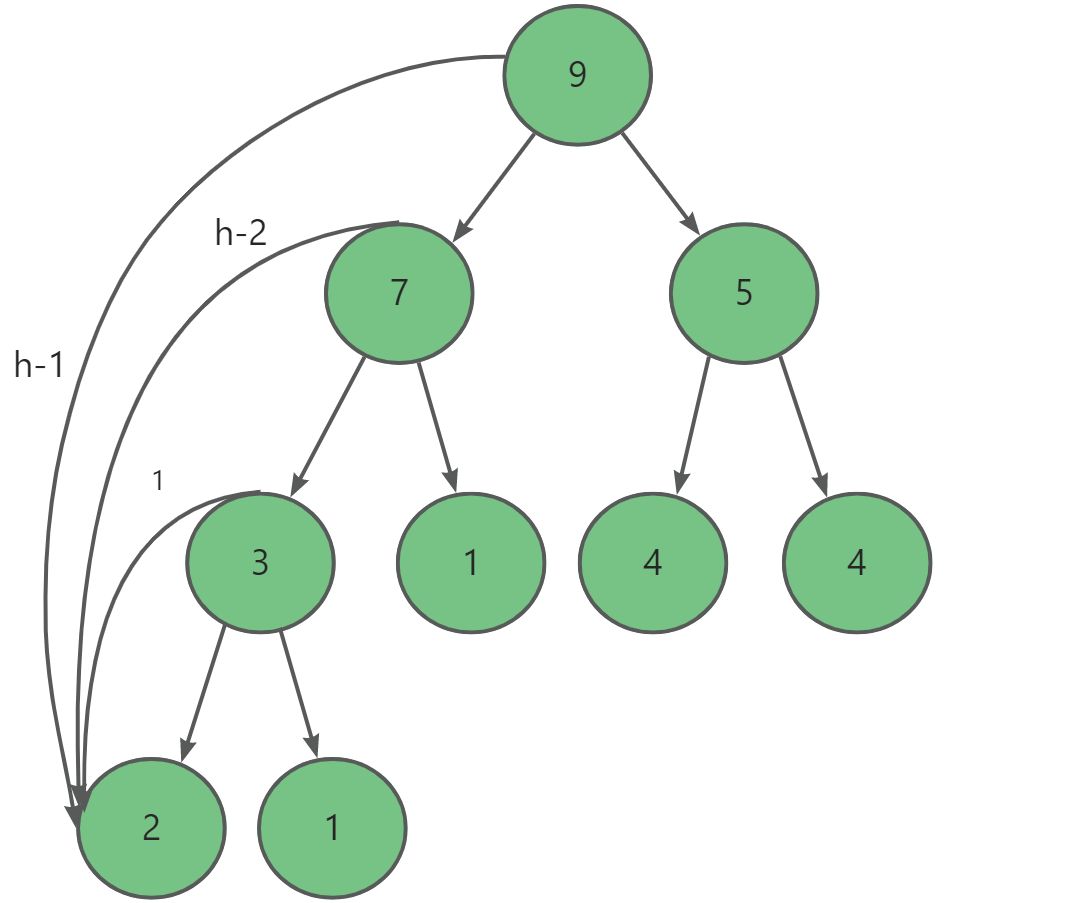
F ( N ) = 2 h ? 2 × 1 + 2 h ? 3 × 2 + . . . + 2 0 × ( h ? 1 ) 2 F ( N ) = 2 h ? 1 × 1 + 2 h ? 2 × 2 + . . . + 2 1 × ( h ? 1 ) 2 F ( N ) ? F ( N ) = 2 h ? 1 + 2 h ? 2 + . . . 2 1 ? 2 0 × ( h ? 1 ) = 2 h ? 1 ? h F ( N ) = 2 h ? 1 ? h , N = 2 h ? 1 F ( N ) = N ? l o g 2 ( N + 1 ) F(N)=2^{h-2}×1+2^{h-3}×2+...+2^0×(h-1)\\ 2F(N)=2^{h-1}×1+2^{h-2}×2+...+2^1×(h-1)\\ 2F(N)-F(N)=2^{h-1}+2^{h-2}+...2^1-2^0×(h-1)=2^h-1-h\\ F(N)=2^h-1-h,N=2^h-1\\ F(N)=N-log2(N+1) F(N)=2h?2×1+2h?3×2+...+20×(h?1)2F(N)=2h?1×1+2h?2×2+...+21×(h?1)2F(N)?F(N)=2h?1+2h?2+...21?20×(h?1)=2h?1?hF(N)=2h?1?h,N=2h?1F(N)=N?log2(N+1)
- 時間復雜度:向上調整建堆最后一排調整h-1次,倒數第二排調整h-2次…時間復雜度為NlogN。向下調整建堆倒數第二排調整1次,倒數第二排調整2…第一排調整h-1次。時間復雜為O(N)。
- 空間復雜度:無論是向上調整建堆還是向下調整建堆都需開辟N個空間,所以空間復雜度為O(N)。
5.9. 銷毀堆
5.9.1. 代碼實現
void HeapDestroy(Heap* hp)//銷毀堆
{assert(hp);free(hp->a);hp->size = hp->capacity = 0;
}
5.9.2. 復雜度分析
- 時間復雜度:沒有額外的時間消耗,時間復雜度為O(1)。
- 空間復雜度:沒有額外的空間消耗,空間復雜度為O(1)。
5.10. 完整代碼
5.10.1. Heap.h
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int HpDataType;
typedef struct Heap
{HpDataType* a;//存儲數據int size;//大小int capacity;//容量
}Heap;
void HeapInit(Heap* hp);//堆的初始化
void AdjustUp(Heap* hp, int child);//向上調整
void HeapPush(Heap* hp, HpDataType x);//堆的插入
bool HeapEmpty(Heap* hp);//判斷堆是否為空
size_t HeapSize(Heap* hp);//堆的大小
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent);//向下調整
void HeapPop(Heap* hp);//刪除堆頂元素
HpDataType HeapTop(Heap* hp);//獲取堆頂元素
void HeapDisplay(Heap* hp);//堆的打印
void HeapDestroy(Heap* hp);//銷毀堆
void HeapCreatUp(Heap* hp,HpDataType* arr, int n);//向上調整建堆
void HeapCreatDown(Heap* hp,HpDataType* arr, int n);//向下調整建堆
5.10.2. Heap.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Heap.h"
void HeapInit(Heap* hp)//堆的初始化
{assert(hp);hp->a = NULL;hp->size = hp->capacity = 0;
}
