合并排序算法排序過程
外部分類 (External sorting)
External sorting is a technique in which the data is stored on the secondary memory, in which part by part data is loaded into the main memory and then sorting can be done over there. Then this sorted data will be stored in the intermediate files. Finally, these files will be merged to get a sorted data. Thus by using the external sorting technique, a huge amount of data can be sorted easily. In case of external sorting, all the data cannot be accommodated on the single memory, in this case, some amount of memory needs to be kept on a memory such as hard disk, compact disk and so on.
外部排序是一種將數據存儲在輔助存儲器中的技術,其中,將部分數據加載到主存儲器中,然后可以在那里進行排序。 然后,將這些排序后的數據存儲在中間文件中 。 最后,這些文件將合并以獲得排序的數據。 因此,通過使用外部分類技術,可以輕松地分類大量數據。 在進行外部排序的情況下,所有數據都無法容納在單個內存中,在這種情況下,需要在硬盤,光盤等內存中保留一定數量的內存。
The requirement of external sorting is there, where the data we have to store in the main memory does not fit into it. Basically, it consists of two phases that are:
存在外部排序的要求,我們必須存儲在主存儲器中的數據不適合其中。 基本上,它包括兩個階段:
Sorting phase: This is a phase in which a large amount of data is sorted in an intermediate file.
排序階段:這是在中間文件中對大量數據進行排序的階段。
Merge phase: In this phase, the sorted files are combined into a single larger file.
合并階段:在此階段,已排序的文件被合并為一個較大的文件。
One of the best examples of external sorting is external merge sort.
外部排序的最佳示例之一是外部合并排序。
外部合并排序 (External merge sort)
The external merge sort is a technique in which the data is stored in intermediate files and then each intermediate files are sorted independently and then combined or merged to get a sorted data.
外部合并排序是一種技術,其中數據存儲在中間文件中,然后將每個中間文件獨立排序,然后合并或合并以獲得排序后的數據。
For example: Let us consider there are 10,000 records which have to be sorted. For this, we need to apply the external merge sort method. Suppose the main memory has a capacity to store 500 records in a block, with having each block size of 100 records.
例如:讓我們考慮必須對10,000條記錄進行排序。 為此,我們需要應用外部合并排序方法。 假設主存儲器具有在一個塊中存儲500條記錄的容量,每個塊的大小為100條記錄。
In this example, we can see 5 blocks will be sorted in intermediate files. This process will be repeated 20 times to get all the records. Then by this, we start merging a pair of intermediate files in the main memory to get a sorted output.
在此示例中,我們可以看到5個塊將在中間文件中排序。 此過程將重復20次以獲取所有記錄。 然后,我們開始在主存儲器中合并一對中間文件,以獲得排序后的輸出。
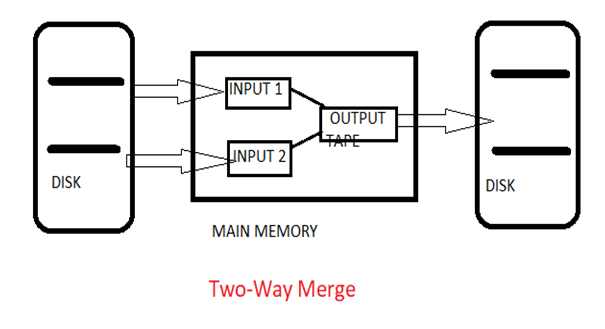
兩路合并排序 (Two-Way Merge Sort)
Two-way merge sort is a technique which works in two stages which are as follows here:
雙向合并排序是一項分兩個階段工作的技術,如下所示:
Stage 1: Firstly break the records into the blocks and then sort the individual record with the help of two input tapes.
階段1 :首先將記錄分成多個塊,然后借助兩個輸入磁帶對單個記錄進行排序。
Stage 2: In this merge the sorted blocks and then create a single sorted file with the help of two output tapes.
第2階段 :在此合并排序的塊,然后借助兩個輸出磁帶創建單個排序的文件。
By this, it can be said that two-way merge sort uses the two input tapes and two output tapes for sorting the data.
這樣,可以說雙向合并排序使用兩個輸入磁帶和兩個輸出磁帶對數據進行排序。
雙向合并排序算法: (Algorithm for Two-Way Merge Sort:)
Step 1) Divide the elements into the blocks of size M. Sort each block and then write on disk.
步驟1)將元素劃分為大小為M的塊。對每個塊進行排序,然后寫入磁盤。
Step 2) Merge two runs
步驟2)合并兩次跑步
Read first value on every two runs.
每兩次運行讀取第一個值。
Then compare it and sort it.
然后對其進行比較和排序。
Write the sorted record on the output tape.
將排序的記錄寫在輸出磁帶上。
Step 3) Repeat the step 2 and get longer and longer runs on alternates tapes. Finally, at last, we will get a single sorted list.
步驟3)重復步驟2,并在備用磁帶上運行的時間越來越長。 最后,最后,我們將獲得一個排序列表。
Analysis
分析
This algorithm requires log(N/M) passes with initial run pass. Therefore, at each pass the N records are processed and at last we will get a time complexity as O(N log(N/M).
該算法需要log(N / M)遍及初始運行遍。 因此,每遍處理N條記錄,最后我們得到的時間復雜度為O(N log(N / M) 。
翻譯自: https://www.includehelp.com/algorithms/external-merge-sorting.aspx
合并排序算法排序過程




方法與示例)

![[轉]Visual Studio 各版本下載](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[轉]Visual Studio 各版本下載)








)



)