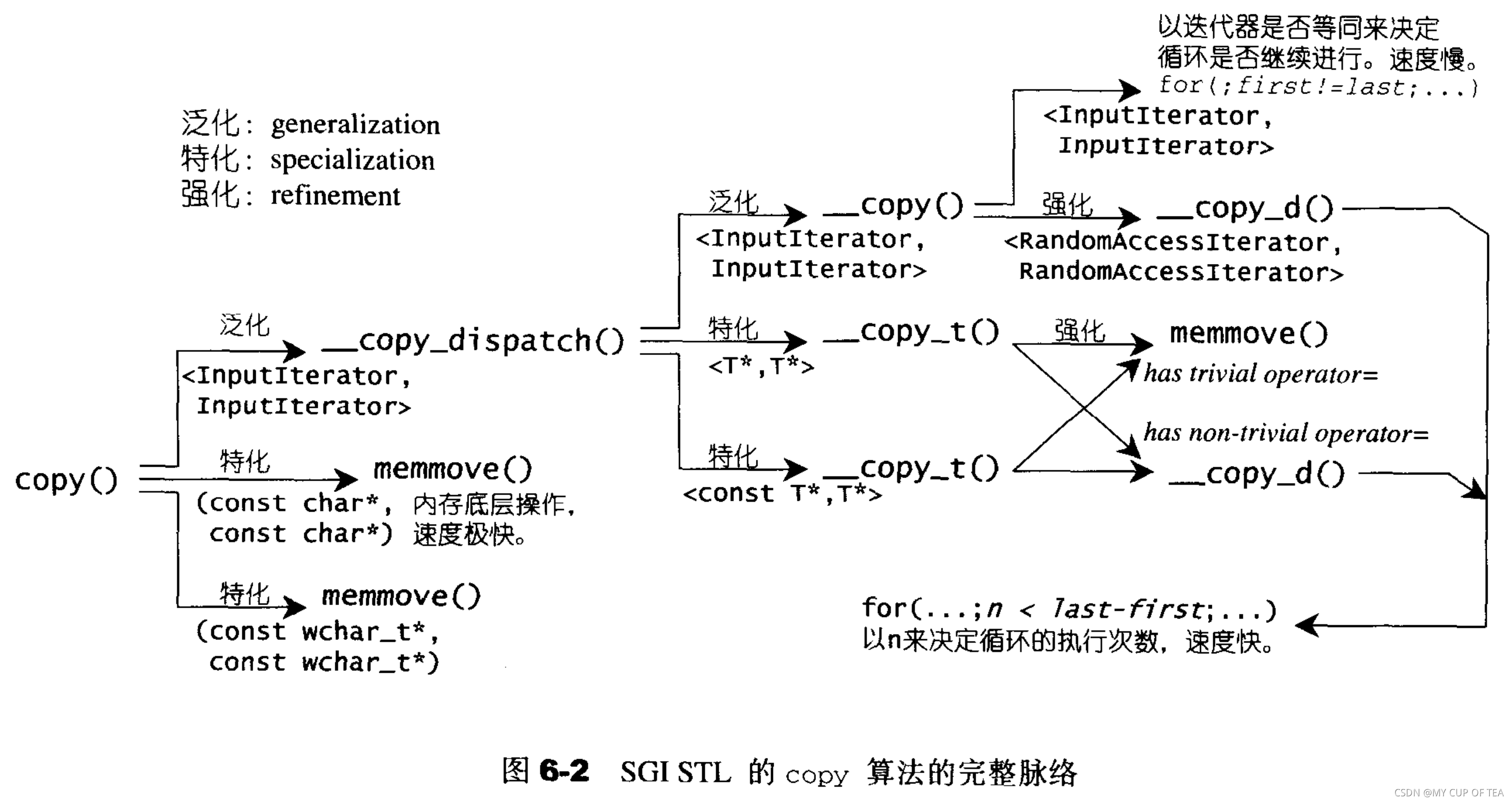
- copy復制操作,其操作通過使用assignment operator 。針對使用trivial assignment operator的元素型別可以直接使用內存直接復制行為(使用C函數 memove或者memcpy)節約時間。
- 還可以通過函數重載(function overloading)、型別特性(type traits)、偏特化(partial specialization)等技巧進一步強化效率。
- copy函數將[first,last) 內的元素復制到區間[result,result+(last-first))內
- 返回迭代器指向的是??result+(last-first)
- 輸入區間使用?InputIterator,輸出區間使用?OutputIterator
- 注意事項:1,result位于[first , last)之內的時候也就是輸出區間的起頭與輸入區間重疊,不能使用copy;如果輸出區間的尾端和輸入區間重疊,就可以使用
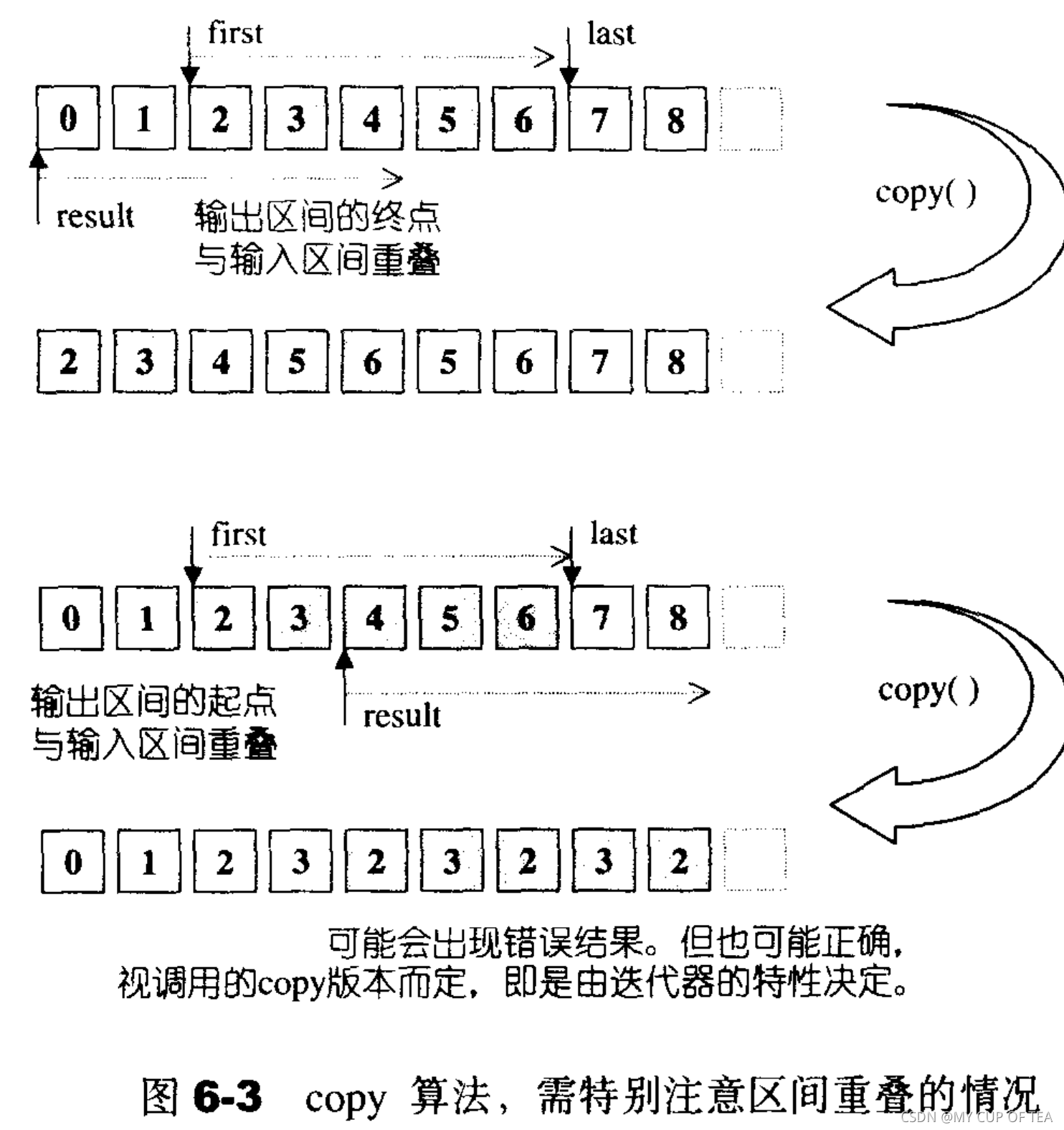
- 上述第二種情況可能出現錯誤,是可能。如果輸出區間的起點位于輸入區間內部,copy算法可能會在輸入區間的(某些)元素尚未復制之前就將其覆蓋其值,導致錯誤
- 如果copy算法根據其所接收的迭代器特性 決定使用memmove()來執行任務,就不會出現問題,因為memmove 會將整個輸入區間的內容復制下來就不會出現覆蓋的危險
#include <iostream> //std::cout
#include <algorithm> //std::fill
#include <vector> //std::vector
#include <deque>template <class T>
struct display{void operator()(const T& value){std::cout << value <<' ';}
