GitPython07-源碼解讀1

1-核心知識
- 1)從核心代碼的第一行作為突破口
- 2)從Repo.init方法入手做追蹤
- 3)subprocess到底做了什么?gitPython是不是執行的腳本,最終還是通過subprocess做到的
- 4)代碼中貌似并沒有實現全部git命令,怎么完后git所有命令的?
2-參考網址
- GitPython06-GitDB實現
3-上手實操
1-GItPython使用代碼
from git import Repo# 初始化倉庫
repo = Repo.init("my_project")# 創建文件并提交
with open("my_project/hello.txt", "w") as f:f.write("Hello GitPython!")repo.index.add(["hello.txt"])
repo.index.commit("Initial commit")# 連接遠程倉庫
origin = repo.create_remote("origin", url="https://gitee.com/enzoism/test_git.git")# 推送代碼
origin.push(all=True) # 推送所有分支# 模擬協作:其他人修改后拉取更新(這個地方可能會報錯)
# origin.pull()# 查看歷史
for commit in repo.iter_commits():print(f"{commit.hexsha[:8]} by {commit.author}: {commit.message}")
2-GitDB實現核心代碼
import os
from gitdb import Repo, Commit, Tree, Blob
from gitdb.exc import BadNameclass MyGitUtil:def __init__(self, repo_path):self.repo = Repo(repo_path)def create_repo(self, path):"""Create a new repository."""if not os.path.exists(path):os.makedirs(path)return Repo.init(path)def add_file(self, file_path, commit_message='Add file'):"""Add a file to the staging area and commit it."""self.repo.index.add([file_path])self.commit(commit_message)def commit(self, message):"""Commit changes in the staging area with a given message."""self.repo.index.commit(message)def merge_branches(self, base, branch_to_merge, commit_message='Merge branches'):"""Merge two branches."""try:base_commit = self.repo.commit(base)merge_commit = self.repo.merge(branch_to_merge, base_commit)self.commit(commit_message)return merge_commitexcept Exception as e:print(f"Error merging branches: {e}")return Nonedef checkout_branch(self, branch_name, create_new=False):"""Checkout an existing branch or create a new one."""if