Upscaling of an image refers to enlarging the size of an image.
圖像放大是指放大圖像的大小。
In this program, we will be using two functions of OpenCV-python (cv2) module.. let's see their syntax and descriptions first
在此程序中,我們將使用OpenCV-python(cv2)模塊的兩個函數。.讓我們首先查看它們的語法和描述。
1) imread():
It takes an absolute path/relative path of your image file as an argument and returns its corresponding image matrix.
1)imread():
它以圖像文件的絕對路徑/相對路徑作為參數,并返回其對應的圖像矩陣。
If flag value is:
如果標志值為:
1: Loads a color image.
1 :加載彩色圖像。
0: Loads image in grayscale mode.
0 :以灰度模式加載圖像。
-1: Loads image as such including alpha channel.
-1 :加載圖像,包括alpha通道。
If the flag value is not given then show the original image, which path is given.
如果未給出標志值,則顯示原始圖像,并給出哪個路徑。
2) imshow():
It takes window name and image matrix as an argument in order to display an image in a display window with a specified window name.
2)imshow():
它以窗口名稱和圖像矩陣為參數,以便在具有指定窗口名稱的顯示窗口中顯示圖像。
Also In this program, we will be using one function of numpy module.
同樣在此程序中,我們將使用numpy模塊的一個功能。
median(): It takes array and returns the median of the array .
平均():它接受array并返回array的中位數。
Also, in this program we are using the concept of array slicing
另外,在此程序中,我們使用數組切片的概念
Let, A is 1-d array:
A[start:stop:step]
設A為一維數組:
A [開始:停止:步驟]
start: Starting number of the sequence.
start:序列的起始編號。
stop: Generate numbers up to, but not including this number.
停止:生成不超過此數字的數字,但不包括此數字。
step: Difference between each number in the sequence.
步驟:序列中每個數字之間的差。
Example:
例:
A = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
print(A[ 1: 5])
Output:
[2,3,4,5]
用于在Python中放大灰度圖像的Python程序 (Python program for upscaling the grayscale image in Python)
# open-cv library is installed as cv2 in python
# import cv2 library into this program
import cv2
# import numpy as np name
import numpy as np
# read an image using imread() function of cv2
# we have to pass only the path of the image
img = cv2.imread(r'C:/Users/user/Desktop/pic6.jpg',0)
# displaying the image using imshow() function of cv2
# In this : 1st argument is name of the frame
# 2nd argument is the image matrix
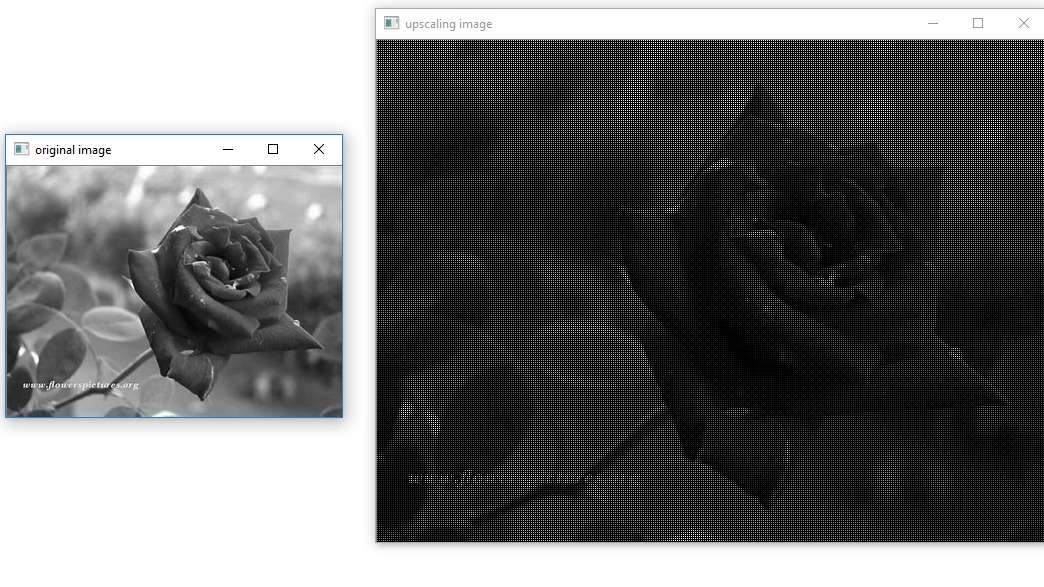
cv2.imshow('original image',img)
# upscaling code
# Upscaling the image x,y times along row and column
x,y = 2, 2
# here image is of class 'uint8', the range of values
# that each colour component can have is [0 - 255]
# create a zero matrix of order of x,y times
# of previous image of 3-dimensions
upscale_img = np.zeros((x*img.shape[0],y*img.shape[1]),np.uint8)
i, m = 0, 0
while m < img.shape[0] :
j, n = 0, 0
while n < img.shape[1]:
# We assign pixel value from original image matrix to the
# new upscaling image matrix in alternate rows and columns
upscale_img[i, j] = img[m, n]
# increment j by y times
j += y
# increment n by one
n += 1
# increment m by one
m += 1
# increment i by x times
i += x
cv2.imshow('upscaling image',upscale_img)
Output
輸出量
翻譯自: https://www.includehelp.com/python/upscaling-the-grayscale-image.aspx







——邏輯推理一)
2種方法)


方法)





+mysql實現的高校實驗室管理系統...)

