一、JDK8新特性
1.Lambda表達式
Lambda表達式是JDK 8開始新增的一種語法形式;作用:用于簡化名內部類的代碼寫法。

注意:Lambda表達式并不是說能簡化全部匿名內部類的寫法,只能簡化函數式接口的匿名內部類。
- 有且僅有一個抽象方法的接口。
- 注意:將來我們見到的大部分函數式接口,上面都可能會有@Functionalinterface的注解,有該注解:的接口就必定是函數式接口。
package com.API;public class LambdaTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Animal a = new Animal() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("汪汪隊立大功!");}};a.run();//對于類無法使用lambda函數的Swim s = new Swim() {@Overridepublic void swim() {System.out.println("小鯉魚歷險記!");}};s.swim();Swim s1 = () -> {System.out.println("小鯉魚歷險記2!");};s1.swim();}
}abstract class Animal {public abstract void run();
}interface Swim {void swim();
}2.Lambda表達式省略規則
- 參數類型可以省略不寫。
- 如果只有一個參數,參數類型可以省略,同時()也可以省略。
- 如果Lambda表達式中的方法體代碼只有一行代碼,可以省略大括號不寫,同時要省略分號!此時,如果這行代碼是return語句,也必須去掉return不寫。
Arrays.setAll(prices,value->prices[value]*0.8);
3.方法引用
3.1靜態方法的引用
靜態方法的引用
類名::靜態方法。
使用場景
- 如果某個Lambda表達式里只是調用一個靜態方法,并且前后參數的形式一致,就可以使用靜態方法引用。
3.2實例方法的引用
實例方法的引用
對象名::實例方法。
使用場景
如果某個Lambda表達式里只是調用一個實例方法,并且前后參數的形式一致,就可以使用實例方法引用。
package com.API;import java.util.Arrays;public class ArrayTest1 {public static void main(String[] args) {Student[] students =new Student[4];students[0]=new Student("蜘姝精",23);students[1]=new Student( "紫假", 26);students[2]=new Student( "紫霞",26);students[3]=new Student( "至蓉寶",24);//靜態方法引用Arrays.sort(students,CompareByData::compareInt);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(students));//實例方法引用CompareByData compareByData = new CompareByData();Arrays.sort(students,compareByData::compareByAge);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(students));}
}
class Student implements Comparable<Student>{private String name;private int age;public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}@Overridepublic int compareTo(Student o) {return this.age-o.age;}
}
class CompareByData{public static int compareInt(Student o1,Student o2){return o1.getAge()-o2.getAge();}public int compareByAge(Student o1,Student o2){return o2.getAge()-o1.getAge();}
}3.3特定類型方法的引用
特定類型的方法引用
類型::方法。
使用場景
如果某個Lambda表達式里只是調用一個實例方法,并且前面參數列表中的第一個參數是作為方法的主調后面的所有參數都是作為該實例方法的入參的,則此時就可以使用特定類型的方法引用
Arrays.sort(names,String::compareToIgnoreCase);
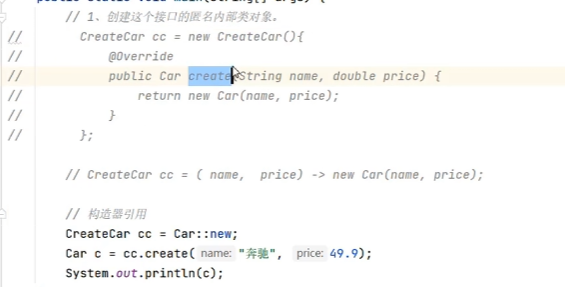
3.4構造器引用
類名::new。
使用場景
如果某個Lambda表達式里只是在創建對象,并且前后參數情況一致,就可以使用構造器引用
二、常見算法
解決某個實際問題的過程和方法!