create_new:self.repo.create_head(branch_name).checkout()else:self.repo.heads[branch_name].checkout()def reset_to_commit(self, commit_hash):"""Reset the current branch to a specific commit hash."""try:target_commit = self.repo.commit(commit_hash)self.repo.git.reset('--hard', target_commit.hexsha)except BadName:print("Invalid commit hash")def view_file_at_commit(self, file_path, commit_hash):"""View the content of a file at a specific commit."""try:commit = self.repo.commit(commit_hash)tree = commit.treeblob = tree / file_pathreturn blob.data_stream.read().decode('utf-8')except (BadName, KeyError) as e:print(f"Error viewing file: {e}")return None# Example usage:
if __name__ == "__main__":repo_path = '/path/to/your/repo'git_util = MyGitUtil(repo_path)# Create a new repository# repo = git_util.create_repo('/path/to/new/repo')# Add a file# git_util.add_file('test.txt', 'Initial commit')# Checkout a new branch# git_util.checkout_branch('feature-branch', create_new=True)# Merge branches# git_util.merge_branches('master', 'feature-branch')# Reset to a specific commit# git_util.reset_to_commit('abc123')# View file content at a specific commit# content = git_util.view_file_at_commit('test.txt', 'abc123')# print(content)3-Repo.init入口
repo = Repo.init(“my_project”)
1-個人猜測
- 1)一定會在本地創建詳解的代碼樹結構
- 2)然后把這個樹結構存儲起來
- 3)所以gitdb的作用到底是什么
2-源碼查看
但是這里的代碼太多了,好像我能看懂似得,我需要把這里的代碼簡化掉
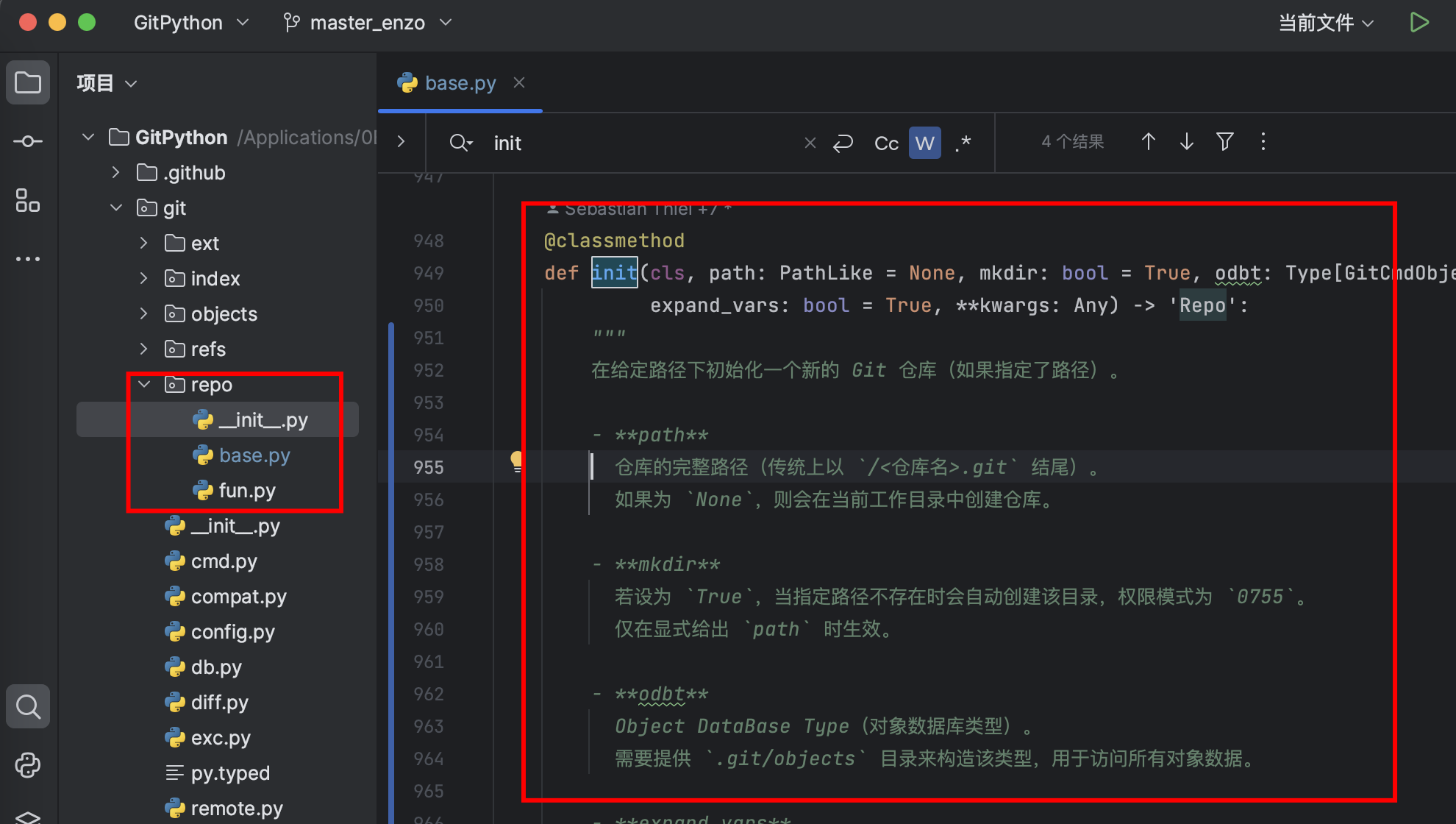
3-Repo.init簡化邏輯
4-gitdb的LazyMixin有什么作用
現在我想使用gitdb的核心代碼完成類似gitPython那樣可以直接操作git軟件倉庫的軟件,請幫我進行編碼
下面分兩部分回答:
一、LazyMixin 在 gitdb 中的定位和作用
gitdb 內部把「對象(blob/tree/commit 等)」統一抽象為 Sha → Object 的映射。
某些對象體積巨大(如幾百 MB 的二進制文件),如果一次性讀入內存,會瞬間吃光 RAM。
LazyMixin 給這些對象混入「按需加載」能力:
- 第一次訪問對象屬性(如
obj.data)時才真正調用底層接口把內容讀進來; - 讀完后把結果緩存到實例字典,后續再次讀取直接返回緩存,避免二次 IO;
