?前言
????????在學習了類和對象的六大成員函數后,為了鞏固我們學習的知識可以手寫一個日期類來幫助我們理解類和對象,加深對于其的了解。
默認函數
? ? 構造函數
? ? ? ? 既然是寫類和對象,我們首先就要定義一個類,然后根據實際需要來加入類的數據與函數。作為一個日期類,肯定要有時間了,我們采用公元紀年法,存儲三個變量,年 月 日,如下。
class Date
{private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};? ? ? ? 注意這里將三個成員變量定義為private:,是為了防止用戶在外面修改,提高安全性。其次這里在每個成員變量前面加了個下劃線。?_year,這里是為了防止后面與函數的參數重名。當然重名也有其他解決方法例如用this.year,也可以。具體選那種看讀者更適合那種編碼風格。
? ? ? ? 寫完上面的變量后,我們第一個想到要寫的函數必定是構造函數了。如下函數
Date(int year=1900, int month=1, int day=1)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;
}? ? ? ? 注意我們這里寫成了全缺省,這樣做的好處是不用寫無參的構造函數,給每個日期對象都有默認值。
拷貝構造函數
? ? ? ? 其次我們要寫的就是拷貝構造函數。注意這里的形參加了個const,這里加了const一是為了方防止修改形參d,二是為了通用性。如下例子
Date(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}? ? ? ? 假如我們沒有加const,有下述程序。這段代碼會報錯!為什么呢?d1的類型為const Date,而拷貝構造函數參數類型為Date& d,如果傳參成功,是不是就可以在構造函數的內部修改原本為const類型的變量,違背了基本的定義語法。但用一個const Date類型拷貝初始化是我們需要的場景,為了讓其正常運行,就需要在拷貝構造函數加const。
int main()
{const Date d1(2024, 4, 16);Date d2(d1);return 0;
}? ? ? ? 有const變量自然也有普通的變量了。我們就可以寫個普通變量的拷貝構造函數。
Date(Date& d)
{_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;
}? ? ? ? 其實在很多地方會將上面兩個構造函數簡化為一個,即保留含const的
Date(const Date& d)
{_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;
}