void swap(HpDataType* x1, HpDataType* x2)
{HpDataType tmp = *x1;*x1 = *x2;*x2 = tmp;
}
void AdjustUp(Heap* hp, int child)//向上調整
{int parent = (child - 1) / 2;while (child > 0){if (hp->a[child] > hp->a[parent]){swap(&hp->a[child], &hp->a[parent]);child = parent;parent = (child - 1) / 2;}else{break;}}
}
void HeapPush(Heap* hp, HpDataType x)//堆的插入
{assert(hp);if (hp->size == hp->capacity){int newCapacity = hp->capacity == 0 ? 4 : hp->capacity * 2;HpDataType* tmp = (HpDataType*)realloc(hp->a, newCapacity * sizeof(HpDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");exit(-1);}hp->a = tmp;hp->capacity = newCapacity;}hp->a[hp->size] = x;hp->size++;AdjustUp(hp, hp->size - 1);//向上調整
}
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent)//向下調整
{int child = parent * 2 + 1;//默認左孩子更大while (child < n){ if (child + 1 < n && a[child + 1]> a[child]){++child;//右孩子}if (a[child] > a[parent]){swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;}else {break;}}
}void HeapPop(Heap* hp)//刪除堆頂元素
{assert(hp);assert(hp->size > 0);swap(&hp->a[0], &hp->a[hp->size - 1]);hp->size--;//刪除最后一個數據AdjustDown(hp->a, hp->size, 0);//向下調整
}HpDataType HeapTop(Heap* hp)//獲取堆頂元素
{assert(hp);assert(hp->size > 0);return hp->a[0];
}bool HeapEmpty(Heap* hp)//判斷堆是否為空
{assert(hp);return hp->size == 0;
}size_t HeapSize(Heap* hp)//堆的大小
{assert(hp);return hp->size;
}void HeapDisplay(Heap* hp)//堆的打印
{for (int i = 0; i < hp->size; ++i){printf("%d ", hp->a[i]);}printf("\n");
}
void HeapCreatUp(Heap* hp,HpDataType* arr,int n)//向上調整建堆
{assert(hp && arr);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){HeapPush(hp, arr[i]);}
}
void HeapCreatDown(Heap* hp, HpDataType* arr, int n)//向下調整建堆
