?
1 查找進程
前些天發現了一個巨牛的人工智能學習網站,通俗易懂,風趣幽默,忍不住分享一下給大家。點擊跳轉到教程。
?
ps -ef | grep?java?? 查看所有關于java的進程?
root?????17540???? 1? 0? 2009 ???????? 01:42:27 /usr/java/jdk1.5.0_15/bin/java -Djava.util.logging.config.file=/usr/local/tomcat/conf/logging.properties -server -Xms800m -Xmx800m -XX:PermSize=64M -XX:MaxNewSize=256m -XX:MaxPermSize=128m -Djava.awt.headless=true -Djava.util.logging.manager=org.apache.juli.ClassLoaderLogManager -Xms256m -Xmx1024m -Djava.endorsed.dirs=/usr/local/tomcat/common/endorsed -classpath :/usr/local/tomcat/bin/bootstrap.jar:/usr/local/tomcat/bin/commons-logging-api.jar -Dcatalina.base=/usr/local/tomcat -Dcatalina.home=/usr/local/tomcat -Djava.io.tmpdir=/usr/local/tomcat/temp org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap start?
root?????19979???? 1? 0 Jan05 ???????? 00:00:51 /usr/java/latest/bin/java -Djava.util.logging.manager=org.apache.juli.ClassLoaderLogManager -Djava.util.logging.config.file=/usr/local/apache-tomcat-6.0.16/conf/logging.properties -Xms256m -Xmx1024m -Djava.endorsed.dirs=/usr/local/apache-tomcat-6.0.16/endorsed -classpath :/usr/local/apache-tomcat-6.0.16/bin/bootstrap.jar -Dcatalina.base=/usr/local/apache-tomcat-6.0.16 -Dcatalina.home=/usr/local/apache-tomcat-6.0.16 -Djava.io.tmpdir=/usr/local/apache-tomcat-6.0.16/temp org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap start?
root?????27120?27015? 0 13:23 pts/4??? 00:00:00 grep java?
通過如下命令查看所有關于java的進程:
ps -ef | grep java 終止線程
在得到相關進程時,將某線程終止時用?
kill -9 XXXXX XXXXX 為上述查出的序號? 如: 19979線程終止為: kill -9 19979?
kill一個線程時需注意不要誤停止了不應該停止的線程造成不必要的麻煩。?
在相當確信時才可用此方法停止線程。
輸入以下命令可以查看關于tomcat的進程:
ps -ef | grep tomcat2 查看當前服務器用戶數量
w和who命令最為簡單。
作為系統管理員,你可能經常會(在某個時候)需要查看系統中有哪些用戶正在活動。有些時候,你甚至需要知道他(她)們正在做什么。本文為我們總結了4種查看系統用戶信息(通過編號(ID))的方法。
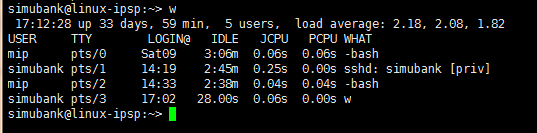
2.1 使用w命令查看登錄用戶正在使用的進程信息
w命令用于顯示已經登錄系統的用戶的名稱,以及他們正在做的事。該命令所使用的信息來源于/var/run/utmp文件。w命令輸出的信息包括:
用戶名稱
用戶的機器名稱或tty號
遠程主機地址
用戶登錄系統的時間
空閑時間(作用不大)
附加到tty(終端)的進程所用的時間(JCPU時間)
當前進程所用時間(PCPU時間)