? ? ? ? 那自然有人問?普通變量的拷貝怎么辦呢?在這里就不得不提C++對于變量類型的處理了。我們首先看段熟悉的代碼。
int a=0;a=1.12;? ? ? ? 這段代碼會報錯么?為什么?大家可以在程序中運行下,結果是不會報錯的,有的編譯器可能會有警告。大家知道整型與浮點型在內存中的存儲方式是不一樣的,即使是對浮點型內存的截斷讀取a也不可能為1.
? ? ? ? 但a的結果卻是一,這是因為編譯器幫我們做了類型轉化,稱之為隱式轉換。如下圖。
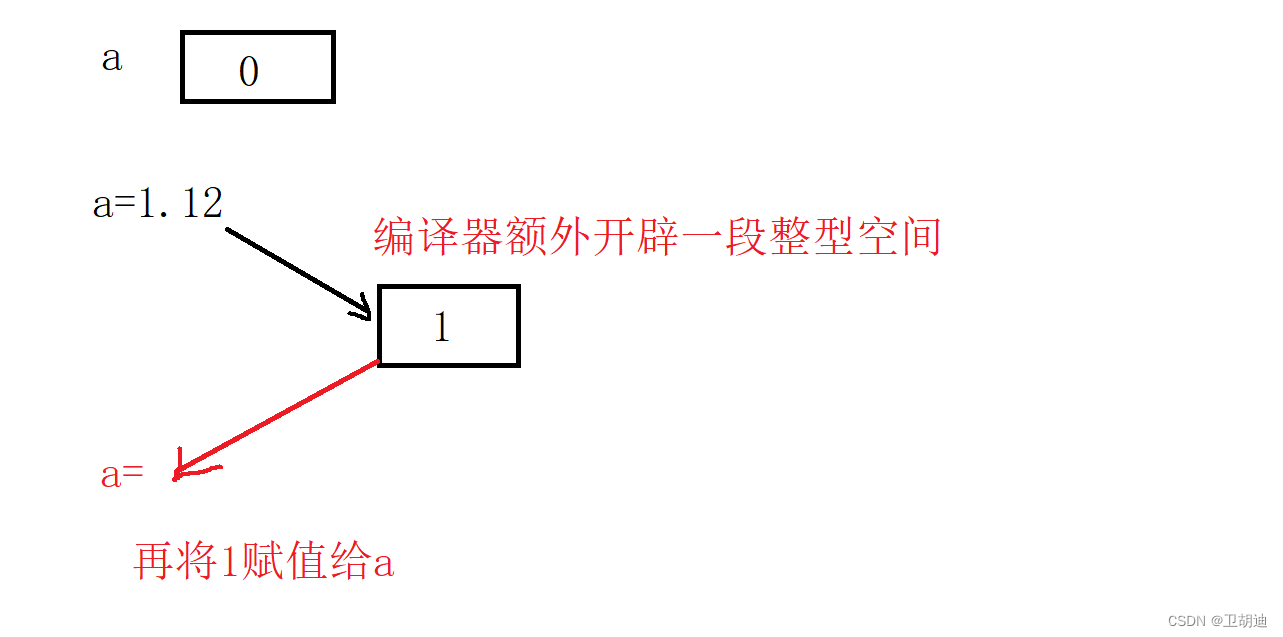
? ? ? ? 同理當我們將Date變量賦給const Date& d,編譯器也會額外開辟空間付給形參d。
? ? ? ? 或許有讀者又有疑問?Date變量賦給const Date& d可以,為什么const Date變量賦給Date& d不可以,因為前者是將內存的權限放小,而后者是將對內存的權限放大。在C++中將權限放小可以,但把權限放大就有可能產生難以預料的后果。
? ? ? ? 接下來我們來實現與拷貝構造函數功能十分像的賦值重載函數。
賦值重載函數
? ? ? ? 代碼如下
Date& operator=(const Date& d){if (&d != this){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}return *this;}? ? ? ? 這里我們任然將參數的類型加上const省去對于普通變量與const變量的分類了,當然對于普通變量會隱式轉換,會減少些效率。
? ? ? ? 注意這里將d的地址與this比較,這是為了防止自己和自己賦值的情況如 a=a,這樣沒有任何的意義。
析構函數
? ? ? ? 在這個對象中我們沒有開辟內存,沒有在堆區申請空間,寫不寫析構函數都可以。
~Date()
{}成員函數
<<重載
? ? ? ? 我們為了后續的方便,首先要實現的便是cout輸出Date類型,對于內置類型cout可以直接的輸出,但是對于自定義類型要我們使用操作符重載.
? ? ? ? 按照習慣我們極大概率會將<<寫在類里面。寫出如下的代碼
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out)
{out << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;return out;
}
? ? ? ? 其中的ostream參數是輸出時要用到的一種類型,返回值為ostream是為了連續輸出的原因。這個看起來沒有什么錯誤,但運行的時候就會報錯!
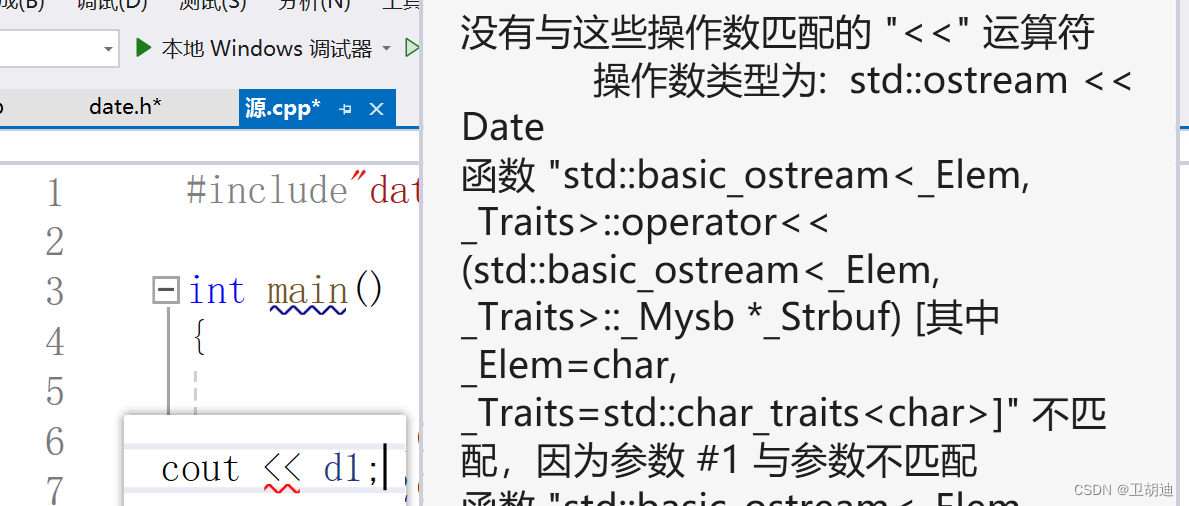
