目錄
學習目標
引言
1.什么是線性表?
2.什么是順序表?
2.1概念及結構
2.2 接口實現
2.2.1順序表的功能
1.順序表的初始化
2.打印數據
3.尾插數據
(1)檢查空間
(2)插入數據
4.尾刪數據
5.頭插數據
6.頭刪數據
7.數據查找
8.指定位置數據修改
9.指定位置數據刪除
10.指定位置數據插入
11.銷毀順序表
完整代碼
1.SeqList.h
2.SeqList.c
2.3 數組相關面試題
2.4 順序表的問題及思考
結束語
學習目標
- 1.什么是線性表?
- 什么是順序表?
- 順序表的接口實現
引言
在?數據結構——lesson1.基礎中我們學習了數據結構的一些基礎知識,今天我們接著來學習一種數據結構——順序表。
在學習順序表之前,我們首先要知道
1.什么是線性表?
- 線性表(linear list)是n個具有相同特性的數據元素的有限序列。 線性表是一種在實際中廣泛使用的數據結 構,常見的線性表:順序表、鏈表、棧、隊列、字符串...
- 線性表在邏輯上是線性結構,也就說是連續的一條直線。但是在物理結構上并不一定是連續的,線性表在物 理上存儲時,通常以數組和鏈式結構的形式存儲。
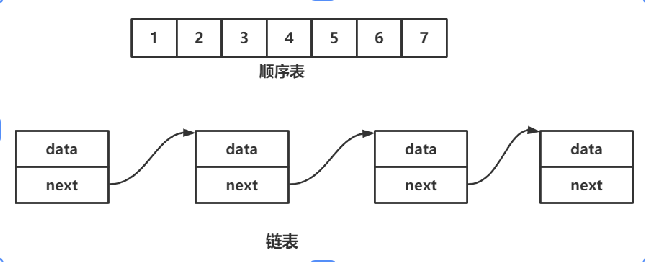
2.什么是順序表?
2.1概念及結構
順序表是用一段物理地址連續的存儲單元依次存儲數據元素的線性結構,一般情況下采用數組存儲。在數組上完成數據的增刪查改。
順序表一般可以分為:
1. 靜態順序表:使用定長數組存儲元素。
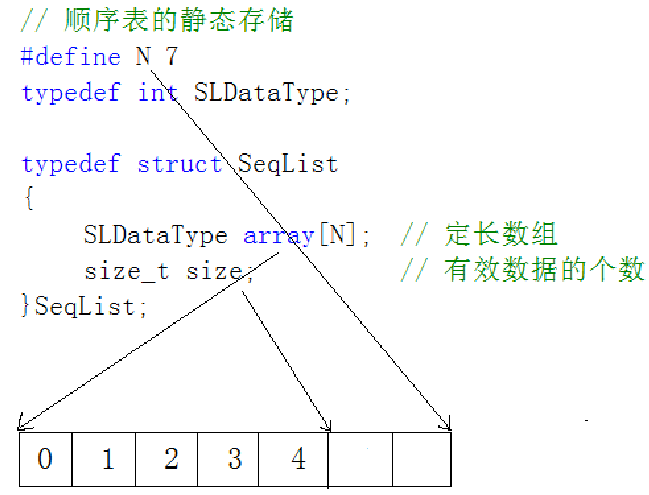
2. 動態順序表:使用動態開辟的數組存儲。
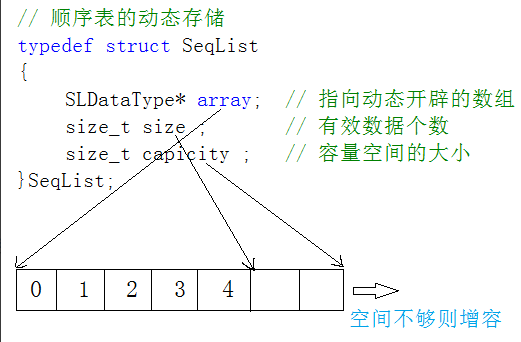
今天我們要學習的是動態順序表。
它與數組非常類似,但是相比于靜態順序表有一個非常明顯的優點——可以動態內存增長空間大小。
2.2 接口實現
靜態順序表只適用于確定知道需要存多少數據的場景。靜態順序表的定長數組導致N定大了,空間開多了浪費,開少了不夠用。所以現實中基本都是使用動態順序表,根據需要動態的分配空間大小,所以下面我們實現動態順序表。
2.2.1順序表的功能
順序表可以大致包含如下幾個功能:
1.初始化順序表中的數據。
2.打印順序表中的數據。
3.對順序表進行尾插(末尾插入數據)。
4.對順序表進行尾刪(末尾刪除數據)。
5.對順序表進行頭插(開頭插入數據)。
6.對順序表進行頭刪(開頭刪除數據)。
7.對順序表數據進行查找。
8.對順序表數據進行修改。
9.對指定位置的數據刪除。
10.對指定位置的數據插入。
11.銷毀順序表。
1.順序表的初始化
順序表的初始化我們可以把空間和有效數據個數都設置為0。
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{ps->arr = NULL;ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}2.打印數據
//順序表的打印
void SLPrint(SL* ps)
{assert(ps);if (ps->size == 0){printf("該順序表為空\n");return;}for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++){printf("%d ", ps->arr[i]);}printf("\n");
}3.尾插數據
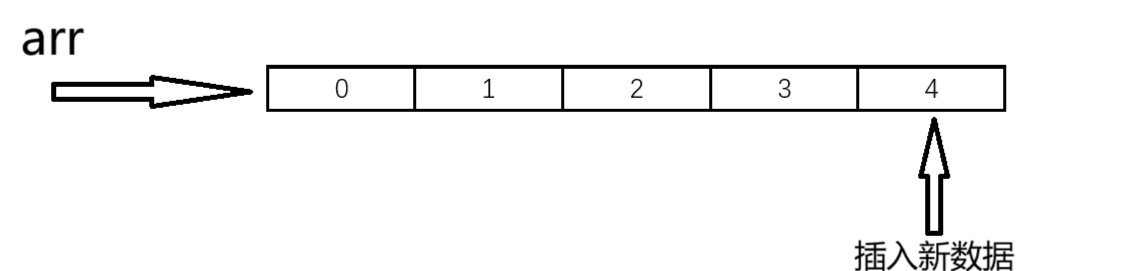
尾插數據就是在順序表的末尾插入數據,在插入數據之前需要先檢查順序表的空間夠不夠,不夠的話我們需要進行擴容處理。