用戶當前正在使用的命令
w命令還可以使用以下選項
-h忽略頭文件信息
-u顯示結果的加載時間
-s不顯示JCPU, PCPU, 登錄時間
2.2?使用who命令查看(登錄)用戶名稱及所啟動的進程
who命令用于列舉出當前已登錄系統的用戶名稱。其輸出為:用戶名、tty號、時間日期、主機地址。
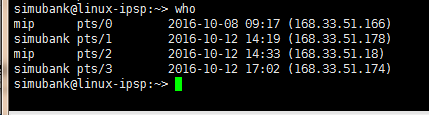
輸入以下命令,可以查看當前linux服務器在線用戶數量:
who | wc -l?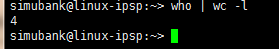
2.3 使用whoami命令查看你所使用的登錄名稱
whoami命令用于顯示登入的用戶名。
2.4 隨時查看系統的歷史信息(曾經使用過系統的用戶信息)
last命令可用于顯示特定用戶登錄系統的歷史記錄。如果沒有指定任何參數,則顯示所有用戶的歷史信息。在默認情況下,這些信息(所顯示的信息)將來源于/var/log/wtmp文件。該命令的輸出結果包含以下幾列信息:
用戶名稱
tty設備號
歷史登錄時間日期
登出時間日期
總工作時間
可以在命令行輸入“last”進行嘗試。

$ last jason jason pts/0 dev-db-server Fri Mar 27 22:57 still logged in
jason pts/0 dev-db-server Fri Mar 27 22:09 - 22:54 (00:45)
jason pts/0 dev-db-server Wed Mar 25 19:58 - 22:26 (02:28)
jason pts/1 dev-db-server Mon Mar 16 20:10 - 21:44 (01:33)
jason pts/0 192.168.201.11 Fri Mar 13 08:35 - 16:46 (08:11)
jason pts/1 192.168.201.12 Thu Mar 12 09:03 - 09:19 (00:15)
jason pts/0 dev-db-server Wed Mar 11 20:11 - 20:50 (00:39)
3 日志搜索
3.1 命令行查看日志
- 首先定位要查找日志的位置
lfcp@lfcp6:~> grep -n '<TxId>1919</TxId>' *.log
GW0001.log:1094194: <TxId>1919</TxId>
lfcp@lfcp6:~> ?
可以參考:Linux命令grep
- 再根據定位的文件和行號查看相應的日志
這里是用vi或者vim命令去查看
vim GW0001.log#設置行號
:set nu#根據查到的行號跳到指定的行即可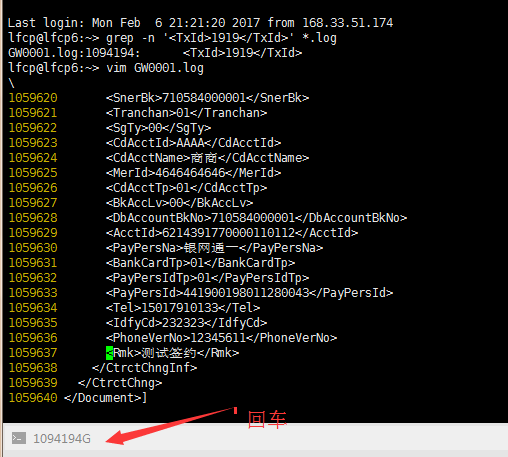
之后就可以上下移動來查看我們要搜尋的日志了。
?3.2 grep命令補充
find . -name "*.log" | xargs grep "^12405"
grep "<TxId>12426</TxId>" *.logLinux查找文件內容的常用命令方法。?
從文件內容查找匹配指定字符串的行:
$ grep "被查找的字符串" 文件名
例子:在當前目錄里第一級文件夾中尋找包含指定字符串的.in文件
grep "thermcontact" */*.in從文件內容查找與正則表達式匹配的行:
$ grep –e “正則表達式” 文件名查找時不區分大小寫:
$ grep –i "被查找的字符串" 文件名查找匹配的行數:
$ grep -c "被查找的字符串" 文件名從文件內容查找不匹配指定字符串的行:
$ grep –v "被查找的字符串" 文件名從根目錄開始查找所有擴展名為.log的文本文件,并找出包含”ERROR”的行
find / -type f -name "*.log" | xargs grep "ERROR"例子:從當前目錄開始查找所有擴展名為.in的文本文件,并找出包含”thermcontact”的行
find . -name "*.in" | xargs grep "thermcontact"4 linux項目部署匯總
部署步驟:
- 下載jdk,tomcat
- 配置tomcat中的java環境變量,主要是bin目錄中catalina.sh文件
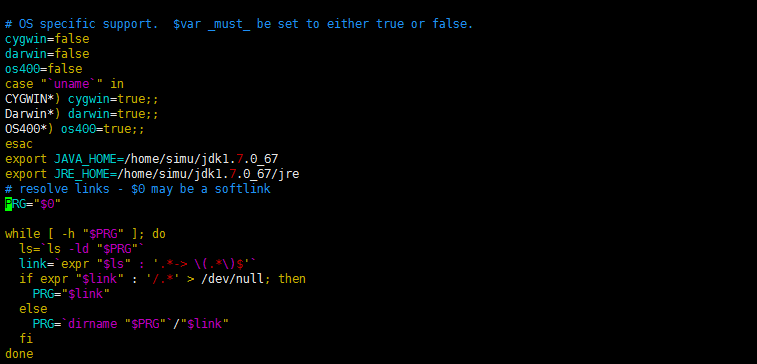
export JAVA_HOME=/home/simu/jdk1.7.0_67
export JRE_HOME=/home/simu/jdk1.7.0_67/jre?