? ? ? ? 我們明明重載了<<操作符,為什么卻提示我們沒有匹配類型呢?這就不得不提到this了,在使用cout << d1操作符重載的時候,我們從左向右顯然要傳遞兩個參數ostream和Date,在類中的成員函數默認第一個參數傳遞Date,即形參this指針,第二個實參初始化函數的形參。
? ? ? ? 關于this指針詳情可以看【C++ 類和對象 上 - CSDN App】http://t.csdnimg.cn/Wx5iO。在這里就不敘述了。
? ? ? ? 于是上面的代碼也不是不可以用,可以采用如下的方法使用
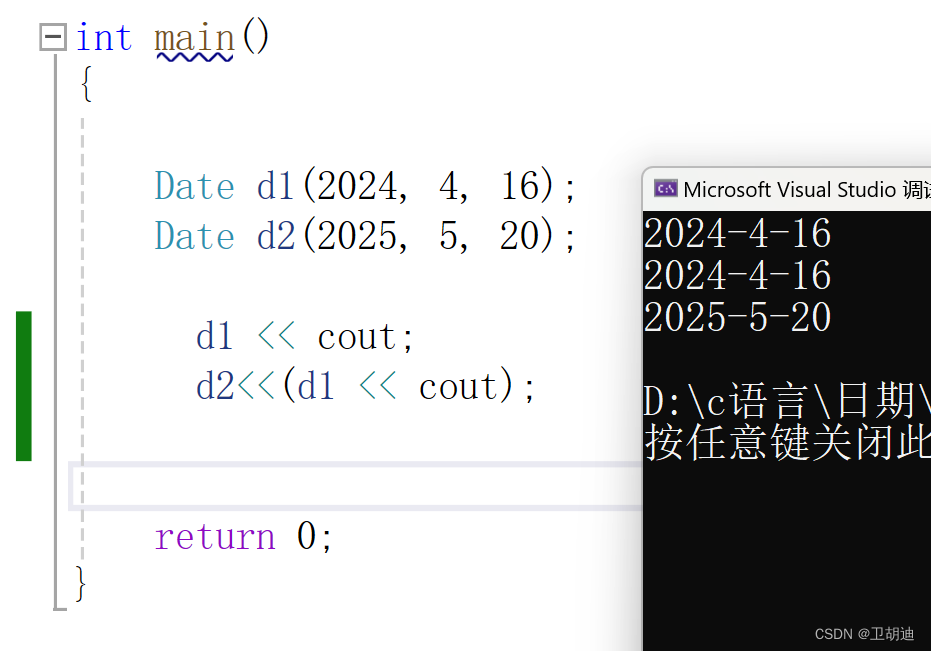
? ? ? ? 但這種方法顯然是不符合我們日常認知的。
? ? ? ? 為了解決這種問題,我們把<<操作符改為全局函數。就可以解決順序的問題了。如下代碼
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;return out;
}? ? ? ? 但此時又有一個新的問題,這個重載函數不可以訪問Date對象中私有的成員變量,這就體現了我們類的安全性高,為了解決我們需要把這個操作符重載函數聲明為友元函數就可以了。
class Date
{
public:Date(int year=1900, int month=1, int day=1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}Date(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}Date& operator=(const Date& d){if (&d != this){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}return *this;}friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};
? ? ? ? 這樣我們就可以正常輸出了。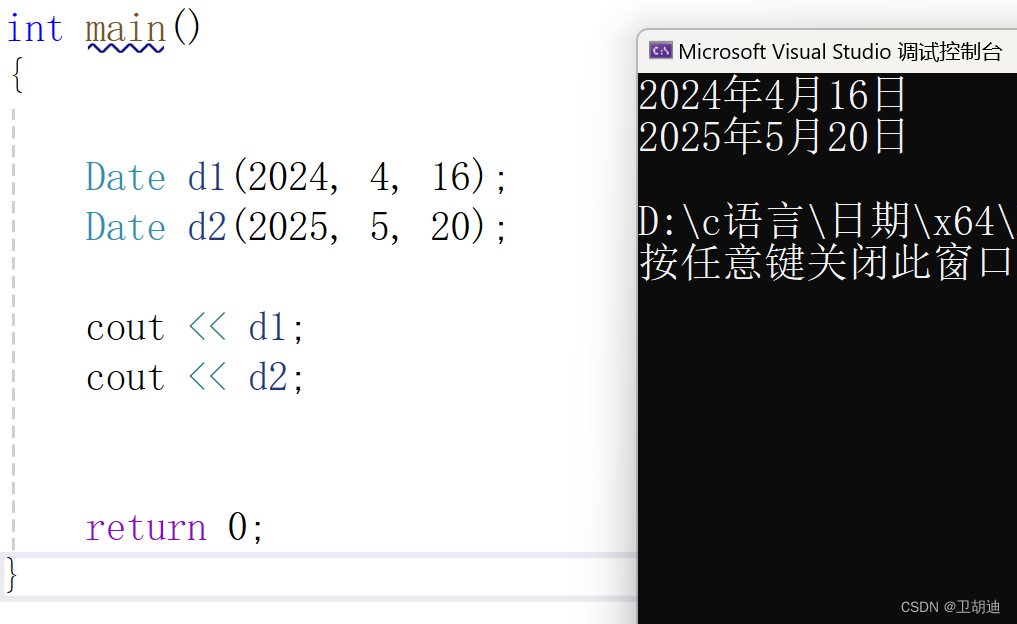
>>重載
? ? ? ? 有了輸出,當然要有其對應的輸入最好。和輸出重載一樣,將>>操作符重載為全局函數,并且在類中聲明為友元函數。
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;return in;
}? ? ? ? 如下圖,剛開始輸出1900時我們寫的全缺省參數的作用,而后輸出的就是我們輸入的2024 5 13.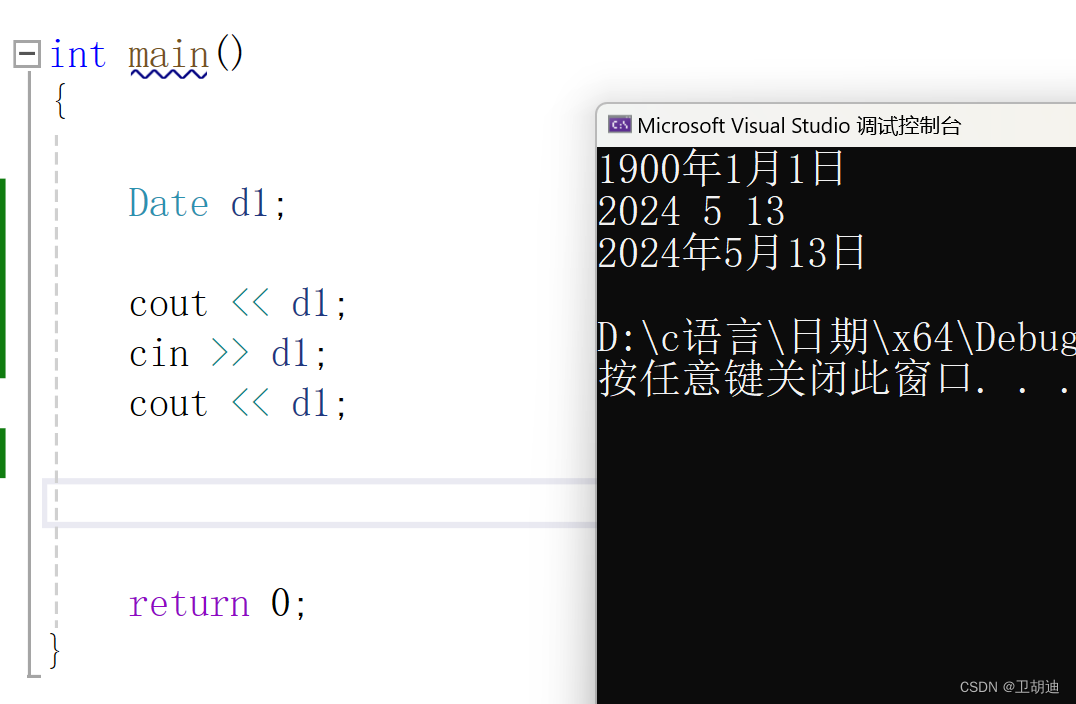
? ? ? ? 光有輸入輸出函數顯然是不可以的,我們也要有對應的函數。
大小比較
? ? ? ? 對于一個日期比較大小是符合實際需求的,我們可以寫個cmp成員,但更好的使用操作符重載,< >,這個我們最熟悉又可以減小記憶的負擔。
>比較