(1)檢查空間
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{//插入數據之前先看空間夠不夠if (ps->capacity == ps->size){//申請空間//malloc calloc realloc int arr[100]--->增容realloc//三目表達式int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;//創建一個變量,避免申請失敗SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(SLDataType));//判斷是否成功if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail:");exit(1); //直接退出程序,不再執行}ps->arr = tmp;ps->capacity = newCapacity;}
}(2)插入數據
//尾插
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{assert(ps);SLCheckCapacity(ps); //檢查空間是否足夠//ps->arr[ps->size] = x;//++ps->size;ps->arr[ps->size++] = x; //尾插數據
}4.尾刪數據
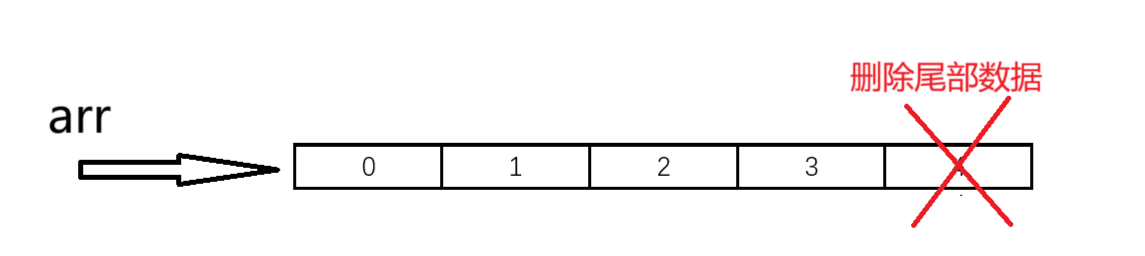
尾刪數據十分容易,只需要size--就可以了。但是,要注意:一定要確保順序表中有數據。
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{assert(ps);//判斷順序表是否為空assert(ps->size);ps->size--;
}5.頭插數據
頭插數據是指在順序表的起始位置插入數據。
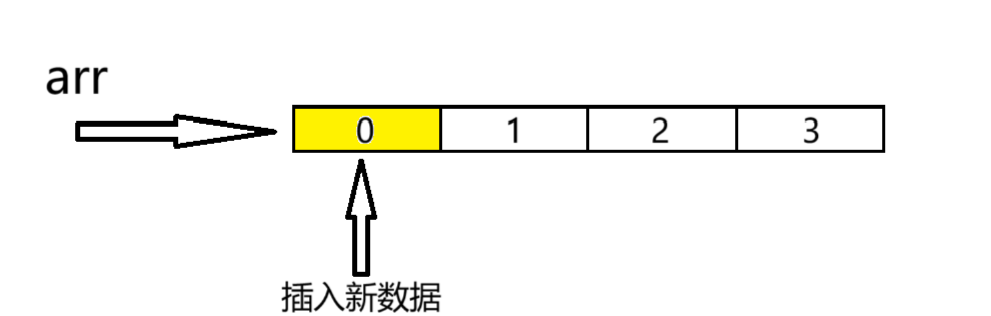
//頭插
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{assert(ps);SLCheckCapacity(ps);//讓順序表中已經存在的數據整體往后挪一位for (int i = ps->size; i > 0; i--){ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i - 1]; //即arr[1]=arr[0]以此類推}ps->arr[0] = x;ps->size++;
}6.頭刪數據
刪除頭部數據,需要依次往前覆蓋。
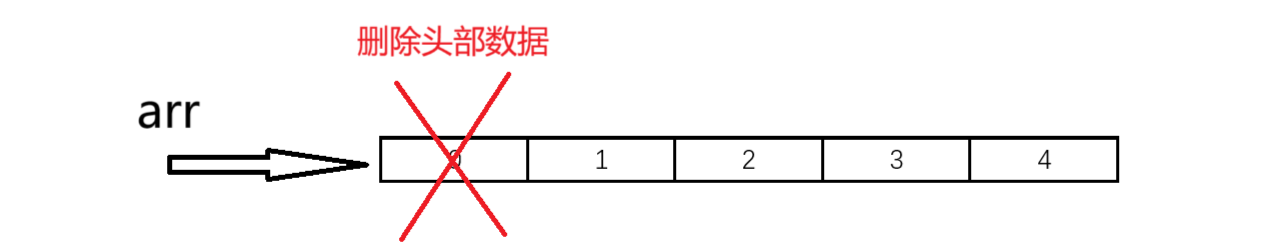
// 頭刪
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{assert(ps);//判斷順序表是否為空assert(ps->size);//數據整體往前移動一位for (int i = 0; i < ps->size - 1; i++){ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1];}ps->size--;
}7.數據查找
輸入參數,在順序表找到指定的值并返回下標,找不到則返回-1。
//順序表的查找
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{assert(ps);for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++){//找到if (ps->arr[i] == x){return i;}}//沒找到return -1;