? ? ? ?3.修改tomcat中conf目錄下的server.xml文件

<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<!--Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or morecontributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed withthis work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0(the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance withthe License. You may obtain a copy of the License athttp://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, softwaredistributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.See the License for the specific language governing permissions andlimitations under the License.
-->
<!-- Note: A "Server" is not itself a "Container", so you may notdefine subcomponents such as "Valves" at this level.Documentation at /docs/config/server.html-->
<Server port="11005" shutdown="SHUTDOWN"><Listener className="org.apache.catalina.startup.VersionLoggerListener" /><!-- Security listener. Documentation at /docs/config/listeners.html<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.security.SecurityListener" />--><!--APR library loader. Documentation at /docs/apr.html --><Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.AprLifecycleListener" SSLEngine="on" /><!-- Prevent memory leaks due to use of particular java/javax APIs--><Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.JreMemoryLeakPreventionListener" /><Listener className="org.apache.catalina.mbeans.GlobalResourcesLifecycleListener" /><Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.ThreadLocalLeakPreventionListener" /><!-- Global JNDI resourcesDocumentation at /docs/jndi-resources-howto.html--><GlobalNamingResources><!-- Editable user database that can also be used byUserDatabaseRealm to authenticate users--><Resource name="UserDatabase" auth="Container"type="org.apache.catalina.UserDatabase"description="User database that can be updated and saved"factory="org.apache.catalina.users.MemoryUserDatabaseFactory"pathname="conf/tomcat-users.xml" /></GlobalNamingResources><!-- A "Service" is a collection of one or more "Connectors" that sharea single "Container" Note: A "Service" is not itself a "Container",so you may not define subcomponents such as "Valves" at this level.Documentation at /docs/config/service.html--><Service name="Catalina"><!--The connectors can use a shared executor, you can define one or more named thread pools--><!--<Executor name="tomcatThreadPool" namePrefix="catalina-exec-"maxThreads="150" minSpareThreads="4"/>--><!-- A "Connector" represents an endpoint by which requests are receivedand responses are returned. Documentation at :Java HTTP Connector: /docs/config/http.html (blocking & non-blocking)Java AJP Connector: /docs/config/ajp.htmlAPR (HTTP/AJP) Connector: /docs/apr.htmlDefine a non-SSL/TLS HTTP/1.1 Connector on port 8080--><Connector port="8090" protocol="HTTP/1.1"connectionTimeout="20000"redirectPort="11443" /><!-- A "Connector" using the shared thread pool--><!--<Connector executor="tomcatThreadPool"port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"connectionTimeout="20000"redirectPort="8443" />--><!-- Define a SSL/TLS HTTP/1.1 Connector on port 8443This connector uses the NIO implementation that requires the JSSEstyle configuration. When using the APR/native implementation, theOpenSSL style configuration is required as described in the APR/nativedocumentation --><!