? ? ? ? 我們有兩種方法比較兩個日期的大小。
方法一
? ? ? ? 不斷地尋找true條件,最后剩下的就是false。注意年數相等的時候要判斷月份
bool Date::operator>(Date& d)
{if (_year > d._year){return true;}else if (_year == d._year){if (_month > d._month){return true;}else if (_month == d._month){if (_day > d._day){return true;}}}return false;
}
方法二
? ? ? ? 將日期的比較轉換為數的比較。月份最多有12月,天最多有31天,我們就可以將年擴大10000倍,月擴大100倍,將2024年5月13日與2023年4月20日比較轉換為2024513與2023420比較。我們知道數的比較大小是從高位往下開始比較的。這與我們比較日期的順序不謀而合,就可以如下的簡化代碼。
bool Date::operator>(Date& d)
{return _day + _month * 100 + _year * 10000 > d._day + d._month * 100 + d._year * 10000;
}同理小于等于。大于等于,小于都可以如上比較。
bool Date::operator<(Date& d)
{return _day + _month * 100 + _year * 10000 <d._day + d._month * 100 + d._year * 10000;
}
bool Date::operator<=(Date& d)
{return _day + _month * 100 + _year * 10000 <=d._day + d._month * 100 + d._year * 10000;
}
bool Date::operator>=(Date& d)
{return _day + _month * 100 + _year * 10000 >=d._day + d._month * 100 + d._year * 10000;
}
bool Date::operator!=(Date& d)
{return _day + _month * 100 + _year * 10000 !=d._day + d._month * 100 + d._year * 10000;
}????????判斷兩個日期是否相等的代碼也十分簡單,如下。
相等判斷
bool Date::operator==(Date& d)
{return _year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day == d._day;