{assert(hp && arr);HpDataType* tmp = (HpDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HpDataType) * n);if (tmp == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}hp->a = tmp;memcpy(hp->a, arr, sizeof(HpDataType) * n);hp->size = n;hp->capacity = n;for (int i = ((n - 1) - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)//從最后一個元素開始{AdjustDown(hp->a, n, i);}
}
void HeapDestroy(Heap* hp)//銷毀堆
{assert(hp);free(hp->a);hp->size = hp->capacity = 0;
}
6. Top-K問題
6.1. 問題分析
Top-K問題簡單來說就是求數據結合中前K個最大的元素或者最小的元素,一般情況下數據量都比較大。這個問題在我們日常生活中非常常見,比如說:游戲中活躍度前十的玩家,世界五百強企業等等。
解決這個問題常見的思路就是遍歷或者排序,但是當數據量較大時這種方法就并不適用了。這時我們就需要建堆來處理,具體操作方法如下:
- 用數據集合中前K個元素來建堆。
- 前k個最大的元素,則建小堆。
- 前k個最小的元素,則建大堆。
- 用剩余的N - K個元素依次與堆頂元素來比較,不滿足條件則替換堆頂元素。
void TopK(int* a, int n, int k)
{//建堆int* kminHeap = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * k);if (kminHeap == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}//將前k個數據放入堆中for (int i = 0; i < k; i++){kminHeap[i] = a[i];}//向下調整法建小堆for (int i = (k - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--){AdjustDown(kminHeap, k, i);}//依次比較for (int i = k; i < n; i++){if (a[i] > kminHeap[0]){kminHeap[0] = a[i];AdjustDown(kminHeap, k, 0);}}for (int i = 0; i < k; i++){printf("%d ", kminHeap[i]);}printf("\n");free(kminHeap);
}
void TestTopk()
{int n = 10000;int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);srand(time(0));for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i){a[i] = rand() % 1000000;}a[5] = 1000000 + 1;a[1231] = 1000000 + 2;a[531] = 1000000 + 3;a[5121] = 1000000 + 4;a[115] = 1000000 + 5;a[2335] = 1000000 + 6;a[9999] = 1000000 + 7;a[76] = 1000000 + 8;a[423] = 1000000 + 9;a[3144] = 1000000 + 10;TopK(a, n, 10);
}
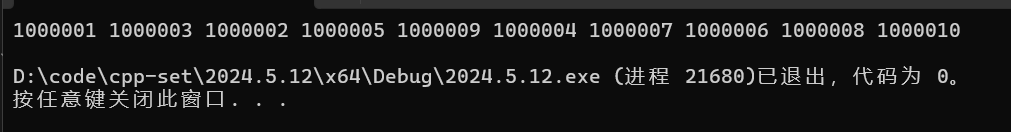
6.2. 復雜度分析
- 時間復雜度:建堆時間為K,向下調整的最壞時間為(N-K)*logK。所以時間復雜度為NlogK。
- 空間復雜度:建堆會開辟K的個空間,所以空間復雜度為logK。

)




Win11復現DepthFM)
![[Cesium]Cesium基礎學習——Primitive](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Cesium]Cesium基礎學習——Primitive)

)
)







)