--<Connector port="8443" protocol="org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol"maxThreads="150" SSLEnabled="true" scheme="https" secure="true"clientAuth="false" sslProtocol="TLS" />--><!-- Define an AJP 1.3 Connector on port 8009 --><Connector port="11007" protocol="AJP/1.3" redirectPort="11443" /><!-- An Engine represents the entry point (within Catalina) that processesevery request. The Engine implementation for Tomcat stand aloneanalyzes the HTTP headers included with the request, and passes themon to the appropriate Host (virtual host).Documentation at /docs/config/engine.html --><!-- You should set jvmRoute to support load-balancing via AJP ie :<Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost" jvmRoute="jvm1">--><Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost"><!--For clustering, please take a look at documentation at:/docs/cluster-howto.html (simple how to)/docs/config/cluster.html (reference documentation) --><!--<Cluster className="org.apache.catalina.ha.tcp.SimpleTcpCluster"/>--><!-- Use the LockOutRealm to prevent attempts to guess user passwordsvia a brute-force attack --><Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.LockOutRealm"><!-- This Realm uses the UserDatabase configured in the global JNDIresources under the key "UserDatabase". Any editsthat are performed against this UserDatabase are immediatelyavailable for use by the Realm. --><Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.UserDatabaseRealm"resourceName="UserDatabase"/></Realm><Host name="localhost" appBase="webapps"unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true"><Context path="simuflcpweb" debug="0" docBase="/home/simu/service" reloadable="true"></Context><!-- SingleSignOn valve, share authentication between web applicationsDocumentation at: /docs/config/valve.html --><!--<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.authenticator.SingleSignOn" />--><!-- Access log processes all example.Documentation at: /docs/config/valve.htmlNote: The pattern used is equivalent to using pattern="common" --><Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve" directory="logs"prefix="localhost_access_log" suffix=".txt"pattern="%h %l %u %t "%r" %s %b" /></Host></Engine></Service>
</Server>
?
?
4.1 跨用戶復制文件
前言
考慮如下情景:foo用戶home目錄下有一文件file.txt,要將其copy至bar用戶的home目錄。Linux對用戶home目錄有嚴格的權限限制,非owner用戶或者同group用戶無權限讀寫,除非是root(至高無上的root)。如果沒有root權限,有什么辦法把file.txt 復制到bar用戶的home目錄下呢?
想到兩個辦法
第一個辦法,先用foo用戶登錄,把文件copy到系統臨時目錄/tmp,然后切換到bar用戶,再從系統臨時目錄/tmp把文件copy到自己的home目錄。這里為什么用cp不用mv?因為復制到/tmp的文件owner還是foo,默認情況下其他用戶自有讀權限,沒有寫權限(自然沒有移動權限)。即使通過修改文件權限,讓bar可寫,移動到bar的home目錄下owner還是foo,而且非得root才能改成bar。這個辦法有點曲折,弊端也很明顯,文件需要復制兩次,花兩倍的時間。
# cp file.txt /tmp/
# su - bar
# cp /tmp/file.txt ~/
# exit
# rm /tmp/file.txt?
第二個辦法,使用scp命令。原本scp是用來在不同主機上通過網絡copy文件,用在這里剛好。用bar用戶登錄
# scp foo@localhost:/home/foo/file.txt ./輸入foo用戶密碼,開始文件傳輸。
也可以用foo用戶登錄,
# scp file.txt bar@localhost:/home/bar/ 下面采用第二種方法操作一遍:
?

simu@LFCP-6:~> ll
總用量 32
-rw------- 1 simu mqm 4546 2月 7 17:42 application.properties
-rw------- 1 simu mqm 2032 2月 7 17:42 autoDeploy.sh
drwxr-xr-x 2 simu mqm 4096 12月 16 21:23 bin
drwx------ 2 simu mqm 4096 2月 7 17:42 key
-rw------- 1 simu mqm 57 2月 7 17:42 log.sh
-rw------- 1 simu mqm 49 2月 7 17:42 startup.sh
-rw------- 1 simu mqm 61 2月 7 17:42 stop.sh
simu@LFCP-6:~> scp lfcp@localhost:/home/lfcp/simu/jdk1.7.0_67.tar ./
The authenticity of host 'localhost (127.0.0.1)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is 0c:99:38:31:34:80:c3:51:ea:9d:97:b7:3d:8c:48:ad [MD5].