}????????到此我們的比較函數就寫完了。但光有比較還不可以,我們可能想要知道50天后是哪一天,50天前是那一天,兩個日期相差多少天。
加減操作
? ? ? ? 在后續的操作中我們不可避免的要訪問某年某月有多少天,我們便可以將他封裝為成員函數,便于我們查找天數。
獲取天數
? ? ? ? 我們可以將每個月的天數寫在一個數組中,然后哪一個月就讀取哪一個數字,但其中2月十分特殊要分為潤年的問題要單獨判斷下。
int Date::GetMonthDay(Date& d)
{static int arr[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if (d._month == 2 && ((d._year % 400 == 0) || (d._year % 4 == 0 && d._year % 100 != 0))){return 29;}return arr[d._month];
}? ? ? ? 這里將數組加上static 是為了避免重復創建,提高效率。然后就是判斷是不是閏年的二月。
+=重載
? ? ? ? 我們可以將一個日期類加上n天返回加n天后的日期。
Date& Date::operator+=(int t)
{_day += t;while (_day > GetMonthDay(*this)){_day -= GetMonthDay(*this);_month++;if (_month == 13){_month = 1;_year++;}}return *this;
}? ? ? ? 我們整體的循環是在找當前月合理的天數,如果不合理就月份加一,天數減去當前月,繼續判斷直到結束。
? ? ? ? 測試結果正確。
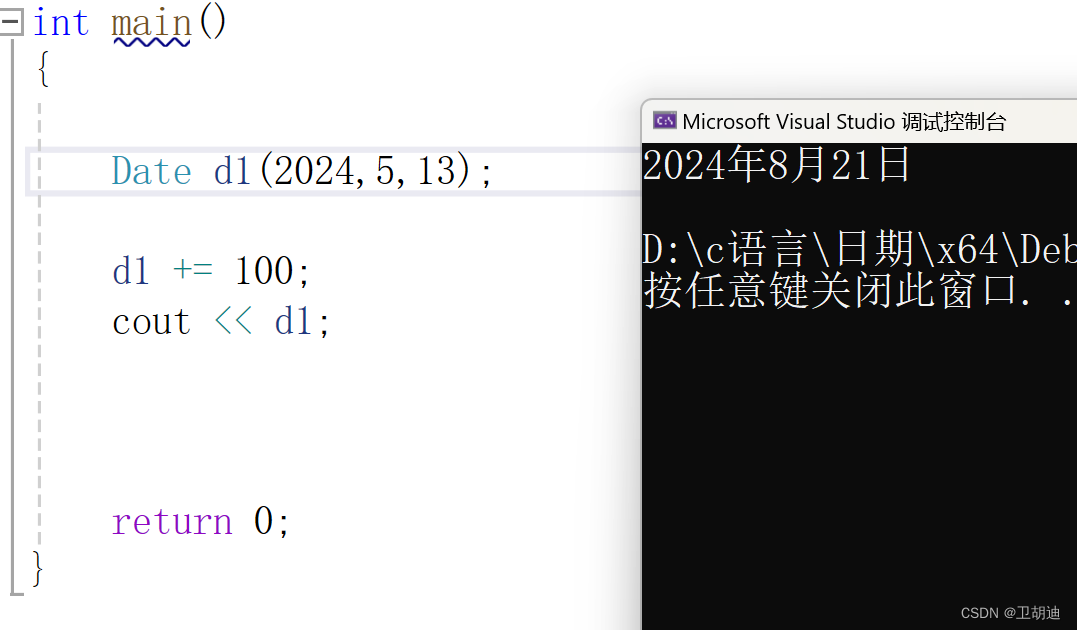
? ? ? ? 大家寫的時候可以用日期計算器 - 天數計算器 | 在線日期計算工具 (sojson.com)這個網站檢測。
+重載
? ? ? ? 我們之前已經寫完+=了,先在寫+的思路是不是與+=類似,我們可以仿照+=寫出+重載,但是我們還有更加簡單的方法,復用+=!!
Date Date::operator+(int t)
{Date t1 = *this;t1 += t;return t1;
}? ? ? ? 這樣復用代碼就大大簡化了我們寫代碼的復雜度。其實上面的判斷也可以復用代碼,讀者可以自行嘗試。
-=重載
? ? ? ? 一個日期減去一個天數,與一個日前加上一個天數十分像。天數小于肯定是不合理的日期就加上當前月數。不斷的循環判斷直到合理數據。
Date& Date::operator-=(int t)
{_day -= t;while ( _day<1 ){_month--;if (_month == 0){_month = 12;_year--;}_day += GetMonthDay(*this);}return *this;