};int main(){{int ia[] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};//輸出區間的終點和輸入區間出現重疊 沒有問題std::copy(ia+2,ia+7,ia);std::for_each(ia,ia+9,display<int>()); //2 3 4 5 6 5 6 7 8std::cout << std::endl;}{int ia[] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};//輸出區間的起點和輸入區間出現重疊 可能會出現問題std::copy(ia+2,ia+7,ia+4);std::for_each(ia,ia+9,display<int>()); //0 1 2 3 2 3 4 5 6std::cout << std::endl;//本例結果正確 因為調用的copy算法使用memmove()執行實際復制操作}{int ia[] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};std::deque<int>id(ia,ia+9);std::deque<int>::iterator first = id.begin();std::deque<int>::iterator last = id.end();++++first; //advance(first,2) 2std::cout << * first << std::endl;----last; //advance(last,-2) 7std::cout << * last << std::endl;std::deque<int>::iterator result = id.begin();std::cout << *result << std::endl; //0//輸出區間的終點和輸入區間重疊 沒有問題std::copy(first,last,result);std::for_each(id.begin(),id.end(),display<int>()); //2 3 4 5 6 5 6 7 8std::cout << std::endl;}{int ia[] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};std::deque<int>id(ia,ia+9);std::deque<int>::iterator first = id.begin();std::deque<int>::iterator last = id.end();++++first; //advance(first,2) 2std::cout << * first << std::endl;----last; //advance(last,-2)std::cout << * last << std::endl;std::deque<int>::iterator result = id.begin();std::advance(result,4);std::cout << *result << std::endl; //4//輸出區間的起點和輸入區間重疊 可能會出現問題std::copy(first,last,result);std::for_each(id.begin(),id.end(),display<int>()); //0 1 2 3 2 3 4 5 6//STL源碼剖析 此處會出現錯誤,原因在于copy算法不再使用memcove()執行實際的復制操作//但是實際沒有出現錯誤std::cout << std::endl;/*2 3 4 5 6 5 6 7 8 0 1 2 3 2 3 4 5 6 2702 3 4 5 6 5 6 7 8 2740 1 2 3 2 3 4 5 6 */}}- 使用vector代替上述的deque進行測試復制結果是正確的,因為vector的迭代器其實就是個原生指針
- copy更改的是迭代器所指向的對象,并不是修改迭代器本身,他會為區間內的元素賦予新的數值,但不是產生新的元素,也不會改變迭代器的個數。即,copy不能用來將元素插入到空的容器中
- 使用copy算法配合序列容器的insert_iterator?