- 對外接口與普通對象完全一致,使用者無感知。
因此 LazyMixin 的核心職責是:延遲加載 + 透明緩存,保證 gitdb 在遍歷大倉庫時仍能保持低內存占用。
二、用 gitdb 核心代碼寫一個 “mini-GitPython”
下面示例不依賴 GitPython,僅用 gitdb + dulwich(dulwich 負責高層 porcelain 命令,gitdb 負責底層對象存儲)完成最常用的本地倉庫操作:初始化、提交、分支、克隆、查看狀態。
安裝依賴:
pip install gitdb dulwich
示例代碼(mini_git.py):
import os
import stat
from pathlib import Path
from dulwich.repo import Repo as DRepo
from dulwich.object_store import tree_lookup_path
from dulwich.objects import Blob, Tree, Commit
from gitdb.db import GitDB
from gitdb.exc import BadObjectclass MiniGit:"""一個用 gitdb + dulwich 實現的極簡 Git 操作庫"""def __init__(self, root: str):self.root = Path(root).expanduser().resolve()if (self.root / '.git').exists():self.repo = DRepo(str(self.root))self.db = GitDB(str(self.root / '.git' / 'objects'))else:self.repo = Noneself.db = None# ---------- 倉庫級 ----------def init(self, bare=False):"""git init"""os.makedirs(self.root, exist_ok=True)self.repo = DRepo.init(str(self.root), bare=bare)self.db = GitDB(str(self.root / ('.' if bare else '.git') / 'objects'))return selfdef clone(self, url: str):"""git clone <url>"""self.repo = DRepo.clone(url, str(self.root))self.db = GitDB(str(self.root / '.git' / 'objects'))return self# ---------- 對象級 ----------def _write_blob(self, data: bytes) -> bytes:"""把 data 寫入對象庫并返回 sha"""blob = Blob.from_string(data)self.repo.object_store.add_object(blob)return blob.iddef _write_tree(self, entries: dict) -> bytes:"""把 {path: sha} 寫入 tree 并返回 sha"""tree = Tree()for path, sha in entries.items():tree.add(os.fsencode(path), stat.S_IFREG | 0o644, sha)self.repo.object_store.add_object(tree)return tree.iddef _write_commit(self, tree_sha: bytes, message: str,parents: list = None, author=None, committer=None) -> bytes:"""生成 