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added 'localhost' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
Password:
jdk1.7.0_67.tar 100% 282MB 93.9MB/s 00:03
simu@LFCP-6:~> ll
總用量 288672
-rw------- 1 simu mqm 4546 2月 7 17:42 application.properties
-rw------- 1 simu mqm 2032 2月 7 17:42 autoDeploy.sh
drwxr-xr-x 2 simu mqm 4096 12月 16 21:23 bin
-rw------- 1 simu mqm 295270400 2月 7 17:51 jdk1.7.0_67.tar
drwx------ 2 simu mqm 4096 2月 7 17:42 key
-rw------- 1 simu mqm 57 2月 7 17:42 log.sh
-rw------- 1 simu mqm 49 2月 7 17:42 startup.sh
-rw------- 1 simu mqm 61 2月 7 17:42 stop.sh
simu@LFCP-6:~> 
5 項目部署問題
5.1 基本問題
- 問題 ——編輯配置文件,出現隱藏文件提示
在編輯tomcat的配置文件catalina.sh 時候提示發現配置文件。
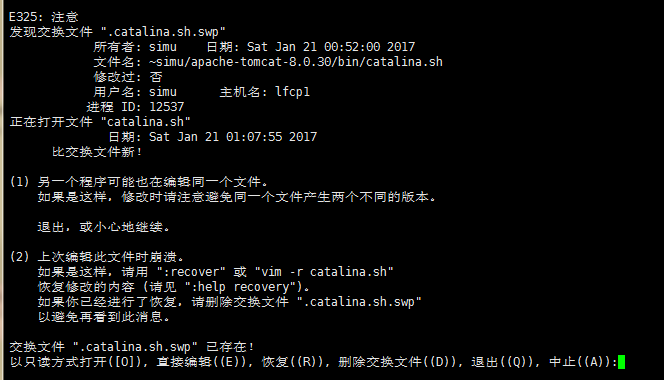
這是因為,在用vim打開一個文件時,其會產生一個filename.swap文件,用于保存數據,當文件非正常關閉時,可用此文件來恢復,當正常關閉時,此文件會被刪除,非正常關閉時,不會被刪除,所以提示存在.swap文件,此時你可以恢復文件:
恢復以后把.swap文件刪掉,在打開時就不會用提示良,注意.swap文件是個隱藏文件。可用:la查看。以.開頭的是隱藏文件。在linux下隱藏文件是以“.”開頭的,單純的使用ls命令是看不到的,加上“-a”參數才可以。刪除則可以使用命令:rm -fr .*(刪除當前目錄下的所有隱藏文件), rm -f .tmp(刪除tmp文件),rm -fr .tmp(刪除tmp目錄或者文件)?
- ?問題——打印日志提示權限不夠
這里的tomcat和jdk都直接解壓而來,在輸出catalina.out 日志時候,提示沒有權限,實際測試時候發現相應的進程也沒有啟動。
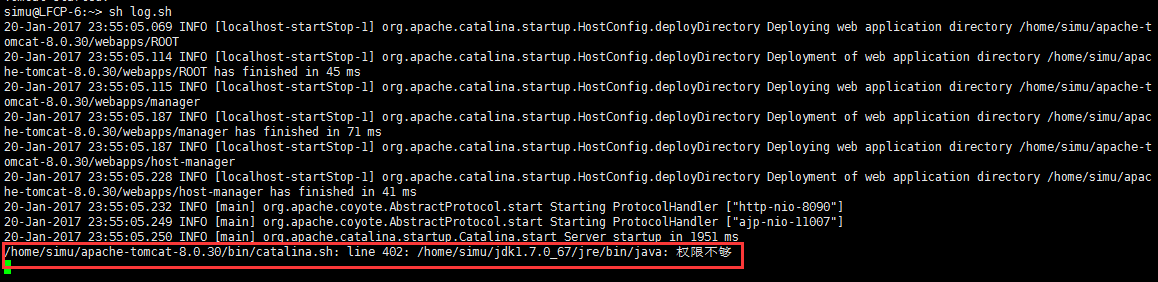
?使用以下方式給jdk整個目錄授權
chmod -R 777 /home/simu/jdk1.7.0_67可以通過查看進程的方式查看tomcat是否啟動:
ps -ef | grep simu(進程的名字)?
如果還不能夠啟動tomcat,嘗試刪除tomcat中的原有日志catalina.out.
?
原文見:
https://www.cnblogs.com/lixuwu/p/5854985.html
?




![[Nikon D80]櫻花盛開的校園](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Nikon D80]櫻花盛開的校園)










)