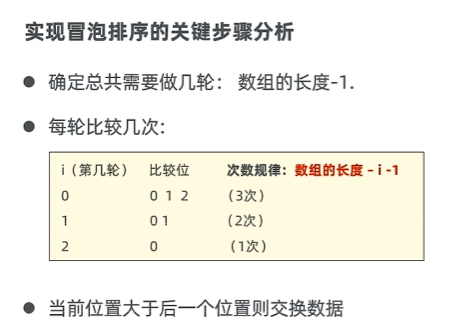
2.1 冒泡排序
每次從數組中找出最大值放在數組的后面去。
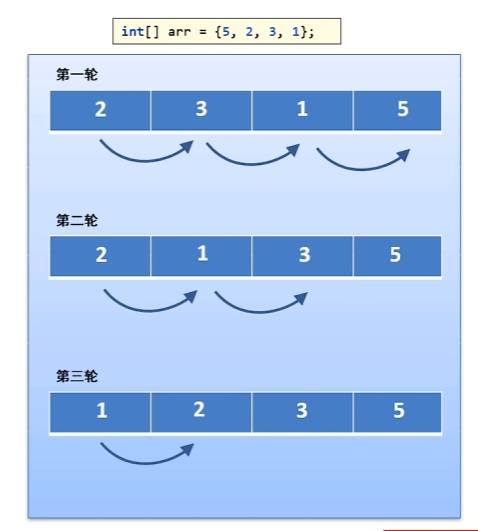
import java.util.Arrays;public class Sort1 {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {5, 2, 3, 1};//控制輪數for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {//i=0 1 2 [5, 2, 3, 1] 次數//i=0 第一輪 0 1 2 3//i=1 第二輪 0 1 2//i=2 第三輪 0 1for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - i - 1; j++) {if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {int temp = arr[j];arr[j] = arr[j + 1];arr[j + 1] = temp;}}}System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));}
}
2.2 選擇排序
每輪選擇當前位置,開始找出后面的較小值與該位置交換
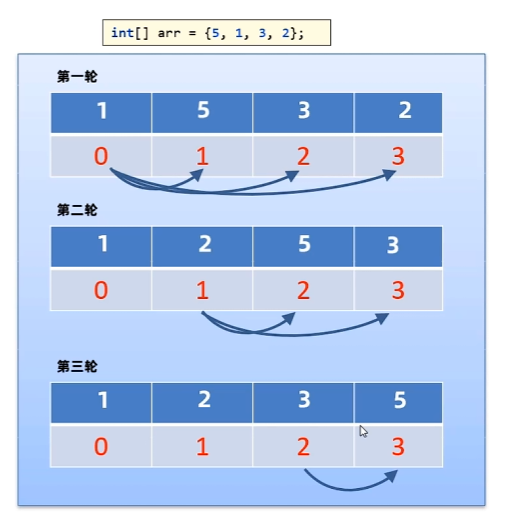
import java.util.Arrays;public class Sort2 {public static void main(String[] args) {//1.準備好一個數組int[] arr = {5, 2, 3, 1};//2.控制輪數for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {//i=0 j=1 2 3//i=1 j=2 3//i=2 j=3//每輪選擇幾次for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {if (arr[i] > arr[j]) {int temp = arr[i];arr[i] = arr[j];arr[j] = temp;}}}System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));}
}優化
import java.util.Arrays;public class Sort2 {public static void main(String[] args) {//1.準備好一個數組int[] arr = {5, 2, 3, 1};//2.控制輪數for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {//i=0 j=1 2 3//i=1 j=2 3//i=2 j=3int minIndex = i;//每輪選擇幾次for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {if (arr[minIndex] > arr[j]) {minIndex = j;}}if (i != minIndex) {int temp = arr[i];arr[i] = arr[minIndex];arr[minIndex] = temp;}}System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));}
}2.3 查找算法
基本查找,順序查找
注意:在數據量特別大的時候,基本查找這種從前往后挨個找的形式,性能是很差的!
二分查找(折半查找)
- 前提條件:數組中的數據必須是有序的。
- 核心思想:每次排除一半的數據,查詢數據的性能明顯提高極多!
- 結論:二分查找正常的折半條件應該是開始位置left<=結束位置right
public class Sort3 {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] a={7,23,79,81,103,127,131,147};System.out.println(binarySearch(a,81));}public static int binarySearch(int[] a,int data){//1、定義兩個交量,一手站在左邊位置,一個站在右邊位置int left=0;int right=a.length-1;//2. 定義一個循環控制while (left<=right){//3.每次折半計算中間位置int mid=(left+right)/2;//4.判斷當前要找的元素值,與中間位置處的元素值的大小情況。if(a[mid]>data){right=mid-1;}else if(a[mid]<data){left=mid+1;}else {return mid;}}return -1;}
}三、正則表達式
就是由一些特定的字符組成,代表的是一個規則
- 用來校驗數據格式是否合法
- 在一段文本中查找滿足要求的內容
public class RegexTest1 {public static void main(String[] args) {String s="1349281263";boolean b = checkQQ(s);System.out.println(b);System.out.println(RegexQQ(s));}public static boolean RegexQQ(String qq){return qq!=null&&qq.matches("[1-9]\\d{5,19}");}public static boolean checkQQ(String qq) {if (qq == null || qq.startsWith("0") || qq.length() < 6 || qq.length() > 20)return false;for (int i = 0; i < qq.length(); i++) {char ch = qq.charAt(i);if (ch < '0' || ch > '9')return false;}return true;}
}String提供了一個匹配正則表達式的方法
public boolean matches(string regex)
判斷字符串是否匹配正則表達式,匹配返回true,不匹配返回false。