}8.指定位置數據修改
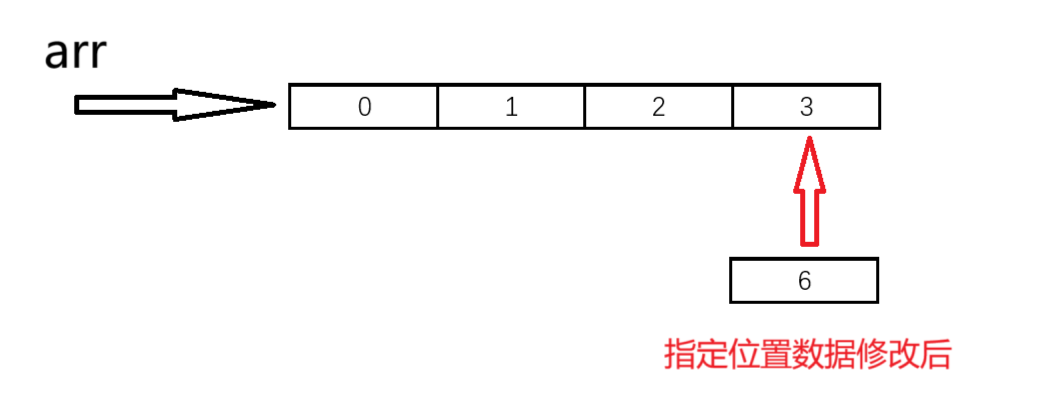
//指定位置數據修改
void SLModify(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->size);assert(pos>=0 && pos < ps->size);ps->arr[pos] = x;
}9.指定位置數據刪除
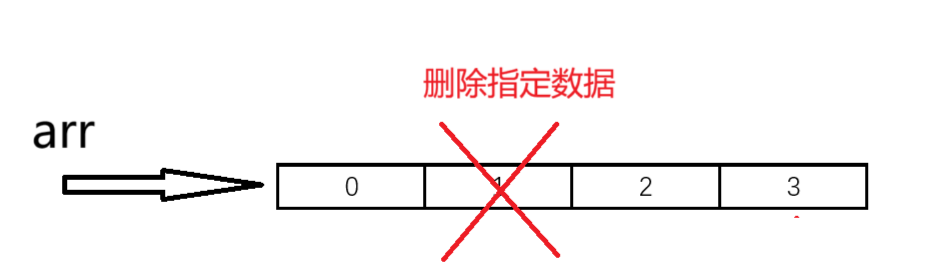
//指定位置刪除數據
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{assert(ps);assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);for (int i = pos; i < ps->size - 1; i++){ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1];}ps->size--; //有效數據-1
}10.指定位置數據插入
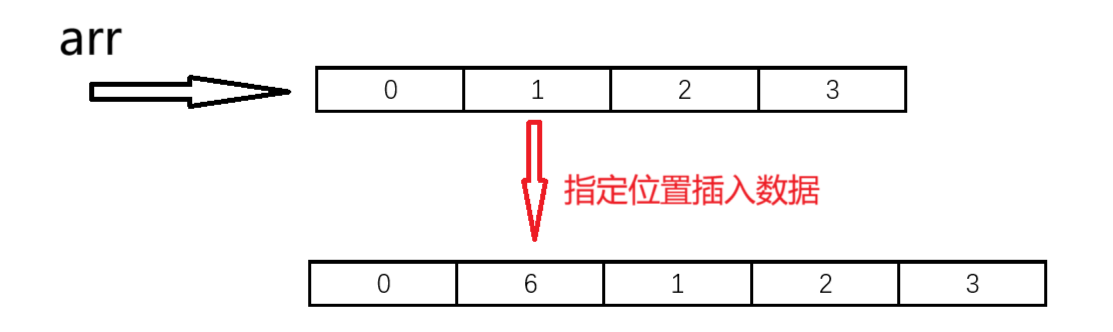
//在指定位置之前插入數據
//pos為指定位置
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{assert(ps);assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);//先檢查空間夠不夠SLCheckCapacity(ps);//讓pos及之后的數據整體向后移動一位for (int i = ps->size; i > pos; i--){ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i - 1];}ps->arr[pos] = x;ps->size++;
}11.銷毀順序表
//順序表的銷毀
void SLDestroy(SL* ps)
{if (ps->arr){free(ps->arr);}ps->arr = NULL;ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}完整代碼
1.SeqList.h
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>//定義順序表的結構//define N 100
//靜態順序表
//struct SeqList
//{
// int arr[N];
// int size; //有效數據個數
//}typedef int SLDataType;
//動態順序表
typedef struct SeqList
{SLDataType* arr;int size; //有效數據個數int capacity; //空間大小
}SL;//順序表初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps);
//順序表的銷毀
void SLDestroy(SL* PS);
//順序表的打印
void SLPrint(SL s);//尾部插入
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
//頭部插入
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//尾部刪除