?
#include <iostream> //std::cout//完全泛化的版本
template <class InputIterator,class OutputIterator>
inline OutputIterator copy(InputIterator first,InputIterator last,OutputIterator result){return __copy_dispatch<InputIterator ,OutputIterator>()(first,last,result);
}//兩個重載函數 針對原生指針(視為一種特殊的迭代器)const char* 和 const wchar_t 進行內存的直接拷貝操作
//特殊版本1 重載形式 const char *
inline char* copy(const char* first,const char* last,char* result){std::memmove(result,first,last - first);return result + (last - first);
}//特殊版本2 重載形式 const wchar_t *
inline wchar_t* copy(const wchar_t* first,const wchar_t* last,wchar_t* result){std::memmove(result,first,sizeof(wchar_t)*(last - first));return result + (last - first);
}//copy泛化版本調用了一個 __copy_dispatch函數,這個函數有一個完全泛化版本和兩個偏特化版本
//完全泛化版本
//__copy_dispatch完全泛化版本根據迭代器的種類不同,調用了不同的__copy(),是因為不同種類的迭代器使用的循環條件不同,有快有慢
template <class InputIterator,class OutputIterator>
struct __copy_dispatch{OutputIterator operator()(InputIterator first,InputIterator last,OutputIterator result){return __copy(first,last,result,iterator_category(first));}
};//InputIterator 版本
template <class InputIterator,class OutputIterator>
inline OutputIterator __copy(InputIterator first,InputIterator last,OutputIterator result,std::input_iterator_tag){//通過迭代器的等同與否 決定循環是否繼續 速度很慢while(first!=last){*result = *first; //assignment operator++first;++result;}return result;
}//RandomAccessIterator 版本
template <class RandomAccessIterator,class OutputIterator>
inline OutputIterator __copy(RandomAccessIterator first,RandomAccessIterator last,OutputIterator result,std::random_access_iterator_tag){//劃分新的函數 為了讓其余地方可以使用return __copy_d(first,last,result, distance_type(first));
}template <class RandomAccessIterator,class OutputIterator,class Distance>
inline OutputIterator __copy_d(RandomAccessIterator first,RandomAccessIterator last,OutputIterator result,Distance*){//使用n決定循環的執行次數 速度快Distance n = last - first;while (n>0){*result = *first; //assignment operator++result;++first;n--;}return result;
}//偏特化版本1 兩個參數的型別都是T* 指針
template<class T>
struct __copy_dispatch<T*,T*>
{T* operator()(T* first,T* last,T* result){typedef typename __type_traits<T>::has_trival_assignment_operator t;return __copy_t(first,last,result,t());}
};//偏特化版本2 第一個參數是constT*指針形式 第二個參數是T* 指針形式
template<class T>
struct __copy_dispatch<const T*,T*>
{T* operator()(const T* first,const T* last,T* result){typedef typename __type_traits<T>::has_trival_assignment_operator t;return __copy_t(first,last,result,t());}
};//在上述偏特化版本指定參數類型為T*和const T*只針的前提下進一步探測
//探測指針所指之物是否具備trivial assignment operator (平凡賦值操作符)
//SGI STL通過使用__type_traits<>編程技巧 和 增加一層間接性 來區分不同的 __copy_t()//適用于指針所指對象具備 trivial assignment operator
template <class T>
inline T* __copy_t(const T* first,const T* last,T* result,__true_type){memmove(result,first, sizeof(T)*(last - first));return result + (last - first);
}//適用于指針所指對象具備 non-trivial assignment operator
template <class T>
inline T* __copy_t(const T* first,const T* last,T* result,__false_type){//原生指針是一種 RandomAccessIterator 所以交給 __copy_d()完成return __copy_d(first,last,result,(std::ptrdiff_t)0);
}?




)











)


