所以說不要怕算法,簡單的題反而出現的頻率最高,不一定非要寫個幾百道才面試
兩數之和
給定一個整數數組 nums?和一個目標值 target,請你在該數組中找出和為目標值的那?兩個?整數,并返回他們的數組下標。
你可以假設每種輸入只會對應一個答案。但是,你不能重復利用這個數組中同樣的元素。
示例:
給定 nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9
因為 nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9
所以返回 [0, 1]
思路:
遇到的數字裝到hashmap中,遇到的新數字查找有沒有答案int dif = target - nums[i];
class Solution {public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();int[] res = new int[2];for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {int dif = target - nums[i];if (map.get(dif) != null) {res[0] = map.get(dif);res[1] = i;return res;}map.put(nums[i],i);}return res;}
}?
?
反轉鏈表
示例:
輸入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
輸出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
進階:
你可以迭代或遞歸地反轉鏈表。你能否用兩種方法解決這道題?
?
經典題,一i個循環做那四個經典操作,自己拿紙筆畫一畫就懂啦。
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {ListNode prev = null;ListNode curr = head;while (curr != null) {ListNode nextTemp = curr.next;curr.next = prev;prev = curr;curr = nextTemp;}return prev;}
}?
有效的括號
給定一個只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']'?的字符串,判斷字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需滿足:
左括號必須用相同類型的右括號閉合。左括號必須以正確的順序閉合。注意空字符串可被認為是有效字符串。
示例 1:
輸入: "()"
輸出: true
示例?2:
輸入: "()[]{}"
輸出: true
示例?3:
輸入: "(]"
輸出: false
示例?4:
輸入: "([)]"
輸出: false
示例?5:
輸入: "{[]}"
輸出: true
思路:
初始化棧 。一次處理表達式的每個括號。
- 如果遇到開括號,我們只需將其推到棧上即可。這意味著我們將稍后處理它。
- 如果我們遇到一個閉括號,那么我們檢查棧頂的元素。如果棧頂的元素是一個 相同類型的 左括號,那么我們將它從棧中彈出并繼續處理。否則表達式無效。
如果到最后我們剩下的棧中仍然有元素,那么表達式無效。
class Solution {// Hash table that takes care of the mappings.private HashMap<Character, Character> mappings;// Initialize hash map with mappings. This simply makes the code easier to read.public Solution() {this.mappings = new HashMap<Character, Character>();this.mappings.put(')', '(');this.mappings.put('}', '{');this.mappings.put(']', '[');}public boolean isValid(String s) {// Initialize a stack to be used in the algorithm.Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<Character>();for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {char c = s.charAt(i);// If the current character is a closing bracket.if (this.mappings.containsKey(c)) {// Get the top element of the stack. If the stack is empty, set a dummy value of '#'char topElement = stack.empty() ? '#' : stack.pop();// If the mapping for this bracket doesn't match the stack's top element, return false.if (topElement != this.mappings.get(c)) {return false;}} else {// If it was an opening bracket, push to the stack.stack.push(c);}}// If the stack still contains elements, then it is an invalid expression.return stack.isEmpty();}
}爬樓梯/跳臺階
一只青蛙一次可以跳上1級臺階,也可以跳上2級。求該青蛙跳上一個n級的臺階總共有多少種跳法。
找遞推關系:
1)跳一階,就一種方法
2)跳兩階,它可以一次跳兩個,也可以一個一個跳,所以有兩種
3)三個及三個以上,假設為n階,青蛙可以是跳一階來到這里,或者跳兩階來到這里,只有這兩種方法。
它跳一階來到這里,說明它上一次跳到n-1階,
同理,它也可以從n-2跳過來
f(n)為跳到n的方法數,所以,f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2)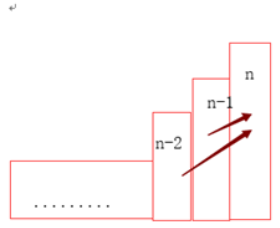
class Solution {public int climbStairs(int n) {int[] dp = new int[n + 1];dp[0] = 1;dp[1] = 1;for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];}return dp[n];}
}合并鏈表
將兩個升序鏈表合并為一個新的 升序 鏈表并返回。新鏈表是通過拼接給定的兩個鏈表的所有節點組成的。?
?
示例 1:
輸入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
輸出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例 2:
輸入:l1 = [], l2 = []
輸出:[]
示例 3:
輸入:l1 = [], l2 = [0]
輸出:[0]
?
提示:
兩個鏈表的節點數目范圍是 [0, 50]
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
l1 和 l2 均按 非遞減順序 排列
思路:歸并的思想,一直比較兩邊的大小并且插入。
class Solution {public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {ListNode prehead = new ListNode(-1);ListNode prev = prehead;while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {if (l1.val <= l2.val) {prev.next = l1;l1 = l1.next;} else {prev.next = l2;l2 = l2.next;}prev = prev.next;}// 合并后 l1 和 l2 最多只有一個還未被合并完,我們直接將鏈表末尾指向未合并完的鏈表即可prev.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;return prehead.next;}
}?
?
?




)


)

-(一千零一拾一元整)輸出。...)







)