}-重載
? ? ? ? 與之前一樣,我們復用-=的函數。
Date Date::operator-(int t)
{Date tmp = *this;tmp -= t;return tmp;
}? ? ? ? 我們如果對+負數,-負數會怎么樣?顯然程序會崩潰但這又可能是我們使用者的操作,于是便可以在不同的重載函數互相調用。
? ? ? ? 如下代碼
Date Date::operator-(int t)
{if (t < 0)return *this + (-t);Date tmp = *this;tmp -= t;return tmp;
}? ??日期相減
方法一
? ? ? ? 我們當然會求兩個日期之間的差數。便可以重載-。我們可以對小的天數一直加一直到二者相等。如下
int Date::operator-(Date& d)
{assert(*this >= d);Date t1 = *this;Date t2 = d;int t = 0;//一直加while (t1 != t2){t2 += 1;t++;}return t;
}? ? ? ? 我們有時也會寫的前一個日期小,導致相差負數,為了達到這種效果也可以對上述代碼稍加修改。
int Date::operator-(Date& d)
{if (*this < d)return d - *this;Date t1 = *this;Date t2 = d;int t = 0;//一直加while (t1 != t2){t2 += 1;t++;}return t;
}方法二
? ? ? ? 上述的代碼十分簡單,效率有些不理想,我們可以換種方法。
????????首先我們先判斷二者是否相同,不相同在判斷t2的天數是否小于t1,小于說明可能只是天數不同,將天數加到t1的天數,然后判斷是否相等。如果t1的天數等于t2的天數,說明月份不同,將t2的月份一次往上加一判斷二者是否相等。
int Date::operator-(Date& d)
{if (*this < d)return d - *this;Date t1 = *this;Date t2 = d;int t = 0;//一直加while (t1 != t2){int c = GetMonthDay(t2);if (t2._day < t1._day && t1._day <= c){t += t1._day - t2._day;t2._day = t1._day;}else {t2._month++;if (t2._month == 13){t2._year++;t2._month = 1;}t += c - t2._day + 1;t2._day = 1;}}return t;
}? ? ? ? 這種方法的效率比第一種高了許多。
結語
? ? ? ? 到這里本篇文章就結束了。喜歡的點點關注!