email.matches(“\w{2,}@\w{2,20}(\.\w{2,10}){1,2”))
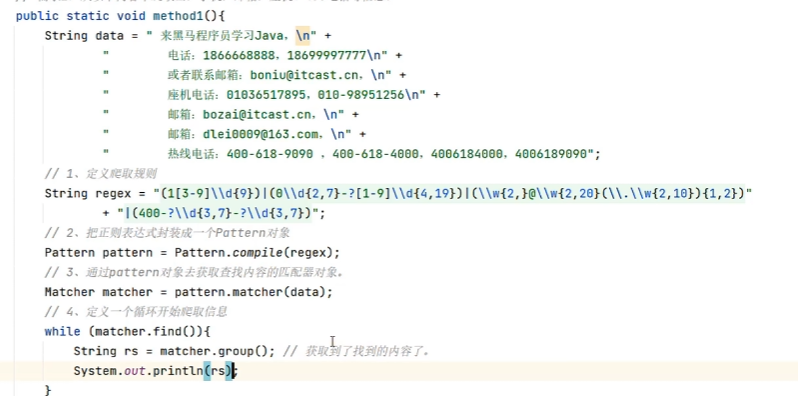

System.out.println(s2.replaceAll( regex “(.)\1+”,replacement: “$1”));
(.)一組:.匹配任意字符的。
\11:為這個組聲明一個組號:1號
+聲明必須是重復的字
$1
$1可以去取到第1組代表的那個重復的字
public class RegexTest6 {public static void main(String[] args) {String str="我我我喜歡歡歡歡歡編編編編程程程程程程程程程";System.out.println(str.replaceAll("(.)\\1+","$1"));}
}
四、異常
異常就是代表程序出現的問題。
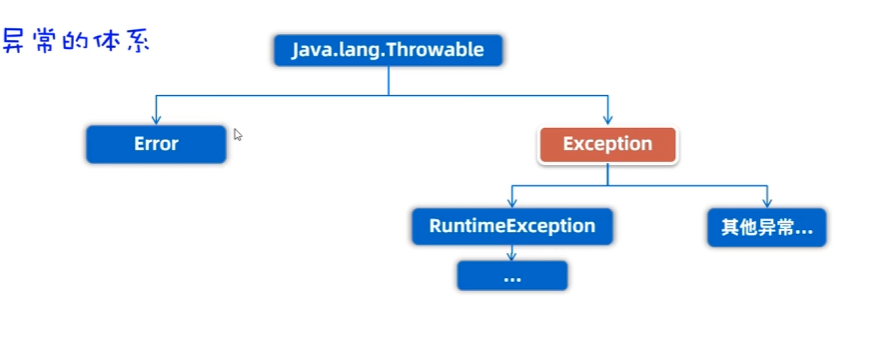
- Error:代表的系統級別錯誤(屬于嚴重問題),也就是說系統一旦出現問題,sun公司會把這些問題封裝成Error對象給出來說白了,Error是給sun公司自己用的,不是給我們程序員用的,因此我們開發人員不用管它。
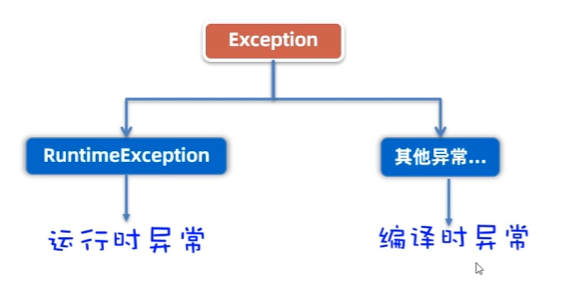
- Exception:叫異常,它代表的才是我們程序可能出現的問題,所以,我們程序員通常會用Exception以及它的孩子來封裝程序出現的問題。
- 運行時異常:RuntimeException及其子類,編譯階段不會出現錯誤提醒,運行時出現的異常(如:數組索引越界異常)
- 編譯時異常:編譯階段就會出現錯誤提醒的。(如:日期解析異常)
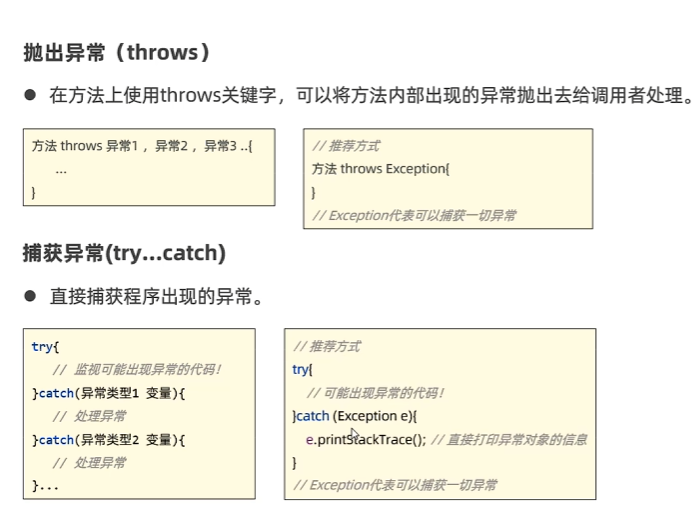
- 使用Ctrl alt T鍵選擇try catch包圍可能出現的異常程序段拋出異常
- 在方法后throws異常,表示將方法內的異常拋出。