void SLPopBack(SL* ps);
//頭部刪除
void SLPopFront(SL* ps);//指定位置之前插入
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);
//指定位置刪除數據
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos);
//查找數據
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x);2.SeqList.c
#include"SeqList.h"void SLInit(SL* ps)
{ps->arr = NULL;ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}//順序表的銷毀
void SLDestroy(SL* ps)
{if (ps->arr){free(ps->arr);}ps->arr = NULL;ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{//插入數據之前先看空間夠不夠if (ps->capacity == ps->size){//申請空間//malloc calloc realloc int arr[100]--->增容realloc//三目表達式int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;//創建一個變量,避免申請失敗SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(SLDataType));//判斷是否成功if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail:");exit(1); //直接退出程序,不再執行}ps->arr = tmp;ps->capacity = newCapacity;}
}//尾插
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{/*if (ps == NULL){return;}*/assert(ps);/*ps->arr[ps->size] = x;++ps->size;*/SLCheckCapacity(ps);ps->arr[ps->size++] = x;
}//頭插
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{assert(ps);SLCheckCapacity(ps);//讓順序表中已經存在的數據整體往后挪一位for (int i = ps->size; i > 0; i--){ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i - 1]; //即arr[1]=arr[0]以此類推}ps->arr[0] = x;ps->size++;
}//順序表的打印
void SLPrint(SL* ps)
{assert(ps);if (ps->size == 0){printf("該順序表為空\n");return;}for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++){printf("%d ", ps->arr[i]);}printf("\n");
}void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{assert(ps);//判斷順序表是否為空assert(ps->size);ps->size--;