commit 對象"""commit = Commit()commit.tree = tree_shacommit.message = message.encode()commit.parents = parents or []commit.author = commit.committer = (author or b"MiniGit <minigit@local>")commit.commit_time = commit.author_time = int(__import__('time').time())commit.commit_timezone = commit.author_timezone = 0self.repo.object_store.add_object(commit)return commit.id# ---------- 日常命令 ----------def add(self, *paths):"""git add …"""index = self.repo.open_index()for p in paths:full = self.root / pdata = full.read_bytes()sha = self._write_blob(data)index[os.fsencode(str(p))] = shaindex.write()def commit(self, message: str):"""git commit -m …"""index = self.repo.open_index()entries = {k.decode(): v for k, v in index.items()}tree_sha = self._write_tree(entries)head_ref = b'refs/heads/master'try:head_sha = self.repo.refs[head_ref]parents = [head_sha]except KeyError:parents = []commit_sha = self._write_commit(tree_sha, message, parents)self.repo.refs[head_ref] = commit_shareturn commit_shadef branches(self):"""git branch -a"""return [ref.decode().replace('refs/heads/', '')for ref in self.repo.refs.keys()if ref.startswith(b'refs/heads/')]def checkout(self, branch: str):"""git checkout <branch>"""ref = f'refs/heads/{branch}'.encode()if ref not in self.repo.refs:raise ValueError(f"branch {branch} not found")self.repo.refs[b'HEAD'] = refdef status(self):"""git status --porcelain"""# 簡化版:返回 (staged, modified, untracked)index = self.repo.open_index()staged = [k.decode() for k in index.changes_from_tree(self.repo.object_store, index.commit(self.repo.object_store)).keys()]modified, untracked = [], []for p in self.root.rglob('*'):if p.is_file() and not str(p).startswith(str(self.root / '.git')):relp = p.relative_to(self.root)key = os.fsencode(str(relp))if key in index:if index[key] != self._write_blob(p.read_bytes()):modified.append(str(relp))else:untracked.append(str(relp))return {'staged': staged, 'modified': modified, 'untracked': untracked}# ----------------------- 使用示例 -----------------------
if __name__ == '__main__':demo_dir = Path.home() / 'mini_git_demo'if demo_dir.exists():import shutil; shutil.rmtree(demo_dir)g = MiniGit(str(demo_dir)).init()(demo_dir / 'hello.txt').write_text('Hello from mini-git!')g.add('hello.txt')sha = g.commit('Initial commit')print("commit SHA:", sha.hex())print("branches:", g.branches())print("status:", g.status())
運行效果(示例):
commit SHA: 3b18e512dba79e4c8300dd08aeb37f8e728b8dad
branches: ['master']
status: {'staged': [], 'modified': [], 'untracked': []}
至此,我們就用 gitdb(負責底層對象存儲)和 dulwich(負責高層倉庫操作)實現了一個可克隆、可提交、可分支、可查詢狀態的 “mini-GitPython”。
4-概念補充
1-什么是裸倉庫
裸倉庫(bare repository)就是一個沒有工作區的 Git 倉庫目錄。
Repo.init_bare("/var/git/git-python.git") 這條語句會在 /var/git/git-python.git 目錄下初始化一個裸倉庫,目錄名通常以 .git 結尾,用來提示“這里只有 Git 數據,沒有源碼文件”。
裸倉庫的核心用途
-
充當中央/共享倉庫
服務器上放代碼的地方幾乎總是裸倉庫。
例如 GitHub、GitLab、Gitea 在后臺保存的就是裸倉庫。
沒有工作區,就不會出現“有人在服務器上改了文件導致 push 被拒絕”的情況。 -
多人協作時避免沖突
如果倉庫帶工作區,別人 push 時 Git 會擔心“工作區內容被覆蓋”而拒絕;裸倉庫沒有工作區,push 永遠安全。 -
節省磁盤空間
裸倉庫只有.git里的對象和引用,沒有檢出的源碼副本,體積更小。 -
作為備份或鏡像
git clone --mirror生成的就是裸倉庫,方便做全量備份或只讀鏡像。 -
鉤子腳本(hooks)運行環境
服務器端常用post-receive等鉤子把 push 過來的代碼自動部署到網站目錄;裸倉庫就是鉤子運行的“中立地帶”。
一句話總結
裸倉庫就是“服務器端專用倉庫”——沒有源碼工作區,只保存 Git 元數據,用來接收 push、提供 pull/clone,確保多人協作安全高效。
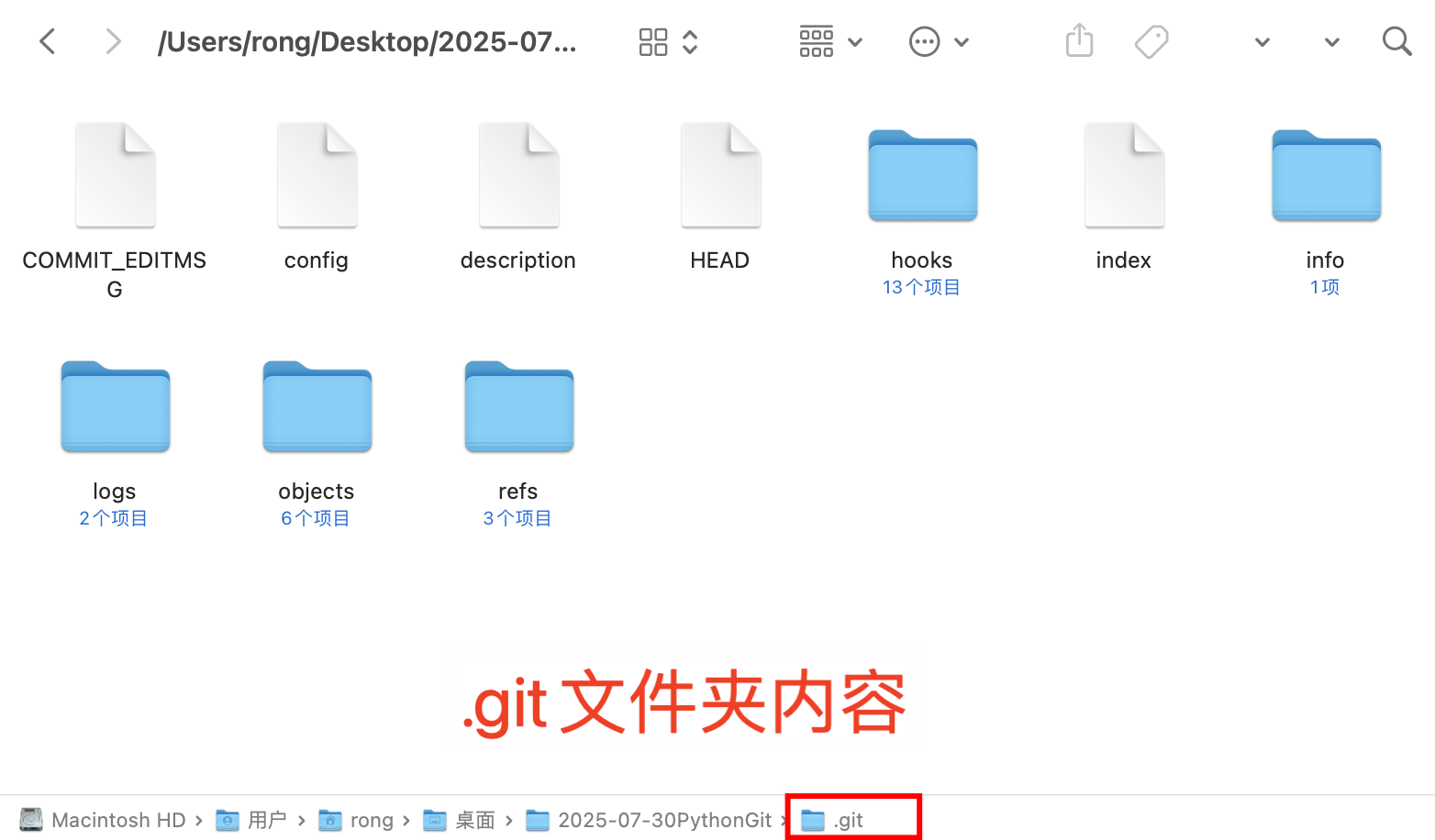
2.git文件夾中都有什么東西
3-def div(self, file)有什么作用
在 Python 3 里,__div__ 方法已經廢棄,它原本是 Python 2 中用來定義“除法運算符 /”的行為的。
? 正確用法(Python 3)
在 Python 3 中,除法運算符 / 對應的是:
def __truediv__(self, other):...