全部代碼如下。
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:Date(int year=1900, int month=1, int day=1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}Date(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}Date& operator=(const Date& d){if (&d != this){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}return *this;}//友元函數聲明friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);//比較函數bool operator==(Date& d);bool operator>(Date& d);bool operator<(Date& d);bool operator<=(Date& d);bool operator>=(Date& d);bool operator!=(Date& d);//加減操作函數Date& operator+=(int t);Date operator+(int t);Date& operator-=(int t);Date operator-(int t);int operator-(Date& d);int GetMonthDay(Date& d);private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};//bool Date::operator>(Date& d)
//{
// if (_year > d._year)
// {
// return true;
// }
// else if (_year == d._year)
// {
// if (_month > d._month)
// {
// return true;
// }
// else if (_month == d._month)
// {
// if (_day > d._day)
// {
// return true;
// }
// }
// }
// return false;
//}
//bool Date::operator<(Date& d)
//{
// return !(*this >= d);
//}
//bool Date::operator<=(Date& d)
//{
// return *this < d || d == *this;
//}
//bool Date::operator>=(Date& d)
//{
// return *this > d || d == *this;
//}
//bool Date::operator!=(Date & d)
//{
// return !(d == *this);
//}bool Date::operator>(Date& d)
{return _day + _month * 100 + _year * 10000 > d._day + d._month * 100 + d._year * 10000;
}bool Date::operator<(Date& d)
{return _day + _month * 100 + _year * 10000 <d._day + d._month * 100 + d._year * 10000;
}
bool Date::operator<=(Date& d)
{return _day + _month * 100 + _year * 10000 <=d._day + d._month * 100 + d._year * 10000;
}
bool Date::operator>=(Date& d)
{return _day + _month * 100 + _year * 10000 >=d._day + d._month * 100 + d._year * 10000;
}
bool Date::operator!=(Date& d)
{return _day + _month * 100 + _year * 10000 !=d._day + d._month * 100 + d._year * 10000;
}
bool Date::operator==(Date& d)
{return _year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day == d._day;
}int Date::GetMonthDay(Date& d)
{static int arr[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if (d._month == 2 && ((d._year % 400 == 0) || (d._year % 4 == 0 && d._year % 100 != 0))){return 29;}return arr[d._month];
}Date& Date::operator+=(int t)
{if (t < 0)return *this -= (-t);_day += t;while (_day > GetMonthDay(*this)){_day -= GetMonthDay(*this);_month++;if (_month == 13){_month = 1;_year++;}}return *this;
}Date Date::operator+(int t)
{Date t1 = *this;t1 += t;return t1;
}Date& Date::operator-=(int t)
{if (t < 0)return *this += (-t);_day -= t;while ( _day<1 ){_month--;if (_month == 0){_month = 12;_year--;}_day += GetMonthDay(*this);}return *this;
}Date Date::operator-(int t)
{if (t < 0)return *this + (-t);Date tmp = *this;tmp -= t;return tmp;
}int Date::operator-(Date& d)
{if (*this < d)return d - *this;Date t1 = *this;Date t2 = d;int t = 0;//一直加while (t1 != t2){int c = GetMonthDay(t2);if (t2._day < t1._day && t1._day <= c){t += t1._day - t2._day;t2._day = t1._day;}else {t2._month++;if (t2._month == 13){t2._year++;t2._month = 1;}t += c - t2._day + 1;t2._day = 1;}}return t;
}ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;return out;
}istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;return in;
}








)

)






】)