}// 頭刪
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{assert(ps);//判斷順序表是否為空assert(ps->size);//數據整體往前移動一位for (int i = 0; i < ps->size - 1; i++){ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1];}ps->size--;
}//在指定位置之前插入數據
//pos為指定位置
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{assert(ps);assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);//先檢查空間夠不夠SLCheckCapacity(ps);//讓pos及之后的數據整體向后移動一位for (int i = ps->size; i > pos; i--){ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i - 1];}ps->arr[pos] = x;ps->size++;
}//指定位置刪除數據
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{assert(ps);assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);for (int i = pos; i < ps->size - 1; i++){ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1];}ps->size--;
}//順序表的查找
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{assert(ps);for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++){//找到if (ps->arr[i] == x){return i;}}//沒找到return -1;
}//指定位置數據修改
void SLModify(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->size);assert(pos>=0 && pos < ps->size);ps->arr[pos] = x;
}2.3 數組相關面試題
- . 原地移除數組中所有的元素val,要求時間復雜度為O(N),空間復雜度為O(1)。OJ鏈接
- 2. 刪除排序數組中的重復項。OJ鏈接
- 3. 合并兩個有序數組。OJ鏈接
2.4 順序表的問題及思考
問題:
- 1. 中間/頭部的插入刪除,時間復雜度為O(N)
- 2. 增容需要申請新空間,拷貝數據,釋放舊空間。會有不小的消耗。
- 3. 增容一般是呈2倍的增長,勢必會有一定的空間浪費。例如當前容量為100,滿了以后增容到200,我們 再繼續插入了5個數據,后面沒有數據插入了,那么就浪費了95個數據空間。
思考:如何解決以上問題呢?下一節內容我們將給出了鏈表的結構來看看。
結束語
這一節我們了解到了第一個數據結構——順序表
非常感謝你的點贊關注和收藏!!!


:多容器管理與集群部署實踐)


:原理、實現與避坑指南】)






)


:專題延伸:JVM vs ART/Dalvik - Android運行時演進深度解析)