自定義異常
Java無法為這個世界上全部的問題都提供異常類來代表,如果企業自己的某種問題,想通過異常來表示,以便用異常來管理該問題,那就需要自己來定義異常類了
- 1、異常是用來查尋系統Bug的關鍵參考信息!
- 2、異常可以作為方法內部的一種特殊返回值,以便通知上層調用者底層的執行情況!

問題嚴重就自定義編譯時異常,問題不嚴重就運行時異常。
public class RegexTest6 {public static void main(String[] args) {try {setAge1(160);}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}public static void setAge(int age){if(age>0&&age<150){System.out.println("successful");}else {//用一個異常對象封裝這個問題,throw拋出去這個異常對象throw new AgeIllegalRuntimeException("/age is illegal, your age is"+age);}}public static void setAge1(int age) throws AgeIllegalException {if(age>0&&age<150){System.out.println("successful");}else {//用一個異常對象封裝這個問題,throw拋出去這個異常對象throw new AgeIllegalException("/age is illegal, your age is"+age);}}
}
異常的處理
開發中對于異常的常見處理方式

可以都寫Exception優化寫法的
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;public class ExceptionTest3 {public static void main(String[] args) {try {test1();} catch (ParseException e) {e.printStackTrace();// 打印出這個異常對象的信息。記錄下來。} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();// 打印出這個異常對象的信息。記錄下來。}finally {System.out.println("異常處理完畢");}}public static void test1() throws ParseException, FileNotFoundException {SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");Date d=simpleDateFormat.parse("2024-1-2 12:21:13");System.out.println(d);test2();}public static void test2() throws FileNotFoundException {InputStream is=new FileInputStream("D:/meinv.jpg");}
}
import java.util.Scanner;public class ExceptionTest4 {public static void main(String[] args) {//嘗試修復while (true) {try {System.out.println(getMoney());break;} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println("請您輸入合法的數字!");}}}public static double getMoney(){Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);while (true) {System.out.println("請輸入價錢!");double v = scanner.nextDouble();if(v>0) {return v;}System.out.println("您輸入的不合格!");}}
}



)


知識點(包括結構體內存對齊的熱門知識點))




---C++)


)




)