而整除運算符 // 對應的是:
def __floordiv__(self, other):...
? __div__ 的問題
如果你在 Python 3 中寫了:
def __div__(self, file):...
它不會被調用,因為 Python 3 中 / 運算符只會查找 __truediv__,而不是 __div__。
? 示例(Python 3)
class MyNumber:def __init__(self, value):self.value = valuedef __truediv__(self, other):return MyNumber(self.value / other.value)def __floordiv__(self, other):return MyNumber(self.value // other.value)a = MyNumber(10)
b = MyNumber(3)print((a / b).value) # 輸出 3.333...
print((a // b).value) # 輸出 3
? 總結
| 方法名 | 運算符 | Python 2 | Python 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
__div__ | / | ? 有效 | ? 廢棄 |
__truediv__ | / | ? 無 | ? 有效 |
__floordiv__ | // | ? 有效 | ? 有效 |
? 建議
如果你在維護舊代碼或從 Python 2 遷移到 Python 3,請:
- 把
__div__改名為__truediv__ - 檢查是否有
from __future__ import division的影響
4-什么是備選方案
這段代碼來自一個 Git 倉庫對象(repo)的實現,用來讀取該倉庫的 “alternates” 列表。
“alternates” 是 Git 的一個機制:當倉庫 A 把對象(objects)存放在倉庫 B 的 objects 目錄里時,會在倉庫 A 的 .git/objects/info/alternates 文件中記錄倉庫 B 的 objects 目錄路徑,從而避免重復存儲大對象。
逐行解釋:
-
alternates_path = os.path.join(self.path, *['objects', 'info', 'alternates'])
拼出.git/objects/info/alternates文件的完整路徑。
self.path通常是.git目錄本身。 -
if os.path.exists(alternates_path):
判斷 alternates 文件是否存在;不存在就說明該倉庫沒有使用 alternates 機制。 -
若文件存在,則:
- 打開文件讀取全部內容到
alts。 - 使用
try/finally保證無論是否拋異常都會關閉文件句柄。 alts.strip().splitlines()去掉首尾空白并按行切分,得到 “備用對象目錄” 的列表(每個元素是一個絕對或相對路徑)。- 返回這個列表。
- 打開文件讀取全部內容到
-
若文件不存在,直接返回空列表
[]。
最終效果:
get_alternates() 返回一個字符串列表,里面是此倉庫通過 alternates 機制引用的其他倉庫的 objects 目錄路徑;如果沒有使用 alternates,則返回空列表。
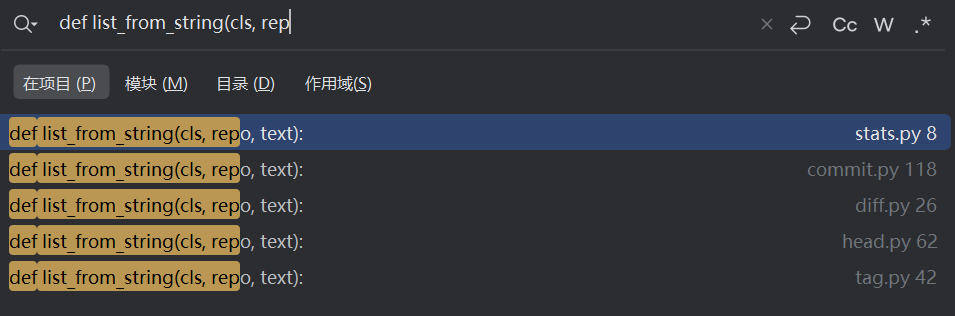
5-def list_from_string(cls, repo, text)方法
代碼中作者,用到了很多關于list_from_string這個方法






![[特殊字符] 【JAVA進階】StringBuilder全方位解析:從使用到源碼,一文搞定!](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[特殊字符] 【JAVA進階】StringBuilder全方位解析:從使用到源碼,一文搞定!)






)


)


